Abstract
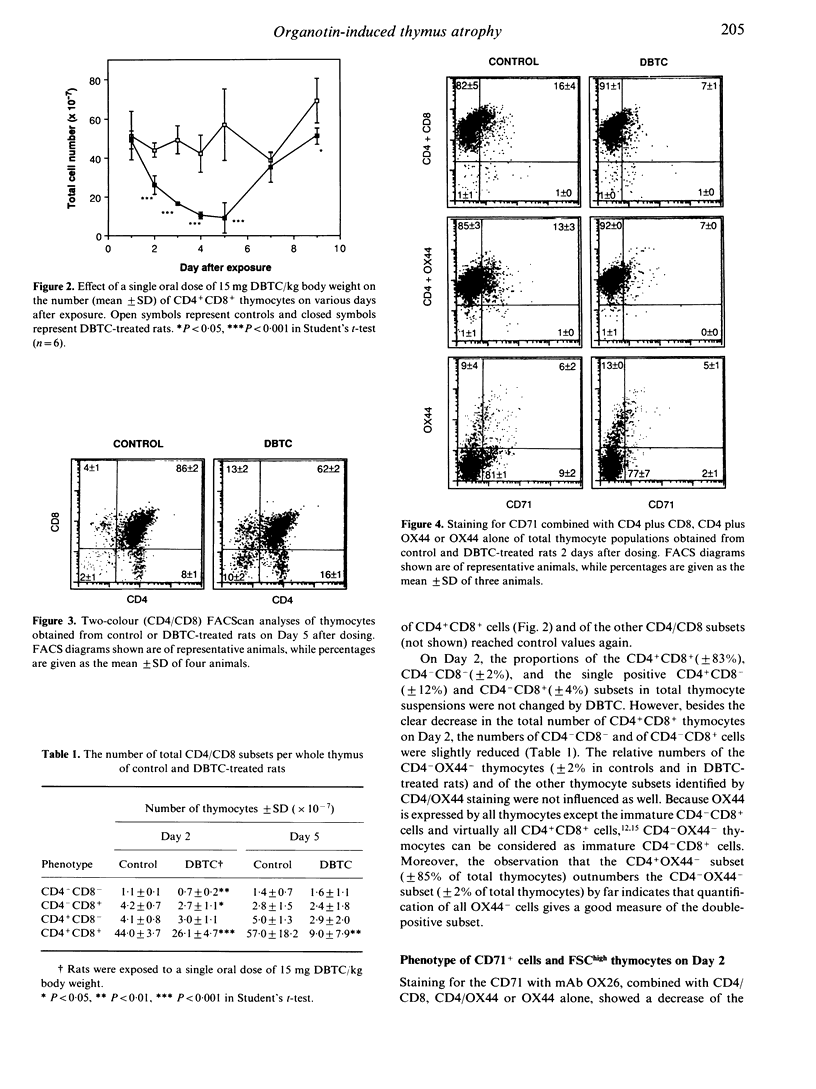
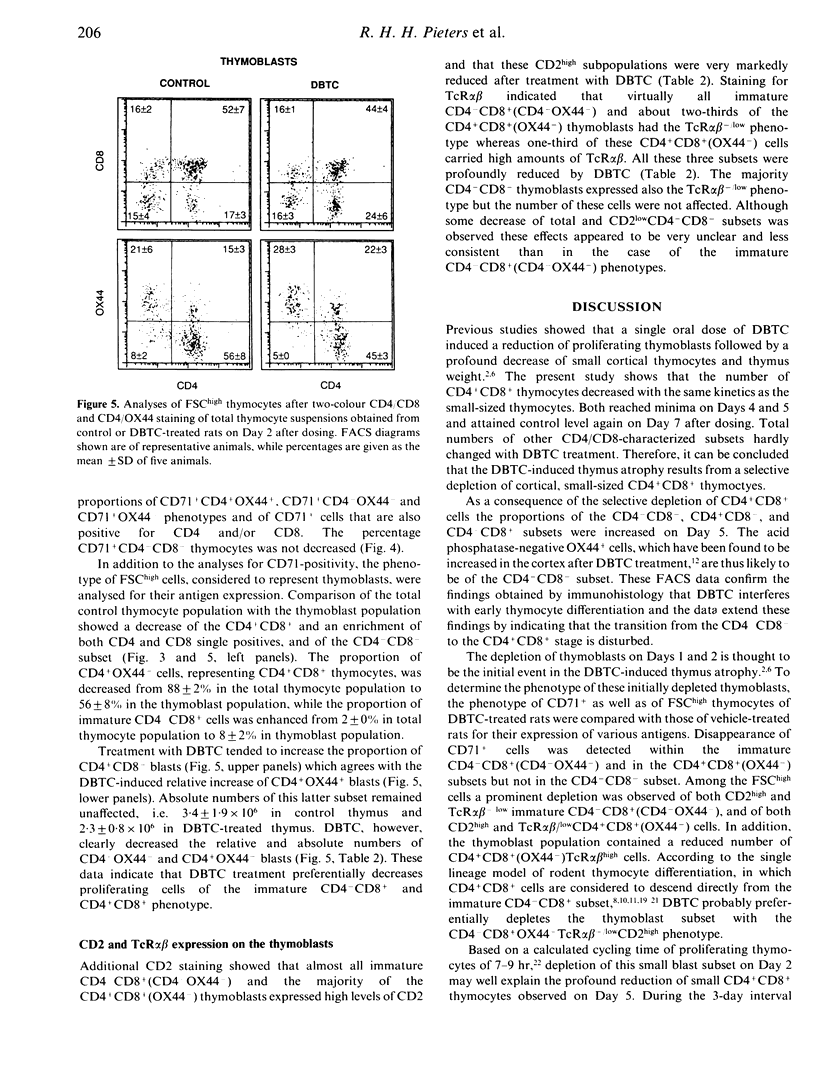
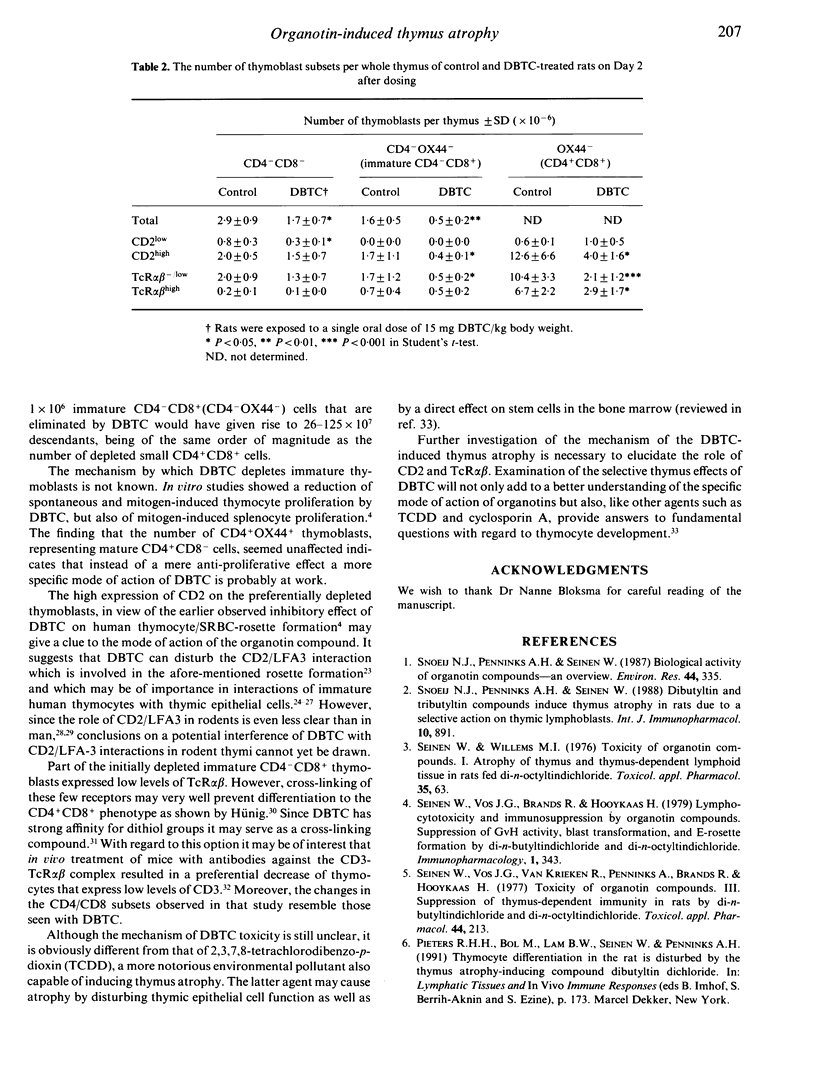
Thymic changes in the rat induced by the thymus atrophy-inducing organotin compound di-n-butyltin dichloride (DBTC) were examined using FACS analyses. The number of CD4+CD8+ thymocytes was reduced by DBTC treatment from Day 2 onwards and reached minimum level on Days 4 and 5 after dosing. On these days the CD4-CD8- and both the CD4-CD8+ and CD4+CD8- subsets were not affected. On Day 2 we observed a reduced proportion of transferrin receptor (CD71)-positive CD4-OX44- cells, representing the cycling immature CD4-CD8+ cells, and of CD71+OX44- cells, representing the cycling CD4+CD8+ cells, but not of CD71+CD4-CD8- cells. When compared to controls, the FSChigh cell population of DBTC-treated rats contained less CD4-OX44- and OX44- cells, which were further characterized as CD2high and T-cell receptor (TcR)alpha beta- low. Moreover, fewer TcR alpha beta high cells were detected in the OX44- thymoblast subset of DBTC-treated rats. The number of CD4-CD8- thymoblasts appeared marginally decreased while the numbers of CD4+OX44+ cells, representing mature CD4+ cells, were not affected. These data indicate that DBTC causes a preferential initial depletion of immature CD4-CD8+CD2high TcR alpha beta-low thymoblasts. This initial event may result in a decreased formation of CD4+CD8+ thymoblasts and of small CD4+CD8+ thymocytes. These characteristics of the initially depleted subset indicate a specific anti-proliferative effect of DBTC and may give clues for the mechanism involved in the induction of thymus atrophy.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angelisová P., Vlcek C., Stefanová I., Lipoldová M., Horejsí V. The human leucocyte surface antigen CD53 is a protein structurally similar to the CD37 and MRC OX-44 antigens. Immunogenetics. 1990;32(4):281–285. doi: 10.1007/BF00187099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aspinall R., Kampinga J., van den Bogaerde J. T-cell development in the fetus and the invariant series hypothesis. Immunol Today. 1991 Jan;12(1):7–10. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyers A. D., Barclay A. N., Law D. A., He Q., Williams A. F. Activation of T lymphocytes via monoclonal antibodies against rat cell surface antigens with particular reference to CD2 antigen. Immunol Rev. 1989 Oct;111:59–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1989.tb00542.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brideau R. J., Carter P. B., McMaster W. R., Mason D. W., Williams A. F. Two subsets of rat T lymphocytes defined with monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Aug;10(8):609–615. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant B. J. Renewal and fate in the mammalian thymus: mechanisms and inferences of thymocytokinetics. Eur J Immunol. 1972 Feb;2(1):38–45. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830020109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denning S. M., Tuck D. T., Vollger L. W., Springer T. A., Singer K. H., Haynes B. F. Monoclonal antibodies to CD2 and lymphocyte function-associated antigen 3 inhibit human thymic epithelial cell-dependent mature thymocyte activation. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 15;139(8):2573–2578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox D. A., Hussey R. E., Fitzgerald K. A., Bensussan A., Daley J. F., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. Activation of human thymocytes via the 50KD T11 sheep erythrocyte binding protein induces the expression of interleukin 2 receptors on both T3+ and T3- populations. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):330–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hünig T. Cross-linking of the T cell antigen receptor interferes with the generation of CD4+8+ thymocytes from their immediate CD4-8+ precursors. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Dec;18(12):2089–2092. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830181234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferies W. A., Brandon M. R., Williams A. F., Hunt S. V. Analysis of lymphopoietic stem cells with a monoclonal antibody to the rat transferrin receptor. Immunology. 1985 Feb;54(2):333–341. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joling P., Tielen F. J., Vaessen L. M., Hesse C. J., Rozing J. Intrathymic differentiation in the rat. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1985;186:235–244. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-2463-8_29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyewski B. A., Jenkinson E. J., Kingston R., Altevogt P., Owen M. J., Owen J. J. The effects of anti-CD2 antibodies on the differentiation of mouse thymocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1989 May;19(5):951–954. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald H. R., Budd R. C., Howe R. C. A CD3- subset of CD4-8+ thymocytes: a rapidly cycling intermediate in the generation of CD4+8+ cells. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Apr;18(4):519–523. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson D. J., Williams A. F. An intermediate cell in thymocyte differentiation that expresses CD8 but not CD4 antigen. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1603–1608. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penit C. In vivo thymocyte maturation. BUdR labeling of cycling thymocytes and phenotypic analysis of their progeny support the single lineage model. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 1;137(7):2115–2121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seinen W., Vos J. G., Brands R., Hooykaas H. Lymphocytotoxicity and immunosuppression by organotin compounds. Suppression of graft-versus-host reactivity, blast transformation, and E-rosette formation by di-n-butyltindichloride and di-n-octyltindichloride. Immunopharmacology. 1979 Jul;1(4):343–355. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(79)90031-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seinen W., Vos J. G., van Krieken R., Penninks A., Brands R., Hooykaas H. Toxicity of organotin compounds. III. Suppression of thymus-dependent immunity in rats by di-n-butyltindichloride and di-n-octyltindichloride. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1977 Oct;42(1):213–224. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(77)90211-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seinen W., Willems M. I. Toxicity of organotin compounds. I. Atrophy of thymus and thymus-dependent lymphoid tissue in rats fed di-n-octyltindichloride. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1976 Jan;35(1):63–75. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(76)90111-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraj P., Dustin M. L., Mitnacht R., Hünig T., Springer T. A., Plunkett M. L. Rosetting of human T lymphocytes with sheep and human erythrocytes. Comparison of human and sheep ligand binding using purified E receptor. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 15;139(8):2690–2695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y. F., Bissonnette R. P., Parfrey N., Szalay M., Kubo R. T., Green D. R. In vivo administration of monoclonal antibodies to the CD3 T cell receptor complex induces cell death (apoptosis) in immature thymocytes. J Immunol. 1991 May 15;146(10):3340–3346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snoeij N. J., Penninks A. H., Seinen W. Biological activity of organotin compounds--an overview. Environ Res. 1987 Dec;44(2):335–353. doi: 10.1016/s0013-9351(87)80242-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snoeij N. J., Penninks A. H., Seinen W. Dibutyltin and tributyltin compounds induce thymus atrophy in rats due to a selective action on thymic lymphoblasts. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1988;10(7):891–899. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(88)90014-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A., Dustin M. L., Kishimoto T. K., Marlin S. D. The lymphocyte function-associated LFA-1, CD2, and LFA-3 molecules: cell adhesion receptors of the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:223–252. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.001255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vollger L. W., Tuck D. T., Springer T. A., Haynes B. F., Singer K. H. Thymocyte binding to human thymic epithelial cells is inhibited by monoclonal antibodies to CD-2 and LFA-3 antigens. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 15;138(2):358–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


