Abstract
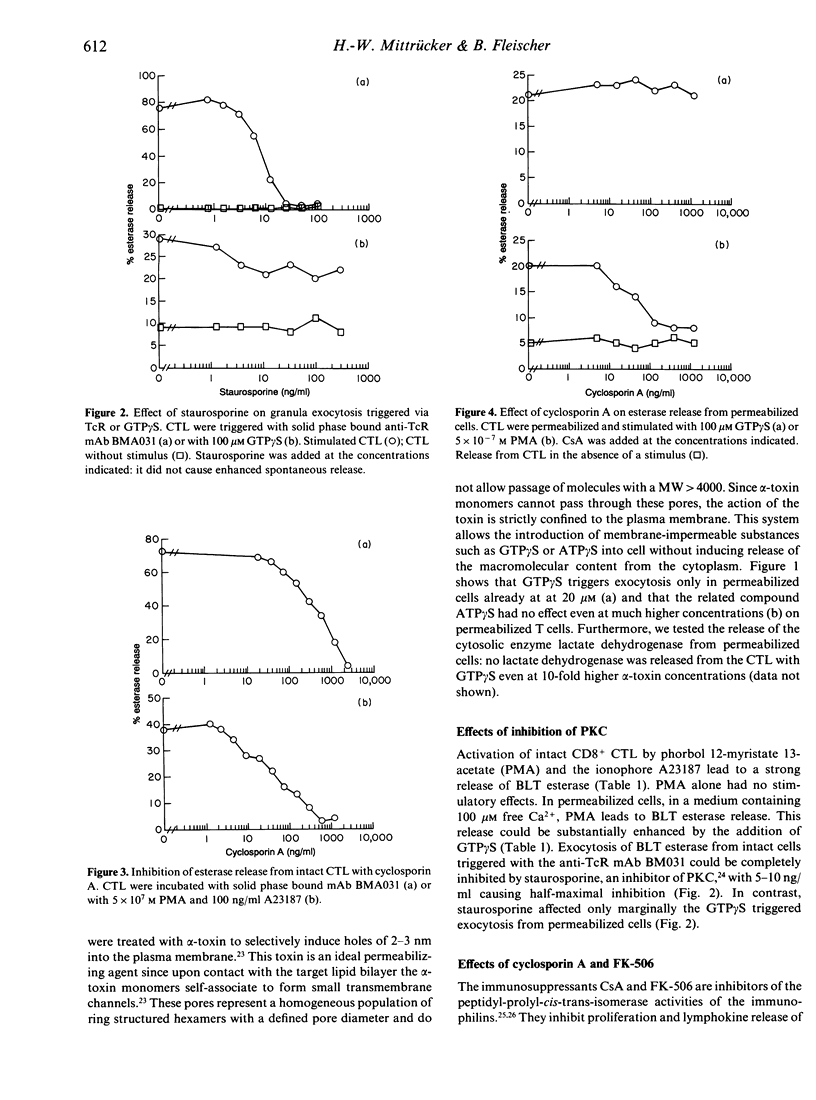
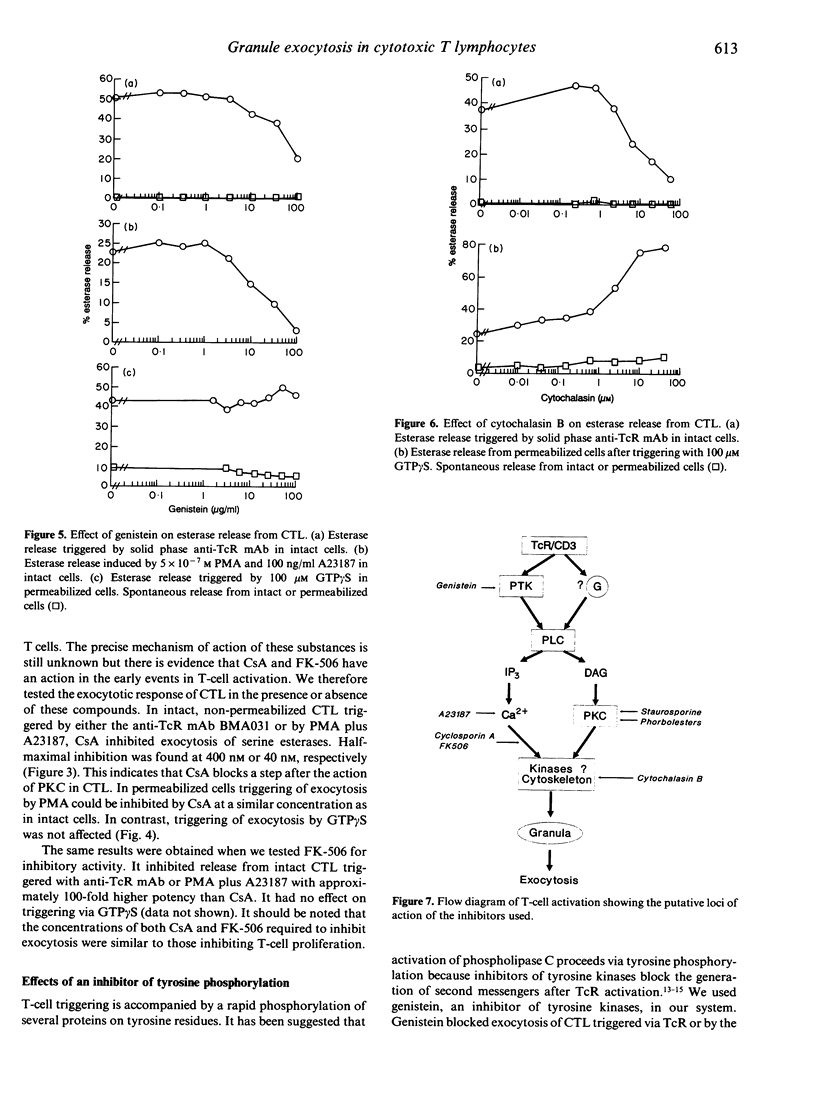
Human cloned CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes permeabilized with alpha-toxin of Staphylococcus aureus can be triggered by the guanosine triphosphate (GTP) analogue GTP gamma S to release the contents of their granula by exocytosis. To localize the guanosine nucleotide-binding protein (G-protein) activated by GTP gamma S in the sequence of events after T-lymphocyte triggering we have used several inhibitors of T-cell activation that inhibit early stages in T-cell triggering. The protein kinase C-inhibitor staurosporine, the immunosuppressants cyclosporin A and FK-506 and genistein, an inhibitor of tyrosine kinases, all inhibited esterase release triggered in intact cells by anti-T-cell receptor antibodies but not GTP gamma S-induced release from permeabilized cells. Cyclosporin A, FK-506 and genistein also blocked exocytosis triggered in intact cells by a combination of phorbolester and the calcium ionophore A23187. In addition, cytochalasin B, an inhibitor of actin polymerization, inhibited exocytosis in intact cells but enhanced exocytosis from permeabilized cells. These data show that the G-protein effecting exocytosis is localized distally in the cascade of events after T-cell activation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahnert-Hilger G., Bhakdi S., Gratzl M. Minimal requirements for exocytosis. A study using PC 12 cells permeabilized with staphylococcal alpha-toxin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12730–12734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aussel C., Mary D., Peyron J. F., Pelassy C., Ferrua B., Fehlmann M. Inhibition and activation of interleukin 2 synthesis by direct modification of guanosine triphosphate-binding proteins. J Immunol. 1988 Jan 1;140(1):215–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balch W. E. Small GTP-binding proteins in vesicular transport. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Dec;15(12):473–477. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90301-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrowman M. M., Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Two roles for guanine nucleotides in the stimulus-secretion sequence of neutrophils. Nature. 1986 Feb 6;319(6053):504–507. doi: 10.1038/319504a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol phosphates and cell signalling. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):197–205. doi: 10.1038/341197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Damage to mammalian cells by proteins that form transmembrane pores. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1987;107:147–223. doi: 10.1007/BFb0027646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Howell T. W., Gomperts B. D. Two G-proteins act in series to control stimulus-secretion coupling in mast cells: use of neomycin to distinguish between G-proteins controlling polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase and exocytosis. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 1):2745–2750. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Calculator programs for computing the composition of the solutions containing multiple metals and ligands used for experiments in skinned muscle cells. J Physiol (Paris) 1979;75(5):463–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer B. Non-specific propagation of human antigen-dependent T lymphocyte clones. J Immunol Methods. 1988 May 9;109(2):215–219. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90245-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerardy-Schahn R., Mittrücker H. W., Schultze U., Fleischer B. Selective loss of pertussis toxin-sensitive G-proteins from the plasma membrane after antibody-induced internalization of T-cell surface molecules. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 15;266(11):6942–6947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves J. D., Cantrell D. A. An analysis of the role of guanine nucleotide binding proteins in antigen receptor/CD3 antigen coupling to phospholipase C. J Immunol. 1991 Apr 1;146(7):2102–2107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkart P. A. Mechanism of lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:31–58. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsi E. D., Siegel J. N., Minami Y., Luong E. T., Klausner R. D., Samelson L. E. T cell activation induces rapid tyrosine phosphorylation of a limited number of cellular substrates. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10836–10842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imboden J. B., Shoback D. M., Pattison G., Stobo J. D. Cholera toxin inhibits the T-cell antigen receptor-mediated increases in inositol trisphosphate and cytoplasmic free calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5673–5677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Samelson L. E. T cell antigen receptor activation pathways: the tyrosine kinase connection. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):875–878. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90310-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvanta A., Nordstedt C., van der Ploeg I., Jondal M., Fredholm B. B. CD3/T-cell receptor coupling to a pertussis and cholera toxin-insensitive G-protein. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 3;250(2):536–540. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80791-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind I., Ahnert-Hilger G., Fuchs G., Gratzl M. Purification of alpha-toxin from Staphylococcus aureus and application to cell permeabilization. Anal Biochem. 1987 Jul;164(1):84–89. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90371-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mire-Sluis A. R., Hoffbrand A. V., Wickremasinghe R. G. Evidence that guanine-nucleotide binding regulatory proteins couple cell-surface receptors to the breakdown of inositol-containing lipids during T-lymphocyte mitogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Nov 13;148(3):1223–1231. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80263-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustelin T., Coggeshall K. M., Isakov N., Altman A. T cell antigen receptor-mediated activation of phospholipase C requires tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1990 Mar 30;247(4950):1584–1587. doi: 10.1126/science.2138816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustelin T., Pösö H., Andersson L. C. Role of G-proteins in T cell activation: non-hydrolysable GTP analogues induce early ornithine decarboxylase activity in human T lymphocytes. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3287–3290. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04641.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The molecular heterogeneity of protein kinase C and its implications for cellular regulation. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):661–665. doi: 10.1038/334661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantaleo G., Olive D., Poggi A., Pozzan T., Moretta L., Moretta A. Antibody-induced modulation of the CD3/T cell receptor complex causes T cell refractoriness by inhibiting the early metabolic steps involved in T cell activation. J Exp Med. 1987 Aug 1;166(2):619–624. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.2.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips R. J., Harnett M. M., Klaus G. G. Antigen receptor-mediated phosphoinositide hydrolysis in murine T cells is not initiated via G-protein activation. Int Immunol. 1991 Jul;3(7):617–621. doi: 10.1093/intimm/3.7.617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinnooy Kan E. A., Platzer E., Welte K., Wang C. Y. Modulation induction of the T3 antigen by OKT3 antibody is monocyte dependent. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):2979–2985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrezenmeier H., Ahnert-Hilger G., Fleischer B. Inactivation of a T cell receptor-associated GTP-binding protein by antibody-induced modulation of the T cell receptor/CD3 complex. J Exp Med. 1988 Aug 1;168(2):817–822. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.2.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shevach E. M. The effects of cyclosporin A on the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:397–423. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.002145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommermeyer H., Schwinzer R., Kaever V., Behl B., Resch K. The G protein coupling T cell antigen receptor/CD3-complex and phospholipase C in the human T cell lymphoma Jurkat is not a target for cholera toxin. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Sep;20(9):1881–1886. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaoki T., Nomoto H., Takahashi I., Kato Y., Morimoto M., Tomita F. Staurosporine, a potent inhibitor of phospholipid/Ca++dependent protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 13;135(2):397–402. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson A. W. FK-506--how much potential? Immunol Today. 1989 Jan;10(1):6–9. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90057-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschopp J., Nabholz M. Perforin-mediated target cell lysis by cytolytic T lymphocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:279–302. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.001431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Liu C. C., Persechini P. M., Cohn Z. A. Perforin-dependent and -independent pathways of cytotoxicity mediated by lymphocytes. Immunol Rev. 1988 Mar;103:161–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1988.tb00755.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


