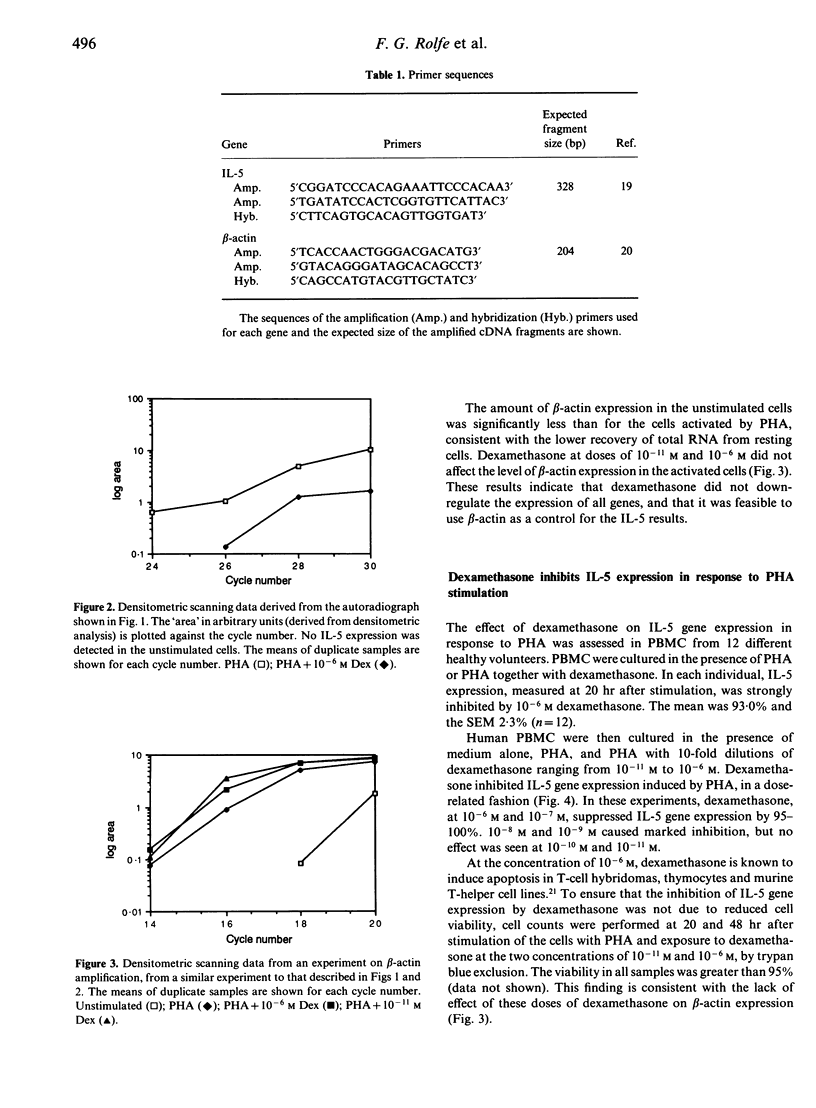
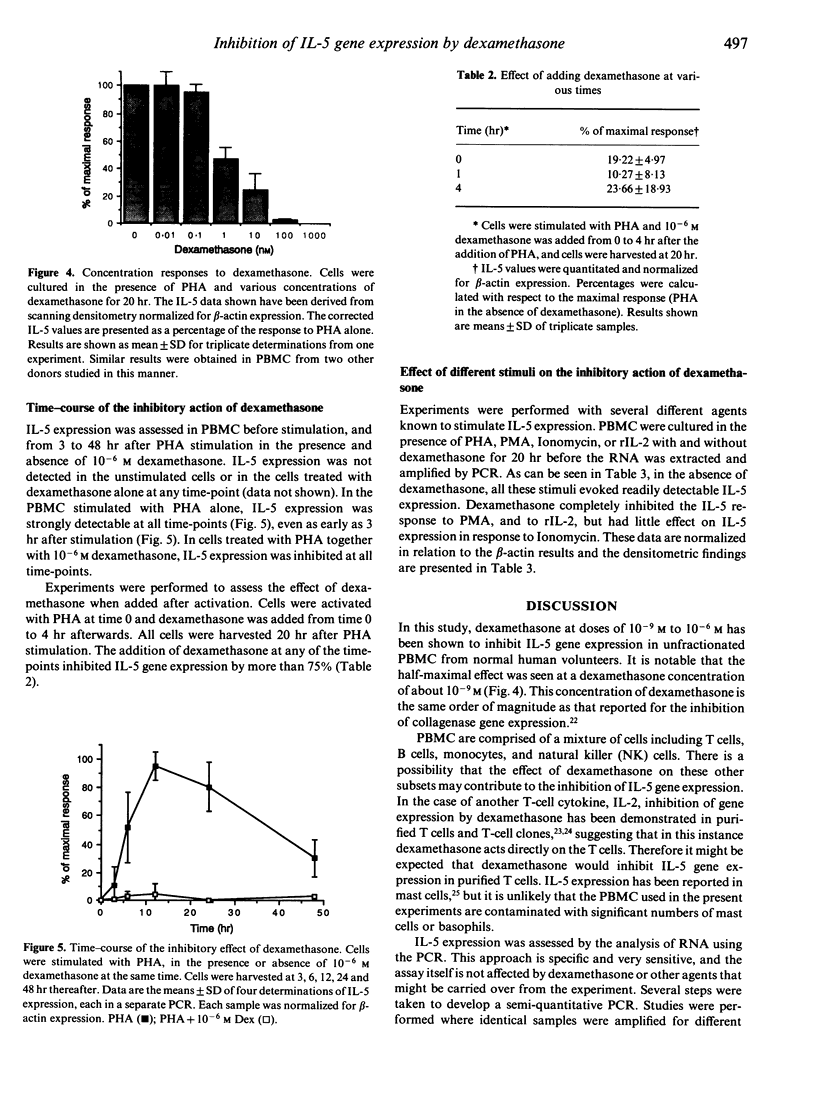
Abstract
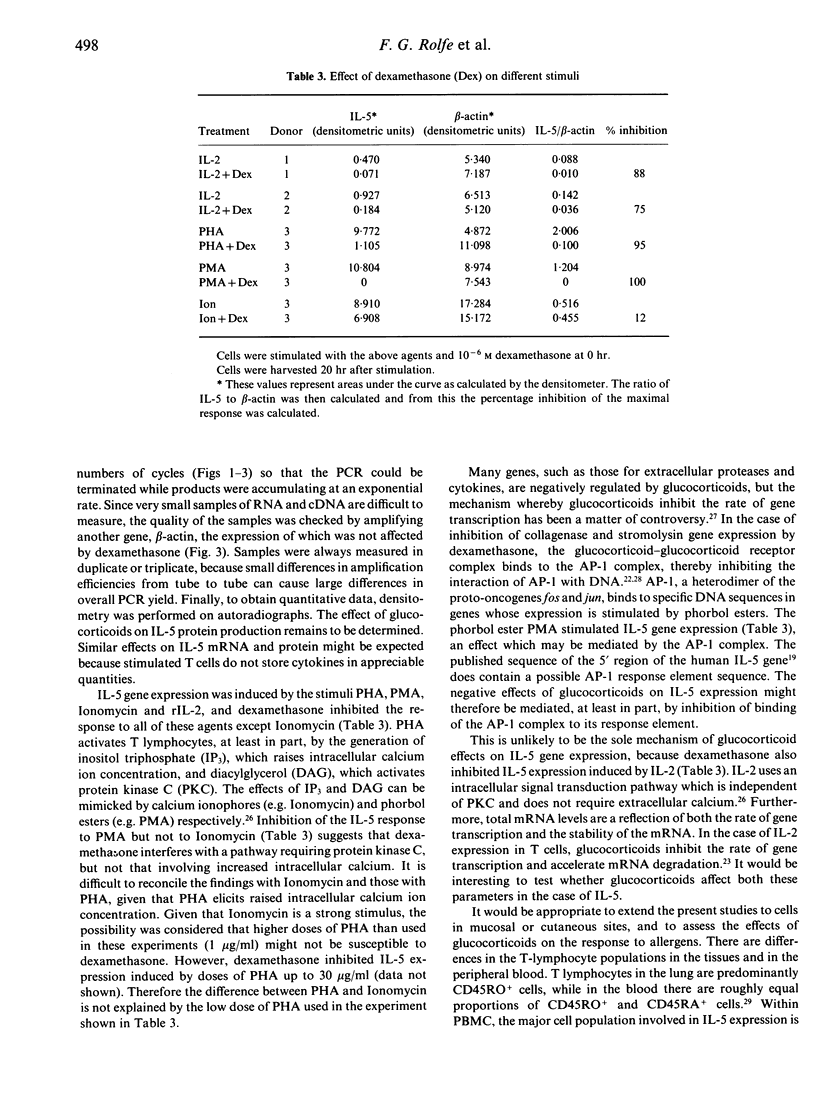
The effect of glucocorticoids on interleukin-5 (IL-5) gene expression was assessed in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. IL-5 expression was stimulated by phytohaemagglutinin (PHA), IL-2, phorbol myristate acetate (PMA) or Ionomycin. A semi-quantitative assay for IL-5 gene expression was developed, based on RNA extraction and the polymerase chain reaction. IL-5 expression in response to PHA was profoundly inhibited by 10(-6) M dexamethasone, and significant inhibition was detected at doses of dexamethasone as low as 10(-9) M. When dexamethasone was added to the cells at the same time as PHA, the inhibitory effect could be detected as early as 3 hr. Dexamethasone at 10(-6) M also profoundly inhibited the IL-5 response to PMA and to IL-2, but the IL-5 response to Ionomycin was not significantly affected. These results suggest that dexamethasone may be capable of interfering with a pathway involving protein kinase C. There is increasing evidence that IL-5 may play a pathogenic role in asthma and other manifestations of acute hypersensitivity. The present findings indicate that inhibition of IL-5 expression may be one of the mechanisms whereby glucocorticoids exert their beneficial effects in diseases such as asthma.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altman A., Mustelin T., Coggeshall K. M. T lymphocyte activation: a biological model of signal transduction. Crit Rev Immunol. 1990;10(4):347–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arya S. K., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C. Dexamethasone-mediated inhibition of human T cell growth factor and gamma-interferon messenger RNA. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):273–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boumpas D. T., Anastassiou E. D., Older S. A., Tsokos G. C., Nelson D. L., Balow J. E. Dexamethasone inhibits human interleukin 2 but not interleukin 2 receptor gene expression in vitro at the level of nuclear transcription. J Clin Invest. 1991 May;87(5):1739–1747. doi: 10.1172/JCI115192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell H. D., Tucker W. Q., Hort Y., Martinson M. E., Mayo G., Clutterbuck E. J., Sanderson C. J., Young I. G. Molecular cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of the gene encoding human eosinophil differentiation factor (interleukin 5). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6629–6633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlesworth E. N., Kagey-Sobotka A., Schleimer R. P., Norman P. S., Lichtenstein L. M. Prednisone inhibits the appearance of inflammatory mediators and the influx of eosinophils and basophils associated with the cutaneous late-phase response to allergen. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 15;146(2):671–676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffman R. L., Seymour B. W., Hudak S., Jackson J., Rennick D. Antibody to interleukin-5 inhibits helminth-induced eosinophilia in mice. Science. 1989 Jul 21;245(4915):308–310. doi: 10.1126/science.2787531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frew A. J., Kay A. B. The relationship between infiltrating CD4+ lymphocytes, activated eosinophils, and the magnitude of the allergen-induced late phase cutaneous reaction in man. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 15;141(12):4158–4164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Crabtree G. R., Smith K. A. Glucocorticoid-induced inhibition of T cell growth factor production. I. The effect on mitogen-induced lymphocyte proliferation. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1624–1631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallahan A. R., Armour C. L., Black J. L. Products of neutrophils and eosinophils increase the responsiveness of human isolated bronchial tissue. Eur Respir J. 1990 May;3(5):554–558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamid Q., Azzawi M., Ying S., Moqbel R., Wardlaw A. J., Corrigan C. J., Bradley B., Durham S. R., Collins J. V., Jeffery P. K. Expression of mRNA for interleukin-5 in mucosal bronchial biopsies from asthma. J Clin Invest. 1991 May;87(5):1541–1546. doi: 10.1172/JCI115166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonat C., Rahmsdorf H. J., Park K. K., Cato A. C., Gebel S., Ponta H., Herrlich P. Antitumor promotion and antiinflammation: down-modulation of AP-1 (Fos/Jun) activity by glucocorticoid hormone. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1189–1204. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90395-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez A. F., Sanderson C. J., Gamble J. R., Campbell H. D., Young I. G., Vadas M. A. Recombinant human interleukin 5 is a selective activator of human eosinophil function. J Exp Med. 1988 Jan 1;167(1):219–224. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.1.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger W. J., Zavala D., Richerson H. B., Moseley P., Iwamota P., Monick M., Sjoerdsma K., Hunninghake G. W. Local allergen challenge and bronchoalveolar lavage of allergic asthmatic lungs. Description of the model and local airway inflammation. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Feb;135(2):433–440. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1987.135.2.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng S. Y., Gunning P., Eddy R., Ponte P., Leavitt J., Shows T., Kedes L. Evolution of the functional human beta-actin gene and its multi-pseudogene family: conservation of noncoding regions and chromosomal dispersion of pseudogenes. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2720–2732. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaut M., Pierce J. H., Watson C. J., Hanley-Hyde J., Nordan R. P., Paul W. E. Mast cell lines produce lymphokines in response to cross-linkage of Fc epsilon RI or to calcium ionophores. Nature. 1989 May 4;339(6219):64–67. doi: 10.1038/339064a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltini C., Kirby M., Trapnell B. C., Tamura N., Crystal R. G. Biased accumulation of T lymphocytes with "memory"-type CD45 leukocyte common antigen gene expression on the epithelial surface of the human lung. J Exp Med. 1990 Apr 1;171(4):1123–1140. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.4.1123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson C. J., Campbell H. D., Young I. G. Molecular and cellular biology of eosinophil differentiation factor (interleukin-5) and its effects on human and mouse B cells. Immunol Rev. 1988 Feb;102:29–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1988.tb00740.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleimer R. P. Effects of glucocorticosteroids on inflammatory cells relevant to their therapeutic applications in asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Feb;141(2 Pt 2):S59–S69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sewell W. A., Valentine J. E., Cooley M. A. Expression of interleukin 5 by the CD4+CD45R0+ subset of human T cells. Growth Factors. 1992;6(4):295–302. doi: 10.3109/08977199209021541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobler A., Meier R., Seitz M., Dewald B., Baggiolini M., Fey M. F. Glucocorticoids downregulate gene expression of GM-CSF, NAP-1/IL-8, and IL-6, but not of M-CSF in human fibroblasts. Blood. 1992 Jan 1;79(1):45–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vacca A., Martinotti S., Screpanti I., Maroder M., Felli M. P., Farina A. R., Gismondi A., Santoni A., Frati L., Gulino A. Transcriptional regulation of the interleukin 2 gene by glucocorticoid hormones. Role of steroid receptor and antigen-responsive 5'-flanking sequences. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8075–8080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegner C. D., Gundel R. H., Reilly P., Haynes N., Letts L. G., Rothlein R. Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) in the pathogenesis of asthma. Science. 1990 Jan 26;247(4941):456–459. doi: 10.1126/science.1967851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. Y., Fargeas C., Nakajima T., Delespesse G. Glucocorticoids suppress the production of interleukin 4 by human lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Oct;21(10):2645–2647. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830211053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Yen H. F., Chambard J. C., Sun Y. L., Smeal T., Schmidt T. J., Drouin J., Karin M. Transcriptional interference between c-Jun and the glucocorticoid receptor: mutual inhibition of DNA binding due to direct protein-protein interaction. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1205–1215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90396-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacharchuk C. M., Merćep M., Chakraborti P. K., Simons S. S., Jr, Ashwell J. D. Programmed T lymphocyte death. Cell activation- and steroid-induced pathways are mutually antagonistic. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 15;145(12):4037–4045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]