Abstract
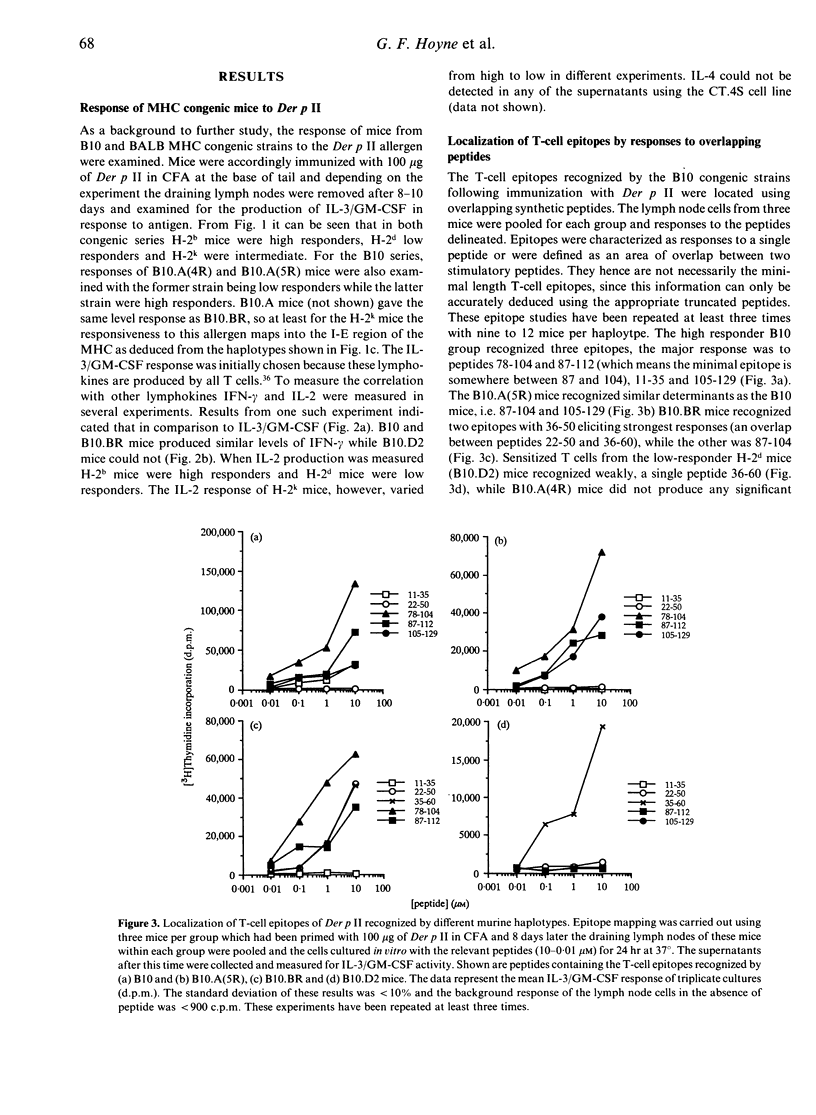
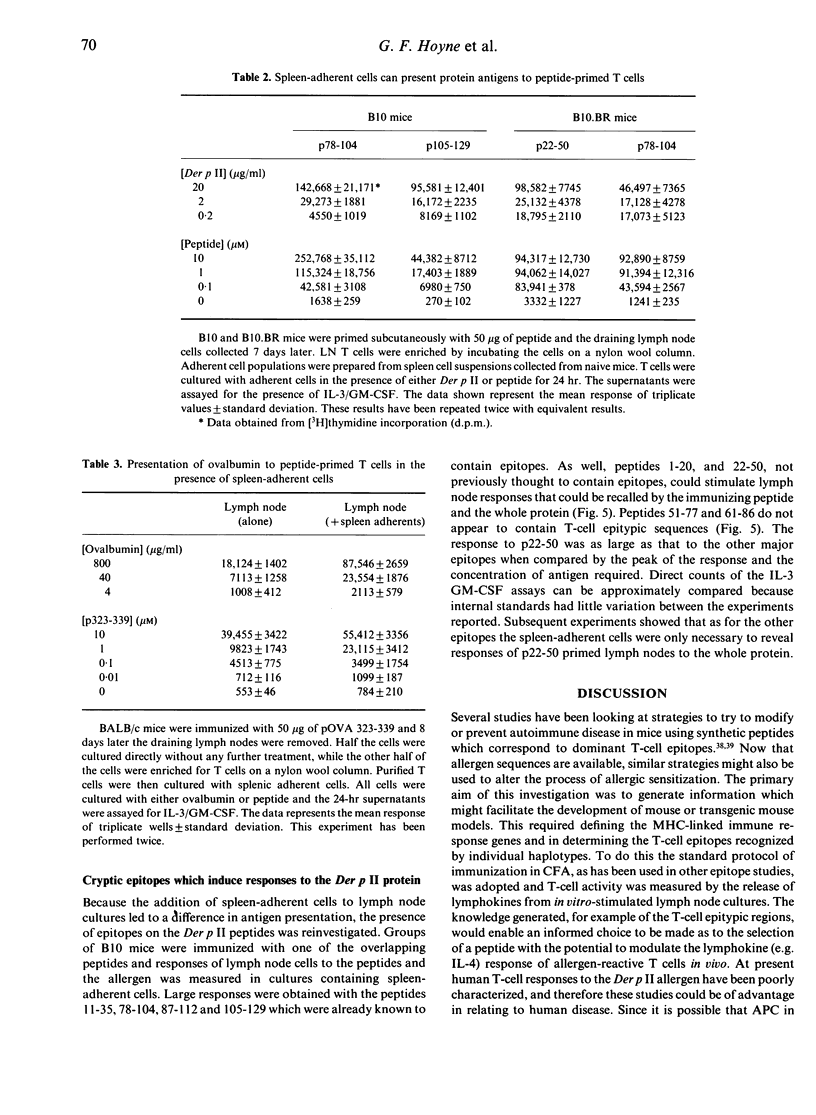
Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) congenic strains can be defined as high and low responders to the major house dust mite allergen Der p II on the basis of the ability to sensitize T cells for in vitro lymphokine release. Mice of the H-2b haplotype were high responders, H-2k were intermediate and H-2d low responders. Like responses to other proteins, only a limited number of epitopes could be located by the response of T cells from mice immunized with allergen to a series of overlapping peptides. The epitopes for H-2b mice were 11-35, 78-104 and 105-129, 36-50 and 78-104 for H-2k mice and 36-60 for H-2d. Immunization with the peptides however revealed that spleen-adherent cells were required for lymph node cells to recall responses to the whole protein and in addition that mice could be sensitized by cryptic epitopes defined by peptides 22-50 and 1-20 for H-2b mice. Peptides containing these cryptic epitopes did not normally induce responses in mice primed with the allergen, but when they were used for immunizing they could prime mice for responses to the peptide and the whole allergen. The results both help to define a model for studying the presentation of allergens and have significant implications for peptide-based immunotherapy.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adorini L., Appella E., Doria G., Cardinaux F., Nagy Z. A. Competition for antigen presentation in living cells involves exchange of peptides bound by class II MHC molecules. Nature. 1989 Dec 14;342(6251):800–803. doi: 10.1038/342800a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adorini L., Appella E., Doria G., Nagy Z. A. Mechanisms influencing the immunodominance of T cell determinants. J Exp Med. 1988 Dec 1;168(6):2091–2104. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.6.2091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen P. M., Unanue E. R. Processing and presentation of hen egg-white lysozyme by macrophages. Immunobiology. 1984 Dec;168(3-5):182–188. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(84)80109-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babbitt B. P., Allen P. M., Matsueda G., Haber E., Unanue E. R. Binding of immunogenic peptides to Ia histocompatibility molecules. 1985 Sep 26-Oct 2Nature. 317(6035):359–361. doi: 10.1038/317359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babbitt B. P., Matsueda G., Haber E., Unanue E. R., Allen P. M. Antigenic competition at the level of peptide-Ia binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4509–4513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H., Seyer J. M., Dale J. B. Protective immunogenicity and T lymphocyte specificity of a trivalent hybrid peptide containing NH2-terminal sequences of types 5, 6, and 24 M proteins synthesized in tandem. J Exp Med. 1987 Sep 1;166(3):647–656. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.3.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkower I., Matis L. A., Buckenmeyer G. K., Gurd F. R., Longo D. L., Berzofsky J. A. Identification of distinct predominant epitopes recognized by myoglobin-specific T cells under the control of different Ir genes and characterization of representative T cell clones. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1370–1378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhayani H., Paterson Y. Analysis of peptide binding patterns in different major histocompatibility complex/T cell receptor complexes using pigeon cytochrome c-specific T cell hybridomas. Evidence that a single peptide binds major histocompatibility complex in different conformations. J Exp Med. 1989 Nov 1;170(5):1609–1625. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.5.1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bland P. W., Warren L. G. Antigen presentation by epithelial cells of the rat small intestine. I. Kinetics, antigen specificity and blocking by anti-Ia antisera. Immunology. 1986 May;58(1):1–7. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breiteneder H., Pettenburger K., Bito A., Valenta R., Kraft D., Rumpold H., Scheiner O., Breitenbach M. The gene coding for the major birch pollen allergen Betv1, is highly homologous to a pea disease resistance response gene. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):1935–1938. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03597.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brett S. J., Cease K. B., Berzofsky J. A. Influences of antigen processing on the expression of the T cell repertoire. Evidence for MHC-specific hindering structures on the products of processing. J Exp Med. 1988 Jul 1;168(1):357–373. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.1.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chua K. Y., Dilworth R. J., Thomas W. R. Expression of Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus allergen, Der p II, in Escherichia coli and the binding studies with human IgE. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1990;91(2):124–129. doi: 10.1159/000235102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chua K. Y., Stewart G. A., Thomas W. R., Simpson R. J., Dilworth R. J., Plozza T. M., Turner K. J. Sequence analysis of cDNA coding for a major house dust mite allergen, Der p 1. Homology with cysteine proteases. J Exp Med. 1988 Jan 1;167(1):175–182. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.1.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. H., Ivanyi J., Young D. B., Lamb J. R., Syred A. D., Francis M. J. Orientation of epitopes influences the immunogenicity of synthetic peptide dimers. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Dec;18(12):2015–2019. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830181222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilworth R. J., Chua K. Y., Thomas W. R. Sequence analysis of cDNA coding for a major house dust mite allergen, Der f I. Clin Exp Allergy. 1991 Jan;21(1):25–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1991.tb00800.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang K. S., Vitale M., Fehlner P., King T. P. cDNA cloning and primary structure of a white-face hornet venom allergen, antigen 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):895–899. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink P. J., Blair M. J., Matis L. A., Hedrick S. M. Molecular analysis of the influences of positive selection, tolerance induction, and antigen presentation on the T cell receptor repertoire. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):139–150. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink P. J., Matis L. A., McElligott D. L., Bookman M., Hedrick S. M. Correlations between T-cell specificity and the structure of the antigen receptor. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):219–226. doi: 10.1038/321219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finnegan A., Smith M. A., Smith J. A., Berzofsky J., Sachs D. H., Hodes R. J. The T cell repertoire for recognition of a phylogenetically distant protein antigen. Peptide specificity and MHC restriction of staphylococcal nuclease-specific T cell clones. J Exp Med. 1986 Sep 1;164(3):897–910. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.3.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox B. S., Carbone F. R., Germain R. N., Paterson Y., Schwartz R. H. Processing of a minimal antigenic peptide alters its interaction with MHC molecules. Nature. 1988 Feb 11;331(6156):538–540. doi: 10.1038/331538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillet J. G., Lai M. Z., Briner T. J., Smith J. A., Gefter M. L. Interaction of peptide antigens and class II major histocompatibility complex antigens. Nature. 1986 Nov 20;324(6094):260–262. doi: 10.1038/324260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick S. M., Matis L. A., Hecht T. T., Samelson L. E., Longo D. L., Heber-Katz E., Schwartz R. H. The fine specificity of antigen and Ia determinant recognition by T cell hybridoma clones specific for pigeon cytochrome c. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):141–152. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz J. L., Herber-Katz E., Hackett C. J., Gerhard W. Characterization of the murine TH response to influenza virus hemagglutinin: evidence for three major specificities. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):3371–3377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelso A. Frequency analysis of lymphokine-secreting CD4+ and CD8+ T cells activated in a graft-versus-host reaction. J Immunol. 1990 Oct 1;145(7):2167–2176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurisaki J., Atassi H., Atassi M. Z. T cell recognition of ragweed allergen Ra3: localization of the full T cell recognition profile by synthetic overlapping peptides representing the entire protein chain. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Mar;16(3):236–240. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. Z., Ross D. T., Guillet J. G., Briner T. J., Gefter M. L., Smith J. A. T lymphocyte response to bacteriophage lambda repressor cI protein. Recognition of the same peptide presented by Ia molecules of different haplotypes. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 15;139(12):3973–3980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Z. R., Williams K. P., Chang Y. H., Smith J. A. Single amino acid substitution alters T cell determinant selection during antigen processing of Staphylococcus aureus nuclease. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 15;146(2):438–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matis L. A., Longo D. L., Hedrick S. M., Hannum C., Margoliash E., Schwartz R. H. Clonal analysis of the major histocompatibility complex restriction and the fine specificity of antigen recognition in the T cell proliferative response to cytochrome C. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1527–1535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hehir R. E., Garman R. D., Greenstein J. L., Lamb J. R. The specificity and regulation of T-cell responsiveness to allergens. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:67–95. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds D. S., Boom W. H., Abbas A. K. Inhibition of B lymphocyte activation by interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 1;139(3):767–773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy S., Scherer M. T., Briner T. J., Smith J. A., Gefter M. L. Murine MHC polymorphism and T cell specificities. Science. 1989 May 5;244(4904):572–575. doi: 10.1126/science.2470147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai K., Sinha A. A., Mitchell D. J., Zamvil S. S., Rothbard J. B., McDevitt H. O., Steinman L. Involvement of distinct murine T-cell receptors in the autoimmune encephalitogenic response to nested epitopes of myelin basic protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8608–8612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai K., Zamvil S. S., Mitchell D. J., Hodgkinson S., Rothbard J. B., Steinman L. Prevention of experimental encephalomyelitis with peptides that block interaction of T cells with major histocompatibility complex proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9470–9474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapira M., Jibson M., Muller G., Arnon R. Immunity and protection against influenza virus by synthetic peptide corresponding to antigenic sites of hemagglutinin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2461–2465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tovey E. R., Johnson M. C., Roche A. L., Cobon G. S., Baldo B. A. Cloning and sequencing of a cDNA expressing a recombinant house dust mite protein that binds human IgE and corresponds to an important low molecular weight allergen. J Exp Med. 1989 Oct 1;170(4):1457–1462. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.4.1457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ultee M. E., Margoliash E., Lipkowski A., Flouret G., Solinger A. M., Lebwohl D., Matis L. A., Chen C., Schwartz R. H. The T lymphocyte response to cytochrome c--II. Molecular characterization of a pigeon cytochrome c determinant recognized by proliferating T lymphocytes of the B10.A mouse. Mol Immunol. 1980 Jul;17(7):809–822. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(80)90030-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vacchio M. S., Berzofsky J. A., Krzych U., Smith J. A., Hodes R. J., Finnegan A. Sequences outside a minimal immunodominant site exert negative effects on recognition by staphylococcal nuclease-specific T cell clones. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 1;143(9):2814–2819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenta R., Duchêne M., Pettenburger K., Sillaber C., Valent P., Bettelheim P., Breitenbach M., Rumpold H., Kraft D., Scheiner O. Identification of profilin as a novel pollen allergen; IgE autoreactivity in sensitized individuals. Science. 1991 Aug 2;253(5019):557–560. doi: 10.1126/science.1857985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wraith D. C., Smilek D. E., Mitchell D. J., Steinman L., McDevitt H. O. Antigen recognition in autoimmune encephalomyelitis and the potential for peptide-mediated immunotherapy. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):247–255. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90287-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuuki T., Okumura Y., Ando T., Yamakawa H., Suko M., Haida M., Okudaira H. Cloning and sequencing of cDNAs corresponding to mite major allergen Der f II. Arerugi. 1990 Jun;39(6):557–561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamvil S. S., Mitchell D. J., Moore A. C., Kitamura K., Steinman L., Rothbard J. B. T-cell epitope of the autoantigen myelin basic protein that induces encephalomyelitis. Nature. 1986 Nov 20;324(6094):258–260. doi: 10.1038/324258a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



