Abstract
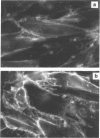
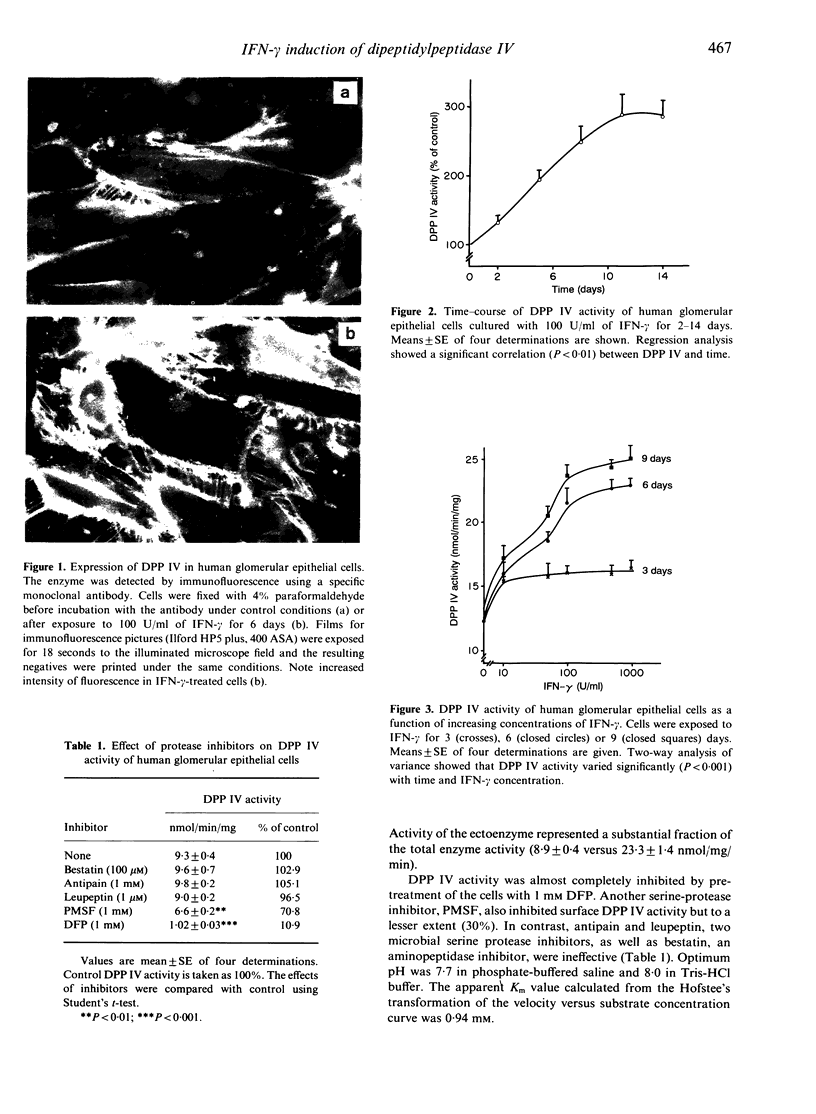
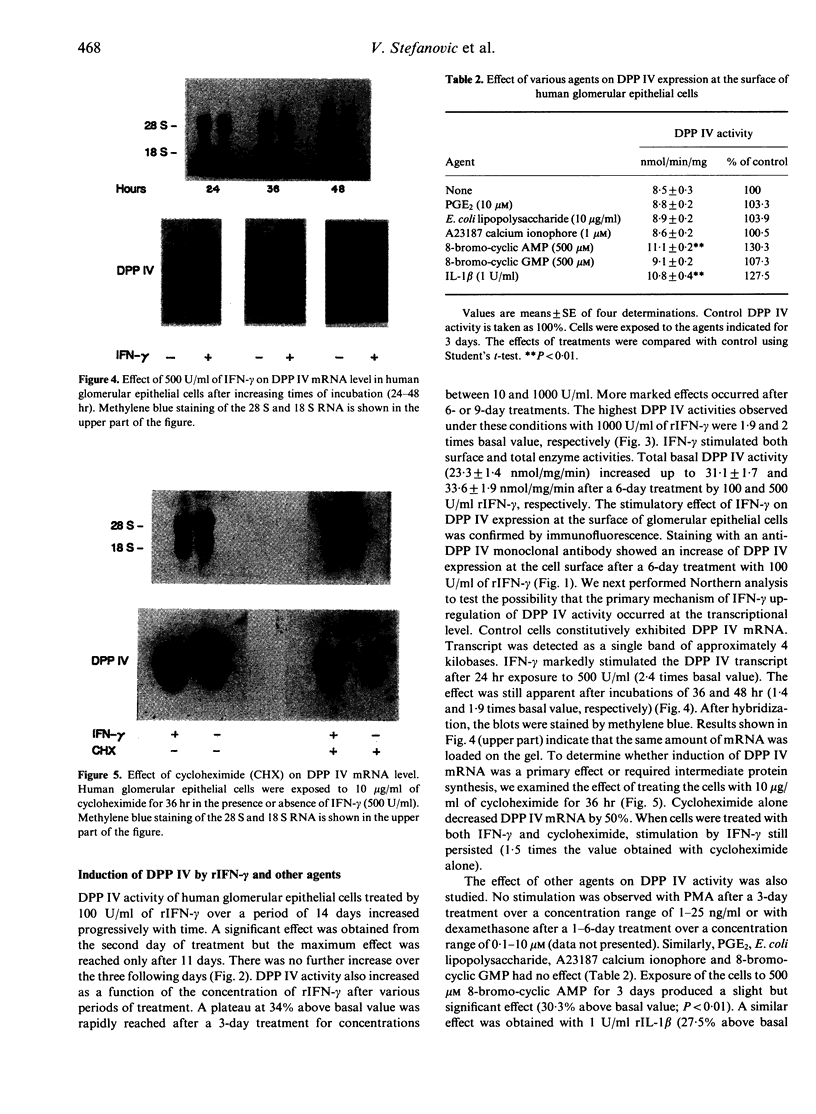
Because dipeptidylpeptidase IV (DPP IV) is present in vivo on glomerular visceral epithelial cells and possesses immunogenic properties, as shown by the capability of anti-DPP IV antibody to induce the Heymann model of glomerulonephritis, we studied the expression and regulation of DPP IV in cultured human glomerular visceral epithelial cells. DPP IV is an ectoenzyme, as indicated by the rapid detection of the product of the reaction in the incubation medium of intact cells and the staining of paraformaldehyde-fixed cells in the presence of a specific anti-DPP IV antibody. DPP IV activity was inhibited by diisopropylfluorophosphate and phenylmethyl sulphonylfluoride. Its optimum pH was alkaline (7.7-8) and it exhibited a Km value of 0.94 mM. DPP IV expression was induced in cells treated by interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma). The effect was significant after a 3-day treatment with 100 U/ml. It increased with time, reaching a plateau after 11 days, and was dose-dependent with a maximum at a concentration of 1000 U/ml. Staining of the cells with anti-DPP IV antibody was also increased after a 6-day treatment with 100 U/ml IFN-gamma. It was shown by Northern analysis that, after 24 hr of exposure to 500 U/ml of IFN-gamma, DPP IV mRNA transcript was stimulated. Transcriptional activation by IFN-gamma did not require new protein synthesis. Interleukin-1 (IL-1) and cyclic AMP had a small stimulatory effect, whereas dexamethasone and phorbol esters were inefficient. These results suggest that DPP IV of glomerular epithelial cells may be up-regulated by IFN-gamma from activated T lymphocytes in glomerular diseases and during lymphocyte-mediated graft rejection.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ardaillou N., Lelongt B., Turner N., Piedagnel R., Baudouin B., Estrade S., Cassingena R., Ronco P. M. Characterization of a simian virus 40-transformed human podocyte cell line producing type IV collagen and exhibiting polarized response to atrial natriuretic peptide. J Cell Physiol. 1992 Sep;152(3):599–616. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041520320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ardaillou N., Nivez M. P., Striker G., Ardaillou R. Prostaglandin synthesis by human glomerular cells in culture. Prostaglandins. 1983 Nov;26(5):773–784. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(83)90061-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauvois B. Murine thymocytes possess specific cell surface-associated exoaminopeptidase activities: preferential expression by immature CD4-CD8- subpopulation. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Mar;20(3):459–468. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauvois B., Sancéau J., Wietzerbin J. Human U937 cell surface peptidase activities: characterization and degradative effect on tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Apr;22(4):923–930. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatelet F., Brianti E., Ronco P., Roland J., Verroust P. Ultrastructural localization by monoclonal antibodies of brush border antigens expressed by glomeruli. I. Renal distribution. Am J Pathol. 1986 Mar;122(3):500–511. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chikuma T., Hama T., Nagatsu T., Kumegawa M., Kato T. Purification and properties of dipeptidyl peptidase IV from human urine. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1990 Apr;371(4):325–330. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1990.371.1.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darmoul D., Lacasa M., Baricault L., Marguet D., Sapin C., Trotot P., Barbat A., Trugnan G. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV (CD 26) gene expression in enterocyte-like colon cancer cell lines HT-29 and Caco-2. Cloning of the complete human coding sequence and changes of dipeptidyl peptidase IV mRNA levels during cell differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4824–4833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darmoul D., Lacasa M., Chantret I., Swallow D. M., Trugnan G. Isolation of a cDNA probe for the human intestinal dipeptidylpeptidase IV and assignment of the gene locus DPP4 to chromosome 2. Ann Hum Genet. 1990 Jul;54(Pt 3):191–197. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1990.tb00377.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont G. P., Huecksteadt T. P., Marshall B. C., Ryan U. S., Michael J. R., Hoidal J. R. Regulation of xanthine dehydrogenase and xanthine oxidase activity and gene expression in cultured rat pulmonary endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jan;89(1):197–202. doi: 10.1172/JCI115563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elleder M., Stejskal J. Induction of dipeptidylpeptidase IV activity in human renal glomeruli--a histochemical study. Acta Histochem. 1985;77(1):75–78. doi: 10.1016/S0065-1281(85)80019-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genton C., Kruithof E. K., Schleuning W. D. Phorbol ester induces the biosynthesis of glycosylated and nonglycosylated plasminogen activator inhibitor 2 in high excess over urokinase-type plasminogen activator in human U-937 lymphoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;104(3):705–712. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.3.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall B. M., Bishop G. A., Duggin G. G., Horvath J. S., Philips J., Tiller D. J. Increased expression of HLA-DR antigens on renal tubular cells in renal transplants: relevance to the rejection response. Lancet. 1984 Aug 4;2(8397):247–251. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90297-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halloran P. F., Wadgymar A., Autenried P. The regulation of expression of major histocompatibility complex products. Transplantation. 1986 Apr;41(4):413–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegen M., Niedobitek G., Klein C. E., Stein H., Fleischer B. The T cell triggering molecule Tp103 is associated with dipeptidyl aminopeptidase IV activity. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 15;144(8):2908–2914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikura H., Takahashi C., Kanagawa K., Hirata H., Imai K., Yoshiki T. Cytokine regulation of ICAM-1 expression on human renal tubular epithelial cells in vitro. Transplantation. 1991 Jun;51(6):1272–1275. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199106000-00024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby J. A., Ikuta S., Clark K., Proud G., Lennard T. W., Taylor R. M. Renal allograft rejection: investigation of alloantigen presentation by cultured human renal epithelial cells. Immunology. 1991 Mar;72(3):411–417. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendrick D. L., Kelly D. M., Rennke H. G. Antigen processing and presentation by glomerular visceral epithelium in vitro. Kidney Int. 1991 Jan;39(1):71–78. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natori Y., Hayakawa I., Shibata S. Identification of gp108, a pathogenic antigen of passive Heymann nephritis, as dipeptidyl peptidase IV. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Nov;70(2):434–439. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natori Y., Hayakawa I., Shibata S. Passive Heymann nephritis with acute and severe proteinuria induced by heterologous antibody against renal tubular brush border glycoprotein gp108. Lab Invest. 1986 Jul;55(1):63–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata S., Misumi Y., Ikehara Y. Primary structure of rat liver dipeptidyl peptidase IV deduced from its cDNA and identification of the NH2-terminal signal sequence as the membrane-anchoring domain. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3596–3601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronco P., Allegri L., Brianti E., Chatelet F., Van Leer E. H., Verroust P. Antigenic targets in epimembranous glomerulonephritis. Experimental data and potential application in human pathology. Appl Pathol. 1989;7(2):85–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronco P., Allegri L., Melcion C., Pirotsky E., Appay M. D., Bariety J., Pontillon F., Verroust P. A monoclonal antibody to brush border and passive Heymann nephritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Feb;55(2):319–332. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronco P., Antoine M., Baudouin B., Geniteau-Legendre M., Lelongt B., Chatelet F., Verroust P., Vandewalle A. Polarized membrane expression of brush-border hydrolases in primary cultures of kidney proximal tubular cells depends on cell differentiation and is induced by dexamethasone. J Cell Physiol. 1990 Nov;145(2):222–237. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041450206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schön E., Demuth H. U., Eichmann E., Horst H. J., Körner I. J., Kopp J., Mattern T., Neubert K., Noll F., Ulmer A. J. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV in human T lymphocytes. Impaired induction of interleukin 2 and gamma interferon due to specific inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase IV. Scand J Immunol. 1989 Feb;29(2):127–132. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1989.tb01108.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schön E., Jahn S., Kiessig S. T., Demuth H. U., Neubert K., Barth A., Von Baehr R., Ansorge S. The role of dipeptidyl peptidase IV in human T lymphocyte activation. Inhibitors and antibodies against dipeptidyl peptidase IV suppress lymphocyte proliferation and immunoglobulin synthesis in vitro. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Dec;17(12):1821–1826. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830171222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulmer A. J., Mattern T., Feller A. C., Heymann E., Flad H. D. CD26 antigen is a surface dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPPIV) as characterized by monoclonal antibodies clone TII-19-4-7 and 4EL1C7. Scand J Immunol. 1990 Apr;31(4):429–435. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1990.tb02789.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf G., Scherberich J. E., Nowack A., Stein O., Schoeppe W. Urinary excretion of dipeptidyl aminopeptidase i.v. in patients with renal diseases. Clin Nephrol. 1990 Mar;33(3):136–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]