Abstract
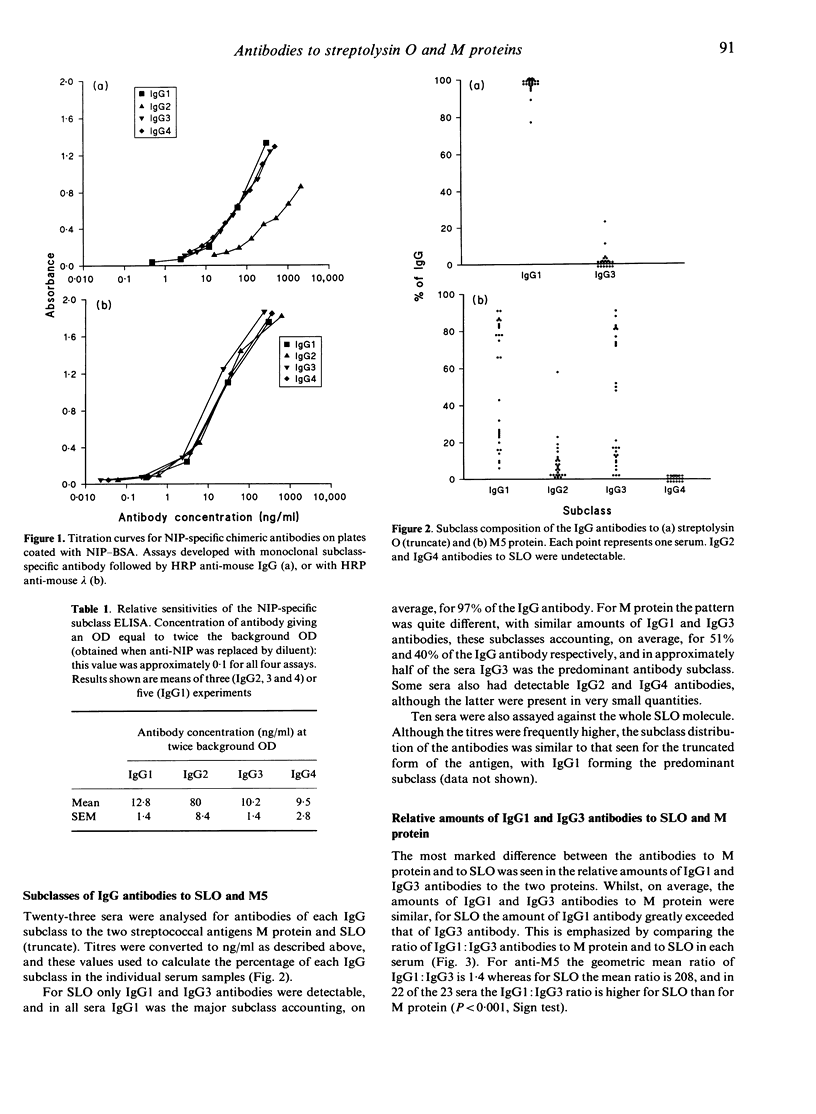
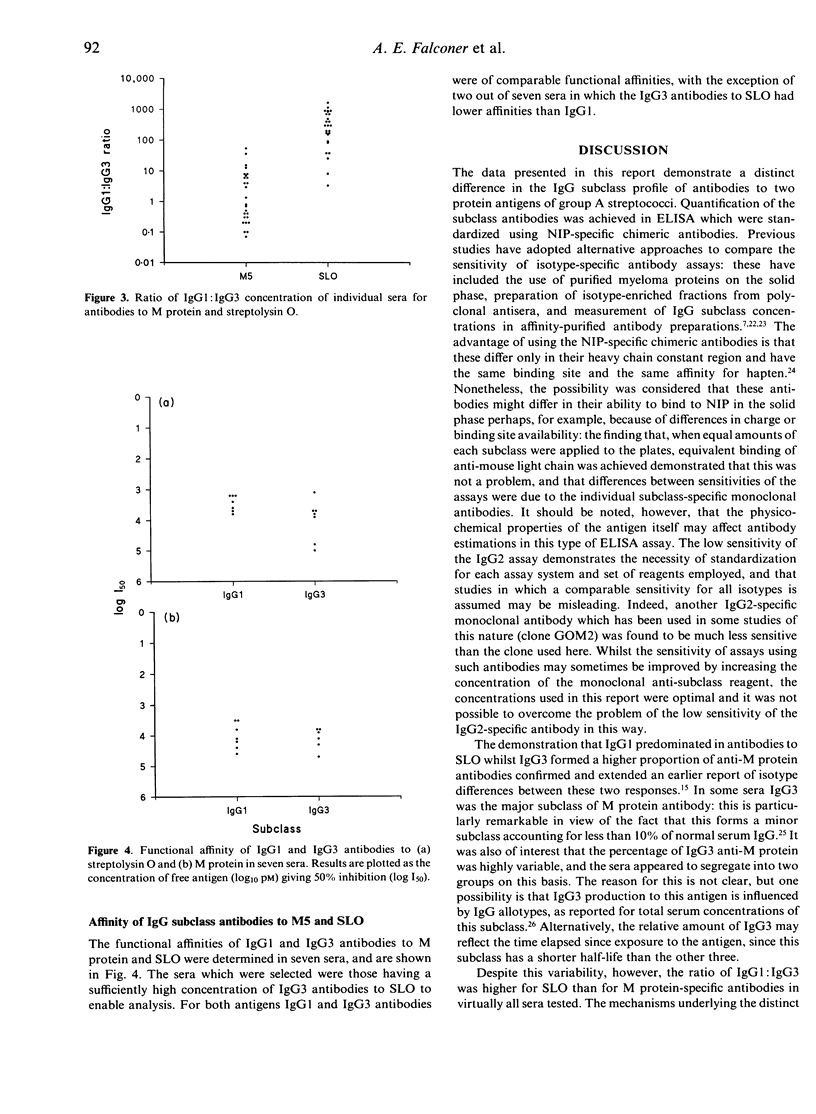
The IgG subclass composition of antibodies to two streptococcal protein antigens in sera following infection was analysed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA). The assays were standardized using 5-iodo-4-hydroxy-nitrophenacetyl (NIP)-specific chimeric antibodies, to permit quantitative comparisons between subclasses. Antibodies to streptolysin O (SLO) were predominantly IgG1, with only minor contributions from the other subclasses. In contrast, antibodies to M protein were distributed between the IgG1 and IgG3 subclasses, and in approximately half the sera IgG3 predominated. The ratio of IgG1:IgG3 was greater for SLO than for M protein in 22/23 sera. Little or no IgG4 antibody was detected to either antigen. Functional affinities of the IgG1 and IgG3 antibodies, determined by inhibition ELISA, were comparable for the two antigens. The demonstration that two protein antigens encountered during streptococcal infection elicit antibody responses with markedly different subclass profiles has implications for IgG subclass regulation and vaccine development.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aalberse R. C., van der Gaag R., van Leeuwen J. Serologic aspects of IgG4 antibodies. I. Prolonged immunization results in an IgG4-restricted response. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):722–726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amlot P. L., Hayes A. E., Gray D., Gordon-Smith E. C., Humphrey J. H. Human immune responses in vivo to protein (KLH) and polysaccharide (DNP-Ficoll) neoantigens: normal subjects compared with bone marrow transplant patients on cyclosporine. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Apr;64(1):125–135. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird P., Calvert J. E., Amlot P. L. Distinctive development of IgG4 subclass antibodies in the primary and secondary responses to keyhole limpet haemocyanin in man. Immunology. 1990 Mar;69(3):355–360. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird P., Calvert J. E., Lowe J., Duggan-Keen M., Forouhi N. G., Seppälä I., Ling N. R. ELISA measurement of IgG subclass production in culture supernatants using monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Nov 23;104(1-2):149–158. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90499-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird P., Lachmann P. J. The regulation of IgG subclass production in man: low serum IgG4 in inherited deficiencies of the classical pathway of C3 activation. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Aug;18(8):1217–1222. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird P., Lowe J., Stokes R. P., Bird A. G., Ling N. R., Jefferis R. The separation of human serum IgG into subclass fractions by immunoaffinity chromatography and assessment of specific antibody activity. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Jun 8;71(1):97–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90209-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brüggemann M., Williams G. T., Bindon C. I., Clark M. R., Walker M. R., Jefferis R., Waldmann H., Neuberger M. S. Comparison of the effector functions of human immunoglobulins using a matched set of chimeric antibodies. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1351–1361. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton D. R., Gregory L., Jefferis R. Aspects of the molecular structure of IgG subclasses. Monogr Allergy. 1986;19:7–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devey M. E., Bleasdale-Barr K. M., Bird P., Amlot P. L. Antibodies of different human IgG subclasses show distinct patterns of affinity maturation after immunization with keyhole limpet haemocyanin. Immunology. 1990 Jun;70(2):168–174. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devey M. E., Wilson D. V., Wheeler A. W. The IgG subclasses of antibodies to grass pollen allergens produced in hay fever patients during hyposensitization. Clin Allergy. 1976 May;6(3):227–236. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1976.tb01901.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falconer A. E., Friedmann P. S., Bird P., Calvert J. E. Abnormal immunoglobulin G subclass production in response to keyhole limpet haemocyanin in atopic patients. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Sep;89(3):495–499. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb06987.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischetti V. A. Streptococcal M protein: molecular design and biological behavior. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jul;2(3):285–314. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.3.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldblatt D., Turner M. W., Levinsky R. J. Branhamella catarrhalis: antigenic determinants and the development of the IgG subclass response in childhood. J Infect Dis. 1990 Nov;162(5):1128–1135. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.5.1128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarström L., Granström M., Oxelius V., Persson M. A., Smith C. I. IgG subclass distribution of antibodies against S. aureus teichoic acid and alpha-toxin in normal and immunodeficient donors. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Mar;55(3):593–601. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarström L., Smith C. I. IgG subclasses in bacterial infections. Monogr Allergy. 1986;19:122–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jertborn M., Svennerholm A. M., Holmgren J. IgG and IgA subclass distribution of antitoxin antibody responses after oral cholera vaccination or cholera disease. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1988;85(3):358–363. doi: 10.1159/000234532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehoe M. A., Poirier T. P., Beachey E. H., Timmis K. N. Cloning and genetic analysis of serotype 5 M protein determinant of group A streptococci: evidence for multiple copies of the M5 determinant in the Streptococcus pyogenes genome. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):190–197. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.190-197.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucisano Valim Y. M., Lachmann P. J. The effect of antibody isotype and antigenic epitope density on the complement-fixing activity of immune complexes: a systematic study using chimaeric anti-NIP antibodies with human Fc regions. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Apr;84(1):1–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb08115.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren M., Persson U., Larsson P., Magnusson C., Smith C. I., Hammarström L., Severinson E. Interleukin 4 induces synthesis of IgE and IgG4 in human B cells. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Jul;19(7):1311–1315. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L., Gray L., Beachey E., Kehoe M. Antigenic variation among group A streptococcal M proteins. Nucleotide sequence of the serotype 5 M protein gene and its relationship with genes encoding types 6 and 24 M proteins. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5668–5673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer G. E., Widdowson J. P. Predominance of immunoglobulin G sub-class 3 among the complement-fixing antibodies to streptococcal M-associated protein. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Aug;37(2):247–258. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson M. A., Brown S. E., Steward M. W., Hammarström L., Smith C. I., Howard C. R., Wahl M., Rynnel-Dagö B., Lefranc G., Carbonara A. O. IgG subclass-associated affinity differences of specific antibodies in humans. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 1;140(11):3875–3879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkney M., Beachey E., Kehoe M. The thiol-activated toxin streptolysin O does not require a thiol group for cytolytic activity. Infect Immun. 1989 Aug;57(8):2553–2558. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.8.2553-2558.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarvas H., Rautonen N., Mäkelä O. Allotype-associated differences in concentrations of human IgG subclasses. J Clin Immunol. 1991 Jan;11(1):39–45. doi: 10.1007/BF00918793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seppälä I. J., Routonen N., Sarnesto A., Mattila P. A., Mäkelä O. The percentages of six immunoglobulin isotypes in human antibodies to tetanus toxoid: standardization of isotype-specific second antibodies in solid-phase assay. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Sep;14(9):868–875. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shackelford P. G., Granoff D. M., Nelson S. J., Scott M. G., Smith D. S., Nahm M. H. Subclass distribution of human antibodies to Haemophilus influenzae type b capsular polysaccharide. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 15;138(2):587–592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skvaril F. IgG subclasses in viral infections. Monogr Allergy. 1986;19:134–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snapper C. M., Paul W. E. Interferon-gamma and B cell stimulatory factor-1 reciprocally regulate Ig isotype production. Science. 1987 May 22;236(4804):944–947. doi: 10.1126/science.3107127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens T. L., Bossie A., Sanders V. M., Fernandez-Botran R., Coffman R. L., Mosmann T. R., Vitetta E. S. Regulation of antibody isotype secretion by subsets of antigen-specific helper T cells. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):255–258. doi: 10.1038/334255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yount W. J., Dorner M. M., Kunkel H. G., Kabat E. A. Studies on human antibodies. VI. Selective variations in subgroup composition and genetic markers. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):633–646. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


