Abstract
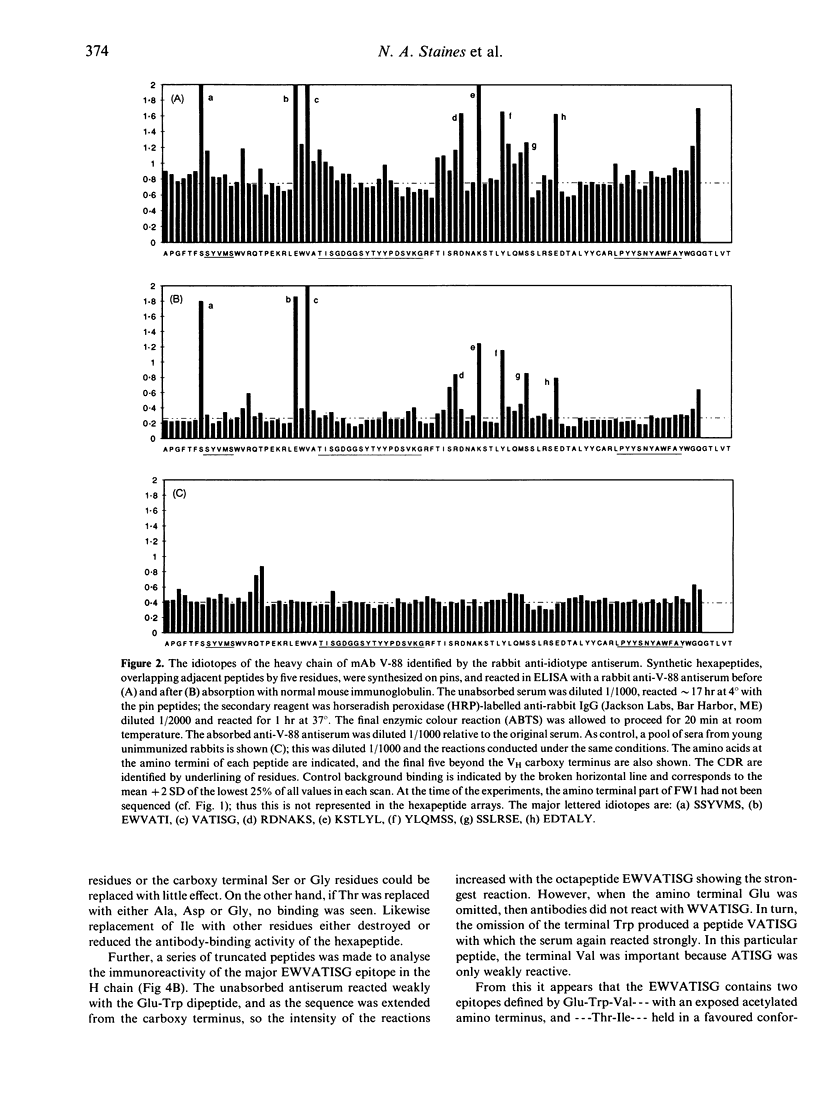
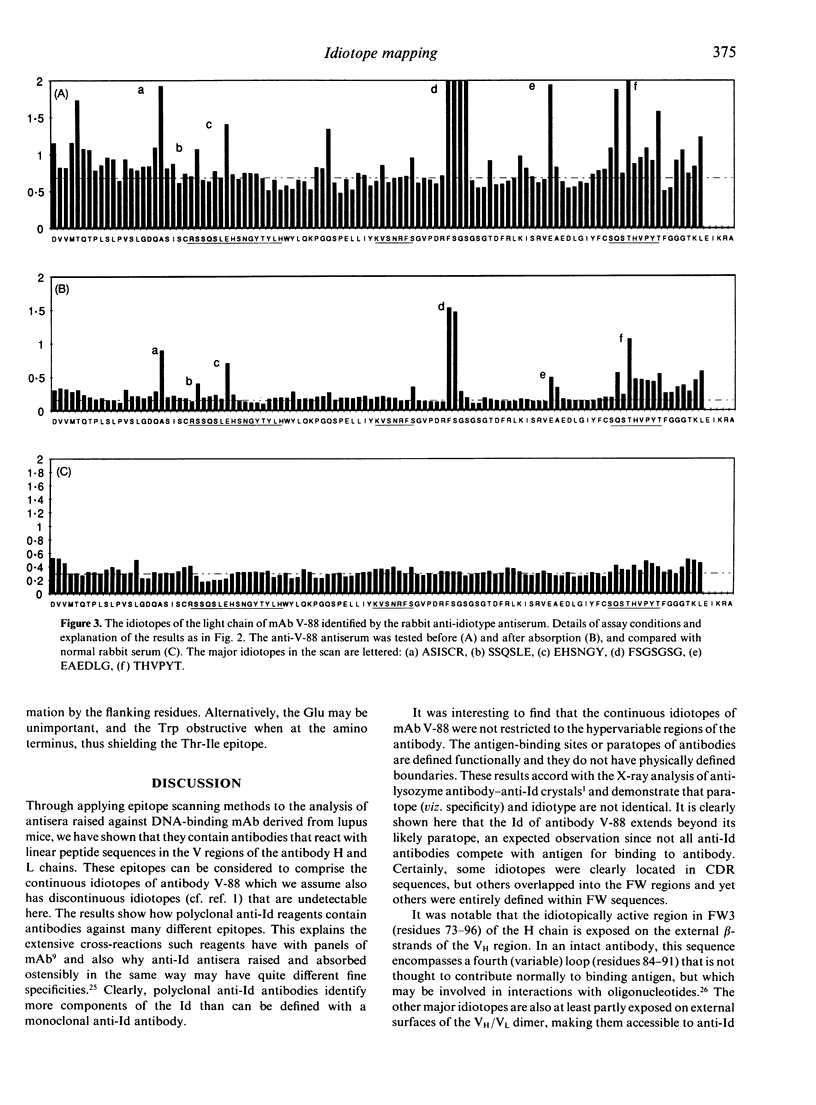
In this study, the primary sequence and location of the idiotopes of monoclonal antibody (mAb) V-88 have been examined. V-88 was derived from an adult (NZB x NZW)F1 mouse, has been partially defined previously with polyclonal anti-idiotype antisera, and is a member of the 16/6 idiotype (Id) family. From the inferred primary amino acid sequence of the antibody, sets of hexapeptides, overlapping by five residues, were synthesized on pins and used to scan the expression of epitopes (idiotopes) in the V regions of the light and heavy chains. A heterologous rabbit antiserum raised against the native antibody V-88, and absorbed to make it idiotype specific, was found to react with eight major epitopes distributed between the VH and VL regions. Half of these determinants mapped to the complementarity determining regions, with the others in framework sequences. Thus, the idiotype of antibody V-88 comprises, at least in part, continuous linear idiotopes in both hypervariable and framework areas. The process of absorbing the anti-idiotype antiserum on normal mouse immunoglobulin removed much of the background antibody activity against V region peptides, but left the activity against the dominant idiotopes. The sequence of a major idiotope, VATISG, in the FW2/CDR2 VH region is homologous to sequences of human antibodies that express the 16/6 idiotype, suggesting that Id.16/6 is at least in part defined by this region of the antibody. The same VH area is also homologous to sequences in bacterial and mammalian heat-shock proteins (hsp60-65). Thus there may be a functional link through idiotype connections, especially those involving Id.16/6, between anti-bacterial responses and production of autoantibodies, and some bacterial antigens may function indirectly as superantigens for B cells.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bentley G. A., Boulot G., Riottot M. M., Poljak R. J. Three-dimensional structure of an idiotope-anti-idiotope complex. Nature. 1990 Nov 15;348(6298):254–257. doi: 10.1038/348254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodeur P. H., Riblet R. The immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region (Igh-V) locus in the mouse. I. One hundred Igh-V genes comprise seven families of homologous genes. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Oct;14(10):922–930. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830141012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caton A. J., Brownlee G. G., Staudt L. M., Gerhard W. Structural and functional implications of a restricted antibody response to a defined antigenic region on the influenza virus hemagglutinin. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1577–1587. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04399.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. P., Liu M. F., Sinha S., Carson D. A. A 16/6 idiotype-positive anti-DNA antibody is encoded by a conserved VH gene with no somatic mutation. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Nov;31(11):1429–1431. doi: 10.1002/art.1780311113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chothia C., Boswell D. R., Lesk A. M. The outline structure of the T-cell alpha beta receptor. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3745–3755. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03258.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbet S., Milili M., Fougereau M., Schiff C. Two V kappa germ-line genes related to the GAT idiotypic network (Ab1 and Ab3/Ab1') account for the major subfamilies of the mouse V kappa-1 variability subgroup. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 1;138(3):932–939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhillon V., Latchman D., Isenberg D. Heat shock proteins and systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 1991 Nov;1(1):3–8. doi: 10.1177/096120339100100102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilat D., Hochberg M., Tron F., Jacob L., Bach J. F. The VH gene sequences of anti-DNA antibodies in two different strains of lupus-prone mice are highly related. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Jul;19(7):1241–1246. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilat D., Webster D. M., Rees A. R. V region sequences of anti-DNA and anti-RNA autoantibodies from NZB/NZW F1 mice. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1745–1753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein A., Greenberg M., Diamond B., Grayzel A. I. Suppression of anti-DNA antibody synthesis in vitro by a cross-reactive antiidiotypic antibody. J Clin Invest. 1987 Mar;79(3):997–1000. doi: 10.1172/JCI112912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geysen H. M., Rodda S. J., Mason T. J., Tribbick G., Schoofs P. G. Strategies for epitope analysis using peptide synthesis. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Sep 24;102(2):259–274. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90085-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn B. H., Ebling F. M. Suppression of murine lupus nephritis by administration of an anti-idiotypic antibody to anti-DNA. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):187–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman A. B., Rudikoff S. VH genes encoding the immune response to beta-(1,6)-galactan: somatic mutation in IgM molecules. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):3023–3030. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02249.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay F. C., Soltys A. J., Tribbick G., Geysen H. M. Framework peptides from kappa IIIb rheumatoid factor light chains with binding activity for aggregated IgG. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Aug;21(8):1837–1841. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmingsen S. M., Woolford C., van der Vies S. M., Tilly K., Dennis D. T., Georgopoulos C. P., Hendrix R. W., Ellis R. J. Homologous plant and bacterial proteins chaperone oligomeric protein assembly. Nature. 1988 May 26;333(6171):330–334. doi: 10.1038/333330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herron J. N., He X. M., Ballard D. W., Blier P. R., Pace P. E., Bothwell A. L., Voss E. W., Jr, Edmundson A. B. An autoantibody to single-stranded DNA: comparison of the three-dimensional structures of the unliganded Fab and a deoxynucleotide-Fab complex. Proteins. 1991;11(3):159–175. doi: 10.1002/prot.340110302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg D. A., Staines N. A. DNA antibody idiotypes. An analysis of their role in health and disease. J Autoimmun. 1990 Aug;3(4):339–356. doi: 10.1016/s0896-8411(05)80002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg D., Williams W., Axford J., Bakimer R., Bell D., Casaseca-Grayson T., Diamond B., Ebling F., Hahn B., Harkiss G. Comparison of DNA antibody idiotypes in human sera: an international collaborative study of 19 idiotypes from 11 different laboratories. J Autoimmun. 1990 Aug;3(4):393–414. doi: 10.1016/s0896-8411(05)80008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaveri S. V., Halpern R., Kang C. Y., Köhler H. Antibodies of different specificities are self-binding: implication for antibody diversity. Mol Immunol. 1991 Jul;28(7):773–778. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(91)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kofler R., Strohal R., Balderas R. S., Johnson M. E., Noonan D. J., Duchosal M. A., Dixon F. J., Theofilopoulos A. N. Immunoglobulin kappa light chain variable region gene complex organization and immunoglobulin genes encoding anti-DNA autoantibodies in lupus mice. J Clin Invest. 1988 Sep;82(3):852–860. doi: 10.1172/JCI113689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krissansen G. W., Owen M. J., Verbi W., Crumpton M. J. Primary structure of the T3 gamma subunit of the T3/T cell antigen receptor complex deduced from cDNA sequences: evolution of the T3 gamma and delta subunits. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1799–1808. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04429.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahana W., Guilbert B., Avrameas S. Suppression of anti-DNA antibody production in MRL mice by treatment with anti-idiotypic antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Dec;70(3):538–545. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion T. N., Lawton A. R., 3rd, Kearney J. F., Briles D. E. Anti-DNA autoantibodies in (NZB X NZW)F1 mice are clonally heterogeneous, but the majority share a common idiotype. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):668–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion T. N., Tillman D. M., Jou N. T. Interclonal and intraclonal diversity among anti-DNA antibodies from an (NZB x NZW)F1 mouse. J Immunol. 1990 Oct 1;145(7):2322–2332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazza G., Ollier P., Sommé G., Moinier D., Rocca-Serra J., Van Rietschoten J., Thèze J., Fougereau M. A structural basis for the internal image in the idiotypic network: antibodies against synthetic Ab2-D regions cross-react with the original antigen. Ann Inst Pasteur Immunol. 1985 Nov-Dec;136D(3):259–269. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2625(85)80111-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meek K., Takei M., Dang H., Sanz I., Dauphinée M. J., Capra J. D., Talal N. Anti-peptide antibodies detect a lupus-related interspecies idiotype that maps to H chain CDR2. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 15;144(4):1375–1381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A., Buchanan R. R., Lew A. M., Olsen I., Staines N. A. Five groups of antigenic determinants on DNA identified by monoclonal antibodies from (NZB X NZW)F1 and MRL/Mp-lpr/lpr mice. Immunology. 1985 May;55(1):75–83. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A., Isenberg D. A., Naparstek Y., Rauch J., Duggan D., Khiroya R., Staines N. A., Schattner A. Shared idiotypes are expressed on mouse and human anti-DNA autoantibodies. Immunology. 1985 Nov;56(3):393–399. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morland C., Michael J., Adu D., Kizaki T., Howie A. J., Morgan A., Staines N. A. Anti-idiotype and immunosuppressant treatment of murine lupus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Jan;83(1):126–132. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05601.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison R. P., Belland R. J., Lyng K., Caldwell H. D. Chlamydial disease pathogenesis. The 57-kD chlamydial hypersensitivity antigen is a stress response protein. J Exp Med. 1989 Oct 1;170(4):1271–1283. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.4.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter M., Newell J. B., Rudikoff S., Haber E. Classification of mouse VK groups based on the partial amino acid sequence to the first invariant tryptophan: impact of 14 new sequences from IgG myeloma proteins. Mol Immunol. 1982 Dec;19(12):1619–1630. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(82)90273-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puccetti A., Koizumi T., Migliorini P., André-Schwartz J., Barrett K. J., Schwartz R. S. An immunoglobulin light chain from a lupus-prone mouse induces autoantibodies in normal mice. J Exp Med. 1990 Jun 1;171(6):1919–1930. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.6.1919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravirajan C. T., Staines N. A. Involvement in lupus disease of idiotypes Id.F-423 and Id.IV-228 defined, respectively, upon foetal and adult MRL/Mp-lpr/lpr DNA-binding monoclonal autoantibodies. Immunology. 1991 Oct;74(2):342–347. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanafelt M. C., Hindersson P., Soderberg C., Mensi N., Turck C. W., Webb D., Yssel H., Peltz G. T cell and antibody reactivity with the Borrelia burgdorferi 60-kDa heat shock protein in Lyme arthritis. J Immunol. 1991 Jun 1;146(11):3985–3992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson S. J., Lin B. F., Mullenix M. C., Mortensen R. F. A synthetic peptide corresponding to the phosphorylcholine (PC)-binding region of human C-reactive protein possesses the TEPC-15 myeloma PC-idiotype. J Immunol. 1991 Mar 1;146(5):1596–1601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venner T. J., Gupta R. S. Nucleotide sequence of rat hsp60 (chaperonin, GroEL homolog) cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5309–5309. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts R. A., Ravirajan C. T., Wilkinson L. S., Williams W., Griffiths M., Butcher D., Horsfall A. T., Staines N. A., Isenberg D. A. Detection of human and murine common idiotypes of DNA antibodies in tissues and sera of patients with autoimmune diseases. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Feb;83(2):267–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05626.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts R., Isenberg D. DNA antibody idiotypes: an analysis of their clinical connections and origins. Int Rev Immunol. 1990;5(3-4):279–293. doi: 10.3109/08830189009056735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young F., Tucker L., Rubinstein D., Guillaume T., André-Schwartz J., Barrett K. J., Schwartz R. S., Logtenberg T. Molecular analysis of a germ line-encoded idiotypic marker of pathogenic human lupus autoantibodies. J Immunol. 1990 Oct 15;145(8):2545–2553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Eden W., Hogervorst E. J., Wauben M. H., van der Zee R., Boog C. J. Heat-shock proteins as antigens in autoimmunity. Biochem Soc Trans. 1991 Feb;19(1):171–175. doi: 10.1042/bst0190171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



