Abstract
Adjuvant arthritis in rats is usually induced by injection of mycobacterium tubercle cell walls suspended in various adjuvant oils such as Freund's incomplete adjuvant (FIA) or pristane. We have recently shown that injection of adjuvant oils without inclusion of mycobacterium tubercle cell walls triggers arthritis [oil adjuvant-induced arthritis (OIA)] in the DA rat strain. The OIA is a genetically restricted disease since only DA rats are susceptible while Lewis, DA-fostered Lewis and F1 (Lew x DA) rats are relatively resistant. Activated alpha beta T cells infiltrate the affected joints of adjuvant oil-injected DA rats and treatment with monoclonal antibodies to the alpha beta T-cell receptor abrogates development of arthritis. These findings show that alpha beta T-cell activation is a critical event in the development of OIA.
Full text
PDF
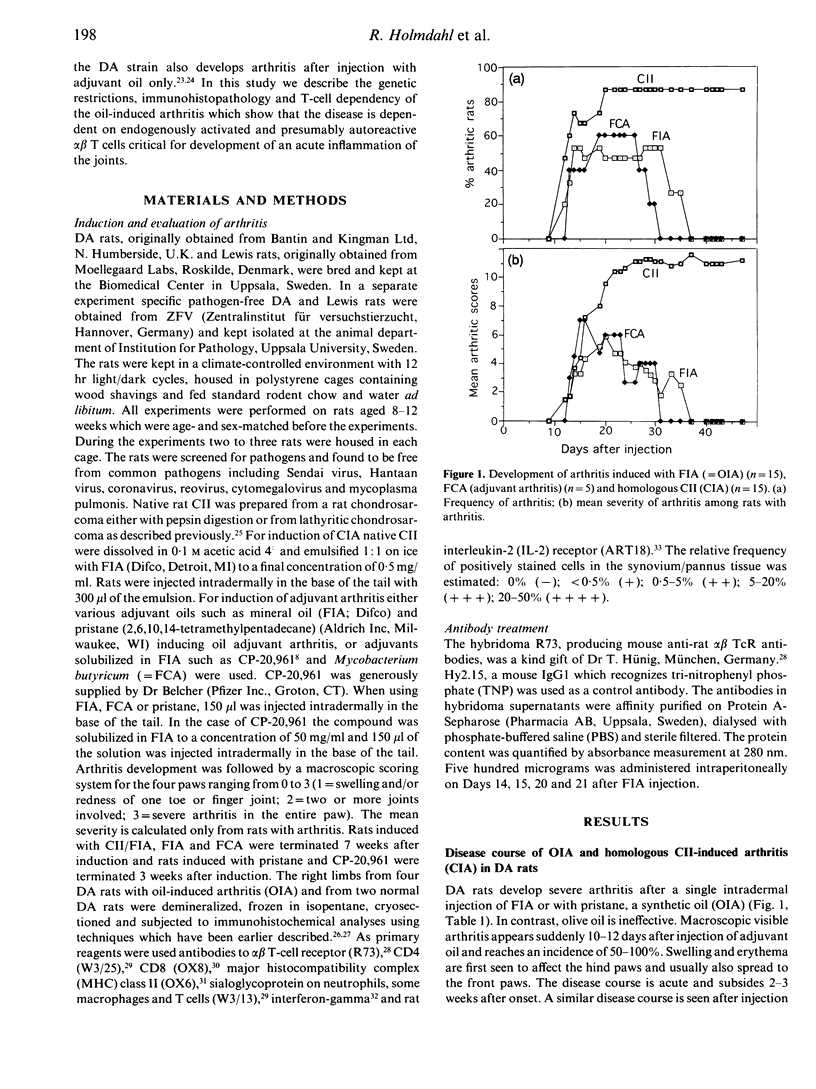
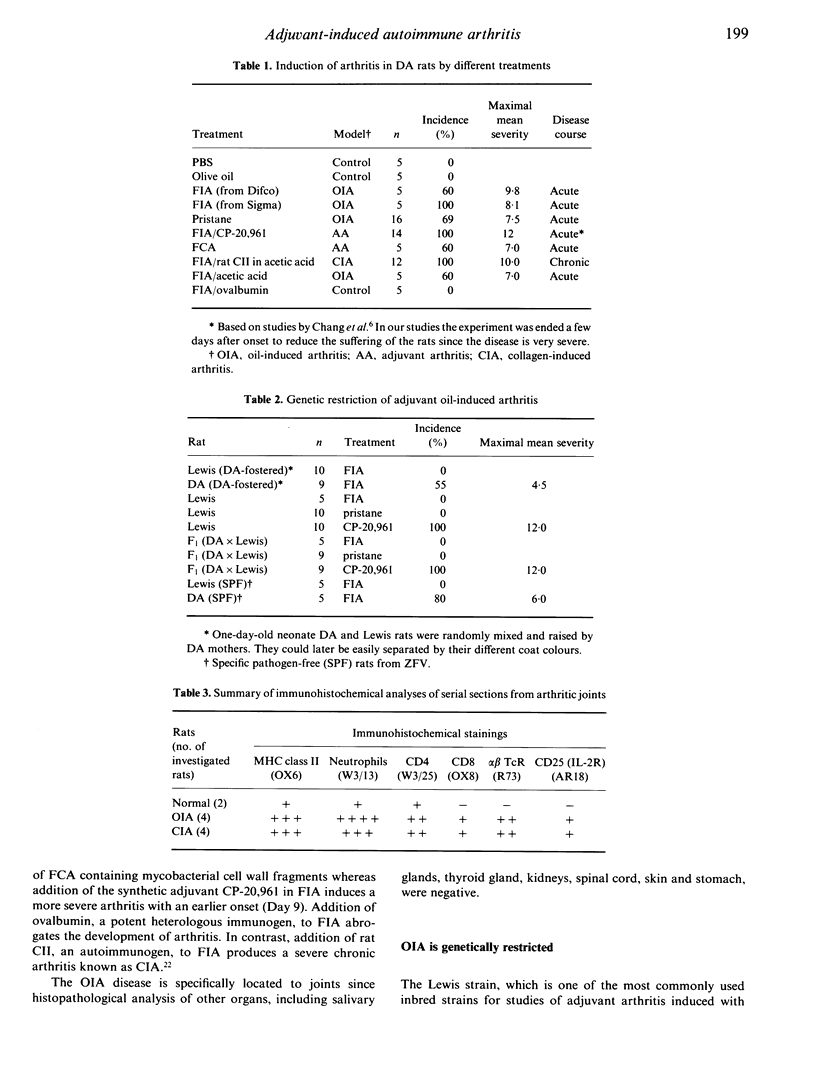
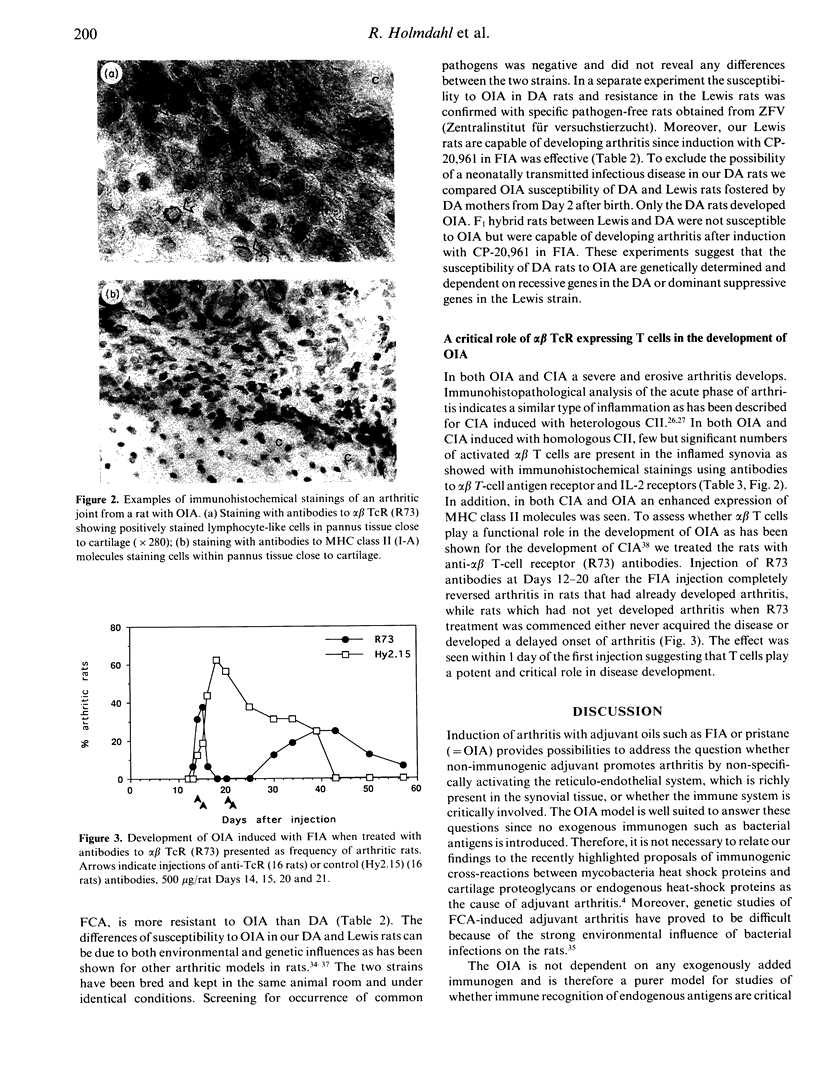


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Battisto J. R., Smith R. N., Beckman K., Sternlicht M., Welles W. L. Susceptibility to adjuvant arthritis in DA and F344 rats. A dominant trait controlled by an autosomal gene locus linked to the major histocompatibility complex. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Oct;25(10):1194–1200. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brideau R. J., Carter P. B., McMaster W. R., Mason D. W., Williams A. F. Two subsets of rat T lymphocytes defined with monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Aug;10(8):609–615. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. H., Pearson C. M., Abe C. Adjuvant polyarthritis. IV. Induction by a synthetic adjuvant: immunologic, histopathologic, and other studies. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Jan;23(1):62–71. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. H., Pearson C. M., Chedid L. Adjuvant polyarthritis. V. Induction by N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanyl-D-isoglutamine, the smallest peptide subunit of bacterial peptidoglycan. J Exp Med. 1981 Apr 1;153(4):1021–1026. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.4.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremer M. A., Hernandez A. D., Townes A. S., Stuart J. M., Kang A. H. Collagen-induced arthritis in rats: antigen-specific suppression of arthritis and immunity by intravenously injected native type II collagen. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2995–3000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremer M. A., Townes A. S., Kang A. H. Adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats. Evidence that autoimmunity to homologous collagens types I, II, IX and XI is not involved in the pathogenesis of arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Nov;82(2):307–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05444.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREUND J. The mode of action of immunologic adjuvants. Bibl Tuberc. 1956;(10):130–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glant T. T., Mikecz K., Arzoumanian A., Poole A. R. Proteoglycan-induced arthritis in BALB/c mice. Clinical features and histopathology. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Feb;30(2):201–212. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt T. J., Holmdahl R. Anti-T cell receptor antibody treatment of rats with established autologous collagen-induced arthritis: suppression of arthritis without reduction of anti-type II collagen autoantibody levels. Eur J Immunol. 1991 May;21(5):1327–1330. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths M. M., DeWitt C. W. Immunogenetic control of experimental collagen-induced arthritis in rats. II. ECIA susceptibility and immune response to type II collagen (CALF) are linked to RT1. J Immunogenet. 1981 Dec;8(6):463–470. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-313x.1981.tb00954.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmdahl R., Jonsson R., Larsson P., Klareskog L. Early appearance of activated CD4+ T lymphocytes and class II antigen-expressing cells in joints of DBA/1 mice immunized with type II collagen. Lab Invest. 1988 Jan;58(1):53–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmdahl R., Kvick C. Vaccination and genetic experiments demonstrate that adjuvant-oil-induced arthritis and homologous type II collagen-induced arthritis in the same rat strain are different diseases. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Apr;88(1):96–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb03045.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmdahl R., Rubin K., Klareskog L., Dencker L., Gustafson G., Larsson E. Appearance of different lymphoid cells in synovial tissue and in peripheral blood during the course of collagen II-induced arthritis in rats. Scand J Immunol. 1985 Mar;21(3):197–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1985.tb01421.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmdahl R., Rubin K., Klareskog L., Larsson E., Wigzell H. Characterization of the antibody response in mice with type II collagen-induced arthritis, using monoclonal anti-type II collagen antibodies. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Mar;29(3):400–410. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmdahl R., Vingsbo C., Hedrich H., Karlsson M., Kvick C., Goldschmidt T. J., Gustafsson K. Homologous collagen-induced arthritis in rats and mice are associated with structurally different major histocompatibility complex DQ-like molecules. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Feb;22(2):419–424. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter R. L., Bennett B. The adjuvant activity of nonionic block polymer surfactants. II. Antibody formation and inflammation related to the structure of triblock and octablock copolymers. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):3167–3175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iizuka Y., Chang Y. H. Adjuvant polyarthritis. VII. The role of type II collagen in pathogenesis. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1325–1332. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaibara N., Hotokebuchi T., Takagishi K., Katsuki I., Morinaga M., Arita C., Jingushi S. Pathogenetic difference between collagen arthritis and adjuvant arthritis. J Exp Med. 1984 May 1;159(5):1388–1396. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.5.1388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinau S., Erlandsson H., Holmdahl R., Klareskog L. Adjuvant oils induce arthritis in the DA rat. I. Characterization of the disease and evidence for an immunological involvement. J Autoimmun. 1991 Dec;4(6):871–880. doi: 10.1016/0896-8411(91)90050-M. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohashi O., Aihara K., Ozawa A., Kotani S., Azuma I. New model of a synthetic adjuvant, N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanyl-D-isoglutamine- induced arthritis: clinical and histologic studies in athymic nude and euthymic rats. Lab Invest. 1982 Jul;47(1):27–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohashi O., Kohashi Y., Takahashi T., Ozawa A., Shigematsu N. Suppressive effect of Escherichia coli on adjuvant-induced arthritis in germ-free rats. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Apr;29(4):547–553. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohashi O., Pearson C. M., Watanabe Y., Kotani S. Preparation of arthritogenic hydrosoluble peptidoglycans from both arthritogenic and non-arthritogenic bacterial cell walls. Infect Immun. 1977 Jun;16(3):861–866. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.3.861-866.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupiec-Weglinski J. W., Diamantstein T., Tilney N. L., Strom T. B. Therapy with monoclonal antibody to interleukin 2 receptor spares suppressor T cells and prevents or reverses acute allograft rejection in rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2624–2627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson P., Kleinau S., Holmdahl R., Klareskog L. Homologous type II collagen-induced arthritis in rats. Characterization of the disease and demonstration of clinically distinct forms of arthritis in two strains of rats after immunization with the same collagen preparation. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 May;33(5):693–701. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster W. R., Williams A. F. Identification of Ia glycoproteins in rat thymus and purification from rat spleen. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Jun;9(6):426–433. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEARSON C. M. Development of arthritis, periarthritis and periostitis in rats given adjuvants. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Jan;91(1):95–101. doi: 10.3181/00379727-91-22179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phadke K., Fouts R., Parrish J. E. Collagen-induced and adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats. Post-immunization treatment with collagen to suppress or abrogate the arthritic response. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Jul;27(7):797–806. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudensky AYu, Preston-Hurlburt P., Hong S. C., Barlow A., Janeway C. A., Jr Sequence analysis of peptides bound to MHC class II molecules. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):622–627. doi: 10.1038/353622a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuelson C. O., Jr, Griffiths M. M., Mathews J. L., Clegg D. O., Ward J. R. Susceptibility and resistance to 6-sulfanilamidoindazole-induced arthritis among inbred strains of rats. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Jun;27(6):689–693. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. B., Griffiths M. M., Wei L. S. Rat cytomegalovirus infection enhances type II collagen arthritis in rats. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Oct;29(10):1263–1268. doi: 10.1002/art.1780291012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taurog J. D., Leary S. L., Cremer M. A., Mahowald M. L., Sandberg G. P., Manning P. J. Infection with Mycoplasma pulmonis modulates adjuvant- and collagen-induced arthritis in Lewis rats. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Aug;27(8):943–946. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trentham D. E., Dynesius-Trentham R. A. Attenuation of an adjuvant arthritis by type II collagen. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2689–2692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trentham D. E., Townes A. S., Kang A. H. Autoimmunity to type II collagen an experimental model of arthritis. J Exp Med. 1977 Sep 1;146(3):857–868. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.3.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren H. S., Vogel F. R., Chedid L. A. Current status of immunological adjuvants. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:369–388. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.002101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. F., Galfrè G., Milstein C. Analysis of cell surfaces by xenogeneic myeloma-hybrid antibodies: differentiation antigens of rat lymphocytes. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):663–673. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90266-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshino S., Kinne R., Hünig T., Emmrich F. The suppressive effect of an antibody to the alpha beta cell receptor in rat adjuvant arthritis: studies on optimal treatment protocols. Autoimmunity. 1990;7(4):255–266. doi: 10.3109/08916939009087585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Z. Y., Lee C. S., Lider O., Weiner H. L. Suppression of adjuvant arthritis in Lewis rats by oral administration of type II collagen. J Immunol. 1990 Oct 15;145(8):2489–2493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Eden W., Hogervorst E. J., Hensen E. J., van der Zee R., van Embden J. D., Cohen I. R. A cartilage-mimicking T-cell epitope on a 65K mycobacterial heat-shock protein: adjuvant arthritis as a model for human rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;145:27–43. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74594-2_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Meide P. H., Dubbeld M., Vijverberg K., Kos T., Schellekens H. The purification and characterization of rat gamma interferon by use of two monoclonal antibodies. J Gen Virol. 1986 Jun;67(Pt 6):1059–1071. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-6-1059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]