Abstract
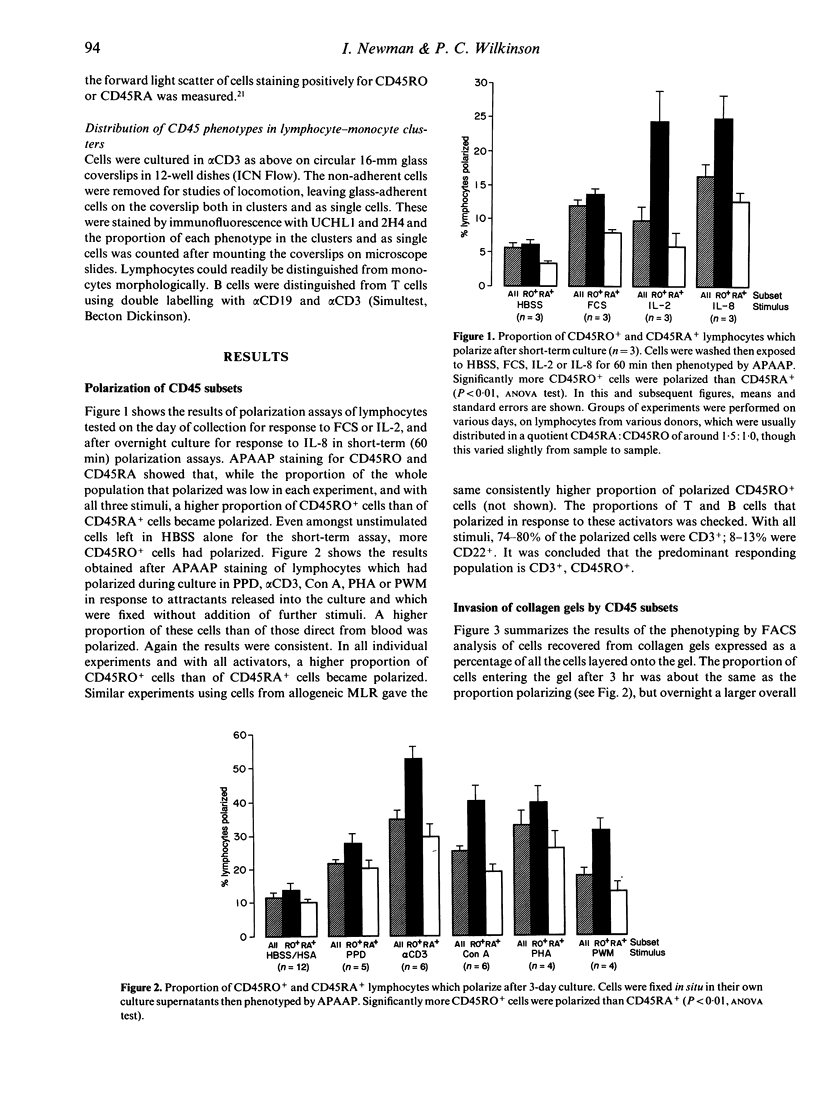
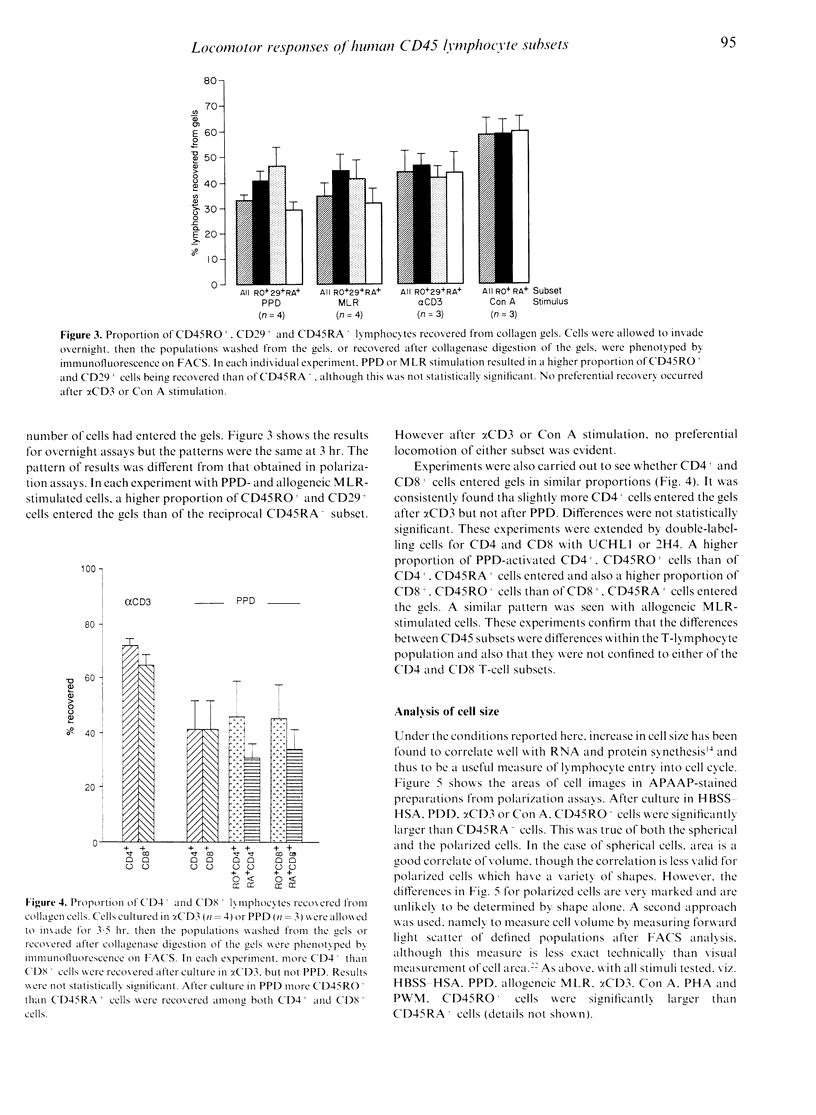
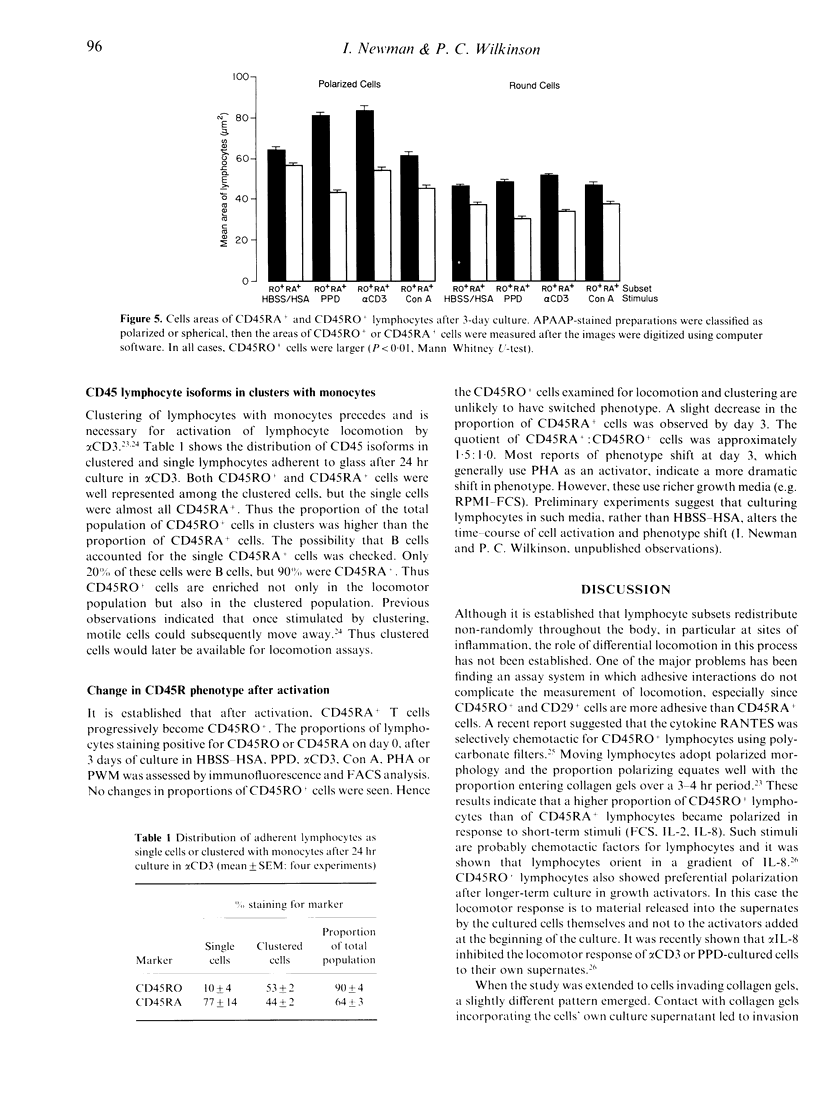
The CD45RO+ population of lymphocytes from human blood contains a higher proportion of locomotor cells than the CD45RA+ population. Direct from blood there were few locomotor lymphocytes (< 15%), but, among these, a higher proportion of CD45RO+ than of CD45RA+ cells responded to the chemotactic stimuli, foetal calf serum (FCS) and interleukin-2 (IL-2) in polarization assays. Likewise, after overnight culture, a higher proportion of CD45RO+ cells responded to IL-8. Culture for 24-72 hr in activators such as anti-CD3, purified protein derivative (PPD), phytohaemagglutinin (PHA), concanavalin A (Con A), pokeweed mitogen (PWM) or in an allogeneic mixed leucocyte reaction (AMLR) increased the proportion of locomotor lymphocytes to 20-60%, and the CD45RO+ subset showed proportionately more polarized cells than the CD45RA+ subset after culture with all the above activators. Preferential migration of CD45RO+ cells into collagen gels was also seen after culture in antigenic stimuli (PPD or AMLR) but not with polyclonal activators (alpha CD3 or Con A). Double labelling showed that, within the CD4+ and CD8+ subsets, antigen-stimulated CD45RO+ T cells invaded collagen gels in higher proportions than CD45RA+ T cells. Clustering of lymphocytes with accessory cells is an essential prerequisite for locomotion and, after culture in alpha CD3, CD45RO+ lymphocytes were found preferentially in clusters with monocytes. In all of the above populations, CD45RO+ lymphocytes were larger in size. These findings suggest that, not only selective adhesion to vascular endothelium as reported earlier, but also selective locomotion recruits CD45RO+ lymphocytes into sites of inflammation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arencibia I., Sundqvist K. G. Collagen receptor on T lymphocytes and the control of lymphocyte motility. Eur J Immunol. 1989 May;19(5):929–934. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell E. B., Sparshott S. M. Interconversion of CD45R subsets of CD4 T cells in vivo. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):163–166. doi: 10.1038/348163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beverley P. C. Human T cell subsets. Immunol Lett. 1987 Apr;14(4):263–267. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(87)90001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. F., Lackie J. M. Fibronectin and collagen inhibit cell-substratum adhesion of neutrophil granulocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Nov;136(1):225–231. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90053-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckle A. M., Hogg N. Human memory T cells express intercellular adhesion molecule-1 which can be increased by interleukin 2 and interferon-gamma. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Feb;20(2):337–341. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. G., Robson R. T., Campbell G. A major difference between serum and fibronectin in the divalent cation requirement for adhesion and spreading of BHK21 cells. J Cell Sci. 1987 Jun;87(Pt 5):657–665. doi: 10.1242/jcs.87.5.657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisele S., Lackie J. M., Riedwyl H., Zimmermann A., Keller H. U. Analysis of lymphocyte shape by visual classification, calculated measures of shape or light scattering. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Apr 8;138(1):103–109. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90069-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery P., Gentry K. C., Mackay I. R., Muirden K. D., Rowley M. Deficiency of the suppressor inducer subset of T lymphocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Aug;30(8):849–856. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALL J. G., MORRIS B. THE ORIGIN OF THE CELLS IN THE EFFERENT LYMPH FROM A SINGLE LYMPH NODE. J Exp Med. 1965 Jun 1;121:901–910. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.6.901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haston W. S., Shields J. M., Wilkinson P. C. Lymphocyte locomotion and attachment on two-dimensional surfaces and in three-dimensional matrices. J Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;92(3):747–752. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.3.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haston W. S., Wilkinson P. C. Visual methods for measuring leukocyte locomotion. Methods Enzymol. 1988;162:17–38. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)62060-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemler M. E. Adhesive protein receptors on hematopoietic cells. Immunol Today. 1988 Apr;9(4):109–113. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91280-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsley G., Pitzalis C., Kyriazis N., Panayi G. S. Abnormal helper-inducer/suppressor-inducer T-cell subset distribution and T-cell activation status are common to all types of chronic synovitis. Scand J Immunol. 1988 Aug;28(2):225–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1988.tb02435.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld H., Berman J. S., Beer D. J., Center D. M. Induction of human T lymphocyte motility by interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):3887–3890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard E. J., Skeel A., Yoshimura T., Noer K., Kutvirt S., Van Epps D. Leukocyte specificity and binding of human neutrophil attractant/activation protein-1. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 15;144(4):1323–1330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay C. R. T-cell memory: the connection between function, phenotype and migration pathways. Immunol Today. 1991 Jun;12(6):189–192. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90051-T. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor D. D., Logie P. S. The mediator of cellular immunity. VII. Localization of sensitized lymphocytes in inflammatory exudates. J Exp Med. 1974 Jun 1;139(6):1415–1430. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.6.1415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman I., Wilkinson P. C. Methods for phenotyping polarized and locomotor human lymphocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1992 Feb 14;147(1):43–50. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(12)80027-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrott D. M., Wilkinson P. C. Lymphocyte locomotion and migration. Prog Allergy. 1981;28:193–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitzalis C., Kingsley G., Haskard D., Panayi G. The preferential accumulation of helper-inducer T lymphocytes in inflammatory lesions: evidence for regulation by selective endothelial and homotypic adhesion. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Sep;18(9):1397–1404. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitzalis C., Kingsley G., Murphy J., Panayi G. Abnormal distribution of the helper-inducer and suppressor-inducer T-lymphocyte subsets in the rheumatoid joint. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1987 Nov;45(2):252–258. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(87)90040-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders M. E., Makgoba M. W., Sharrow S. O., Stephany D., Springer T. A., Young H. A., Shaw S. Human memory T lymphocytes express increased levels of three cell adhesion molecules (LFA-3, CD2, and LFA-1) and three other molecules (UCHL1, CDw29, and Pgp-1) and have enhanced IFN-gamma production. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1401–1407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schall T. J., Bacon K., Toy K. J., Goeddel D. V. Selective attraction of monocytes and T lymphocytes of the memory phenotype by cytokine RANTES. Nature. 1990 Oct 18;347(6294):669–671. doi: 10.1038/347669a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedder T. F., Matsuyama T., Rothstein D., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. Human antigen-specific memory T cells express the homing receptor (LAM-1) necessary for lymphocyte recirculation. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Jun;20(6):1351–1355. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson P. C., Higgins A. OKT3-activated locomotion of human blood lymphocytes: a phenomenon requiring contact of T cells with Fc receptor-bearing cells. Immunology. 1987 Mar;60(3):445–451. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson P. C., Newman I. Identification of IL-8 as a locomotor attractant for activated human lymphocytes in mononuclear cell cultures with anti-CD3 or purified protein derivative of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Immunol. 1992 Oct 15;149(8):2689–2694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson P. C. Relation between locomotion, chemotaxis and clustering of immune cells. Immunology. 1990 Jan;69(1):127–133. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson P. C. The locomotor capacity of human lymphocytes and its enhancement by cell growth. Immunology. 1986 Feb;57(2):281–289. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson P. C., Watson E. A. FK506 and pertussis toxin distinguish growth-induced locomotor activation from attractant-stimulated locomotion in human blood lymphocytes. Immunology. 1990 Nov;71(3):417–422. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



