Abstract
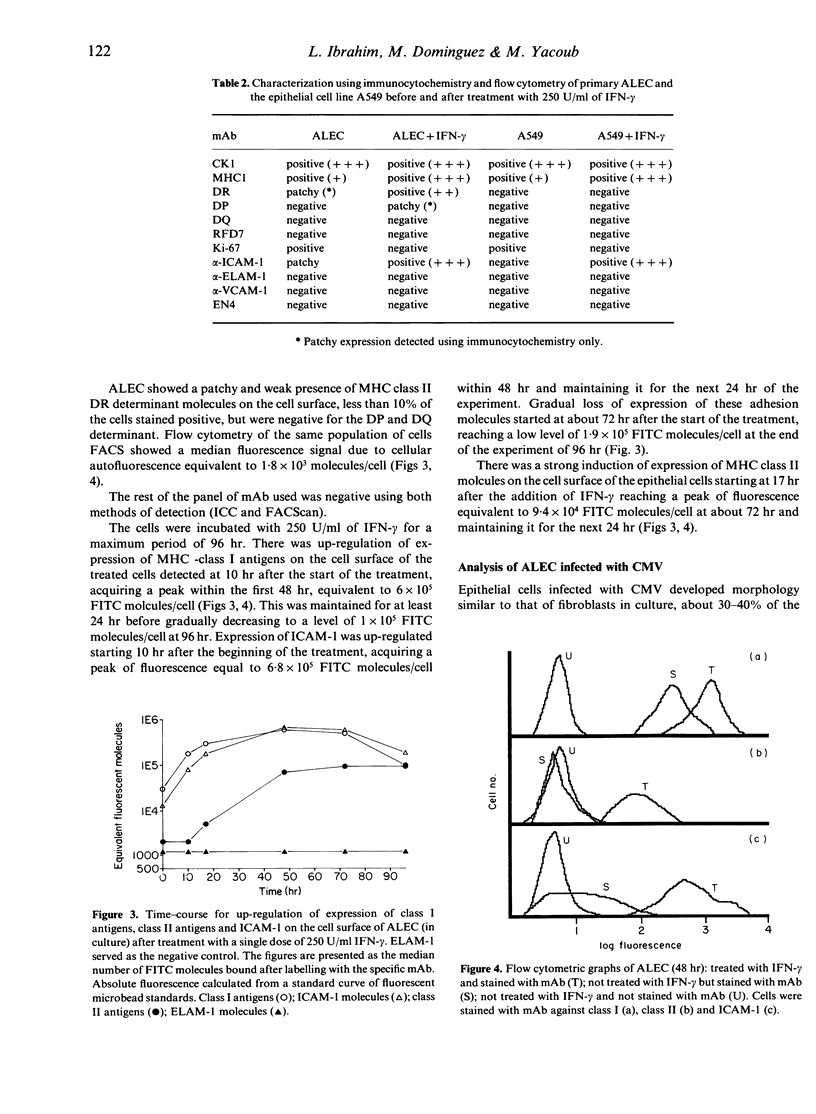
Primary human adult lung epithelial cells (ALEC) were established in culture using the most distal parts of the lung to avoid the airways. Immunocytochemical peroxidase staining and semiquantitative flow cytometry were used to characterize the cells in conjunction with a panel of monoclonal antibodies (mAb). The cells showed a constitutive expression of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I antigens, patchy expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) and a weak patchy expression of MHC class II antigens (detected using immunocytochemical staining). Incubation of the primary ALEC with interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) (250 U/ml) stimulated an up-regulation of the expression of these three antigens to varying degrees; expression of MHC class I antigens and ICAM-1 molecules showed an up-regulation at 10 hr after the start of the treatment, reaching a peak at 48 hr, maintaining it for the next 24 hr and then, steadily and progressively, losing it towards the end of the experiment at 96 hr. Expression of HLA-DR showed an up-regulation at 17 hr after the start of the treatment, reaching a peak at 72 hr and maintaining it for the next 24 hr. Cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection of ALEC in culture caused an up-regulation of expression of class I antigens and ICAM-1, but not DR. However, when the infected cells were incubated with IFN-gamma, an up-regulation in the expression of DR took place. Therefore, within the micro-environment of the transplanted lung the presence of cytokines (IFN-gamma) produced by infiltrating activated mononuclear cells, may render the lung epithelial cells capable of acting as antigen-presenting cells, expressing high levels of class I antigens, ICAM-1 and class II antigens, activating CD8 and CD4 cells thus playing a major part in the process of rejection of the lung allograft; themselves becoming a primary target in the process.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishop G. A., Hall B. M., Suranyi M. G., Tiller D. J., Horvath J. S., Duggin G. G. Expression of HLA antigens on renal tubular cells in culture. I. Evidence that mixed lymphocyte culture supernatants and gamma interferon increase both class I and class II HLA antigens. Transplantation. 1986 Dec;42(6):671–679. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198612000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop G. A., Waugh J. A., Hall B. M. Expression of HLA antigens on renal tubular cells in culture. II. Effect of increased HLA antigen expression on tubular cell stimulation of lymphocyte activation and on their vulnerability to cell-mediated lysis. Transplantation. 1988 Aug;46(2):303–310. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198808000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke C. M., Glanville A. R., Theodore J., Robin E. D. Lung immunogenicity, rejection, and obliterative bronchiolitis. Chest. 1987 Sep;92(3):547–549. doi: 10.1378/chest.92.3.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke C. M., Theodore J., Baldwin J. C., Tazelaar H. D., Morris A. J., McGregor C., Shumway N. E., Robin E. D., Jamieson S. W. Twenty-eight cases of human heart-lung transplantation. Lancet. 1986 Mar 8;1(8480):517–519. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90881-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke C. M., Theodore J., Dawkins K. D., Yousem S. A., Blank N., Billingham M. E., Van Kessel A., Jamieson S. W., Oyer P. E., Baldwin J. C. Post-transplant obliterative bronchiolitis and other late lung sequelae in human heart-lung transplantation. Chest. 1984 Dec;86(6):824–829. doi: 10.1378/chest.86.6.824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esquenazi V., Fuller L., Pardo V., Roth D., Milgrom M., Miller J. In vivo and in vitro induction of class II molecules on canine renal cells and their effect on the mixed lymphocyte kidney cell culture. Transplantation. 1987 Nov;44(5):680–692. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198711000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Weber K., Osborn M., Schmid E., Freudenstein C. Antibody to prekeratin. Decoration of tonofilament like arrays in various cells of epithelial character. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Oct 15;116(2):429–445. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90466-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glanville A. R., Tazelaar H. D., Theodore J., Imoto E., Rouse R. V., Baldwin J. C., Robin E. D. The distribution of MHC class I and II antigens on bronchial epithelium. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Feb;139(2):330–334. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/139.2.330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith B. P., Hardesty R. L., Trento A., Paradis I. L., Duquesnoy R. J., Zeevi A., Dauber J. H., Dummer J. S., Thompson M. E., Gryzan S. Heart-lung transplantation: lessons learned and future hopes. Ann Thorac Surg. 1987 Jan;43(1):6–16. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(10)60157-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland V. A., Cagle P. T., Windsor N. T., Noon G. P., Greenberg S. D., Lawrence E. C. Lymphocyte subset populations in bronchiolitis obliterans after heart-lung transplantation. Transplantation. 1990 Dec;50(6):955–959. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199012000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye M. P. The Registry of the International Society for Heart Transplantation: fourth official report--1987. J Heart Transplant. 1987 Mar-Apr;6(2):63–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby J. A., Forsythe J. L., Simm A., Proud G., Taylor R. M. Renal allograft rejection: protection of renal tubular epithelial cells from lymphokine activated killer cell mediated lysis by pretreatment with cytokines. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1989;4(9):824–828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence E. C., Holland V. A., Young J. B., Windsor N. T., Brousseau K. P., Noon G. P., Whisennand H. H., Debakey M. E., Nelson D. L. Dynamic changes in soluble interleukin-2 receptor levels after lung or heart-lung transplantation. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Sep;140(3):789–796. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.3.789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marck K. W., Prop J., Wildevuur C. R., Nieuwenhuis P. Lung transplantation in the rat: histopathology of left lung iso- and allografts. J Heart Transplant. 1985 Feb;4(2):263–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt J. L., LeBien T. W., Michael A. F. Interstitial mononuclear cell populations in renal graft rejection. Identification by monoclonal antibodies in tissue sections. J Exp Med. 1982 Jan 1;155(1):17–30. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.1.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romaniuk A., Prop J., Petersen A. H., Wildevuur C. R., Nieuwenhuis P. Expression of class II major histocompatibility complex antigens by bronchial epithelium in rat lung allografts. Transplantation. 1987 Aug;44(2):209–214. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198708000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. L., Coles M. I., Griffin R. J., Pomerance A., Yacoub M. H. Expression of class I and class II major histocompatibility antigens in normal and transplanted human heart. Transplantation. 1986 Jun;41(6):776–780. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198606000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothlein R., Dustin M. L., Marlin S. D., Springer T. A. A human intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM-1) distinct from LFA-1. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 15;137(4):1270–1274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. P., Higenbottam T. W., Clelland C. A., Stewart S., Smyth R. L., McGoldrick J. P., Otulana B. A., Wallwork J. Natural history of chronic rejection in heart-lung transplant recipients. J Heart Transplant. 1990 Sep-Oct;9(5):510–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. M., Rose M. L., Yacoub M. H. Expression of MHC antigens in normal human lungs and transplanted lungs with obliterative bronchiolitis. Transplantation. 1989 Sep;48(3):506–510. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198909000-00030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tazelaar H. D., Prop J., Nieuwenhuis P., Billingham M. E., Wildevuur C. R. Airway pathology in the transplanted rat lung. Transplantation. 1988 May;45(5):864–869. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198805000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tazelaar H. D., Yousem S. A. The pathology of combined heart-lung transplantation: an autopsy study. Hum Pathol. 1988 Dec;19(12):1403–1416. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(88)80233-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veith F. J., Hagstrom J. W. Alveolar manifestations of rejection: an important cause of the poor results with human lung transplantation. Ann Surg. 1972 Mar;175(3):336–348. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197203000-00006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veith F. J., Kamholz S. L., Mollenkopf F. P., Montefusco C. M. Lung transplantation 1983. Transplantation. 1983 Apr;35(4):271–278. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198304000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veith F. J., Koerner S. K., Siegelman S. S., Kawakami M., Kaufman S., Attai L. A., Hagstrom J. W., Gliedman M. L. Diagnosis and reversal of rejection in experimental and clinical lung allografts. Ann Thorac Surg. 1973 Aug;16(2):172–183. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(10)65834-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veith F. J., Sinha S. B., Blümcke S., Dougherty J. C., Becker N. H., Siegelman S. S., Hagstrom J. W. Nature and evolution of lung allograft rejection with and without immunosuppression. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1972 Apr;63(4):509–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]