Abstract
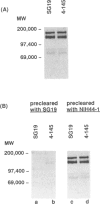
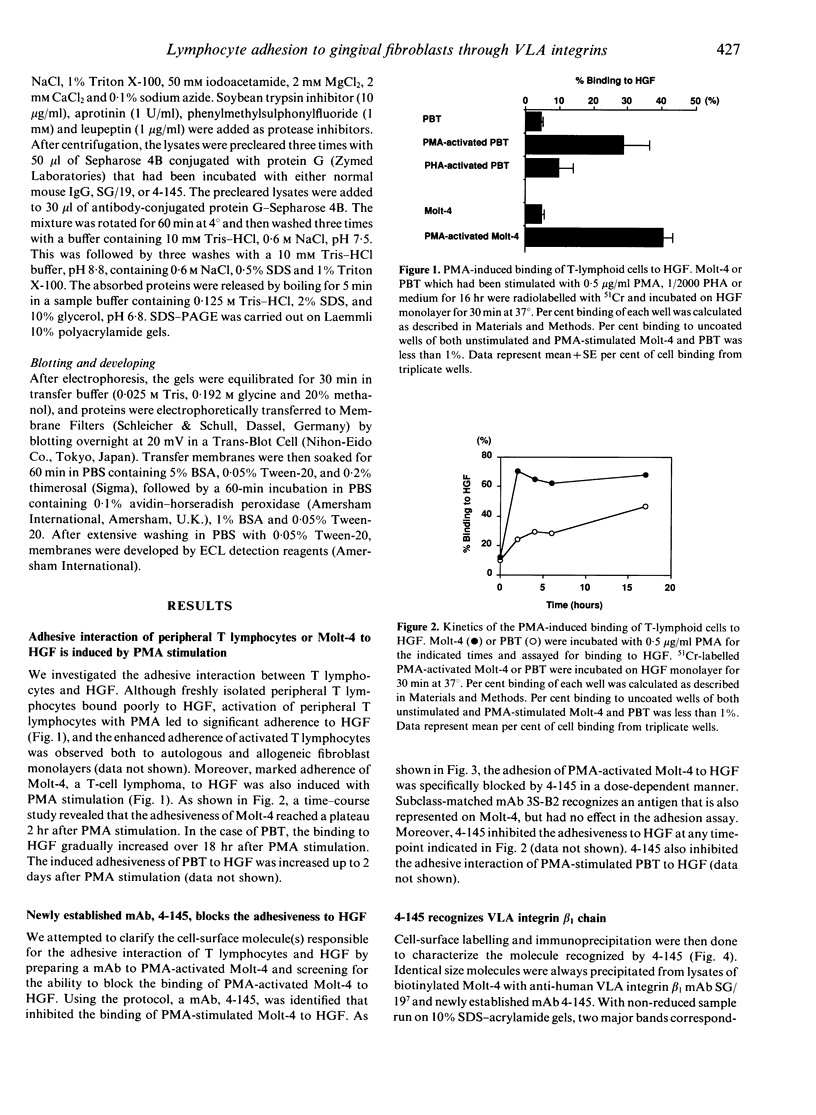
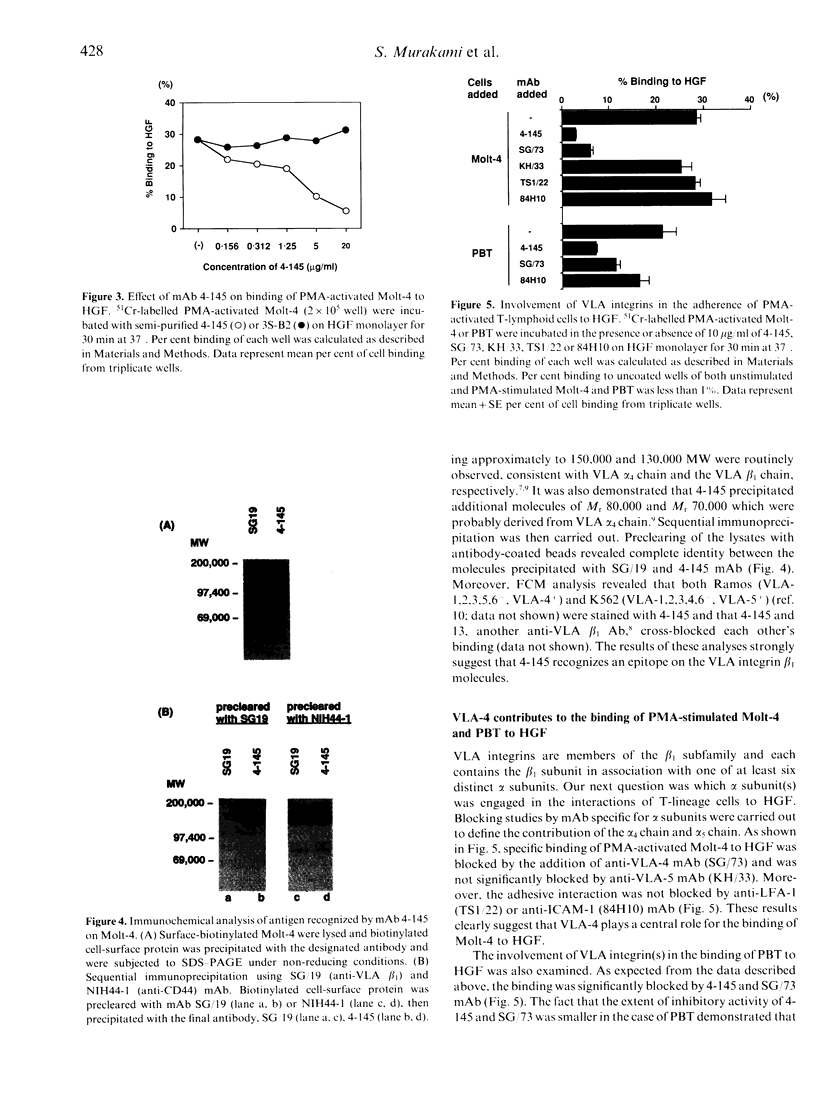
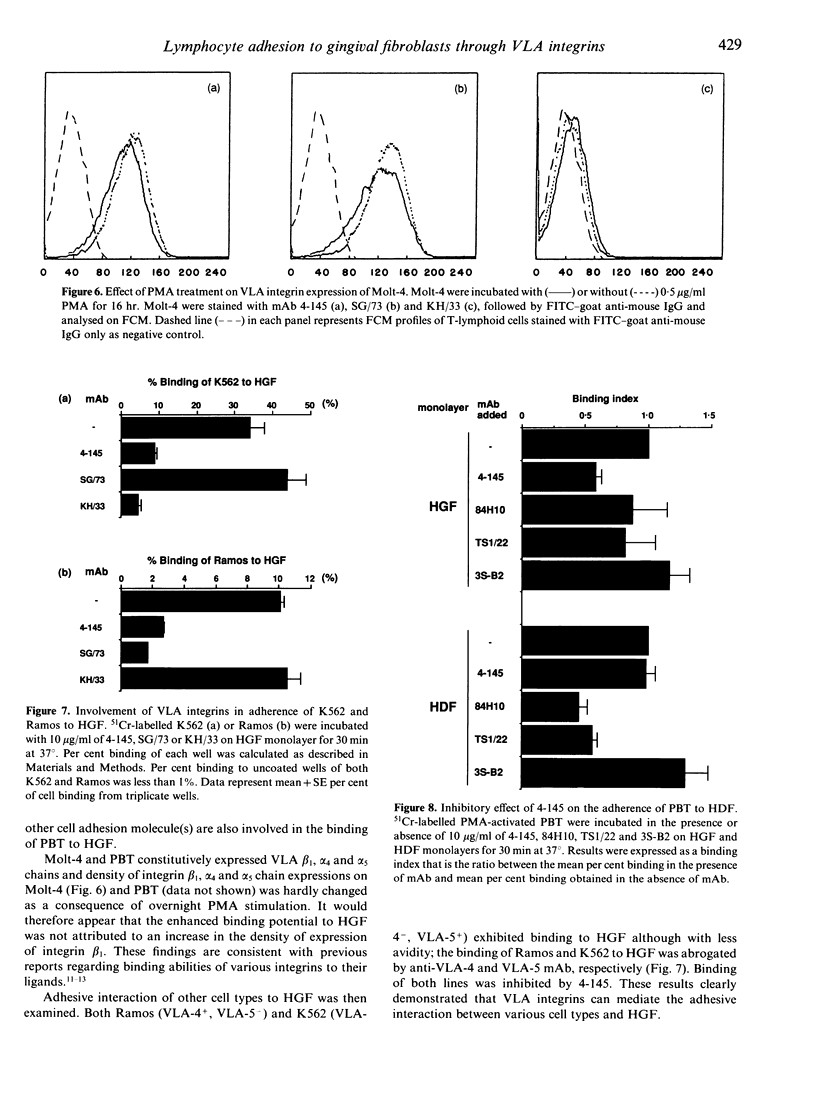
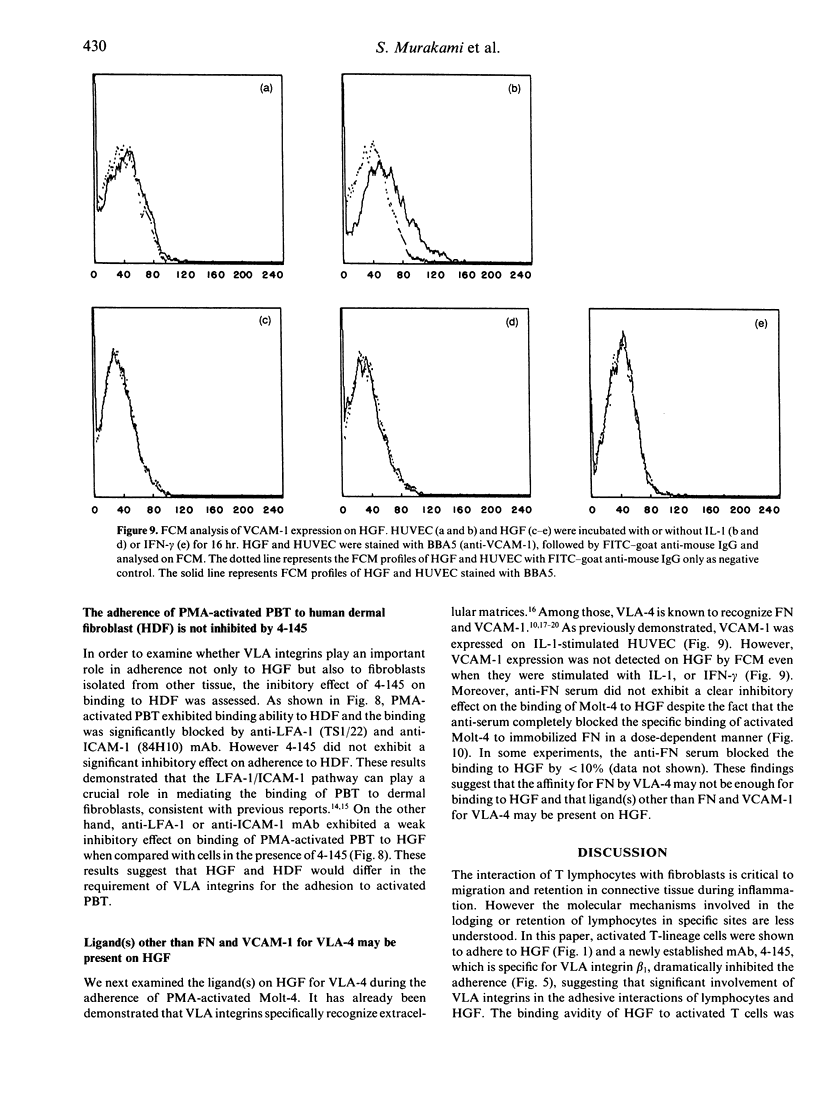
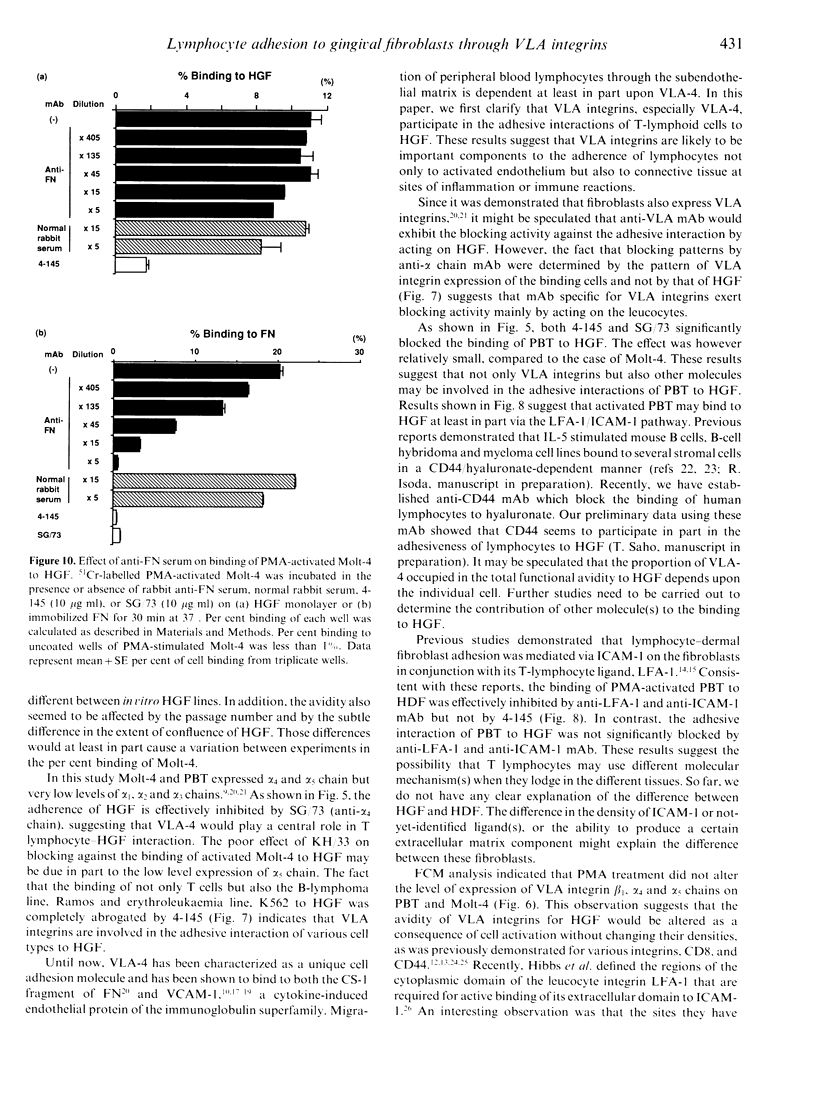
To date, it is still unclear how the trafficking and retention of activated lymphocytes in periodontal lesions are regulated. In this study, we investigated the molecular basis for the adhesive interactions between lymphocytes and human gingival fibroblasts (HGF). Peripheral blood T lymphocytes (PBT) exhibited binding ability, but only when the calls were activated with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA). Among several human cell lines tested, PMA-stimulated Molt-4, a human T-cell leukaemia line, also displayed significant binding ability to HGF. In order to clarify the molecule(s) involved in this cell-cell interaction, a panel of monoclonal antibodies (mAb) was prepared to PMA-activated Molt-4 and one clone, 4-145, was selected on the basis of its ability to block the binding of PMA-activated Molt-4 to HGF. Moreover, 4-145 inhibited the binding of not only activated Molt-4 but also activated PBT and other cell types to HGF. Biochemical and flow cytometric analyses revealed that 4-145 probably recognizes the beta 1 chain of very late antigen (VLA) integrins. Blocking experiments using mAb specific for the alpha-chain of VLA integrins demonstrated the involvement of alpha 4 (VLA-4) and, to a lesser extent, alpha 5 (VLA-5) chains in the adhesive interactions between T cells and HGF. Despite the significant involvement of VLA integrins in the adhesive interaction between PBT and HGF, the binding of PBT to human dermal fibroblasts (HDF) was not abrogated by 4-145, suggesting that HGF and HDF differ in their requirement of VLA integrins for adhesion to activated PBT. Furthermore, the fact that vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1), one of the ligands of VLA-4, was not detected on HGF by flow cytometry and anti-fibronectin (FN) Ab did not block the adhesive interaction to HGF suggests that not-yet-identified ligand(s) for VLA-4 might be present on HGF.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama S. K., Yamada S. S., Chen W. T., Yamada K. M. Analysis of fibronectin receptor function with monoclonal antibodies: roles in cell adhesion, migration, matrix assembly, and cytoskeletal organization. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):863–875. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Pober J. S., Mendrick D. L., Cotran R. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Identification of an inducible endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9238–9242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. S., Oppenheimer-Marks N., Bednarczyk J. L., McIntyre B. W., Lipsky P. E. Fibronectin promotes proliferation of naive and memory T cells by signaling through both the VLA-4 and VLA-5 integrin molecules. J Immunol. 1990 Aug 1;145(3):785–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dustin M. L., Rothlein R., Bhan A. K., Dinarello C. A., Springer T. A. Induction by IL 1 and interferon-gamma: tissue distribution, biochemistry, and function of a natural adherence molecule (ICAM-1). J Immunol. 1986 Jul 1;137(1):245–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dustin M. L., Springer T. A. Lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 (LFA-1) interaction with intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) is one of at least three mechanisms for lymphocyte adhesion to cultured endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):321–331. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dustin M. L., Springer T. A. T-cell receptor cross-linking transiently stimulates adhesiveness through LFA-1. Nature. 1989 Oct 19;341(6243):619–624. doi: 10.1038/341619a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elices M. J., Osborn L., Takada Y., Crouse C., Luhowskyj S., Hemler M. E., Lobb R. R. VCAM-1 on activated endothelium interacts with the leukocyte integrin VLA-4 at a site distinct from the VLA-4/fibronectin binding site. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):577–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90661-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haskard D., Cavender D., Beatty P., Springer T., Ziff M. T lymphocyte adhesion to endothelial cells: mechanisms demonstrated by anti-LFA-1 monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 1;137(9):2901–2906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemler M. E., Huang C., Schwarz L. The VLA protein family. Characterization of five distinct cell surface heterodimers each with a common 130,000 molecular weight beta subunit. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3300–3309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemler M. E., Huang C., Takada Y., Schwarz L., Strominger J. L., Clabby M. L. Characterization of the cell surface heterodimer VLA-4 and related peptides. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11478–11485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemler M. E. VLA proteins in the integrin family: structures, functions, and their role on leukocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:365–400. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs M. L., Jakes S., Stacker S. A., Wallace R. W., Springer T. A. The cytoplasmic domain of the integrin lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 beta subunit: sites required for binding to intercellular adhesion molecule 1 and the phorbol ester-stimulated phosphorylation site. J Exp Med. 1991 Nov 1;174(5):1227–1238. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.5.1227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama T., Yamada A., Kay J., Yamada K. M., Akiyama S. K., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. Activation of CD4 cells by fibronectin and anti-CD3 antibody. A synergistic effect mediated by the VLA-5 fibronectin receptor complex. J Exp Med. 1989 Oct 1;170(4):1133–1148. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.4.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake K., Hasunuma Y., Yagita H., Kimoto M. Requirement for VLA-4 and VLA-5 integrins in lymphoma cells binding to and migration beneath stromal cells in culture. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(3):653–662. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.3.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake K., Underhill C. B., Lesley J., Kincade P. W. Hyaluronate can function as a cell adhesion molecule and CD44 participates in hyaluronate recognition. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):69–75. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami S., Miyake K., June C. H., Kincade P. W., Hodes R. J. IL-5 induces a Pgp-1 (CD44) bright B cell subpopulation that is highly enriched in proliferative and Ig secretory activity and binds to hyaluronate. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 1;145(11):3618–3627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami S., Miyake K., Kincade P. W., Hodes R. J. Functional role of CD44 (Pgp-1) on activated B cells. Immunol Res. 1991;10(1):15–27. doi: 10.1007/BF02918164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nojima Y., Humphries M. J., Mould A. P., Komoriya A., Yamada K. M., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. VLA-4 mediates CD3-dependent CD4+ T cell activation via the CS1 alternatively spliced domain of fibronectin. J Exp Med. 1990 Oct 1;172(4):1185–1192. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.4.1185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Rourke A. M., Rogers J., Mescher M. F. Activated CD8 binding to class I protein mediated by the T-cell receptor results in signalling. Nature. 1990 Jul 12;346(6280):187–189. doi: 10.1038/346187a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Toole T. E., Loftus J. C., Du X. P., Glass A. A., Ruggeri Z. M., Shattil S. J., Plow E. F., Ginsberg M. H. Affinity modulation of the alpha IIb beta 3 integrin (platelet GPIIb-IIIa) is an intrinsic property of the receptor. Cell Regul. 1990 Nov;1(12):883–893. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.12.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada H., Kida T., Yamagami H. Identification and distribution of immunocompetent cells in inflamed gingiva of human chronic periodontitis. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):365–374. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.365-374.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn L., Hession C., Tizard R., Vassallo C., Luhowskyj S., Chi-Rosso G., Lobb R. Direct expression cloning of vascular cell adhesion molecule 1, a cytokine-induced endothelial protein that binds to lymphocytes. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1203–1211. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90775-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piela T. H., Korn J. H. ICAM-1-dependent fibroblast-lymphocyte adhesion: discordance between surface expression and function of ICAM-1. Cell Immunol. 1990 Aug;129(1):125–137. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(90)90192-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice G. E., Bevilacqua M. P. An inducible endothelial cell surface glycoprotein mediates melanoma adhesion. Science. 1989 Dec 8;246(4935):1303–1306. doi: 10.1126/science.2588007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz B. R., Wayner E. A., Carlos T. M., Ochs H. D., Harlan J. M. Identification of surface proteins mediating adherence of CD11/CD18-deficient lymphoblastoid cells to cultured human endothelium. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):2019–2022. doi: 10.1172/JCI114668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimabukuro Y., Murakami S., Okada H. Interferon-gamma-dependent immunosuppressive effects of human gingival fibroblasts. Immunology. 1992 Jun;76(2):344–347. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu Y., Newman W., Gopal T. V., Horgan K. J., Graber N., Beall L. D., van Seventer G. A., Shaw S. Four molecular pathways of T cell adhesion to endothelial cells: roles of LFA-1, VCAM-1, and ELAM-1 and changes in pathway hierarchy under different activation conditions. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;113(5):1203–1212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.5.1203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu Y., Van Seventer G. A., Horgan K. J., Shaw S. Regulated expression and binding of three VLA (beta 1) integrin receptors on T cells. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):250–253. doi: 10.1038/345250a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streeter P. R., Berg E. L., Rouse B. T., Bargatze R. F., Butcher E. C. A tissue-specific endothelial cell molecule involved in lymphocyte homing. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):41–46. doi: 10.1038/331041a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vonderheide R. H., Springer T. A. Lymphocyte adhesion through very late antigen 4: evidence for a novel binding site in the alternatively spliced domain of vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 and an additional alpha 4 integrin counter-receptor on stimulated endothelium. J Exp Med. 1992 Jun 1;175(6):1433–1442. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.6.1433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wayner E. A., Garcia-Pardo A., Humphries M. J., McDonald J. A., Carter W. G. Identification and characterization of the T lymphocyte adhesion receptor for an alternative cell attachment domain (CS-1) in plasma fibronectin. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1321–1330. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Fougerolles A. R., Springer T. A. Intercellular adhesion molecule 3, a third adhesion counter-receptor for lymphocyte function-associated molecule 1 on resting lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1992 Jan 1;175(1):185–190. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.1.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Fougerolles A. R., Stacker S. A., Schwarting R., Springer T. A. Characterization of ICAM-2 and evidence for a third counter-receptor for LFA-1. J Exp Med. 1991 Jul 1;174(1):253–267. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.1.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]