Abstract
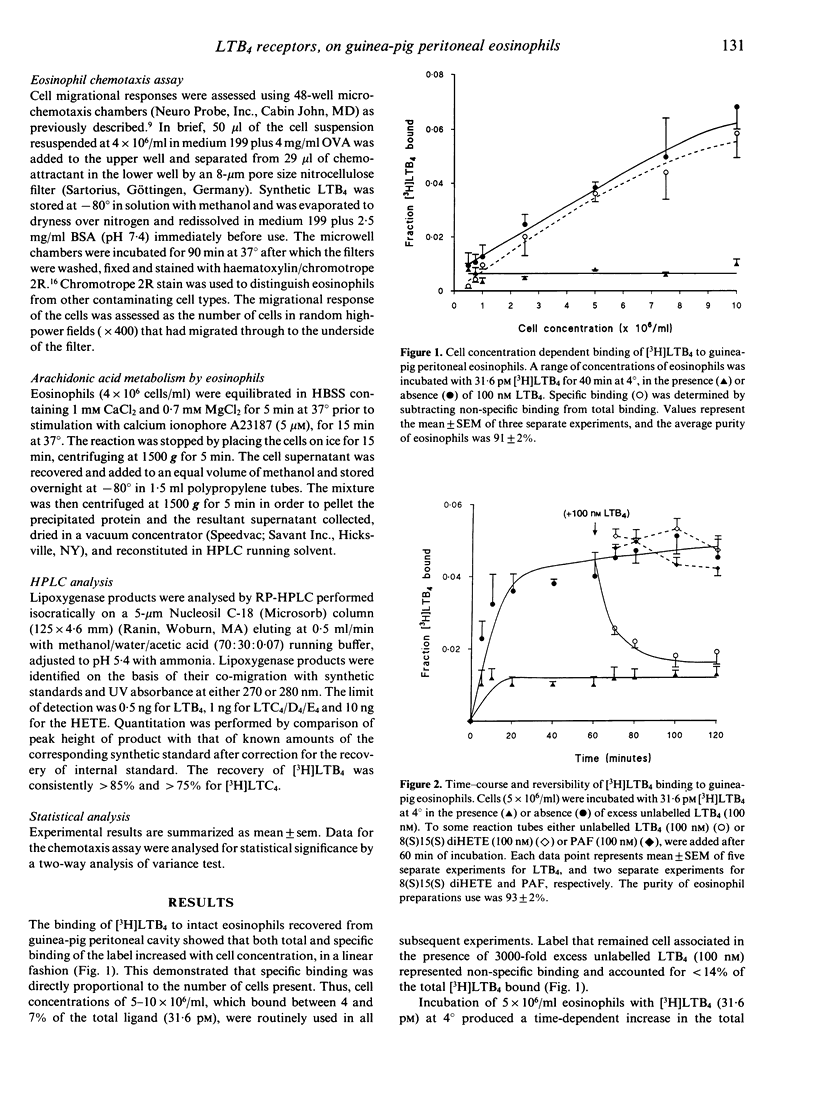
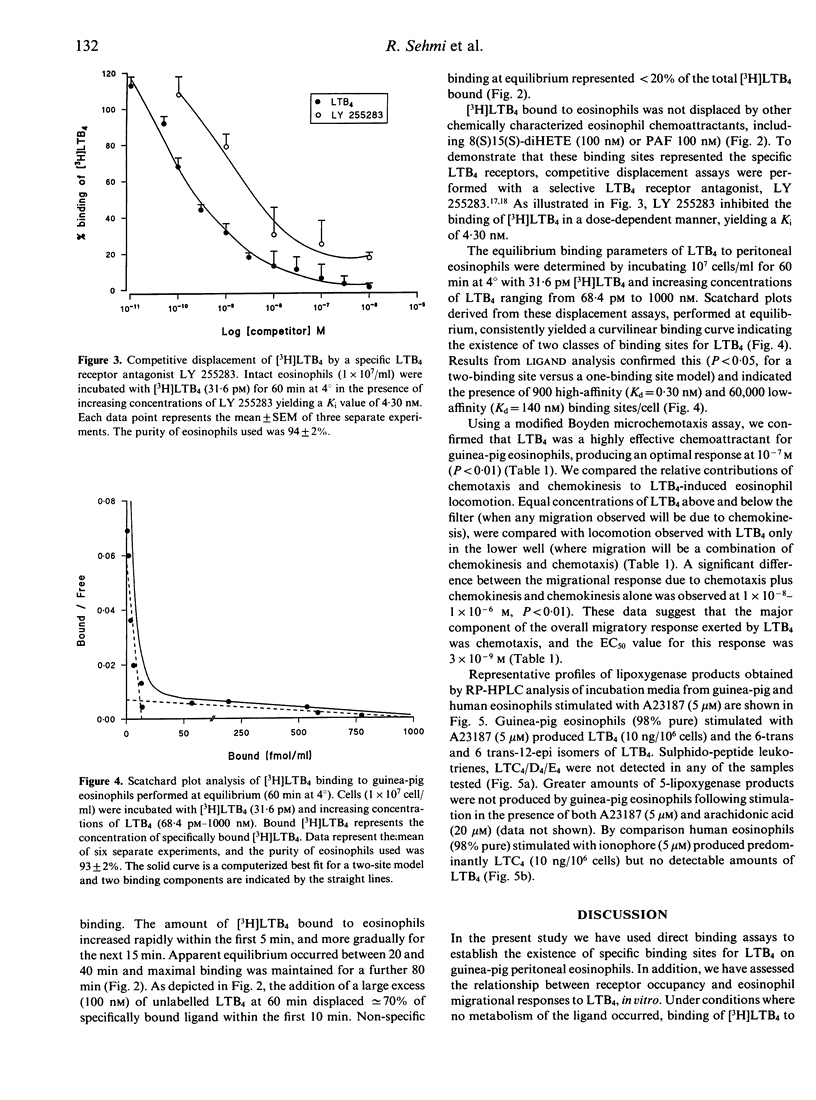
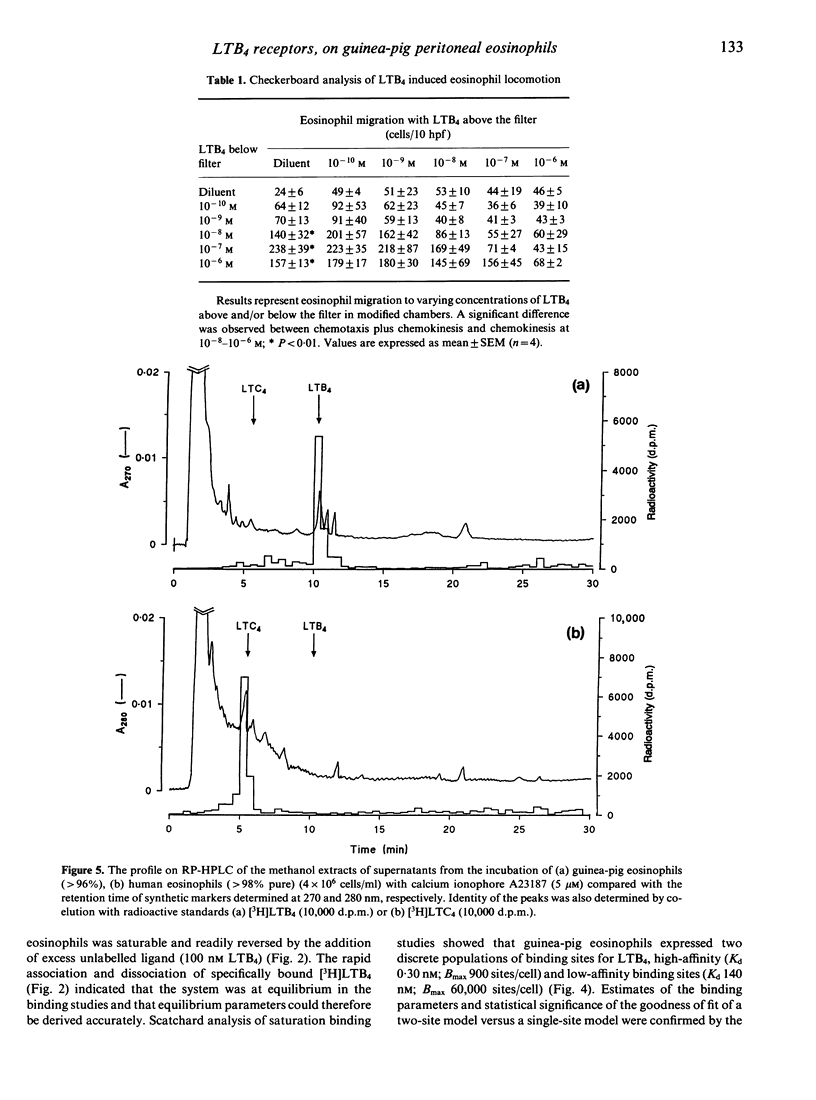
We have recently reported that guinea-pig eosinophil chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis (ECF-A), an activity present in diffusates from antigen-challenged sensitized lung, is largely accounted for by leukotriene B4 (LTB4) and to a lesser extent 8(S)15(S)-dihydroxy 5,9,11,13 (Z,E,Z,E) eicosatetraenoic acid. We characterized cell surface receptors for LTB4 on guinea-pig eosinophils in order to demonstrate an association between receptor occupancy and eosinophiliotactic activity of guinea-pig ECF-A. Equilibrium binding studies showed that peritoneal eosinophils bound [3H]LTB4 in a cell concentration and time-dependent fashion. The binding was saturable and specific for LTB4 as other eosinophil chemoattractants, i.e. platelet-activating factor (PAF) and 8(S)15(S)-diHETE, were unable to displace significant amounts of [3H]LTB4. In addition the binding was readily reversed by the LTB4 receptor antagonist LY 255283 (Ki 4.30 nM). Scatchard plot analysis revealed two discrete populations of binding sites, high affinity (Kd1 = 0.30 nM; Bmax = 900 sites/cell) and low-affinity sites (Kd2 = 140 nM; Bmax = 60,000 sites/cell). The major migratory component of LTB4-stimulated eosinophil locomotion was chemotaxis, optimal at 1 x 10(-7) M (P < 0.01) with EC50 value of 3 x 10(-9) M. A comparison of the profile of arachidonic acid metabolism by RP-HPLC analysis showed that following stimulation with calcium ionophore (A23187) guinea-pig eosinophils preferentially synthesized LTB4 (10 ng/10(6) cells) while in contrast human eosinophils synthesized LTC4 (10 ng/10(6) cells). Therefore our data show that guinea-pig eosinophils express both high- and low-affinity receptors for LTB4 and that the chemotactic response to this mediator may be mediated by ligation of the high-affinity binding site. Furthermore guinea-pig peritoneal eosinophils can synthesize LTB4, a mediator which constitutes > 60% of guinea-pig ECF-A.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benjamin C. W., Rupple P. L., Gorman R. R. Appearance of specific leukotriene B4 binding sites in myeloid differentiated HL-60 cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14208–14213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faccioli L. H., Nourshargh S., Moqbel R., Williams F. M., Sehmi R., Kay A. B., Williams T. J. The accumulation of 111In-eosinophils induced by inflammatory mediators, in vivo. Immunology. 1991 Jun;73(2):222–227. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleich G. J. The eosinophil and bronchial asthma: current understanding. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1990 Feb;85(2):422–436. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(90)90151-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J., Austen K. F. Purification and synthesis of eosinophilotactic tetrapeptides of human lung tissue: identification as eosinophil chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):4123–4127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.4123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman D. W., Goetzl E. J. Heterogeneity of human polymorphonuclear leukocyte receptors for leukotriene B4. Identification of a subset of high affinity receptors that transduce the chemotactic response. J Exp Med. 1984 Apr 1;159(4):1027–1041. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.4.1027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulbenkian A. R., Fernandez X., Kreutner W., Minnicozzi M., Watnick A. S., Kung T., Egan R. W. Anaphylactic challenge causes eosinophil accumulation in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of guinea pigs. Modulation by betamethasone, phenidone, indomethacin, WEB 2086, and a novel antiallergy agent, SCH 37224. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Sep;142(3):680–685. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/142.3.680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gärtner I. Separation of human eosinophils in density gradients of polyvinylpyrrolidone-coated silica gel (Percoll). Immunology. 1980 May;40(1):133–136. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata K., Maghni K., Borgeat P., Sirois P. Guinea pig alveolar eosinophils and macrophages produce leukotriene B4 but no peptido-leukotriene. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 1;144(5):1880–1885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay A. B., Austen K. F. The IgE-mediated release of an eosinophil leukocyte chemotactic factor from human lung. J Immunol. 1971 Sep;107(3):899–902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay A. B., Shin H. S., Austen K. F. Selective attraction of eosinophils and synergism between eosinophil chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis (ECF-A) and a fragment cleaved from the fifth component of complement (C5a). Immunology. 1973 Jun;24(6):969–976. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay A. B., Stechschulte D. J., Austen K. F. An eosinophil leukocyte chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis. J Exp Med. 1971 Mar 1;133(3):602–619. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.3.602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay A. B. Studies on eosinophil leucocyte migration. II. Factors specifically chemotactic for eosinophils and neutrophils generated from guinea-pig serum by antigen-antibody complexes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Nov;7(5):723–737. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura I., Moritani Y., Tanizaki Y. Basophils in bronchial asthma with reference to reagin-type allergy. Clin Allergy. 1973 Jun;3(2):195–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1973.tb01321.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin A. H., Ruppel P. L., Gorman R. R. Leukotriene B4 binding to human neutrophils. Prostaglandins. 1984 Dec;28(6):837–849. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(84)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maghni K., de Brum-Fernandes A. J., Földes-Filep E., Gaudry M., Borgeat P., Sirois P. Leukotriene B4 receptors on guinea pig alveolar eosinophils. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Sep;258(3):784–789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng C. F., Sun F. F., Taylor B. M., Wolin M. S., Wong P. Y. Functional properties of guinea pig eosinophil leukotriene B4 receptor. J Immunol. 1991 Nov 1;147(9):3096–3103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J., Kosfeld S., Nishihira J. Binding and metabolism of leukotriene B4 by neutrophils and their subcellular organelles. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Mar;126(3):359–370. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041260306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards I. M., Griffin R. L., Oostveen J. A., Morris J., Wishka D. G., Dunn C. J. Effect of the selective leukotriene B4 antagonist U-75302 on antigen-induced bronchopulmonary eosinophilia in sensitized guinea pigs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Dec;140(6):1712–1716. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.6.1712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehmi R., Cromwell O., Taylor G. W., Kay A. B. Identification of guinea pig eosinophil chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis as leukotriene B4 and 8(S),15(S)-dihydroxy-5,9,11,13(Z,E,Z,E)-eicosatetraenoic acid. J Immunol. 1991 Oct 1;147(7):2276–2283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehmi R., Wardlaw A. J., Cromwell O., Kurihara K., Waltmann P., Kay A. B. Interleukin-5 selectively enhances the chemotactic response of eosinophils obtained from normal but not eosinophilic subjects. Blood. 1992 Jun 1;79(11):2952–2959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shay A., Connolly T., Smith D. N., Crean G. L. Ultrastructural analysis of leukocytes recruited into the guinea pig lung by LTB4 aerosol. Agents Actions. 1989 Jun;27(3-4):361–364. doi: 10.1007/BF01972823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun F. F., Czuk C. I., Taylor B. M. Arachidonic acid metabolism in guinea pig eosinophils: synthesis of thromboxane B2 and leukotriene B4 in response to soluble or particulate activators. J Leukoc Biol. 1989 Aug;46(2):152–160. doi: 10.1002/jlb.46.2.152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk J., Maas R. L., Brash A. R., Roberts L. J., 2nd, Oates J. A. Arachidonic acid 15-lipoxygenase products from human eosinophils. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):7068–7076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardlaw A. J., Kay A. B. The role of the eosinophil in the pathogenesis of asthma. Allergy. 1987 Jul;42(5):321–335. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1987.tb02218.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardlaw A. J., Moqbel R., Cromwell O., Kay A. B. Platelet-activating factor. A potent chemotactic and chemokinetic factor for human eosinophils. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1701–1706. doi: 10.1172/JCI112765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


