Abstract
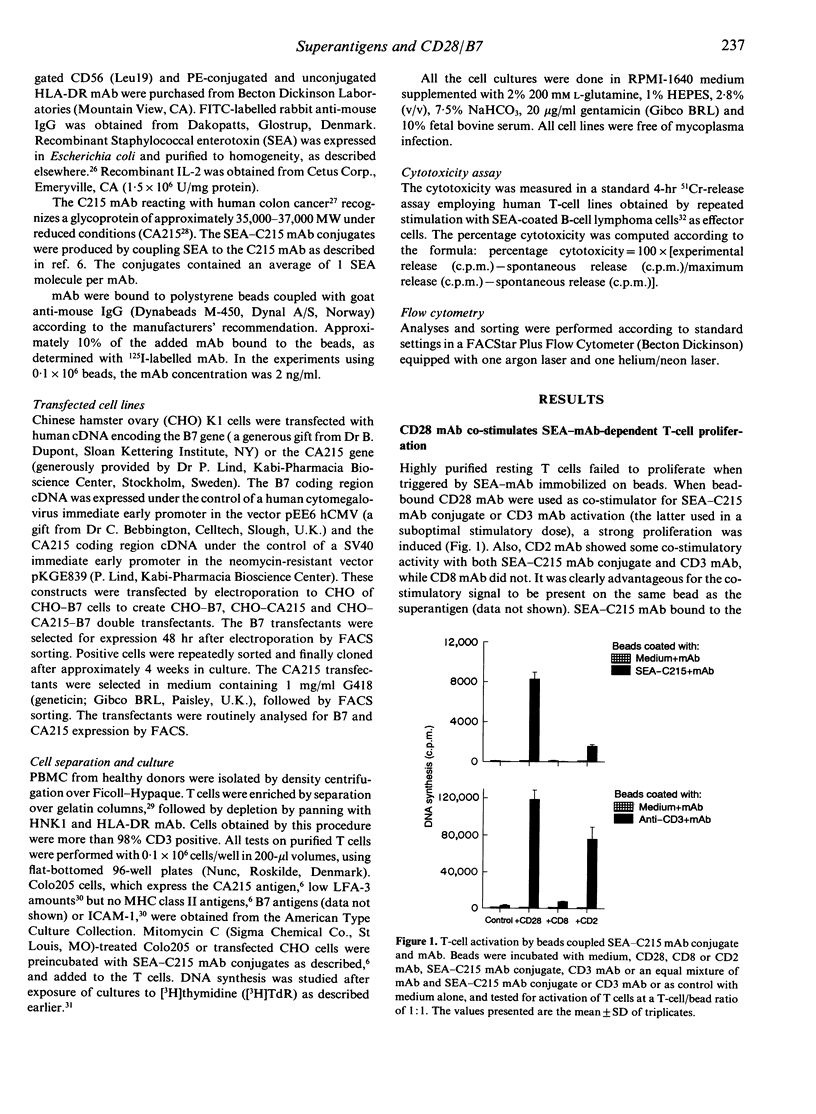
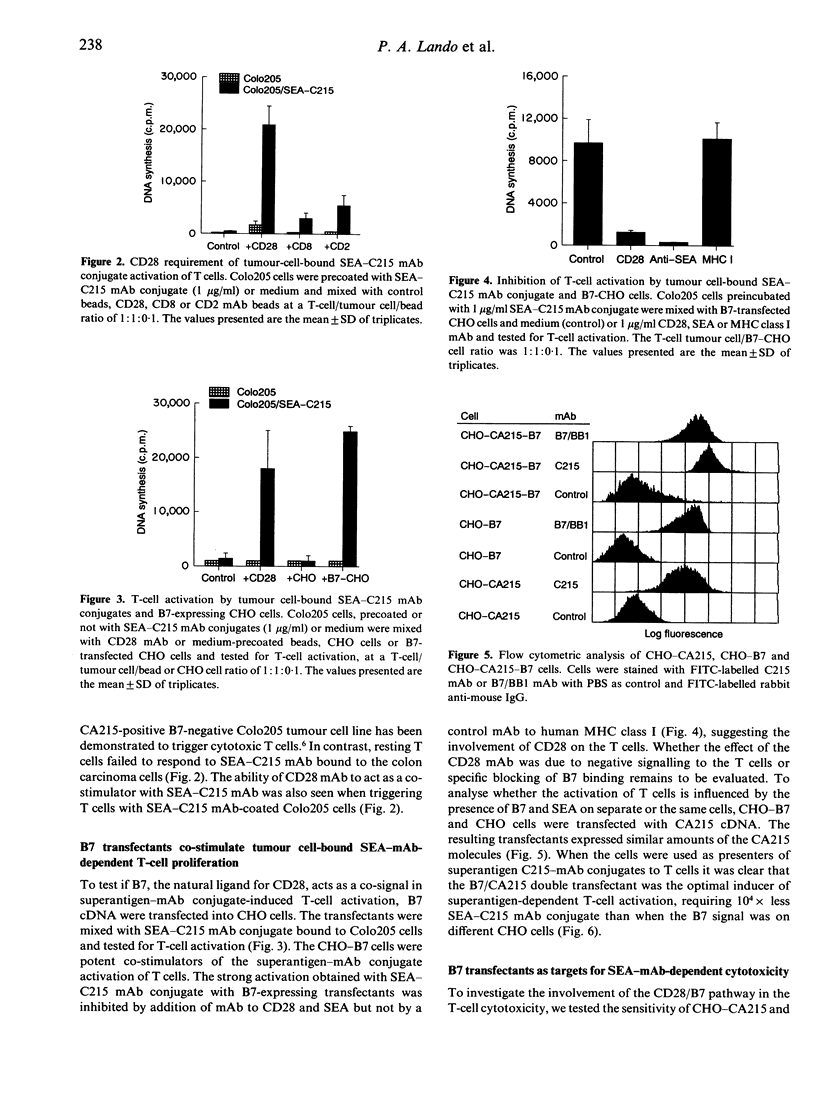
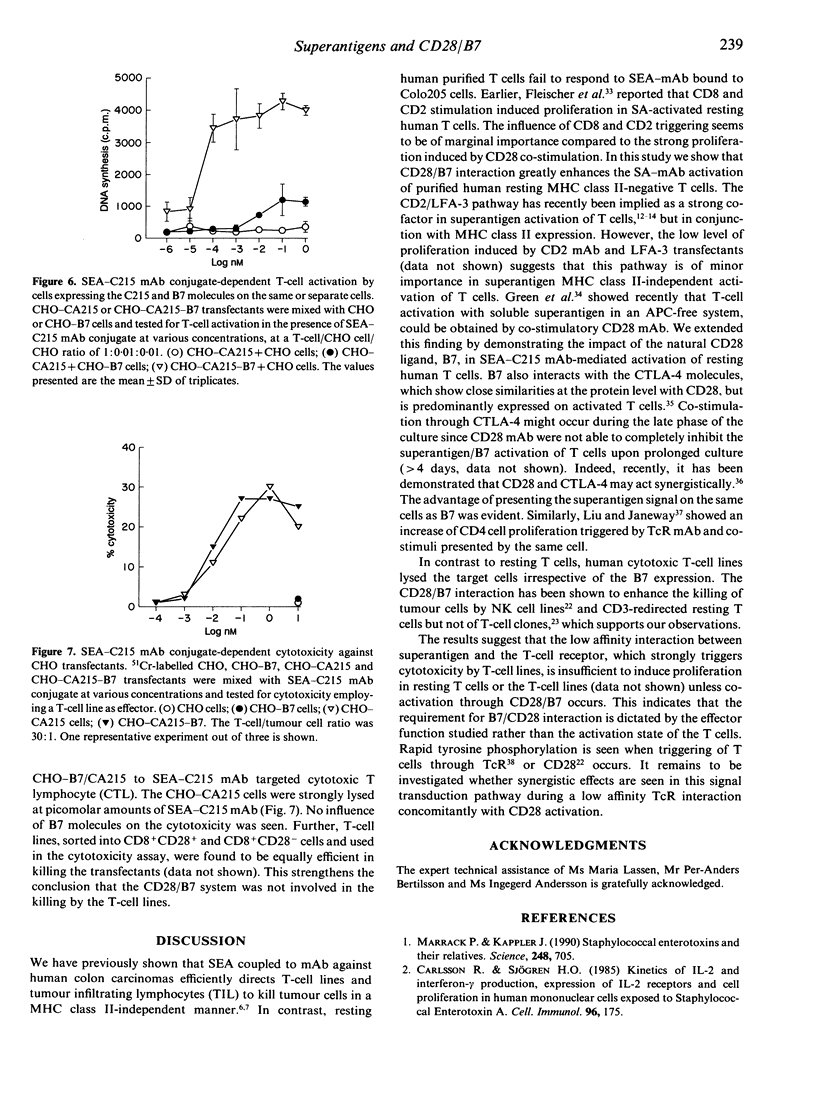
The superantigen Staphylococcal enterotoxin A (SEA) conjugated to tumour-specific monoclonal antibodies (mAb) directs T cells to lyse tumour cells in the absence of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II. In contrast, the conjugate bound to MHC class II-negative tumour cells did not activate resting T cells to proliferate. The SEA-C215 mAb conjugate, when presented on the CA215 antigen-expressing Colo205 cells, required either signalling with CD28 mAb or CHO cells expressing the natural CD28 ligand, B7, to activate the T cells. The CD28/B7 co-stimulatory effect was further enhanced when the B7 and the tumour antigen were present on the same cell, decreasing the superantigen amount required for activation with a factor of 10(4). No influence of B7 was seen when the single CA215 or double CA215/B7 transfectants were used as targets for superantigen conjugate-dependent cytotoxicity. This suggests that the low affinity T-cell receptor (TcR) interaction of superantigen in the absence of MHC class II antigens is sufficient for induction of cytotoxicity but requires additional CD28/B7 signalling to result in proliferation of resting T cells.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azuma M., Cayabyab M., Buck D., Phillips J. H., Lanier L. L. CD28 interaction with B7 costimulates primary allogeneic proliferative responses and cytotoxicity mediated by small, resting T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1992 Feb 1;175(2):353–360. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.2.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azuma M., Cayabyab M., Buck D., Phillips J. H., Lanier L. L. Involvement of CD28 in MHC-unrestricted cytotoxicity mediated by a human natural killer leukemia cell line. J Immunol. 1992 Aug 15;149(4):1115–1123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson R., Fischer H., Sjögren H. O. Binding of staphylococcal enterotoxin A to accessory cells is a requirement for its ability to activate human T cells. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 15;140(8):2484–2488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson R., Sjögren H. O. Kinetics of IL-2 and interferon-gamma production, expression of IL-2 receptors, and cell proliferation in human mononuclear cells exposed to staphylococcal enterotoxin A. Cell Immunol. 1985 Nov;96(1):175–183. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90349-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlsten M., Hedlund G., Akerblom E., Lando P. A., Kalland T. Monoclonal antibody-targeted superantigens: a different class of anti-tumor agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9287–9291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlsten M., Hedlund G., Kalland T. Staphylococcal-enterotoxin-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Immunol Today. 1991 May;12(5):147–150. doi: 10.1016/S0167-5699(05)80043-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlsten M., Hedlund G., Lando P. A., Trowsdale J., Altmann D., Patarroyo M., Fischer H., Kalland T. Role of the adhesion molecule ICAM-1 (CD54) in staphylococcal enterotoxin-mediated cytotoxicity. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Jan;21(1):131–135. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlsten M., Hedlund G., Sjögren H. O., Carlsson R. Two subsets of human CD4+ T helper cells differing in kinetics and capacities to produce interleukin 2 and interferon-gamma can be defined by the Leu-18 and UCHL1 monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Aug;18(8):1173–1178. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer H., Gjörloff A., Hedlund G., Hedman H., Lundgren E., Kalland T., Sjögren H. O., Dohlsten M. Stimulation of human naive and memory T helper cells with bacterial superantigen. Naive CD4+45RA+ T cells require a costimulatory signal mediated through the LFA-1/ICAM-1 pathway. J Immunol. 1992 Apr 1;148(7):1993–1998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer B., Gerardy-Schahn R., Metzroth B., Carrel S., Gerlach D., Köhler W. An evolutionary conserved mechanism of T cell activation by microbial toxins. Evidence for different affinities of T cell receptor-toxin interaction. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 1;146(1):11–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer B., Schrezenmeier H., Conradt P. T lymphocyte activation by staphylococcal enterotoxins: role of class II molecules and T cell surface structures. Cell Immunol. 1989 Apr 15;120(1):92–101. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(89)90177-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser J. D., Irving B. A., Crabtree G. R., Weiss A. Regulation of interleukin-2 gene enhancer activity by the T cell accessory molecule CD28. Science. 1991 Jan 18;251(4991):313–316. doi: 10.1126/science.1846244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser J. D., Newton M. E., Weiss A. CD28 and T cell antigen receptor signal transduction coordinately regulate interleukin 2 gene expression in response to superantigen stimulation. J Exp Med. 1992 Apr 1;175(4):1131–1134. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.4.1131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimmi C. D., Freeman G. J., Gribben J. G., Sugita K., Freedman A. S., Morimoto C., Nadler L. M. B-cell surface antigen B7 provides a costimulatory signal that induces T cells to proliferate and secrete interleukin 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6575–6579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gjörloff A., Hedlund G., Kalland T., Sansom D., Fischer H., Trowsdale J., Sjögren H. O., Dohlsten M. The LFA-3 adhesion pathway is differently utilized by superantigen-activated human CD4+ T-cell subsets. Scand J Immunol. 1992 Aug;36(2):243–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1992.tb03096.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J. M., Turka L. A., June C. H., Thompson C. B. CD28 and staphylococcal enterotoxins synergize to induce MHC-independent T-cell proliferation. Cell Immunol. 1992 Nov;145(1):11–20. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(92)90308-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedlund G., Dohlsten M., Herrmann T., Buell G., Lando P. A., Segrén S., Schrimsher J., MacDonald H. R., Sjögren H. O., Kalland T. A recombinant C-terminal fragment of staphylococcal enterotoxin A binds to human MHC class II products but does not activate T cells. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 15;147(12):4082–4085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedlund G., Dohlsten M., Lando P. A., Kalland T. Staphylococcal enterotoxins direct and trigger CTL killing of autologous HLA-DR+ mononuclear leukocytes and freshly prepared leukemia cells. Cell Immunol. 1990 Sep;129(2):426–434. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(90)90218-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- June C. H., Ledbetter J. A., Gillespie M. M., Lindsten T., Thompson C. B. T-cell proliferation involving the CD28 pathway is associated with cyclosporine-resistant interleukin 2 gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4472–4481. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lando P. A., Dohlsten M., Hedlund G., Akerblom E., Kalland T. T cell killing of human colon carcinomas by monoclonal-antibody-targeted superantigens. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1993;36(4):223–228. doi: 10.1007/BF01740903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lando P. A., Hedlund G., Dohlsten M., Kalland T. Bacterial superantigens as anti-tumour agents: induction of tumour cytotoxicity in human lymphocytes by staphylococcal enterotoxin A. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1991;33(4):231–237. doi: 10.1007/BF01744942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson L. N., Johansson C., Lindholm L., Holmgren J. Mouse monoclonal antibodies for experimental immunotherapy promotes killing of tumor cells. Int J Cancer. 1988 Dec 15;42(6):877–882. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910420615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsley P. S., Greene J. L., Tan P., Bradshaw J., Ledbetter J. A., Anasetti C., Damle N. K. Coexpression and functional cooperation of CTLA-4 and CD28 on activated T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1992 Dec 1;176(6):1595–1604. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.6.1595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu Y., Granelli-Piperno A., Bjorndahl J. M., Phillips C. A., Trevillyan J. M. CD28-induced T cell activation. Evidence for a protein-tyrosine kinase signal transduction pathway. J Immunol. 1992 Jul 1;149(1):24–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makgoba M. W., Sanders M. E., Shaw S. The CD2-LFA-3 and LFA-1-ICAM pathways: relevance to T-cell recognition. Immunol Today. 1989 Dec;10(12):417–422. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90039-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrack P., Kappler J. The staphylococcal enterotoxins and their relatives. Science. 1990 May 11;248(4956):705–711. doi: 10.1126/science.2185544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patarroyo M., Makgoba M. W. Leucocyte adhesion to cells. Molecular basis, physiological relevance, and abnormalities. Scand J Immunol. 1989 Aug;30(2):129–164. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1989.tb01197.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholl P. R., Trede N., Chatila T. A., Geha R. S. Role of protein tyrosine phosphorylation in monokine induction by the staphylococcal superantigen toxic shock syndrome toxin-1. J Immunol. 1992 Apr 1;148(7):2237–2241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A., Dustin M. L., Kishimoto T. K., Marlin S. D. The lymphocyte function-associated LFA-1, CD2, and LFA-3 molecules: cell adhesion receptors of the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:223–252. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.001255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. B., Lindsten T., Ledbetter J. A., Kunkel S. L., Young H. A., Emerson S. G., Leiden J. M., June C. H. CD28 activation pathway regulates the production of multiple T-cell-derived lymphokines/cytokines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1333–1337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokochi T., Holly R. D., Clark E. A. B lymphoblast antigen (BB-1) expressed on Epstein-Barr virus-activated B cell blasts, B lymphoblastoid cell lines, and Burkitt's lymphomas. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):823–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Seventer G. A., Newman W., Shimizu Y., Nutman T. B., Tanaka Y., Horgan K. J., Gopal T. V., Ennis E., O'Sullivan D., Grey H. Analysis of T cell stimulation by superantigen plus major histocompatibility complex class II molecules or by CD3 monoclonal antibody: costimulation by purified adhesion ligands VCAM-1, ICAM-1, but not ELAM-1. J Exp Med. 1991 Oct 1;174(4):901–913. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.4.901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


