Abstract
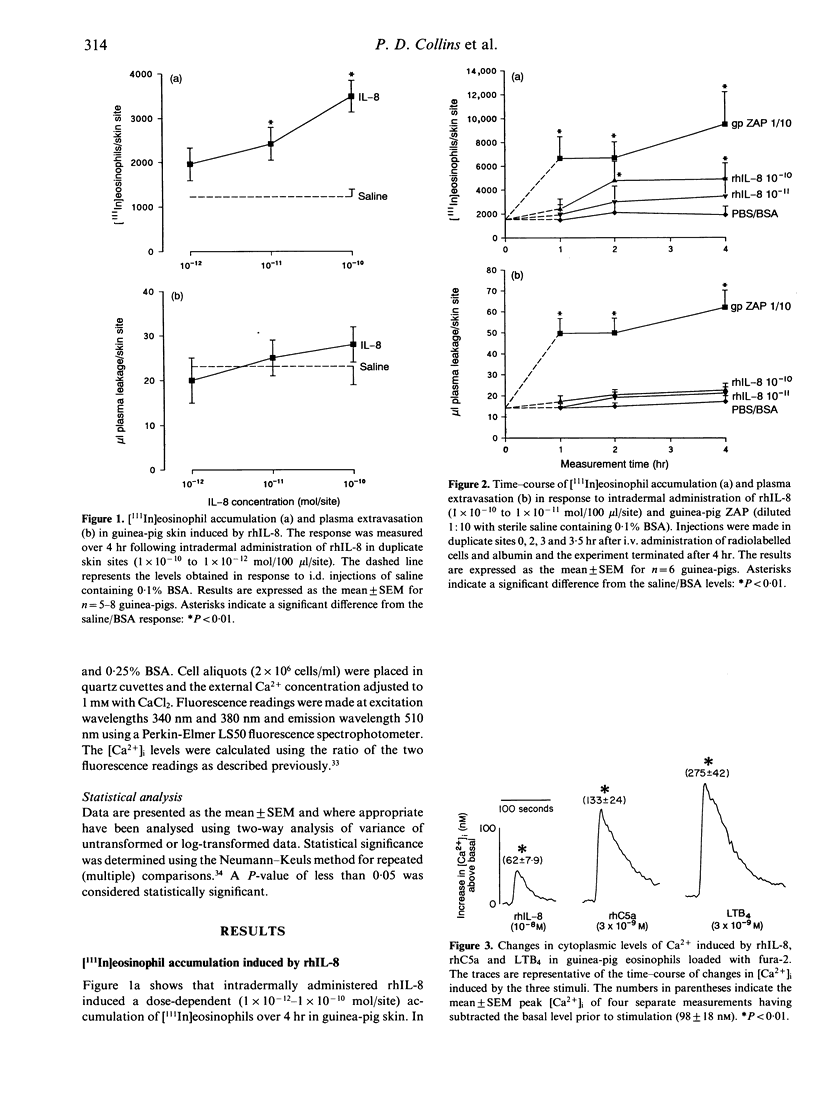
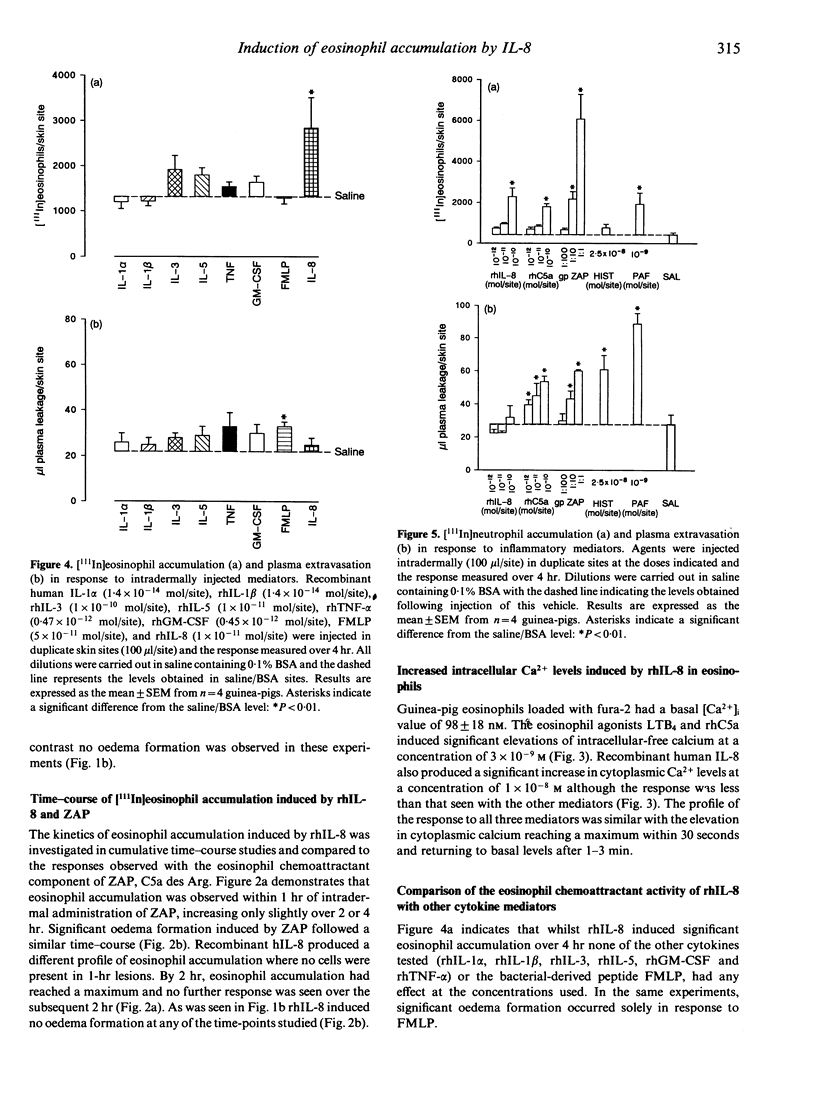
Interleukin-8 (IL-8) is a neutrophil chemoattractant cytokine. Initially IL-8 appeared to exhibit specificity for neutrophils over other cells of the immune system. However, several recent studies have shown that this mediator can also activate other leucocyte types in vitro. In this study we have used an in vivo model of local [111In]leucocyte accumulation in the guinea-pig and an in vitro assay of leucocyte activation (changes in cytosolic-free Ca2+) to investigate the eosinophil chemoattractant activity of IL-8. The intradermal injection of recombinant human (rh)IL-8 induced a dose-dependent accumulation of intravenously administered [111In]eosinophils into the skin sites over 4 hr. Time-course experiments revealed that this cell infiltration was delayed in onset, occurring between 1 and 2 hr after injection of IL-8. The delay may indicate that IL-8 operates via an indirect mechanism. In contrast, eosinophil accumulation induced by the complement fragment C5a occurred within the first hour following injection. Other human cytokines, IL-1, IL-3, IL-5, tumour necrosis factor (TNF) and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), were not eosinophil chemoattractants in this in vivo test system. Direct activation of eosinophils by IL-8 was demonstrated in vitro by a transient elevation in cytoplasmic-free Ca2+ levels where it was less potent than either rhC5a or leukotriene B4 (LTB4). Experiments using [111In]neutrophils in vivo indicated that rhIL-8 and rhC5a were similar in potency in inducing local neutrophil infiltration into guinea-pig skin. The demonstration of the eosinophil chemoattractant activity of IL-8 in vivo raises the possibility that this cytokine, or a structurally related molecule, contributes towards eosinophil infiltration in a number of inflammatory conditions such as asthma, helminthic infections and adult respiratory distress syndrome.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnoux B., Denjean A., Page C. P., Nolibe D., Morley J., Benveniste J. Accumulation of platelets and eosinophils in baboon lung after paf-acether challenge. Inhibition by ketotifen. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Apr;137(4):855–860. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.4.855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazzoni F., Cassatella M. A., Rossi F., Ceska M., Dewald B., Baggiolini M. Phagocytosing neutrophils produce and release high amounts of the neutrophil-activating peptide 1/interleukin 8. J Exp Med. 1991 Mar 1;173(3):771–774. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.3.771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun R. K., Franchini M., Erard F., Rihs S., De Vries I. J., Blaser K., Hansel T. T., Walker C. Human peripheral blood eosinophils produce and release interleukin-8 on stimulation with calcium ionophore. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Apr;23(4):956–960. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrows L. J., Piper P. J., Lindley I. D., Westwick J. Intraperitoneal injection of human recombinant neutrophil-activating factor/interleukin 8 (hrNAF/IL-8) produces a T cell and eosinophil infiltrate in the guinea pig lung. Effect of PAF antagonist WEB2086. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;629:422–424. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb38004.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carré P. C., Mortenson R. L., King T. E., Jr, Noble P. W., Sable C. L., Riches D. W. Increased expression of the interleukin-8 gene by alveolar macrophages in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. A potential mechanism for the recruitment and activation of neutrophils in lung fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 1991 Dec;88(6):1802–1810. doi: 10.1172/JCI115501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colditz I., Zwahlen R., Dewald B., Baggiolini M. In vivo inflammatory activity of neutrophil-activating factor, a novel chemotactic peptide derived from human monocytes. Am J Pathol. 1989 Apr;134(4):755–760. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coëffier E., Joseph D., Vargaftig B. B. Activation of guinea pig eosinophils by human recombinant IL-5. Selective priming to platelet-activating factor-acether and interference of its antagonists. J Immunol. 1991 Oct 15;147(8):2595–2602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czarnetzki B. M., Mertensmeier R. In vitro and in vivo chemotaxis of guinea pig leukocytes toward leukotriene B4 and its w-oxidation products. Prostaglandins. 1985 Jul;30(1):5–11. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(85)80006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darbonne W. C., Rice G. C., Mohler M. A., Apple T., Hébert C. A., Valente A. J., Baker J. B. Red blood cells are a sink for interleukin 8, a leukocyte chemotaxin. J Clin Invest. 1991 Oct;88(4):1362–1369. doi: 10.1172/JCI115442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faccioli L. H., Nourshargh S., Moqbel R., Williams F. M., Sehmi R., Kay A. B., Williams T. J. The accumulation of 111In-eosinophils induced by inflammatory mediators, in vivo. Immunology. 1991 Jun;73(2):222–227. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster S. J., Aked D. M., Schröder J. M., Christophers E. Acute inflammatory effects of a monocyte-derived neutrophil-activating peptide in rabbit skin. Immunology. 1989 Jun;67(2):181–183. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Obin M. S., Brock A. F., Luis E. A., Hass P. E., Hébert C. A., Yip Y. K., Leung D. W., Lowe D. G., Kohr W. J. Endothelial interleukin-8: a novel inhibitor of leukocyte-endothelial interactions. Science. 1989 Dec 22;246(4937):1601–1603. doi: 10.1126/science.2688092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory H., Young J., Schröder J. M., Mrowietz U., Christophers E. Structure determination of a human lymphocyte derived neutrophil activating peptide (LYNAP). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Mar 15;151(2):883–890. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80364-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kameyoshi Y., Dörschner A., Mallet A. I., Christophers E., Schröder J. M. Cytokine RANTES released by thrombin-stimulated platelets is a potent attractant for human eosinophils. J Exp Med. 1992 Aug 1;176(2):587–592. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.2.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kernen P., Wymann M. P., von Tscharner V., Deranleau D. A., Tai P. C., Spry C. J., Dahinden C. A., Baggiolini M. Shape changes, exocytosis, and cytosolic free calcium changes in stimulated human eosinophils. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jun;87(6):2012–2017. doi: 10.1172/JCI115230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel S. L., Standiford T., Kasahara K., Strieter R. M. Interleukin-8 (IL-8): the major neutrophil chemotactic factor in the lung. Exp Lung Res. 1991 Jan-Feb;17(1):17–23. doi: 10.3109/01902149109063278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen C. G., Anderson A. O., Appella E., Oppenheim J. J., Matsushima K. The neutrophil-activating protein (NAP-1) is also chemotactic for T lymphocytes. Science. 1989 Mar 17;243(4897):1464–1466. doi: 10.1126/science.2648569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen C. G., Anderson A. O., Oppenheim J. J., Matsushima K. Production of interleukin-8 by human dermal fibroblasts and keratinocytes in response to interleukin-1 or tumour necrosis factor. Immunology. 1989 Sep;68(1):31–36. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lellouch-Tubiana A., Lefort J., Simon M. T., Pfister A., Vargaftig B. B. Eosinophil recruitment into guinea pig lungs after PAF-acether and allergen administration. Modulation by prostacyclin, platelet depletion, and selective antagonists. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Apr;137(4):948–954. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.4.948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard E. J., Skeel A., Yoshimura T., Noer K., Kutvirt S., Van Epps D. Leukocyte specificity and binding of human neutrophil attractant/activation protein-1. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 15;144(4):1323–1330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez A. F., Williamson D. J., Gamble J. R., Begley C. G., Harlan J. M., Klebanoff S. J., Waltersdorph A., Wong G., Clark S. C., Vadas M. A. Recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor stimulates in vitro mature human neutrophil and eosinophil function, surface receptor expression, and survival. J Clin Invest. 1986 Nov;78(5):1220–1228. doi: 10.1172/JCI112705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nourshargh S., Perkins J. A., Showell H. J., Matsushima K., Williams T. J., Collins P. D. A comparative study of the neutrophil stimulatory activity in vitro and pro-inflammatory properties in vivo of 72 amino acid and 77 amino acid IL-8. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 1;148(1):106–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peveri P., Walz A., Dewald B., Baggiolini M. A novel neutrophil-activating factor produced by human mononuclear phagocytes. J Exp Med. 1988 May 1;167(5):1547–1559. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.5.1547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rot A. Some aspects of NAP-1 pathophysiology: lung damage caused by a blood-borne cytokine. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1991;305:127–135. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-6009-4_15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothenberg M. E., Petersen J., Stevens R. L., Silberstein D. S., McKenzie D. T., Austen K. F., Owen W. F., Jr IL-5-dependent conversion of normodense human eosinophils to the hypodense phenotype uses 3T3 fibroblasts for enhanced viability, accelerated hypodensity, and sustained antibody-dependent cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 1;143(7):2311–2316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder J. M., Christophers E. Secretion of novel and homologous neutrophil-activating peptides by LPS-stimulated human endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 1;142(1):244–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder J. M., Sticherling M., Henneicke H. H., Preissner W. C., Christophers E. IL-1 alpha or tumor necrosis factor-alpha stimulate release of three NAP-1/IL-8-related neutrophil chemotactic proteins in human dermal fibroblasts. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 15;144(6):2223–2232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehmi R., Cromwell O., Taylor G. W., Kay A. B. Identification of guinea pig eosinophil chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis as leukotriene B4 and 8(S),15(S)-dihydroxy-5,9,11,13(Z,E,Z,E)-eicosatetraenoic acid. J Immunol. 1991 Oct 1;147(7):2276–2283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehmi R., Wardlaw A. J., Cromwell O., Kurihara K., Waltmann P., Kay A. B. Interleukin-5 selectively enhances the chemotactic response of eosinophils obtained from normal but not eosinophilic subjects. Blood. 1992 Jun 1;79(11):2952–2959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silbaugh S. A., Stengel P. W., Williams G. D., Herron D. K., Gallagher P., Baker S. R. Effects of leukotriene B4 inhalation. Airway sensitization and lung granulocyte infiltration in the guinea pig. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Oct;136(4):930–934. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.4.930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takafuji S., Bischoff S. C., De Weck A. L., Dahinden C. A. IL-3 and IL-5 prime normal human eosinophils to produce leukotriene C4 in response to soluble agonists. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 1;147(11):3855–3861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelen M., Peveri P., Kernen P., von Tscharner V., Walz A., Baggiolini M. Mechanism of neutrophil activation by NAF, a novel monocyte-derived peptide agonist. FASEB J. 1988 Aug;2(11):2702–2706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Damme J., Van Beeumen J., Opdenakker G., Billiau A. A novel, NH2-terminal sequence-characterized human monokine possessing neutrophil chemotactic, skin-reactive, and granulocytosis-promoting activity. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1364–1376. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walz A., Peveri P., Aschauer H., Baggiolini M. Purification and amino acid sequencing of NAF, a novel neutrophil-activating factor produced by monocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Dec 16;149(2):755–761. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90432-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warringa R. A., Schweizer R. C., Maikoe T., Kuijper P. H., Bruijnzeel P. L., Koendermann L. Modulation of eosinophil chemotaxis by interleukin-5. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1992 Dec;7(6):631–636. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/7.6.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitcomb E. A., Dinarello C. A., Pincus S. H. Differential effects of interleukin-1 alpha and interleukin-1 beta on human peripheral blood eosinophils. Blood. 1989 May 15;73(7):1904–1908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems J., Joniau M., Cinque S., van Damme J. Human granulocyte chemotactic peptide (IL-8) as a specific neutrophil degranulator: comparison with other monokines. Immunology. 1989 Aug;67(4):540–542. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura T., Matsushima K., Oppenheim J. J., Leonard E. J. Neutrophil chemotactic factor produced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated human blood mononuclear leukocytes: partial characterization and separation from interleukin 1 (IL 1). J Immunol. 1987 Aug 1;139(3):788–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler B., Gay R. E., Huang G. Q., Fassbender H. G., Gay S. Immunohistochemical localization of HTLV-I p19- and p24-related antigens in synovial joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Pathol. 1989 Jul;135(1):1–5. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



