Abstract
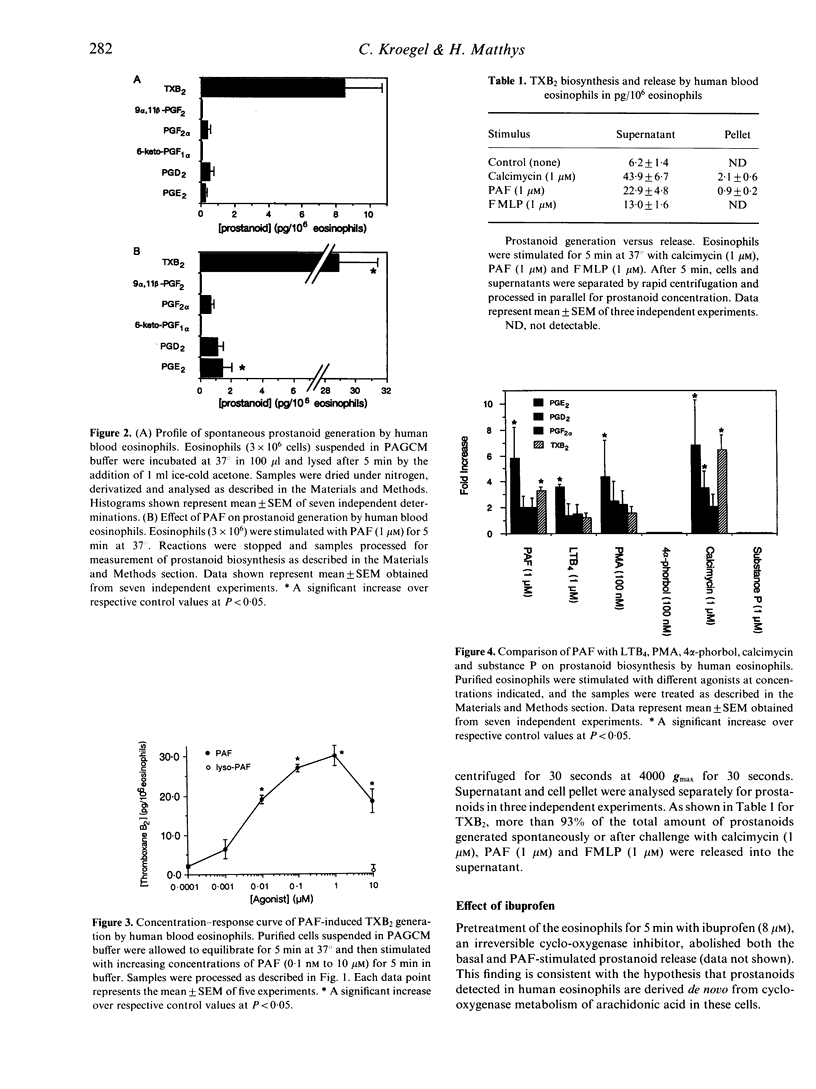
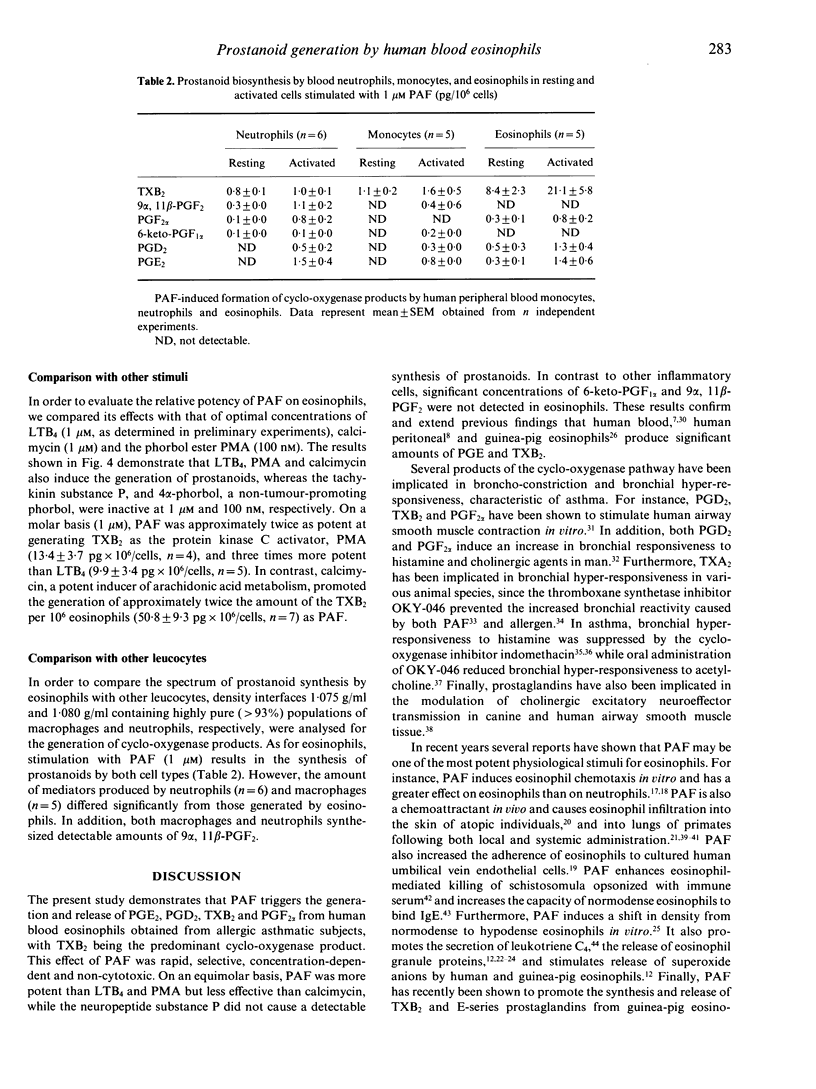
The spontaneous and stimulated generation of fatty acid cyclo-oxygenase pathway-derived products of arachidonic acid from highly purified (91.6 +/- 1.3%, n = 23) human blood eosinophils obtained from asthmatics were examined using combined gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Under resting conditions, eosinophils spontaneously generated 0.24 +/- 0.10 pg prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), 0.51 +/- 0.20 prostaglandin D2 (PGD2), 0.35 +/- 0.10 pg prostaglandin F2 alpha (PGF2 alpha) and 8.5 +/- 2.2 pg thromboxane B2 (TXB2), the stable metabolite of TXA2 per 10(6) cells. In contrast, 6-keto-prostaglandin F1 alpha and 9 alpha,11 beta-prostaglandin F2 were not detectable. Stimulation of eosinophils with platelet-activating factor (PAF) for 5 min induced a two- to sixfold increase in the biosynthesis of prostanoids. More than 95% of the generated prostanoids were released into the surrounding medium. The response to PAF was inhibited by the PAF receptor antagonist WEB 2086 (1 microM). The fatty acid cyclo-oxygenase inhibitor, ibuprofen, abolished both the spontaneous and PAF-stimulated generation of prostanoids by eosinophils. LTB4, PMA and calcimycin also produced an increase in prostanoid production, whereas lyso-PAF, the PAF precursor and metabolite, failed to induce prostanoid generation over basal production. In conclusion, the results demonstrate that PAF potently activates human eosinophils to generate and release several fatty acid cyclo-oxygenase metabolites of the arachidonic acid pathway, with TXB2 being the most abundant. These data are in agreement with previous observations suggesting that PAF may be an important stimulus for prostanoid release by the eosinophil in allergic diseases such as asthma.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes P. J., Chung K. F., Page C. P. Inflammatory mediators and asthma. Pharmacol Rev. 1988 Mar;40(1):49–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruijnzeel P. L., Kok P. T., Hamelink M. L., Kijne A. M., Verhagen J. Platelet-activating factor induces leukotriene C4 synthesis by purified human eosinophils. Prostaglandins. 1987 Aug;34(2):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(87)90244-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung K. F., Aizawa H., Becker A. B., Frick O., Gold W. M., Nadel J. A. Inhibition of antigen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness by a thromboxane synthetase inhibitor (OKY-046) in allergic dogs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Aug;134(2):258–261. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.134.2.258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung K. F., Aizawa H., Leikauf G. D., Ueki I. F., Evans T. W., Nadel J. A. Airway hyperresponsiveness induced by platelet-activating factor: role of thromboxane generation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Mar;236(3):580–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuss F. M., Dixon C. M., Barnes P. J. Effects of inhaled platelet activating factor on pulmonary function and bronchial responsiveness in man. Lancet. 1986 Jul 26;2(8500):189–192. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92489-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denjean A., Arnoux B., Masse R., Lockhart A., Benveniste J. Acute effects of intratracheal administration of platelet-activating factor in baboons. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 Sep;55(3):799–804. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.55.3.799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T. W., Chung K. F., Rogers D. F., Barnes P. J. Effect of platelet-activating factor on airway vascular permeability: possible mechanisms. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Aug;63(2):479–484. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.63.2.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavahan N. A., Slifman N. R., Gleich G. J., Vanhoutte P. M. Human eosinophil major basic protein causes hyperreactivity of respiratory smooth muscle. Role of the epithelium. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Sep;138(3):685–688. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/138.3.685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foegh M. L., Maddox Y. T., Ramwell P. W. Human peritoneal eosinophils and formation of arachidonate cyclooxygenase products. Scand J Immunol. 1986 May;23(5):599–603. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1986.tb01993.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frigas E., Loegering D. A., Gleich G. J. Cytotoxic effects of the guinea pig eosinophil major basic protein on tracheal epithelium. Lab Invest. 1980 Jan;42(1):35–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura M., Sasaki F., Nakatsumi Y., Takahashi Y., Hifumi S., Taga K., Mifune J., Tanaka T., Matsuda T. Effects of a thromboxane synthetase inhibitor (OKY-046) and a lipoxygenase inhibitor (AA-861) on bronchial responsiveness to acetylcholine in asthmatic subjects. Thorax. 1986 Dec;41(12):955–959. doi: 10.1136/thx.41.12.955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda T., Dunnette S. L., Reed C. E., Ackerman S. J., Peters M. S., Gleich G. J. Increased numbers of hypodense eosinophils in the blood of patients with bronchial asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Nov;132(5):981–985. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.5.981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. W., Dixon C. M., Dollery C. T., Barnes P. J. Prostaglandin D2 potentiates airway responsiveness to histamine and methacholine. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Feb;133(2):252–254. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.133.2.252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giembycz M. A., Kroegel C., Barnes P. J. Platelet activating factor stimulates cyclo-oxygenase activity in guinea pig eosinophils. Concerted biosynthesis of thromboxane A2 and E-series prostaglandins. J Immunol. 1990 May 1;144(9):3489–3497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleich G. G. The role of the eosinophilic leukocyte in bronchial asthma. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1986;22 (Suppl 7):62–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleich G. J., Flavahan N. A., Fujisawa T., Vanhoutte P. M. The eosinophil as a mediator of damage to respiratory epithelium: a model for bronchial hyperreactivity. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1988 May;81(5 Pt 1):776–781. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(88)90931-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundel R. H., Letts L. G., Gleich G. J. Human eosinophil major basic protein induces airway constriction and airway hyperresponsiveness in primates. J Clin Invest. 1991 Apr;87(4):1470–1473. doi: 10.1172/JCI115155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henocq E., Vargaftig B. B. Skin eosinophilia in atopic patients. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1988 Apr;81(4):691–695. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(88)91040-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubscher T. Role of the eosinophil in the allergic reactions. II. Release of prostaglandins from human eosinophilic leukocytes. J Immunol. 1975 Apr;114(4):1389–1393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y. Prejunctional control of excitatory neuroeffector transmission by prostaglandins in the airway smooth muscle tissue. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1991 Mar;143(3 Pt 2):S6–10. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/143.3_Pt_2.S6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura I., Moritani Y., Tanizaki Y. Basophils in bronchial asthma with reference to reagin-type allergy. Clin Allergy. 1973 Jun;3(2):195–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1973.tb01321.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroegel C. Does airway smooth muscle care about platelet-activating factor? Eur Respir J. 1992 Sep;5(8):915–918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroegel C., Yukawa T., Dent G., Chanez P., Chung K. F., Barnes P. J. Platelet-activating factor induces eosinophil peroxidase release from purified human eosinophils. Immunology. 1988 Jul;64(3):559–561. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroegel C., Yukawa T., Dent G., Venge P., Chung K. F., Barnes P. J. Stimulation of degranulation from human eosinophils by platelet-activating factor. J Immunol. 1989 May 15;142(10):3518–3526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamas A. M., Mulroney C. M., Schleimer R. P. Studies on the adhesive interaction between purified human eosinophils and cultured vascular endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1500–1505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T., Lenihan D. J., Malone B., Roddy L. L., Wasserman S. I. Increased biosynthesis of platelet-activating factor in activated human eosinophils. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5526–5530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lellouch-Tubiana A., Lefort J., Pfister A., Vargaftig B. B. Interactions between granulocytes and platelets with the guinea-pig lung in passive anaphylactic shock. Correlations with PAF-acether-induced lesion. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1987;83(2):198–205. doi: 10.1159/000234356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lellouch-Tubiana A., Lefort J., Pirotzky E., Vargaftig B. B., Pfister A. Ultrastructural evidence for extravascular platelet recruitment in the lung upon intravenous injection of platelet-activating factor (PAF-acether) to guinea-pigs. Br J Exp Pathol. 1985 Jun;66(3):345–355. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motojima S., Frigas E., Loegering D. A., Gleich G. J. Toxicity of eosinophil cationic proteins for guinea pig tracheal epithelium in vitro. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Mar;139(3):801–805. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/139.3.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moy J. N., Gleich G. J., Thomas L. L. Noncytotoxic activation of neutrophils by eosinophil granule major basic protein. Effect on superoxide anion generation and lysosomal enzyme release. J Immunol. 1990 Oct 15;145(8):2626–2632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell S. R., Barnett C. J. Microvascular leakage to platelet activating factor in guinea-pig trachea and bronchi. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jun 26;138(3):385–396. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90477-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen W. F., Jr, Soberman R. J., Yoshimoto T., Sheffer A. L., Lewis R. A., Austen K. F. Synthesis and release of leukotriene C4 by human eosinophils. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 15;138(2):532–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons W. G., 3rd, Roberts L. J., 2nd Transformation of prostaglandin D2 to isomeric prostaglandin F2 compounds by human eosinophils. A potential mast cell-eosinophil interaction. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 1;141(7):2413–2419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson R., Bernstein P. R., Harris K. E., Krell R. D. Airway responses to sequential challenges with platelet-activating factor and leukotriene D4 in rhesus monkeys. J Lab Clin Med. 1984 Sep;104(3):340–345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin A. H., Smith L. J., Patterson R. The bronchoconstrictor properties of platelet-activating factor in humans. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Nov;136(5):1145–1151. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.5.1145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigal C. E., Valone F. H., Holtzman M. J., Goetzl E. J. Preferential human eosinophil chemotactic activity of the platelet-activating factor (PAF) 1-0-hexadecyl-2-acetyl-sn-glyceryl-3-phosphocholine (AGEPC). J Clin Immunol. 1987 Mar;7(2):179–184. doi: 10.1007/BF00916012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WROBLEWSKI F., LADUE J. S. Lactic dehydrogenase activity in blood. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Oct;90(1):210–213. doi: 10.3181/00379727-90-21985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh G. M., Nagakura T., Iikura Y. Flow-cytometric analysis of increased IgE uptake by normal eosinophils following activation with PAF-acether and other inflammatory mediators. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1989;88(1-2):194–196. doi: 10.1159/000234783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walters E. H., Bevan C., Parrish R. W., Davies B. H., Smith A. P. Time-dependent effect of prostaglandin E2 inhalation on airway responses to bronchoconstrictor agents in normal subjects. Thorax. 1982 Jun;37(6):438–442. doi: 10.1136/thx.37.6.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walters E. H., Parrish R. W., Bevan C., Smith A. P. Induction of bronchial hypersensitivity: evidence for a role for prostaglandins. Thorax. 1981 Aug;36(8):571–574. doi: 10.1136/thx.36.8.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardlaw A. J., Moqbel R., Cromwell O., Kay A. B. Platelet-activating factor. A potent chemotactic and chemokinetic factor for human eosinophils. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1701–1706. doi: 10.1172/JCI112765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yukawa T., Kroegel C., Evans P., Fukuda T., Chung K. F., Barnes P. J. Density heterogeneity of eosinophil leucocytes: induction of hypodense eosinophils by platelet-activating factor. Immunology. 1989 Sep;68(1):140–143. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yukawa T., Read R. C., Kroegel C., Rutman A., Chung K. F., Wilson R., Cole P. J., Barnes P. J. The effects of activated eosinophils and neutrophils on guinea pig airway epithelium in vitro. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1990 Apr;2(4):341–353. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/2.4.341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]