Abstract
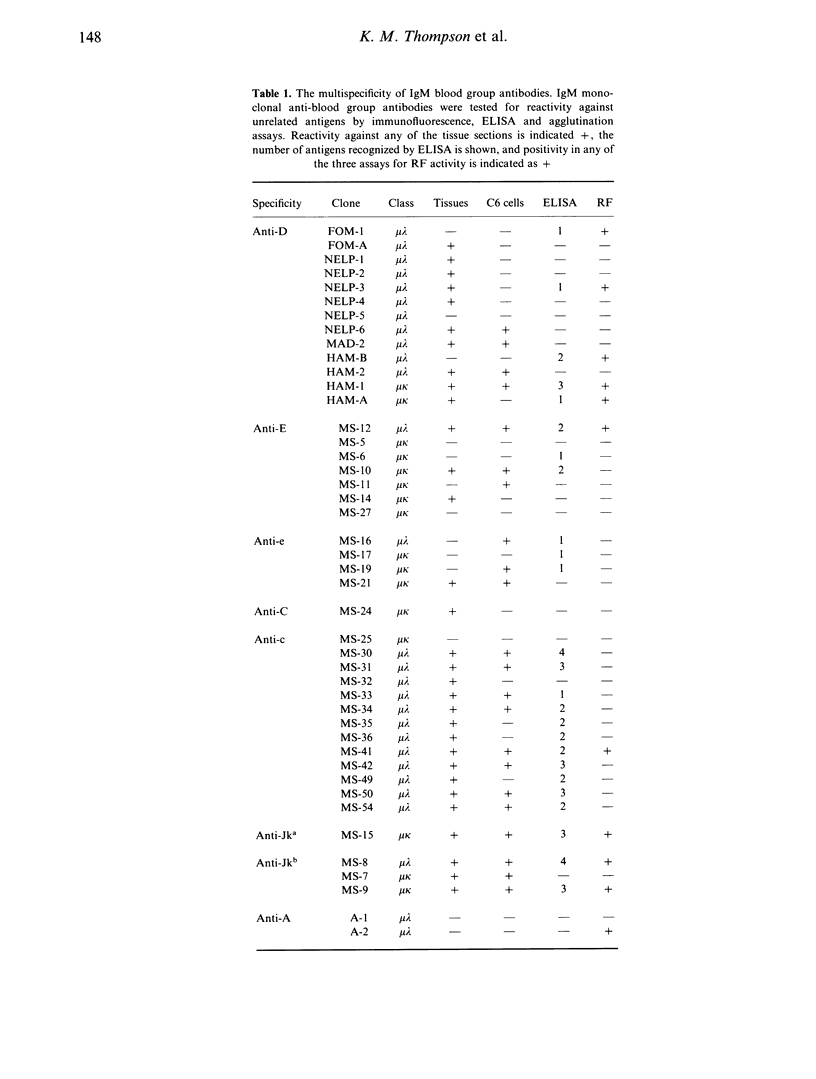
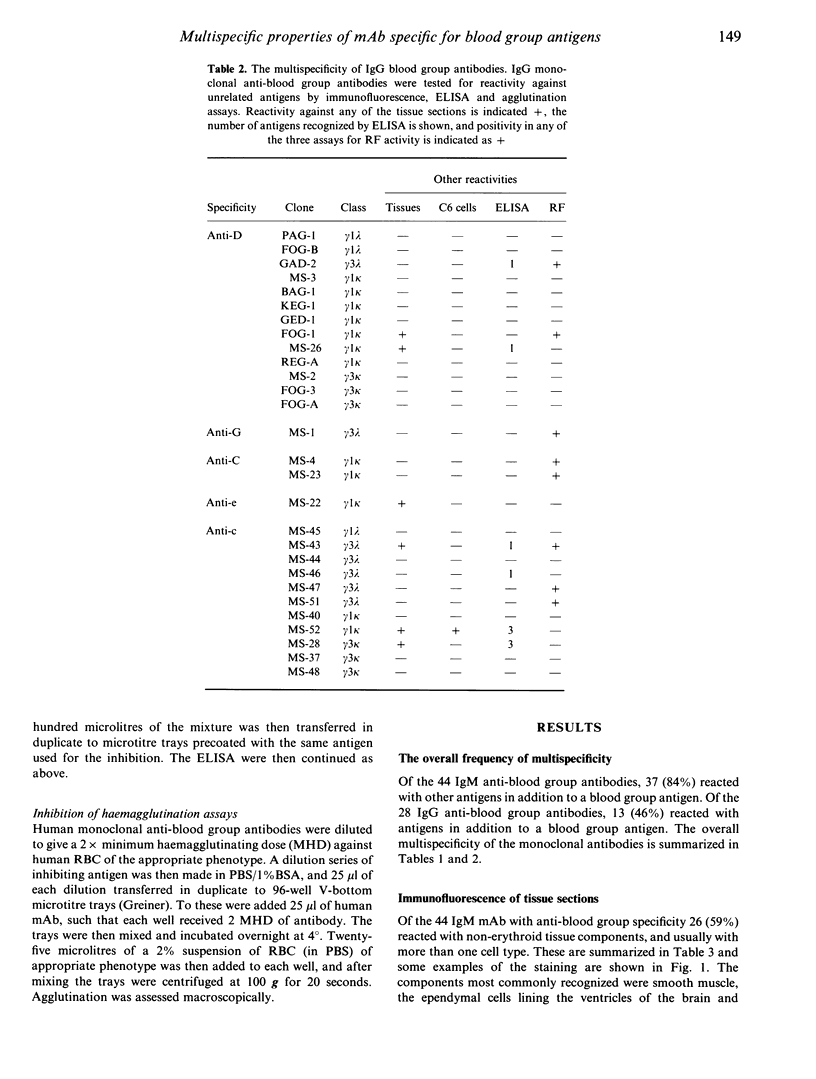
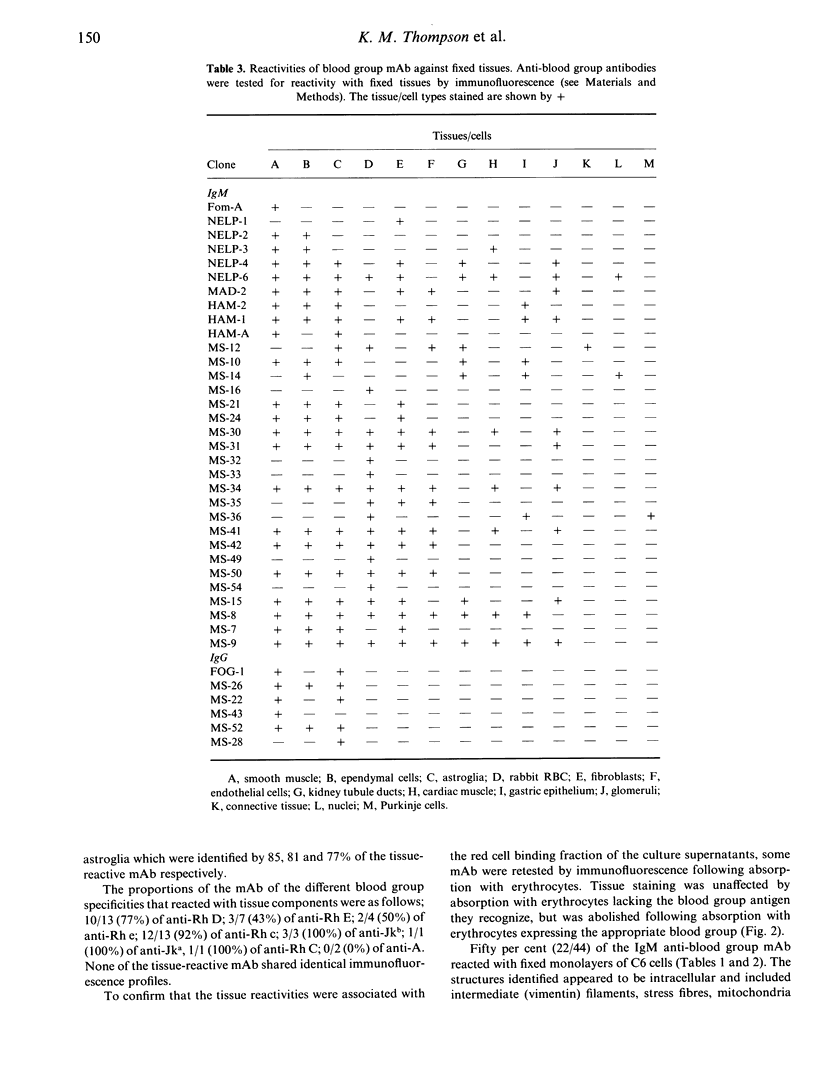
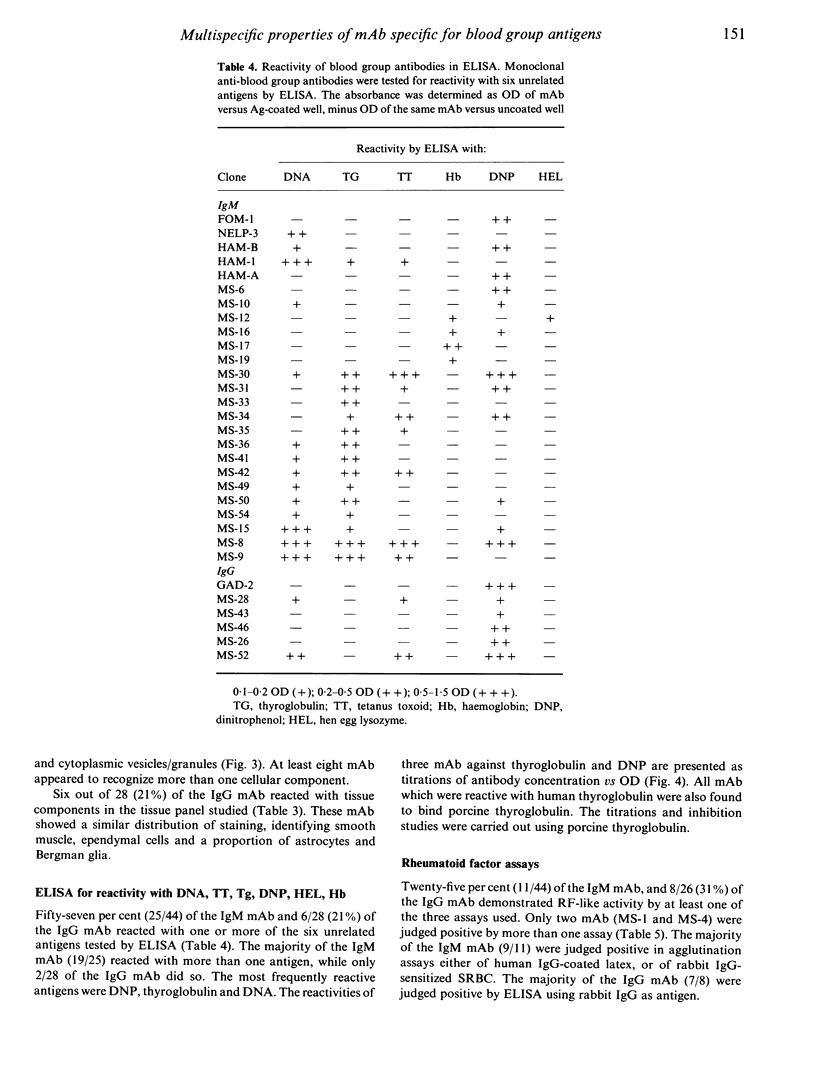
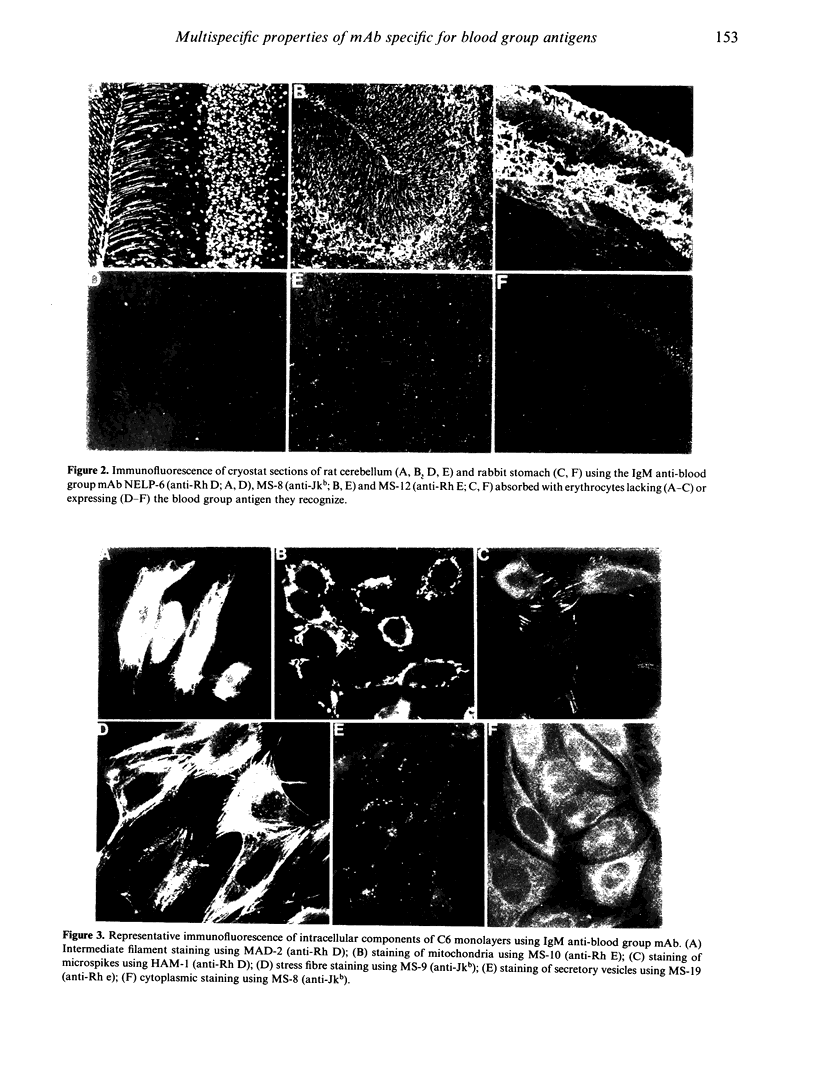
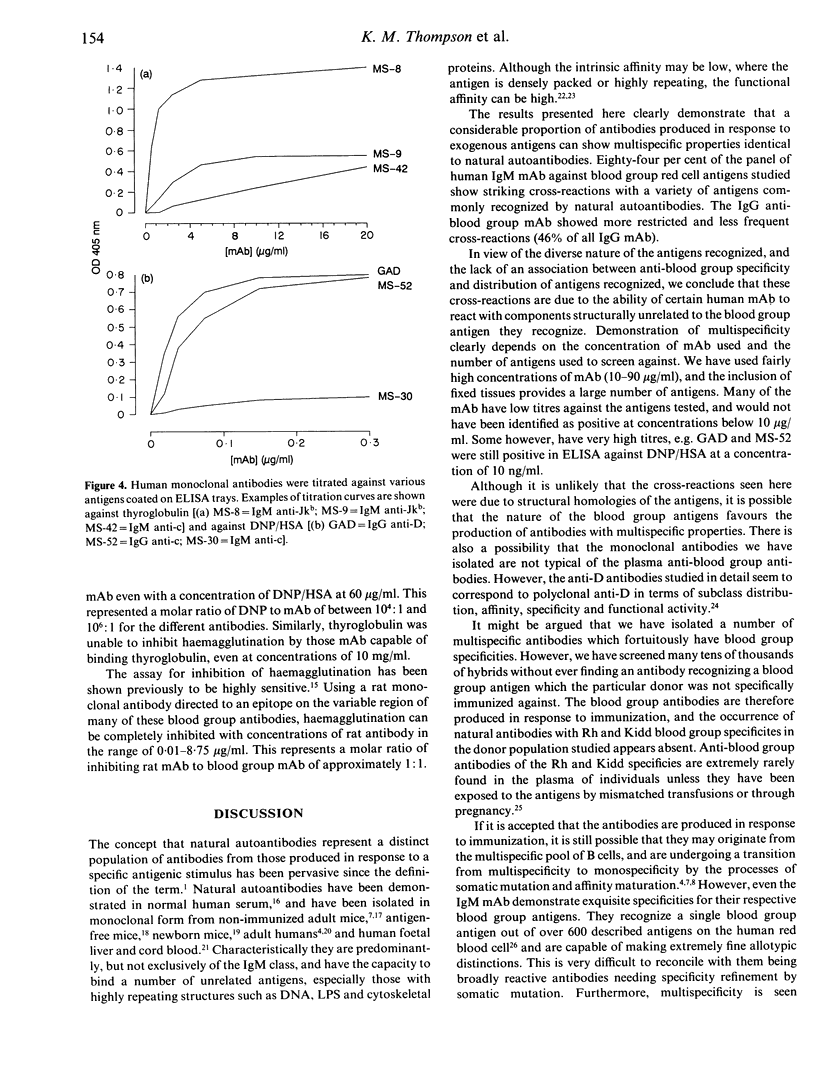
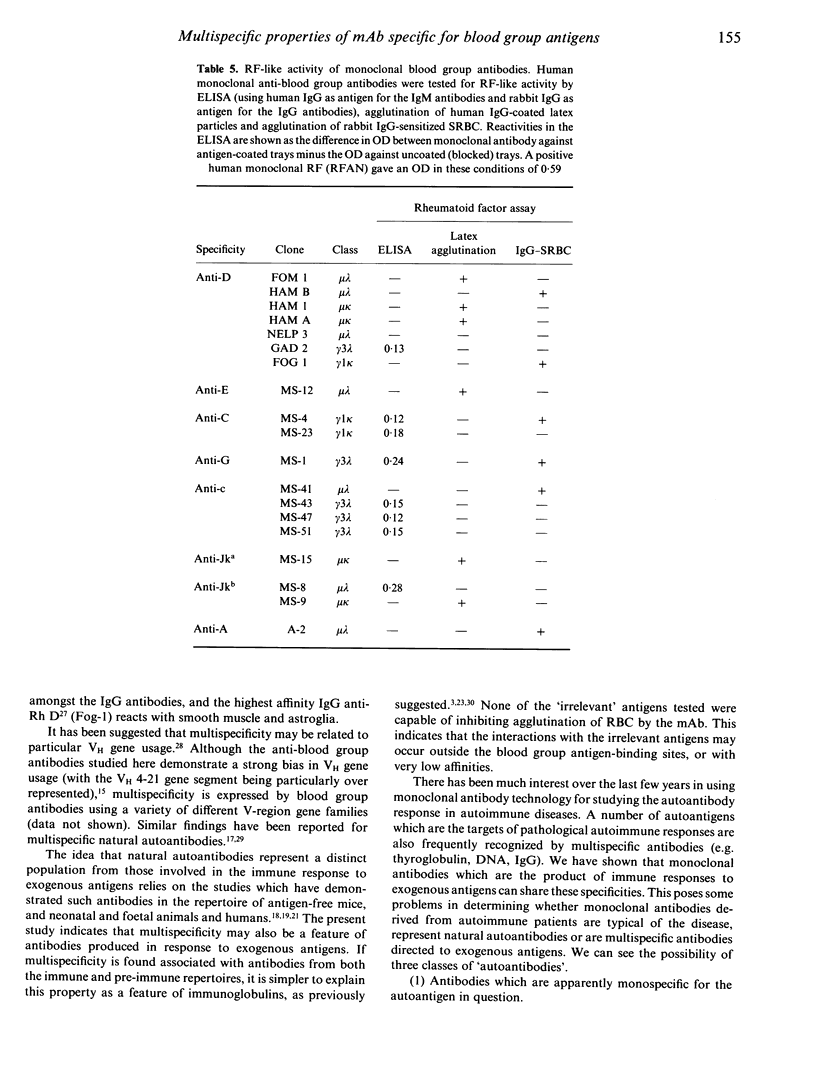
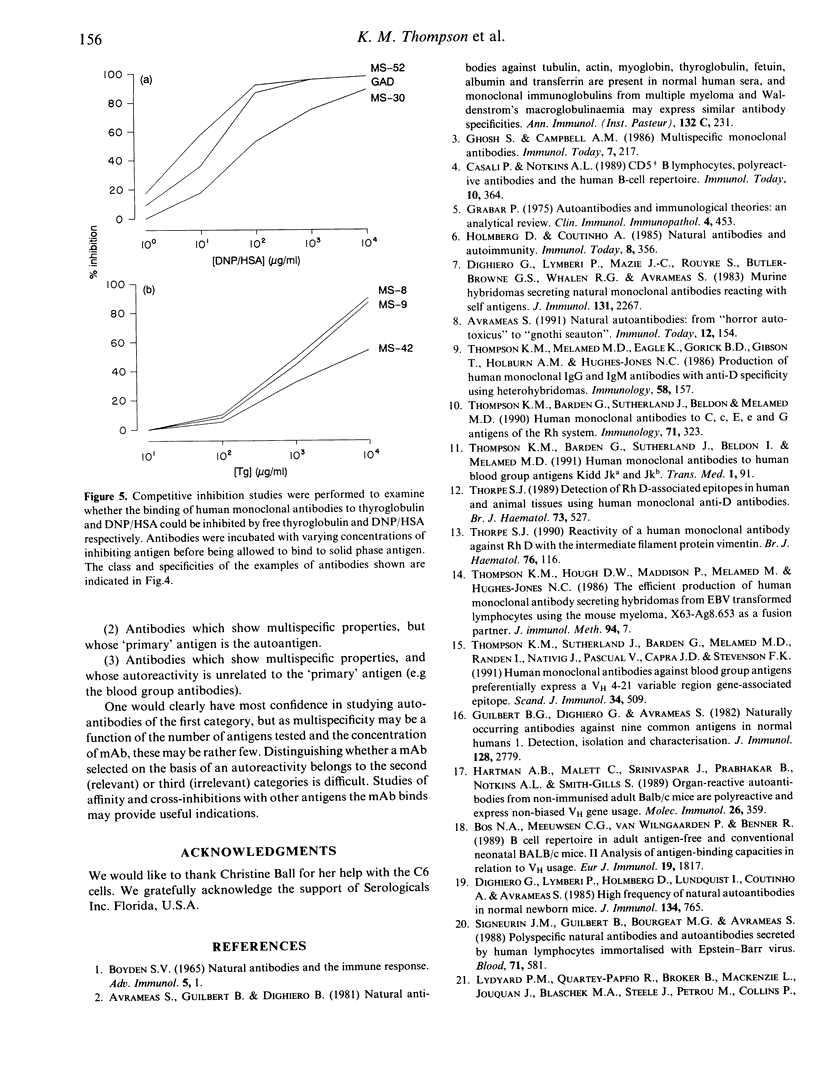
A panel of 72 human monoclonal antibodies with specificities for blood group antigens, A, Rh D, Rh C, Rh c, Rh E, Rh e, Rh G, Jka and Jkb, has been established from the peripheral blood of deliberately immunized donors. Previous work has established that the antibodies are highly specific for their respective blood group antigens, and a number of them are in routine clinical use as blood grouping reagents. This panel was screened for reactivity against six unrelated foreign and autoantigens by ELISA, for rheumatoid factor activity by ELISA and agglutination techniques, and for reactivity with a number of different tissues by immunofluorescence. Binding of the monoclonal antibodies to unrelated exo- and autoantigens was commonly seen amongst the antibodies of the IgM class, and to a lesser degree amongst the IgG class, with reaction patterns similar to those given by natural autoantibodies. Only five of the IgM antibodies failed to demonstrate any unexpected cross-reactivities and these included 1/13 anti-D, 2/7 anti-E, 1/13 anti-c and 1/2 anti-A. We propose that rather than natural autoantibodies representing a distinct population of immunoglobulins, multispecificity (polyspecificity, or polyreactivity) may be a feature of antibodies produced in response to exogenous antigens. The implications of this for the study of autoantibodies are discussed.
Full text
PDF



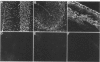
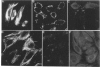
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avrameas S., Guilbert B., Dighiero G. Natural antibodies against tubulin, actin myoglobin, thyroglobulin, fetuin, albumin and transferrin are present in normal human sera, and monoclonal immunoglobulins from multiple myeloma and Waldenström's macroglobulinemia may express similar antibody specificities. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1981 Mar-Apr;132C(2):231–236. doi: 10.1016/0769-2625(81)90031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avrameas S. Natural autoantibodies: from 'horror autotoxicus' to 'gnothi seauton'. Immunol Today. 1991 May;12(5):154–159. doi: 10.1016/S0167-5699(05)80045-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos N. A., Meeuwsen C. G., Van Wijngaarden P., Benner R. B cell repertoire in adult antigen-free and conventional neonatal BALB/c mice. II. Analysis of antigen-binding capacities in relation to VH gene usage. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Oct;19(10):1817–1822. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830191009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyden S. V. Natural antibodies and the immune response. Adv Immunol. 1966;5:1–28. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60271-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell A. M., Whitford P., Leake R. E. Human monoclonal antibodies and monoclonal antibody multispecificity. Br J Cancer. 1987 Dec;56(6):709–713. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1987.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casali P., Notkins A. L. CD5+ B lymphocytes, polyreactive antibodies and the human B-cell repertoire. Immunol Today. 1989 Nov;10(11):364–368. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90268-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dighiero G., Lymberi P., Holmberg D., Lundquist I., Coutinho A., Avrameas S. High frequency of natural autoantibodies in normal newborn mice. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):765–771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dighiero G., Lymberi P., Mazié J. C., Rouyre S., Butler-Browne G. S., Whalen R. G., Avrameas S. Murine hybridomas secreting natural monoclonal antibodies reacting with self antigens. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2267–2272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorick B. D., Thompson K. M., Melamed M. D., Hughes-Jones N. C. Three epitopes on the human Rh antigen D recognized by 125I-labelled human monoclonal IgG antibodies. Vox Sang. 1988;55(3):165–170. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1988.tb05086.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabar P. Hypothesis. Auto-antibodies and immunological theories: an analytical review. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1975 Nov;4(4):453–466. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(75)90087-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guigou V., Guilbert B., Moinier D., Tonnelle C., Boubli L., Avrameas S., Fougereau M., Fumoux F. Ig repertoire of human polyspecific antibodies and B cell ontogeny. J Immunol. 1991 Feb 15;146(4):1368–1374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilbert B., Dighiero G., Avrameas S. Naturally occurring antibodies against nine common antigens in human sera. I. Detection, isolation and characterization. J Immunol. 1982 Jun;128(6):2779–2787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman A. B., Mallett C. P., Srinivasappa J., Prabhakar B. S., Notkins A. L., Smith-Gill S. J. Organ reactive autoantibodies from non-immunized adult BALB/c mice are polyreactive and express non-biased VH gene usage. Mol Immunol. 1989 Apr;26(4):359–370. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(89)90125-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanz I., Casali P., Thomas J. W., Notkins A. L., Capra J. D. Nucleotide sequences of eight human natural autoantibody VH regions reveals apparent restricted use of VH families. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 1;142(11):4054–4061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seigneurin J. M., Guilbert B., Bourgeat M. J., Avrameas S. Polyspecific natural antibodies and autoantibodies secreted by human lymphocytes immortalized with Epstein-Barr virus. Blood. 1988 Mar;71(3):581–585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TALMAGE D. W. Immunological specificity, unique combinations of selected natural globulins provide an alternative to the classical concept. Science. 1959 Jun 19;129(3364):1643–1648. doi: 10.1126/science.129.3364.1643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson K. M., Hough D. W., Maddison P. J., Melamed M. D., Hughes-Jones N. The efficient production of stable, human monoclonal antibody-secreting hybridomas from EBV-transformed lymphocytes using the mouse myeloma X63-Ag8.653 as a fusion partner. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Nov 20;94(1-2):7–12. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90208-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson K. M., Hughes-Jones N. C. Production and characterization of monoclonal anti-Rh. Baillieres Clin Haematol. 1990 Apr;3(2):243–253. doi: 10.1016/s0950-3536(05)80049-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson K. M., Melamed M. D., Eagle K., Gorick B. D., Gibson T., Holburn A. M., Hughes-Jones N. C. Production of human monoclonal IgG and IgM antibodies with anti-D (rhesus) specificity using heterohybridomas. Immunology. 1986 May;58(1):157–160. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson K., Barden G., Sutherland J., Beldon I., Melamed M. Human monoclonal antibodies to C, c, E, e and G antigens of the Rh system. Immunology. 1990 Nov;71(3):323–327. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson K., Barden G., Sutherland J., Beldon I., Melamed M. Human monoclonal antibodies to human blood group antigens Kidd Jka and Jkb. Transfus Med. 1991 Jun;1(2):91–96. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3148.1991.tb00015.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe S. J. Detection of Rh D-associated epitopes in human and animal tissues using human monoclonal anti-D antibodies. Br J Haematol. 1989 Dec;73(4):527–536. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1989.tb00292.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe S. J. Reactivity of a human monoclonal antibody against Rh D with the intermediate filament protein vimentin. Br J Haematol. 1990 Sep;76(1):116–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1990.tb07845.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]