Abstract
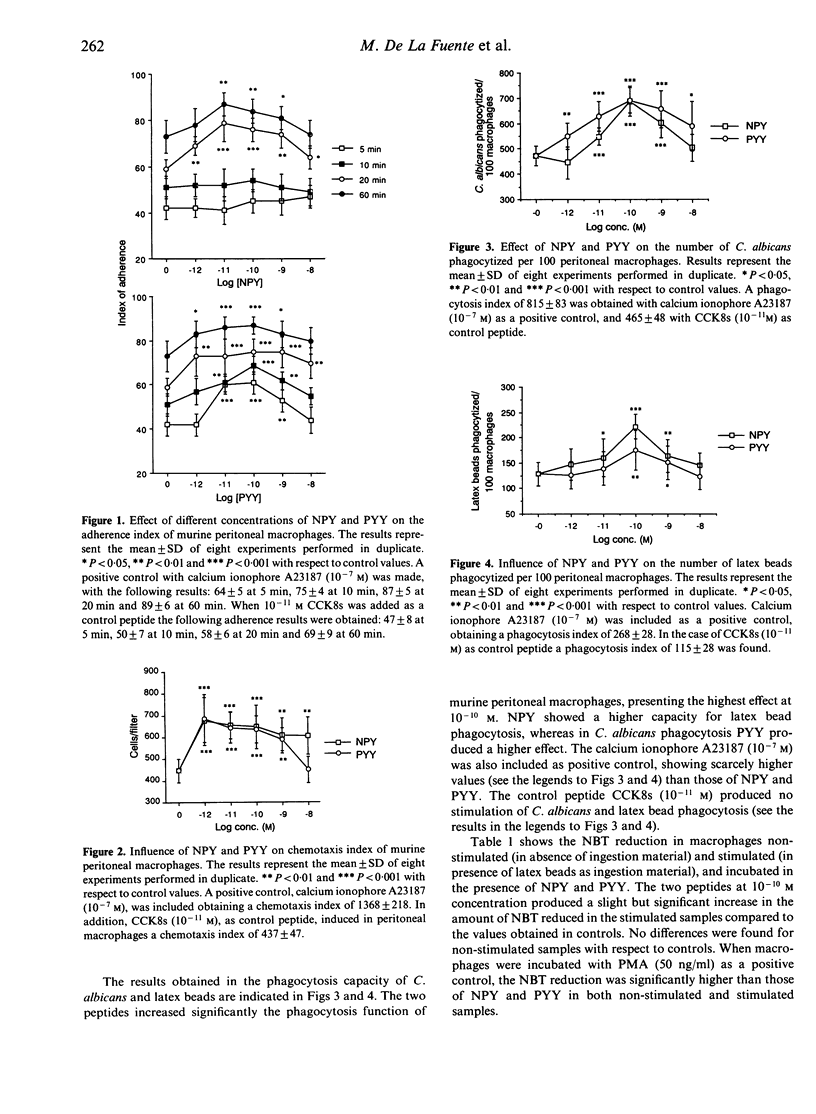
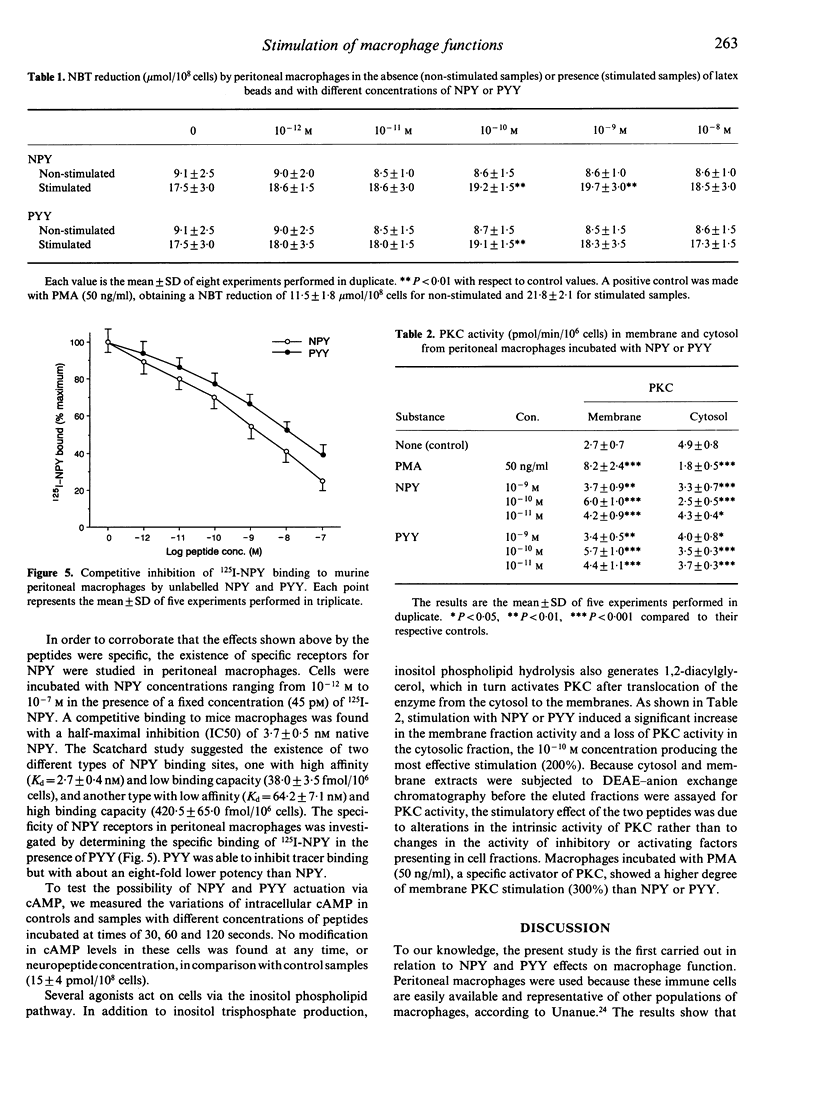
The peptides neuropeptide Y (NPY) and peptide YY (PYY) at concentrations from 10(-12) M to 10(-8) M have been shown in this study to stimulate significantly, in vitro, several functions of resting peritoneal macrophages from BALB/c mice: adherence to substrate, chemotaxis, ingestion of inert particles (latex beads) and foreign cells (Candida albicans), and production of superoxide anion measured by nitroblue tetrazolium reduction. A dose-response relationship was observed, with a maximal stimulation of the macrophage functions studied at 10(-10) M. These effects seem to be produced by specific receptors for the neuropeptides studied in peritoneal macrophages. Whereas the two peptides induced no change of intracellular cyclic AMP, they caused a significant stimulation of protein kinase C (PKC) in murine macrophages. These results suggest that NPY and PYY produce their effects on macrophage function through PKC activation.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOYDEN S. The chemotactic effect of mixtures of antibody and antigen on polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J Exp Med. 1962 Mar 1;115:453–466. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.3.453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagasra O., Howeedy A., Kajdacsy-Balla A. Macrophage function in chronic experimental alcoholism. I. Modulation of surface receptors and phagocytosis. Immunology. 1988 Nov;65(3):405–409. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danger J. M., Tonon M. C., Jenks B. G., Saint-Pierre S., Martel J. C., Fasolo A., Breton B., Quirion R., Pelletier G., Vaudry H. Neuropeptide Y: localization in the central nervous system and neuroendocrine functions. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 1990;4(3):307–340. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-8206.1990.tb00497.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels A. J., Lazarowski E. R., Matthews J. E., Lapetina E. G. Neuropeptide Y mobilizes intracellular Ca2+ and increases inositol phosphate production in human erythroleukemia cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Dec 29;165(3):1138–1144. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92721-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De la Fuente M., Del Rio M., Ferrandez M. D., Hernanz A. Modulation of phagocytic function in murine peritoneal macrophages by bombesin, gastrin-releasing peptide and neuromedin C. Immunology. 1991 Jun;73(2):205–211. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De la Fuente M., Garrido J. J., Arahuetes R. M., Hernanz A. Stimulation of phagocytic function in mouse macrophages by neurotensin and neuromedin N. J Neuroimmunol. 1993 Jan;42(1):97–104. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(93)90216-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glowa J. R., Insel T. R. Effects of chlordiazepoxide and beta-carboline 3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester on non-suppressed and minimally-suppressed responding in the squirrel monkey. Life Sci. 1992;50(1):7–14. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(92)90191-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopalakrishna R., Barsky S. H., Thomas T. P., Anderson W. B. Factors influencing chelator-stable, detergent-extractable, phorbol diester-induced membrane association of protein kinase C. Differences between Ca2+-induced and phorbol ester-stabilized membrane bindings of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 15;261(35):16438–16445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan D., Maouyo D., Taylor I. L., Gettys T. W., Greeley G. H., Jr, Morisset J. Peptide-YY, a new partner in the negative feedback control of pancreatic secretion. Endocrinology. 1991 Feb;128(2):911–916. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-2-911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilig M., Widerlöv E. Neuropeptide Y: an overview of central distribution, functional aspects, and possible involvement in neuropsychiatric illnesses. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1990 Aug;82(2):95–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1990.tb01366.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irwin M., Brown M., Patterson T., Hauger R., Mascovich A., Grant I. Neuropeptide Y and natural killer cell activity: findings in depression and Alzheimer caregiver stress. FASEB J. 1991 Dec;5(15):3100–3107. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.15.1743441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson O., Sandberg G. Effect of the neuropeptides beta-MSH, neurotensin, NPY, PHI, somatostatin and substance P on proliferation of lymphocytes in vitro. Acta Physiol Scand. 1989 Sep;137(1):107–111. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1989.tb08726.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolicoeur F. B., Michaud J. N., Menard D., Fournier A. In vivo structure activity study supports the existence of heterogeneous neuropeptide Y receptors. Brain Res Bull. 1991 Feb;26(2):309–311. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(91)90243-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korchak H. M., Vosshall L. B., Haines K. A., Wilkenfeld C., Lundquist K. F., Weissmann G. Activation of the human neutrophil by calcium-mobilizing ligands. II. Correlation of calcium, diacyl glycerol, and phosphatidic acid generation with superoxide anion generation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11098–11105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Anggård A., Pernow J., Hökfelt T. Neuropeptide Y-, substance P- and VIP-immunoreactive nerves in cat spleen in relation to autonomic vascular and volume control. Cell Tissue Res. 1985;239(1):9–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00214896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Tatemoto K. Pancreatic polypeptide family (APP, BPP, NPY and PYY) in relation to sympathetic vasoconstriction resistant to alpha-adrenoceptor blockade. Acta Physiol Scand. 1982 Dec;116(4):393–402. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1982.tb07157.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Tatemoto K., Terenius L., Hellström P. M., Mutt V., Hökfelt T., Hamberger B. Localization of peptide YY (PYY) in gastrointestinal endocrine cells and effects on intestinal blood flow and motility. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4471–4475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marotti T., Haberstok H., Sverko V., Hrsak I. Met- and Leu-enkephalin modulate superoxide anion release from human polymorphonuclear cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992 Apr 15;650:146–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1992.tb49112.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):305–312. doi: 10.1126/science.3014651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noga S. J., Normann S. J., Weiner R. S. Methods in laboratory investigation. Isolation of guinea pig monocytes and Kurloff cells: characterization of monocyte subsets by morphology, cytochemistry, and adherence. Lab Invest. 1984 Aug;51(2):244–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel K. V., Schrey M. P. Activation of inositol phospholipid signaling and Ca2+ efflux in human breast cancer cells by bombesin. Cancer Res. 1990 Jan 15;50(2):235–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romano T. A., Felten S. Y., Felten D. L., Olschowka J. A. Neuropeptide-Y innervation of the rat spleen: another potential immunomodulatory neuropeptide. Brain Behav Immun. 1991 Mar;5(1):116–131. doi: 10.1016/0889-1591(91)90011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruff M. R., Wahl S. M., Pert C. B. Substance P receptor-mediated chemotaxis of human monocytes. Peptides. 1985;6 (Suppl 2):107–111. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(85)90142-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segura J. J., Guerrero J. M., Goberna R., Calvo J. R. Characterization of functional receptors for vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) in rat peritoneal macrophages. Regul Pept. 1991 Apr 25;33(2):133–143. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(91)90208-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segura J. J., Guerrero J. M., Goberna R., Calvo J. R. Stimulatory effect of vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) on cyclic AMP production in rat peritoneal macrophages. Regul Pept. 1992 Feb 18;37(3):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(92)90614-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh G., Singh L., Raufman J. P. Y2 receptors for peptide YY and neuropeptide Y on dispersed chief cells from guinea pig stomach. Am J Physiol. 1992 Apr;262(4 Pt 1):G756–G762. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.262.4.G756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley B. G., Daniel D. R., Chin A. S., Leibowitz S. F. Paraventricular nucleus injections of peptide YY and neuropeptide Y preferentially enhance carbohydrate ingestion. Peptides. 1985 Nov-Dec;6(6):1205–1211. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(85)90452-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söder O., Hellström P. M. Neuropeptide regulation of human thymocyte, guinea pig T lymphocyte and rat B lymphocyte mitogenesis. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1987;84(2):205–211. doi: 10.1159/000234424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K., Carlquist M., Mutt V. Neuropeptide Y--a novel brain peptide with structural similarities to peptide YY and pancreatic polypeptide. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):659–660. doi: 10.1038/296659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K. Isolation and characterization of peptide YY (PYY), a candidate gut hormone that inhibits pancreatic exocrine secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2514–2518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K. Isolation and characterization of peptide YY (PYY), a candidate gut hormone that inhibits pancreatic exocrine secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2514–2518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westlind-Danielsson A., Undén A., Abens J., Andell S., Bartfai T. Neuropeptide Y receptors and the inhibition of adenylate cyclase in the human frontal and temporal cortex. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Feb 24;74(2):237–242. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90156-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedermann C. J., Niedermühlbichler M., Zilian U., Geissler D., Lindley I., Braunsteiner H. Priming of normal human neutrophils by tachykinins: tuftsin-like inhibition of in vitro chemotaxis stimulated by formylpeptide or interleukin-8. Regul Pept. 1991 Nov 26;36(3):359–368. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(91)90069-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozniak A., Scicchitano R., Betts W. H., McLennan G. The effect of substance P on neutrophil function in normal and asthmatic subjects. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992 Apr 15;650:154–159. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1992.tb49113.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabrenetzky V., Gallin E. K. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate concentrations increase after adherence in the macrophage-like cell line J774.1. Biochem J. 1988 Nov 1;255(3):1037–1043. doi: 10.1042/bj2551037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


