Abstract
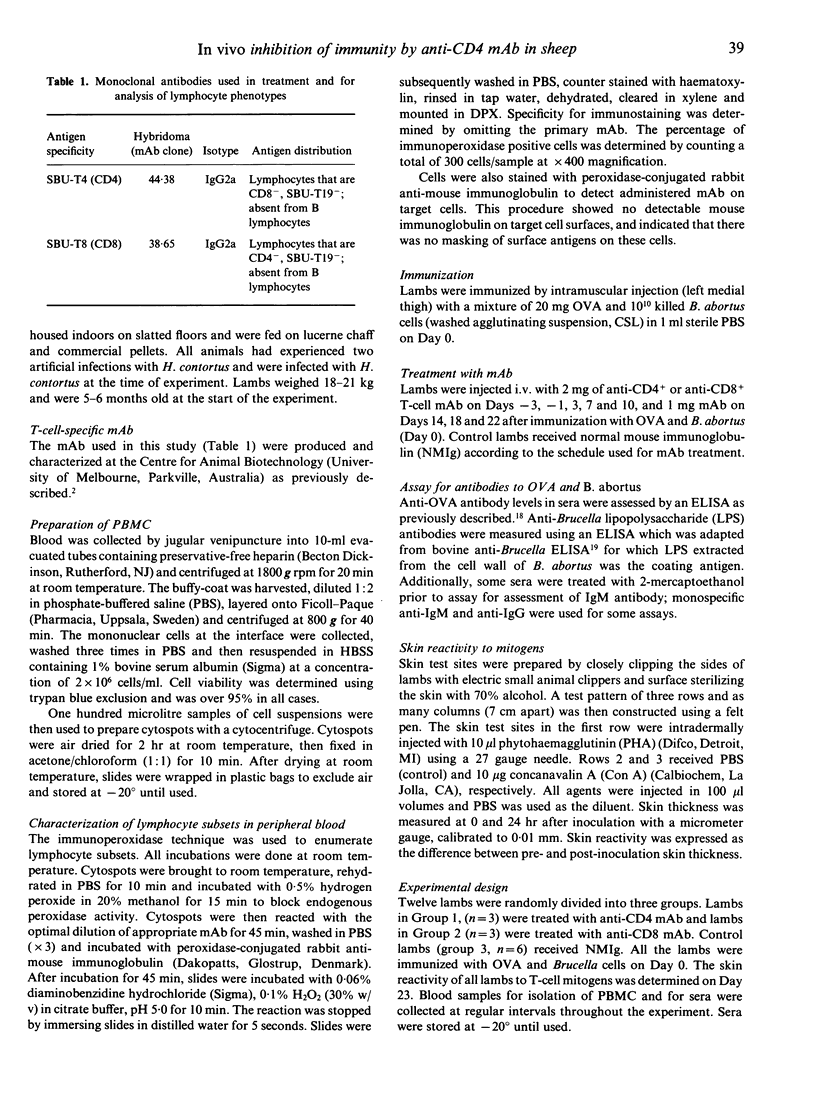
The ability of intravenously injected anti-CD4 and anti-CD8 monoclonal antibody (mAb) to deplete specific lymphocyte subsets in vivo and their effects on antibody responses to ovalbumin (OVA) and Brucella abortus, and skin reactivity to T-cell mitogens was examined in merino lambs. Repeated administration of anti-CD4 or anti-CD8 mAb caused a specific and sustained depletion of target cells from peripheral blood. Anti-CD4 mAb significantly inhibited the in vivo antibody response to OVA but had no effect on the antibody response to LPS of B. abortus. In contrast, antibody responses to both OVA and B. abortus lipopolysaccharides (LPS) remained unaffected in lambs depleted of their CD8+ T lymphocytes. These results confirm the T-cell dependence and independence of antibody responses to OVA and LPS, respectively. Skin reactions elicited by intradermal injections of phytohaemagglutinin (PHA) and concanavalin A (Con A) were also significantly suppressed in lambs depleted of their CD4+ T cells, but treatment with anti-CD8 mAb had no effect on skin responsiveness. Together, these results suggest that mAb can be extremely effective at selectively depleting lymphocyte subsets in vivo and can be used for studying various aspects of immunoregulation and immunity in sheep.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albers G. A., Gray G. D., Piper L. R., Barker J. S., Le Jambre L. F., Barger I. A. The genetics of resistance and resilience to Haemonchus contortus infection in young merino sheep. Int J Parasitol. 1987 Oct;17(7):1355–1363. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(87)90103-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin C. L., Teale A. J., Naessens J. G., Goddeeris B. M., MacHugh N. D., Morrison W. I. Characterization of a subset of bovine T lymphocytes that express BoT4 by monoclonal antibodies and function: similarity to lymphocytes defined by human T4 and murine L3T4. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4385–4391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobbold S. P., Jayasuriya A., Nash A., Prospero T. D., Waldmann H. Therapy with monoclonal antibodies by elimination of T-cell subsets in vivo. Nature. 1984 Dec 6;312(5994):548–551. doi: 10.1038/312548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulie P. G., Coutelier J. P., Uyttenhove C., Lambotte P., Van Snick J. In vivo suppression of T-dependent antibody responses by treatment with a monoclonal anti-L3T4 antibody. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Jun;15(6):638–640. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis J. A., Baldwin C. L., MacHugh N. D., Bensaid A., Teale A. J., Goddeeris B. M., Morrison W. I. Characterization by a monoclonal antibody and functional analysis of a subset of bovine T lymphocytes that express BoT8, a molecule analogous to human CD8. Immunology. 1986 Jul;58(3):351–358. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard C. J., Sopp P., Parsons K. R., Finch J. In vivo depletion of BoT4 (CD4) and of non-T4/T8 lymphocyte subsets in cattle with monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Apr;19(4):757–764. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay C. R., Maddox J. F., Gogolin-Ewens K. J., Brandon M. R. Characterization of two sheep lymphocyte differentiation antigens, SBU-T1 and SBU-T6. Immunology. 1985 Aug;55(4):729–737. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddox J. F., Mackay C. R., Brandon M. R. Surface antigens, SBU-T4 and SBU-T8, of sheep T lymphocyte subsets defined by monoclonal antibodies. Immunology. 1985 Aug;55(4):739–748. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. A., Oseroff A. R., Stratte P. T., Levy R. Monoclonal antibody therapeutic trials in seven patients with T-cell lymphoma. Blood. 1983 Nov;62(5):988–995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nauciel C. Role of CD4+ T cells and T-independent mechanisms in acquired resistance to Salmonella typhimurium infection. J Immunol. 1990 Aug 15;145(4):1265–1269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedrazzini T., Hug K., Louis J. A. Importance of L3T4+ and Lyt-2+ cells in the immunologic control of infection with Mycobacterium bovis strain bacillus Calmette-Guérin in mice. Assessment by elimination of T cell subsets in vivo. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 15;139(6):2032–2037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pescovitz M. D., Lunney J. K., Sachs D. H. Murine anti-swine T4 and T8 monoclonal antibodies: distribution and effects on proliferative and cytotoxic T cells. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):37–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips S. M., Walker D., Abdel-Hafez S. K., Linette G. P., Doughty B. L., Perrin P. J., el Fathelbab N. The immune response to Schistosoma mansoni infections in inbred rats. VI. Regulation by T cell subpopulations. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 15;139(8):2781–2787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podoba J. E., Stevenson M. M. CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes both contribute to acquired immunity to blood-stage Plasmodium chabaudi AS. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):51–58. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.51-58.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentice H. G., Blacklock H. A., Janossy G., Bradstock K. F., Skeggs D., Goldstein G., Hoffbrand A. V. Use of anti-T-cell monoclonal antibody OKT3 to prevent acute graft-versus-host disease in allogeneic bone-marrow transplantation for acute leukaemia. Lancet. 1982 Mar 27;1(8274):700–703. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)92619-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Goldstein G., Schlossman S. F. Separation of functional subsets of human T cells by a monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):4061–4065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.4061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears H. F., Herlyn D., Steplewski Z., Koprowski H. Phase II clinical trial of a murine monoclonal antibody cytotoxic for gastrointestinal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 1985 Nov;45(11 Pt 2):5910–5913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain S. L., Dialynas D. P., Fitch F. W., English M. Monoclonal antibody to L3T4 blocks the function of T cells specific for class 2 major histocompatibility complex antigens. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1118–1123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain S. L. T cell subsets and the recognition of MHC class. Immunol Rev. 1983;74:129–142. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb01087.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassmer P., Chan C., Lögdberg L., Shevach E. M. Role of the L3T4-antigen in T cell activation. II. Inhibition of T cell activation by monoclonal anti-L3T4 antibodies in the absence of accessory cells. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2237–2242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. L., Gill H. S. Post natal ontogeny of immunological responsiveness in Merino sheep. Res Vet Sci. 1991 Jul;51(1):88–93. doi: 10.1016/0034-5288(91)90037-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wofsy D., Mayes D. C., Woodcock J., Seaman W. E. Inhibition of humoral immunity in vivo by monoclonal antibody to L3T4: studies with soluble antigens in intact mice. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):1698–1701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wofsy D., Seaman W. E. Successful treatment of autoimmunity in NZB/NZW F1 mice with monoclonal antibody to L3T4. J Exp Med. 1985 Feb 1;161(2):378–391. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.2.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


