Abstract
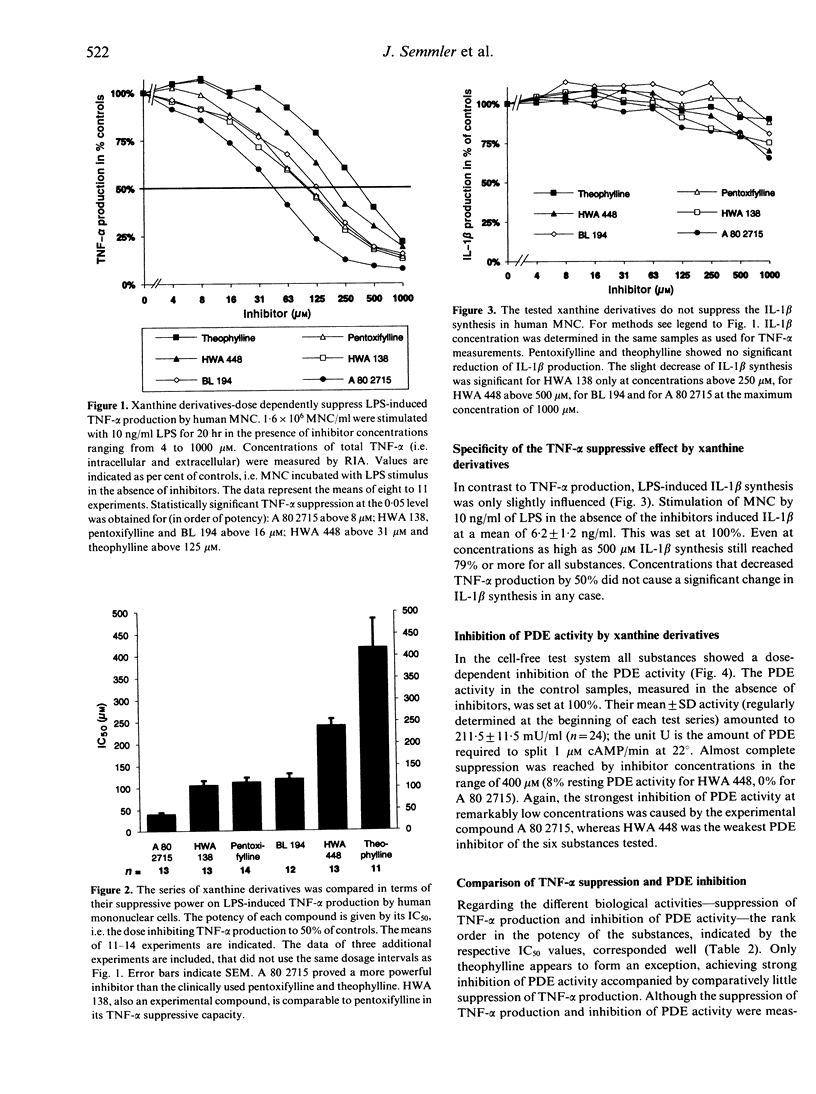
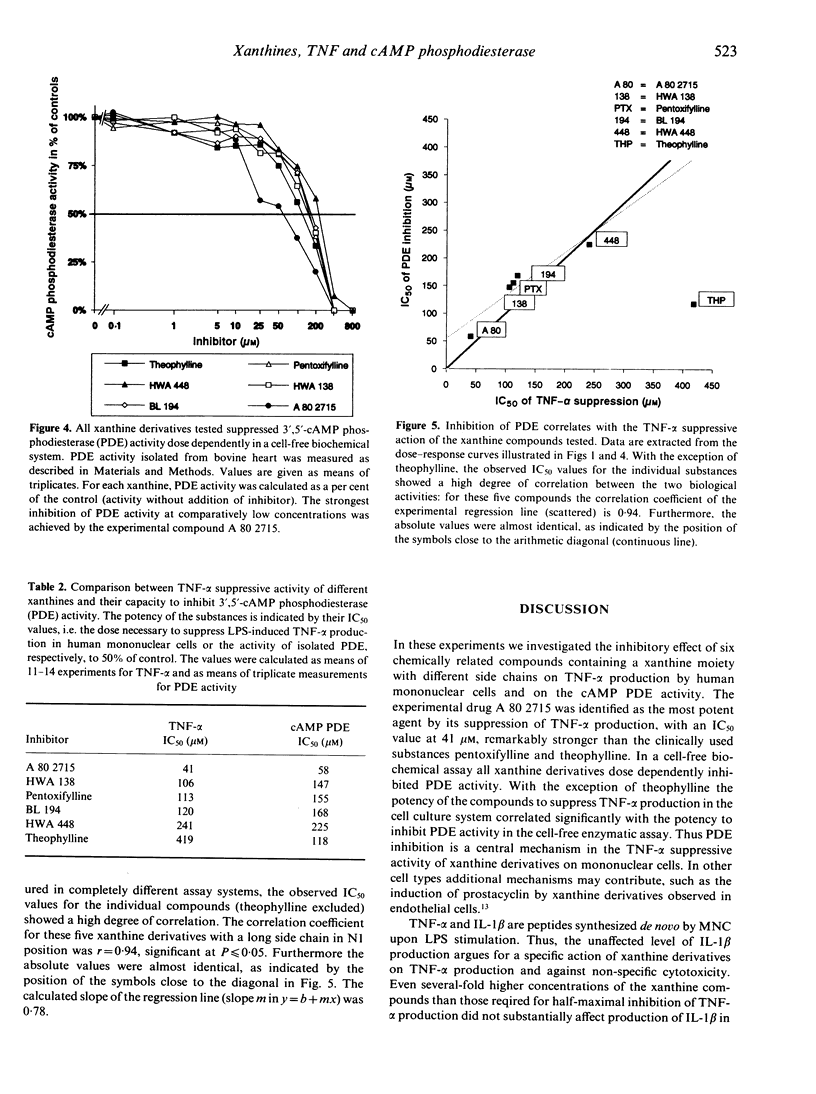
Several in vitro and in vivo studies have demonstrated suppression of tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) synthesis by pentoxifylline. In the present study we compared the effect of pentoxifylline with that of five other xanthine derivatives. We addressed two questions. First, what is the relative potency of those chemically related compounds in suppressing the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced production of TNF-alpha in human mononuclear cells? Second, does suppression of TNF-alpha production by these xanthine derivatives correlate with their capacity to inhibit 3',5'-cAMP phosphodiesterase (PDE) activity? The experimental drug A 80 2715 [1-(5-hydroxy-5-methylhexyl)-3-methyl-7-propylxanthine] was identified as the most potent agent with an IC50 (concentration exerting 50% suppression of LPS-induced TNF-alpha production) of 41 microM (mean of 13 individuals). The IC50 values of the other substances ranged between 106 microM for HWA 138 and 419 microM for theophylline. The LPS-induced interleukin-1 beta (IL-1 beta) production was not influenced by all substances tested at comparable concentrations. Inhibition of PDE activity was determined in a cell-free system using PDE isolated from bovine heart. All xanthine derivatives dose-dependently inhibited PDE activity. Furthermore, with the exception of theophylline, there was a high degree of correlation between the potency to suppress TNF-alpha production in the cell culture system and the potency to inhibit PDE activity in the cell-free enzymatic assay. This argues for a crucial role of PDE inhibition in the suppression of TNF-alpha synthesis by xanthine derivatives.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beavo J. A., Reifsnyder D. H. Primary sequence of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase isozymes and the design of selective inhibitors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Apr;11(4):150–155. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90066-H. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coccia M. T., Waxman K., Soliman M. H., Tominaga G., Pinderski L. Pentoxifylline improves survival following hemorrhagic shock. Crit Care Med. 1989 Jan;17(1):36–38. doi: 10.1097/00003246-198901000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endres S., Fülle H. J., Sinha B., Stoll D., Dinarello C. A., Gerzer R., Weber P. C. Cyclic nucleotides differentially regulate the synthesis of tumour necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1 beta by human mononuclear cells. Immunology. 1991 Jan;72(1):56–60. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endres S., Ghorbani R., Lonnemann G., van der Meer J. W., Dinarello C. A. Measurement of immunoreactive interleukin-1 beta from human mononuclear cells: optimization of recovery, intrasubject consistency, and comparison with interleukin-1 alpha and tumor necrosis factor. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1988 Dec;49(3):424–438. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(88)90130-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han J., Thompson P., Beutler B. Dexamethasone and pentoxifylline inhibit endotoxin-induced cachectin/tumor necrosis factor synthesis at separate points in the signaling pathway. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):391–394. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatherill J. R., Yonemaru M., Zheng H., Hoffmann H., Fujishima S., Ishizaka A., Raffin T. A. Attenuation of acute lung injury in septic guinea-pigs by a new xanthine derivative (HWA-138). Pharmatherapeutica. 1989;5(6):407–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka A., Wu Z. H., Stephens K. E., Harada H., Hogue R. S., O'Hanley P. T., Raffin T. A. Attenuation of acute lung injury in septic guinea pigs by pentoxifylline. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Aug;138(2):376–382. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/138.2.376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katakami Y., Nakao Y., Koizumi T., Katakami N., Ogawa R., Fujita T. Regulation of tumour necrosis factor production by mouse peritoneal macrophages: the role of cellular cyclic AMP. Immunology. 1988 Aug;64(4):719–724. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson C. D., Challiss R. A., Shahid M. Differential modulation of tissue function and therapeutic potential of selective inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase isoenzymes. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991 Jan;12(1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(91)90484-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel P., Nelson S., Bokulic R., Bagby G., Lippton H., Lipscomb G., Summer W. Pentoxifylline inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced serum tumor necrosis factor and mortality. Life Sci. 1990;47(12):1023–1029. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(90)90474-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler R., Dinarello C. A. A method for removing interleukin-1- and tumor necrosis factor-inducing substances from bacterial cultures by ultrafiltration with polysulfone. J Immunol Methods. 1989 Jan 17;116(2):159–165. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90199-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strieter R. M., Remick D. G., Ward P. A., Spengler R. N., Lynch J. P., 3rd, Larrick J., Kunkel S. L. Cellular and molecular regulation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha production by pentoxifylline. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Sep 30;155(3):1230–1236. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81271-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taffet S. M., Singhel K. J., Overholtzer J. F., Shurtleff S. A. Regulation of tumor necrosis factor expression in a macrophage-like cell line by lipopolysaccharide and cyclic AMP. Cell Immunol. 1989 May;120(2):291–300. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(89)90198-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torphy T. J., Undem B. J. Phosphodiesterase inhibitors: new opportunities for the treatment of asthma. Thorax. 1991 Jul;46(7):512–523. doi: 10.1136/thx.46.7.512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabel P., Wolter D. T., Schönharting M. M., Schade U. F. Oxpentifylline in endotoxaemia. Lancet. 1989 Dec 23;2(8678-8679):1474–1477. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92929-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Meer J. W., Endres S., Lonnemann G., Cannon J. G., Ikejima T., Okusawa S., Gelfand J. A., Dinarello C. A. Concentrations of immunoreactive human tumor necrosis factor alpha produced by human mononuclear cells in vitro. J Leukoc Biol. 1988 Mar;43(3):216–223. doi: 10.1002/jlb.43.3.216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



