Abstract
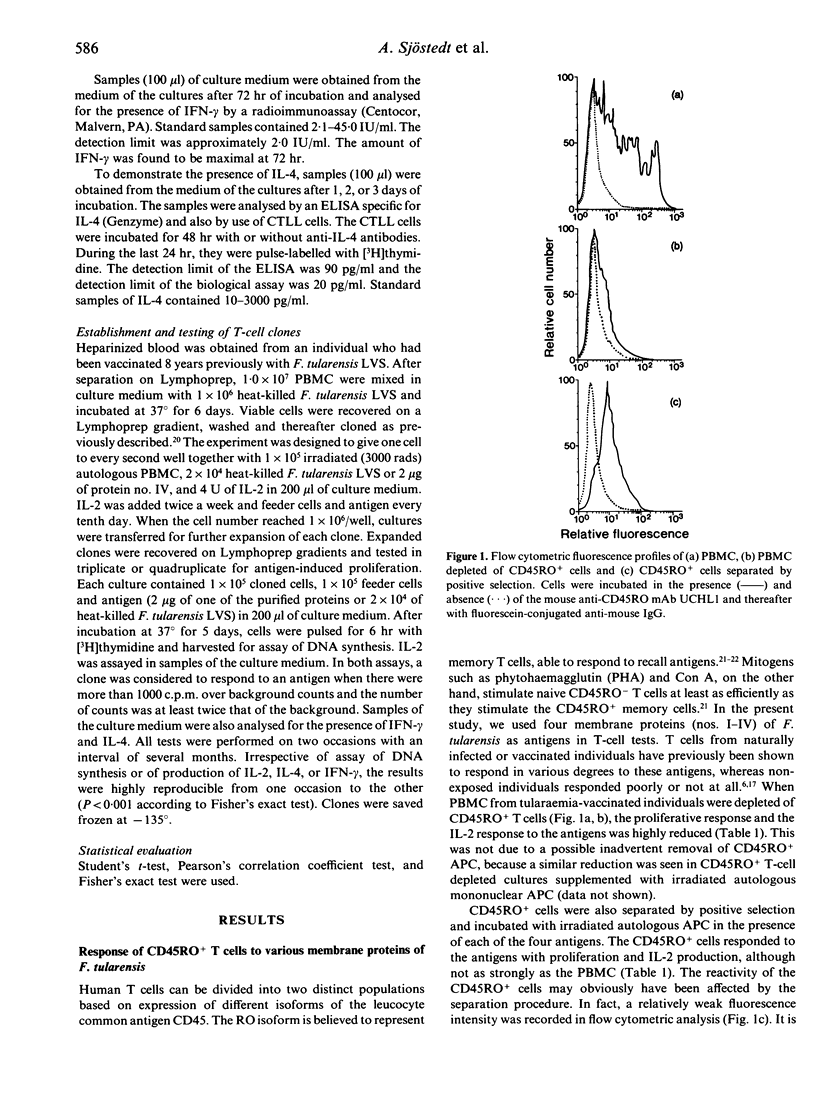
Tularaemia is an intracellular infection, which is controlled by the host as a result of an immunospecific T-cell response. A crucial product of the responding T cells is interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma), which acts by enhancing the microbicidal activity of macrophages. T cells of tularaemia-vaccinated individuals respond in vitro to a multitude of protein antigens of the vaccine strain Francisella tularensis LVS. In the present study, the responses to four of these antigens were shown to be confined mostly to the CD45RO+ memory T-cell subset. To characterize further the phenotype of the responding cells, purified CD4+ and CD8+ T cells were stimulated with the antigens. CD4+ T cells, but not CD8+ T cells, proliferated and produced IFN-gamma. However, when CD8+ T cells were isolated from bulk cultures of lymphocytes, which had been stimulated with antigen for 3 days, they responded to an extent similar to that of CD4+ T cells. Purified CD8+ T cells also responded when they were supplemented with interleukin-2 (IL-2). There was a direct quantitative correlation between the proliferative response of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells and their production of IFN-gamma. IL-2 was produced in the cultures, the amounts being higher in the cultures of CD4+ than in those of CD8+ cells. IL-4 was not detected in the culture medium of any of the T-cell subsets. Seventeen human alpha beta + CD4+ CD8- CD3+ T-cell clones, specific to antigens of F. tularensis, were raised. When proliferating, these clones did invariably produce IL-2 and IFN-gamma but no IL-4. In conclusion, both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells of tularaemia-vaccinated individuals respond with proliferation to various protein antigens of F. tularensis, and the proliferative response is strictly associated with IFN-gamma production. The CD8+ T-cell response seems to depend on cytokines supplied by proliferating CD4+ T cells.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anthony L. S., Ghadirian E., Nestel F. P., Kongshavn P. A. The requirement for gamma interferon in resistance of mice to experimental tularemia. Microb Pathog. 1989 Dec;7(6):421–428. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthony L. S., Kongshavn P. A. H-2 restriction in acquired cell-mediated immunity to infection with Francisella tularensis LVS. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):452–456. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.452-456.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiplunkar S., De Libero G., Kaufmann S. H. Mycobacterium leprae-specific Lyt-2+ T lymphocytes with cytolytic activity. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):793–797. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.793-797.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dannenberg A. M., Jr Delayed-type hypersensitivity and cell-mediated immunity in the pathogenesis of tuberculosis. Immunol Today. 1991 Jul;12(7):228–233. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90035-R. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Libero G., Kaufmann S. H. Antigen-specific Lyt-2+ cytolytic T lymphocytes from mice infected with the intracellular bacterium Listeria monocytogenes. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 15;137(8):2688–2694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Prete G. F., De Carli M., Mastromauro C., Biagiotti R., Macchia D., Falagiani P., Ricci M., Romagnani S. Purified protein derivative of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and excretory-secretory antigen(s) of Toxocara canis expand in vitro human T cells with stable and opposite (type 1 T helper or type 2 T helper) profile of cytokine production. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jul;88(1):346–350. doi: 10.1172/JCI115300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EIGELSBACH H. T., DOWNS C. M. Prophylactic effectiveness of live and killed tularemia vaccines. I. Production of vaccine and evaluation in the white mouse and guinea pig. J Immunol. 1961 Oct;87:415–425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudernack G., Leivestad T., Ugelstad J., Thorsby E. Isolation of pure functionally active CD8+ T cells. Positive selection with monoclonal antibodies directly conjugated to monosized magnetic microspheres. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Jun 24;90(2):179–187. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90074-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haanen J. B., de Waal Malefijt R., Res P. C., Kraakman E. M., Ottenhoff T. H., de Vries R. R., Spits H. Selection of a human T helper type 1-like T cell subset by mycobacteria. J Exp Med. 1991 Sep 1;174(3):583–592. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.3.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inaba K., Young J. W., Steinman R. M. Direct activation of CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes by dendritic cells. J Exp Med. 1987 Jul 1;166(1):182–194. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.1.182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin Y., Shih W. K., Berkower I. Human T cell response to the surface antigen of hepatitis B virus (HBsAg). Endosomal and nonendosomal processing pathways are accessible to both endogenous and exogenous antigen. J Exp Med. 1988 Jul 1;168(1):293–306. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.1.293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karttunen R., Andersson G., Ekre H. P., Juutinen K., Surcel H. M., Syrjälä H., Herva E. Interleukin 2 and gamma interferon production, interleukin 2 receptor expression, and DNA synthesis induced by tularemia antigen in vitro after natural infection or vaccination. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jun;25(6):1074–1078. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.6.1074-1078.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H. CD8+ T lymphocytes in intracellular microbial infections. Immunol Today. 1988 Jun;9(6):168–174. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91292-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koskela P., Herva E. Cell-mediated and humoral immunity induced by a live Francisella tularensis vaccine. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):983–989. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.983-989.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koskela P., Herva E. Cell-mediated immunity against Francisella tularensis after natural infection. Scand J Infect Dis. 1980;12(4):281–287. doi: 10.3109/inf.1980.12.issue-4.08. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leivestad T., Halvorsen R., Gaudernack G., Thorsby E. Ability of pure resting CD8+ human T cells to respond to alloantigen. Scand J Immunol. 1989 May;29(5):543–553. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1989.tb01157.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merkenschlager M., Ikeda H., Wilkinson D., Beverly P. C., Trowsdale J., Fisher A. G., Altmann D. M. Allorecognition of HLA-DR and -DQ transfectants by human CD45RA and CD45R0 CD4 T cells: repertoire analysis and activation requirements. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Jan;21(1):79–88. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neefjes J. J., Stollorz V., Peters P. J., Geuze H. J., Ploegh H. L. The biosynthetic pathway of MHC class II but not class I molecules intersects the endocytic route. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):171–183. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90224-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oftung F., Mustafa A. S., Husson R., Young R. A., Godal T. Human T cell clones recognize two abundant Mycobacterium tuberculosis protein antigens expressed in Escherichia coli. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 1;138(3):927–931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paliard X., de Vries J. E., Spits H. Comparison of lymphokine secretion and responsiveness of human T cell clones isolated in IL-4 and in IL-2. Cell Immunol. 1991 Jul;135(2):383–393. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(91)90283-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paliard X., de Waal Malefijt R., Yssel H., Blanchard D., Chrétien I., Abrams J., de Vries J., Spits H. Simultaneous production of IL-2, IL-4, and IFN-gamma by activated human CD4+ and CD8+ T cell clones. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):849–855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce E. J., Caspar P., Grzych J. M., Lewis F. A., Sher A. Downregulation of Th1 cytokine production accompanies induction of Th2 responses by a parasitic helminth, Schistosoma mansoni. J Exp Med. 1991 Jan 1;173(1):159–166. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfefferkorn E. R. Interferon gamma blocks the growth of Toxoplasma gondii in human fibroblasts by inducing the host cells to degrade tryptophan. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):908–912. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Röcken M., Müller K. M., Saurat J. H., Hauser C. Lectin-mediated induction of IL-4-producing CD4+ T cells. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 15;146(2):577–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders M. E., Makgoba M. W., Shaw S. Human naive and memory T cells: reinterpretation of helper-inducer and suppressor-inducer subsets. Immunol Today. 1988 Jul-Aug;9(7-8):195–199. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91212-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandström G., Tärnvik A., Wolf-Watz H. Immunospecific T-lymphocyte stimulation by membrane proteins from Francisella tularensis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Apr;25(4):641–644. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.4.641-644.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandström G., Tärnvik A., Wolf-Watz H., Löfgren S. Antigen from Francisella tularensis: nonidentity between determinants participating in cell-mediated and humoral reactions. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):101–106. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.101-106.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöstedt A., Sandström G., Tärnvik A. Several membrane polypeptides of the live vaccine strain Francisella tularensis LVS stimulate T cells from naturally infected individuals. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jan;28(1):43–48. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.1.43-48.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surcel H. M. Diversity of Francisella tularensis antigens recognized by human T lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1990 Aug;58(8):2664–2668. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.8.2664-2668.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surcel H. M., Ilonen J., Poikonen K., Herva E. Francisella tularensis-specific T-cell clones are human leukocyte antigen class II restricted, secrete interleukin-2 and gamma interferon, and induce immunoglobulin production. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2906–2908. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2906-2908.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surcel H. M., Tapaninaho S., Herva E. Cytotoxic CD4+ T cells specific for Francisella tularensis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Jan;83(1):112–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05598.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tärnvik A., Löfgren S. Stimulation of human lymphocytes by a vaccine strain of Francisella tularensis. Infect Immun. 1975 Nov;12(5):951–957. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.5.951-957.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tärnvik A. Nature of protective immunity to Francisella tularensis. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 May-Jun;11(3):440–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Via C. S., Tsokos G. C., Stocks N. I., Clerici M., Shearer G. M. Human in vitro allogeneic responses. Demonstration of three pathways of T helper cell activation. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 1;144(7):2524–2528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wierenga E. A., Snoek M., de Groot C., Chrétien I., Bos J. D., Jansen H. M., Kapsenberg M. L. Evidence for compartmentalization of functional subsets of CD2+ T lymphocytes in atopic patients. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 15;144(12):4651–4656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


