Abstract
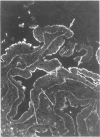
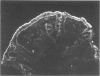
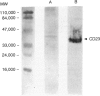
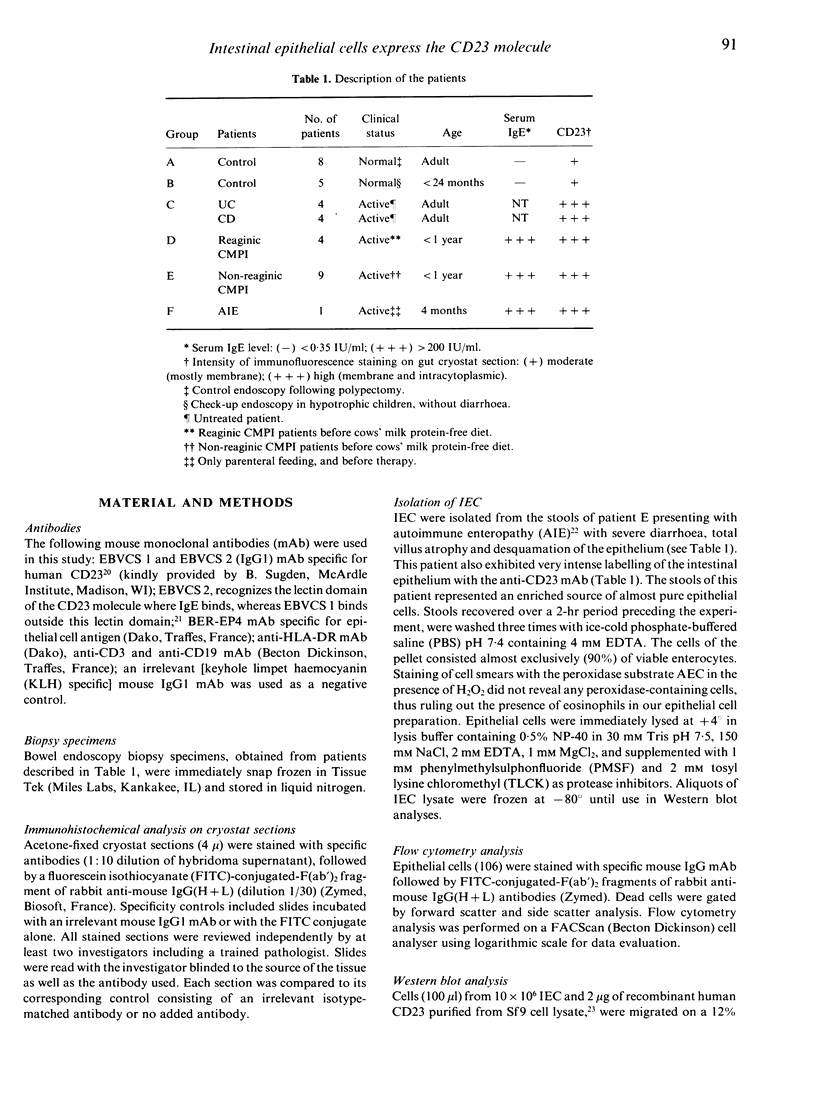
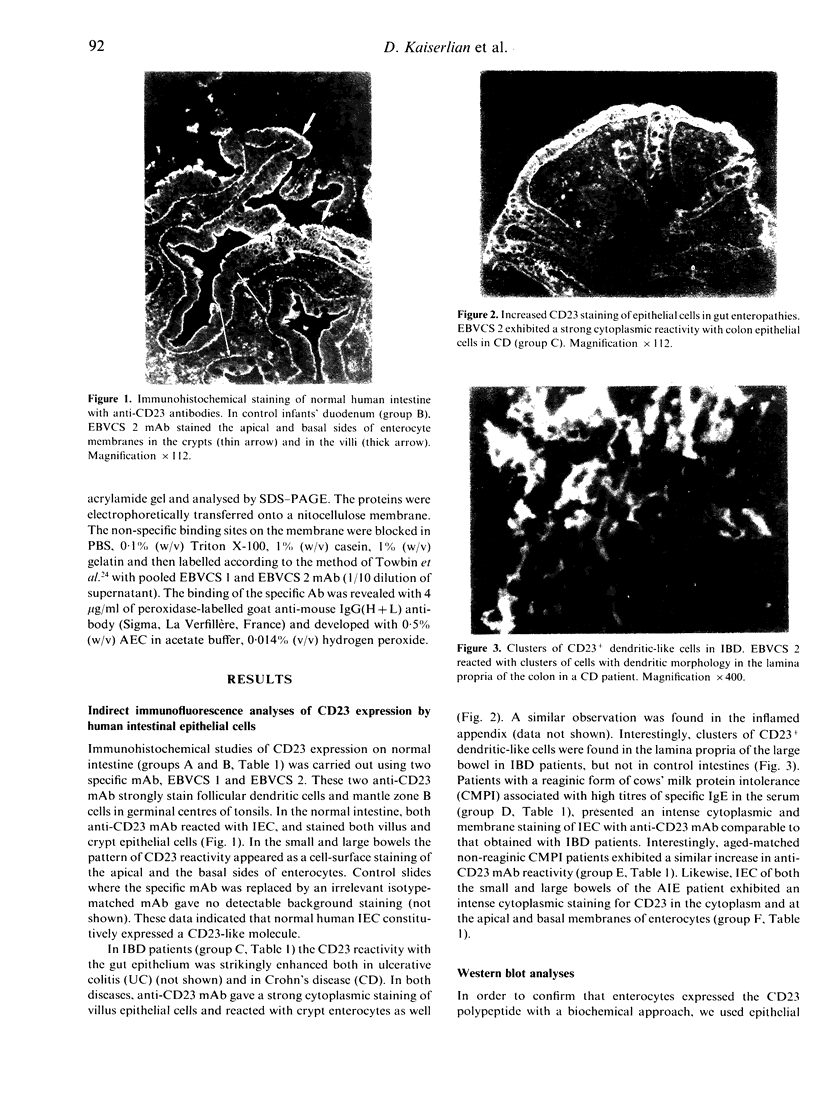
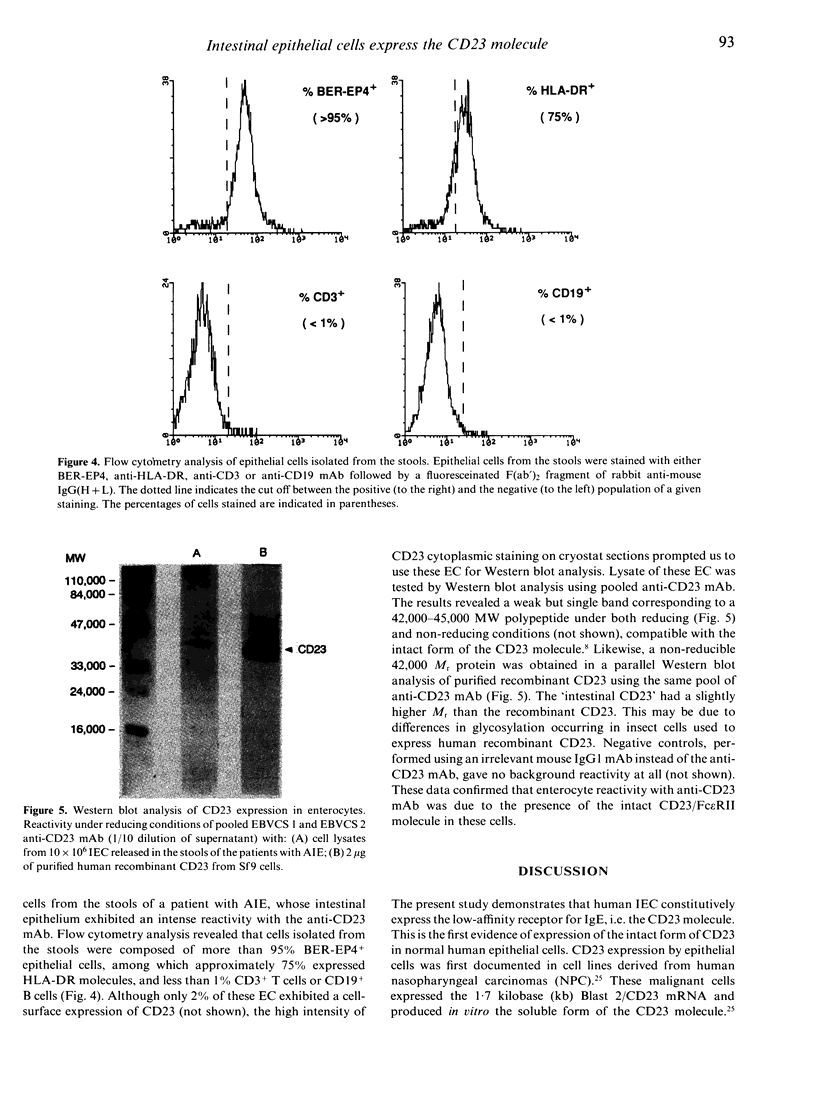
Immunohistochemical analysis of normal human intestine revealed that two anti-CD23 monoclonal antibodies (mAb), EBVCS 1 and EBVCS 2, reacted with human intestinal epithelial cells. Both mAb exhibited an exclusive reactivity with epithelial cells of the small and large bowels. Staining with both EBVCS 1 and EBVCS 2 was localized on the apical and basal sides of enterocytes. Enhanced expression of CD23 on gut epithelial cells was found in inflammatory bowel diseases, in children with food intolerance to cows' milk proteins and in a young infant with severe autoimmune enteropathy. Western blot analysis of anti-CD23 mAb reactivity with gut epithelial cell extracts showed the presence of a non-reducible 42,000-45,000 M(r) polypeptide compatible with the membrane form of the intact CD23 molecule. These data show that CD23 is constitutively expressed by intestinal epithelial cells and that its expression is enhanced in enteropathies.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aubry J. P., Pochon S., Graber P., Jansen K. U., Bonnefoy J. Y. CD21 is a ligand for CD23 and regulates IgE production. Nature. 1992 Aug 6;358(6386):505–507. doi: 10.1038/358505a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aubry J. P., Shields J. G., Jansen K. U., Bonnefoy J. Y. A multiparameter flow cytometric method to study surface molecules involved in interactions between subpopulations of cells. J Immunol Methods. 1993 Feb 26;159(1-2):161–171. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(93)90154-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bettler B., Hofstetter H., Rao M., Yokoyama W. M., Kilchherr F., Conrad D. H. Molecular structure and expression of the murine lymphocyte low-affinity receptor for IgE (Fc epsilon RII). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7566–7570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieber T., Rieger A., Neuchrist C., Prinz J. C., Rieber E. P., Boltz-Nitulescu G., Scheiner O., Kraft D., Ring J., Stingl G. Induction of Fc epsilon R2/CD23 on human epidermal Langerhans cells by human recombinant interleukin 4 and gamma interferon. J Exp Med. 1989 Jul 1;170(1):309–314. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.1.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billaud M., Busson P., Huang D., Mueller-Lantzch N., Rousselet G., Pavlish O., Wakasugi H., Seigneurin J. M., Tursz T., Lenoir G. M. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-containing nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells express the B-cell activation antigen blast2/CD23 and low levels of the EBV receptor CR2. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4121–4128. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4121-4128.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bland P. W., Warren L. G. Antigen presentation by epithelial cells of the rat small intestine. I. Kinetics, antigen specificity and blocking by anti-Ia antisera. Immunology. 1986 May;58(1):1–7. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnefoy J. Y., Aubry J. P., Peronne C., Wijdenes J., Banchereau J. Production and characterization of a monoclonal antibody specific for the human lymphocyte low affinity receptor for IgE: CD 23 is a low affinity receptor for IgE. J Immunol. 1987 May 1;138(9):2970–2978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnefoy J. Y., Guillot O., Spits H., Blanchard D., Ishizaka K., Banchereau J. The low-affinity receptor for IgE (CD23) on B lymphocytes is spatially associated with HLA-DR antigens. J Exp Med. 1988 Jan 1;167(1):57–72. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.1.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnefoy J. Y., Shields J., Mermod J. J. Inhibition of human interleukin 4-induced IgE synthesis by a subset of anti-CD23/Fc epsilon RII monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Jan;20(1):139–144. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad D. H. Fc epsilon RII/CD23: the low affinity receptor for IgE. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:623–645. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.003203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalloul A. H., Fourcade C., Debré P., Mossalayi M. D. Thymic epithelial cell-derived supernatants sustain the maturation of human prothymocytes: involvement of interleukin 1 and CD23. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Oct;21(10):2633–2636. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830211050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defrance T., Aubry J. P., Rousset F., Vanbervliet B., Bonnefoy J. Y., Arai N., Takebe Y., Yokota T., Lee F., Arai K. Human recombinant interleukin 4 induces Fc epsilon receptors (CD23) on normal human B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1987 Jun 1;165(6):1459–1467. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.6.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores-Romo L., Johnson G. D., Ghaderi A. A., Stanworth D. R., Veronesi A., Gordon J. Functional implication for the topographical relationship between MHC class II and the low-affinity IgE receptor: occupancy of CD23 prevents B lymphocytes from stimulating allogeneic mixed lymphocyte responses. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Nov;20(11):2465–2469. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830201116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J., Cairns J. A., Millsum M. J., Gillis S., Guy G. R. Interleukin 4 and soluble CD23 as progression factors for human B lymphocytes: analysis of their interactions with agonists of the phosphoinositide "dual pathway" of signalling. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Oct;18(10):1561–1565. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830181014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen K. U., Shields J., Gordon J., Cairns J., Graber P., Bonnefoy J. Y. Expression of human recombinant CD23 in insect cells. J Recept Res. 1991;11(1-4):507–520. doi: 10.3109/10799899109066424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiserlian D., Vidal K., Revillard J. P. Murine enterocytes can present soluble antigen to specific class II-restricted CD4+ T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Aug;19(8):1513–1516. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kintner C., Sugden B. Identification of antigenic determinants unique to the surfaces of cells transformed by Epstein-Barr virus. Nature. 1981 Dec 3;294(5840):458–460. doi: 10.1038/294458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y. J., Cairns J. A., Holder M. J., Abbot S. D., Jansen K. U., Bonnefoy J. Y., Gordon J., MacLennan I. C. Recombinant 25-kDa CD23 and interleukin 1 alpha promote the survival of germinal center B cells: evidence for bifurcation in the development of centrocytes rescued from apoptosis. Eur J Immunol. 1991 May;21(5):1107–1114. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer L., Eisenhardt D., Salomon P., Bauer W., Plous R., Piccinini L. Expression of class II molecules on intestinal epithelial cells in humans. Differences between normal and inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1991 Jan;100(1):3–12. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90575-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mossalayi M. D., Arock M., Bertho J. M., Blanc C., Dalloul A. H., Hofstetter H., Sarfati M., Delespesse G., Debré P. Proliferation of early human myeloid precursors induced by interleukin-1 and recombinant soluble CD23. Blood. 1990 May 15;75(10):1924–1927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mossalayi M. D., Lecron J. C., Dalloul A. H., Sarfati M., Bertho J. M., Hofstetter H., Delespesse G., Debre P. Soluble CD23 (Fc epsilon RII) and interleukin 1 synergistically induce early human thymocyte maturation. J Exp Med. 1990 Mar 1;171(3):959–964. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.3.959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Náray-Fejes-Tóth A., Guyre P. M. Recombinant human immune interferon induces increased IgE receptor expression on the human monocyte cell line U-937. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):1914–1919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pochon S., Graber P., Yeager M., Jansen K., Bernard A. R., Aubry J. P., Bonnefoy J. Y. Demonstration of a second ligand for the low affinity receptor for immunoglobulin E (CD23) using recombinant CD23 reconstituted into fluorescent liposomes. J Exp Med. 1992 Aug 1;176(2):389–397. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.2.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pène J., Rousset F., Brière F., Chrétien I., Wideman J., Bonnefoy J. Y., De Vries J. E. Interleukin 5 enhances interleukin 4-induced IgE production by normal human B cells. The role of soluble CD23 antigen. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jun;18(6):929–935. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsoukas C. D., Lambris J. D. Expression of EBV/C3d receptors on T cells: biological significance. Immunol Today. 1993 Feb;14(2):56–59. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90059-T. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yukawa K., Kikutani H., Owaki H., Yamasaki K., Yokota A., Nakamura H., Barsumian E. L., Hardy R. R., Suemura M., Kishimoto T. A B cell-specific differentiation antigen, CD23, is a receptor for IgE (Fc epsilon R) on lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 15;138(8):2576–2580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]