Abstract
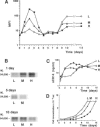
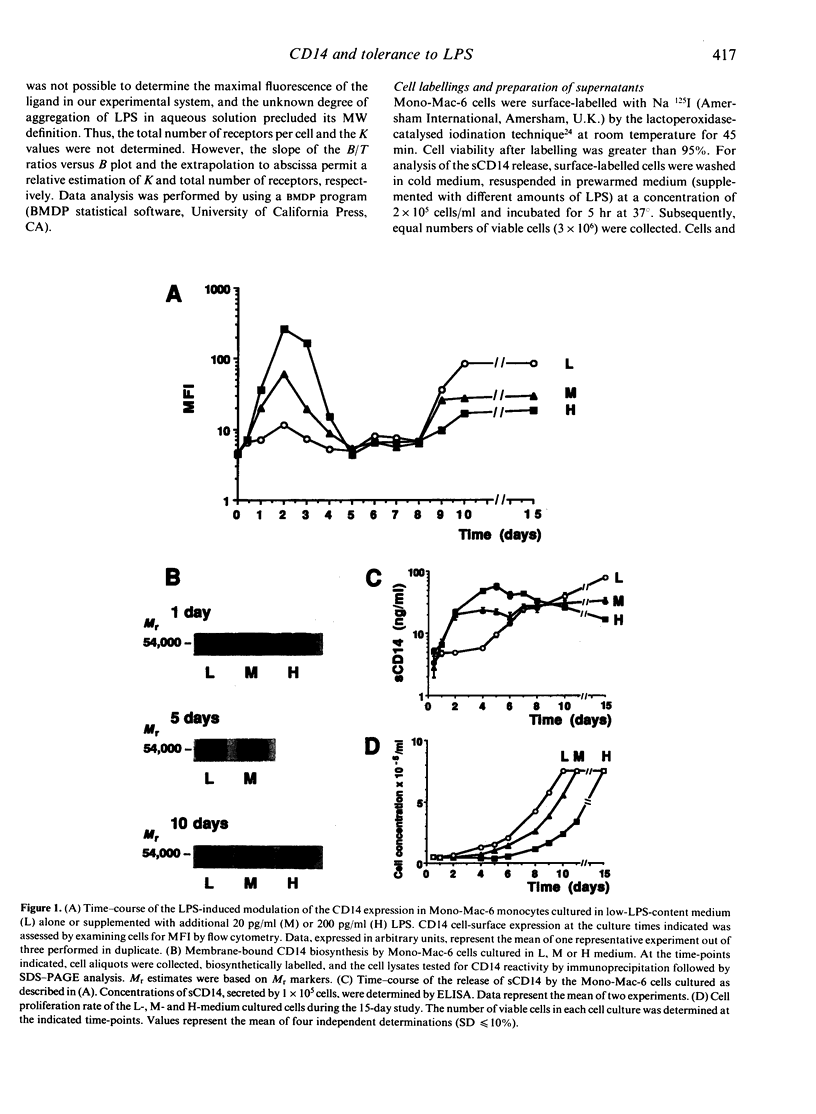
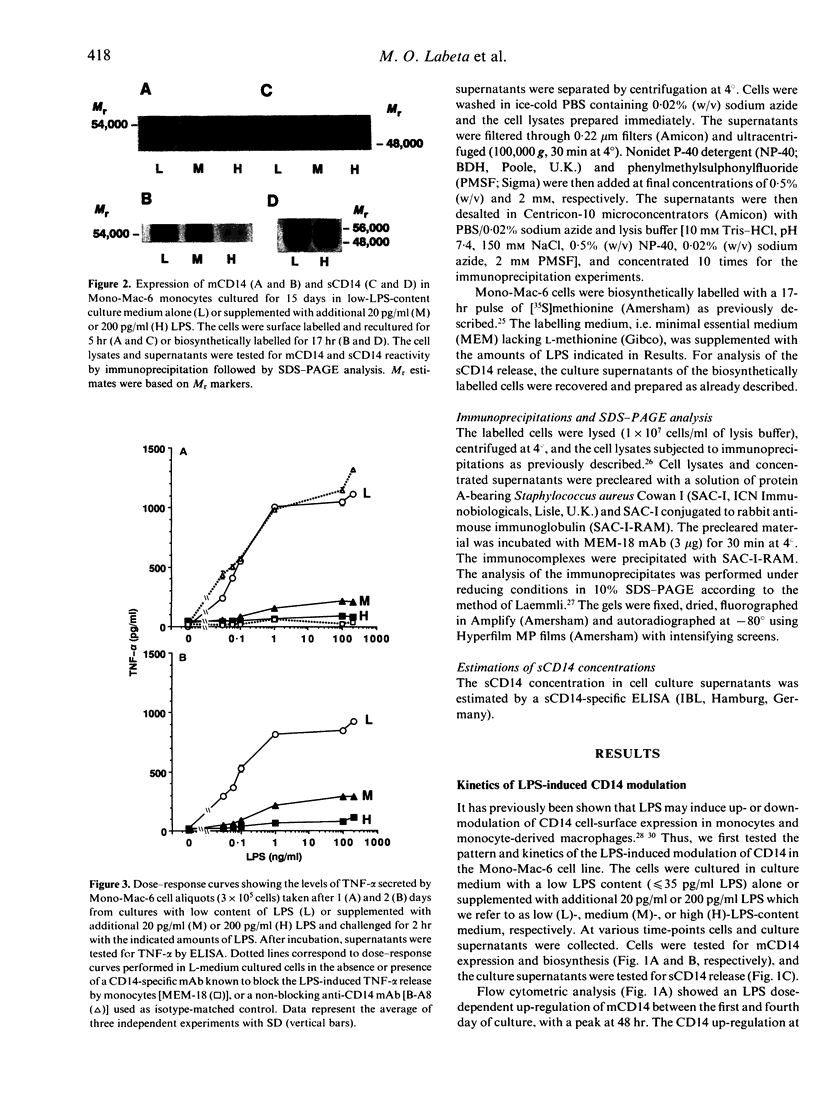
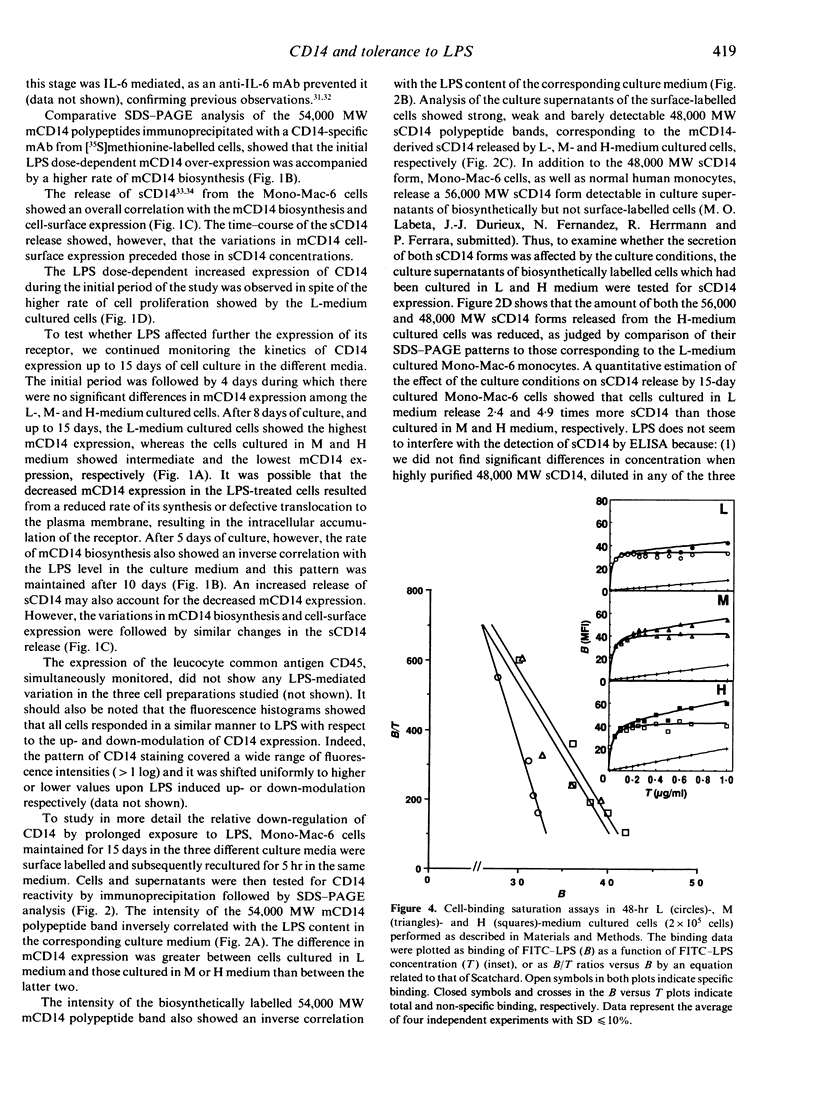
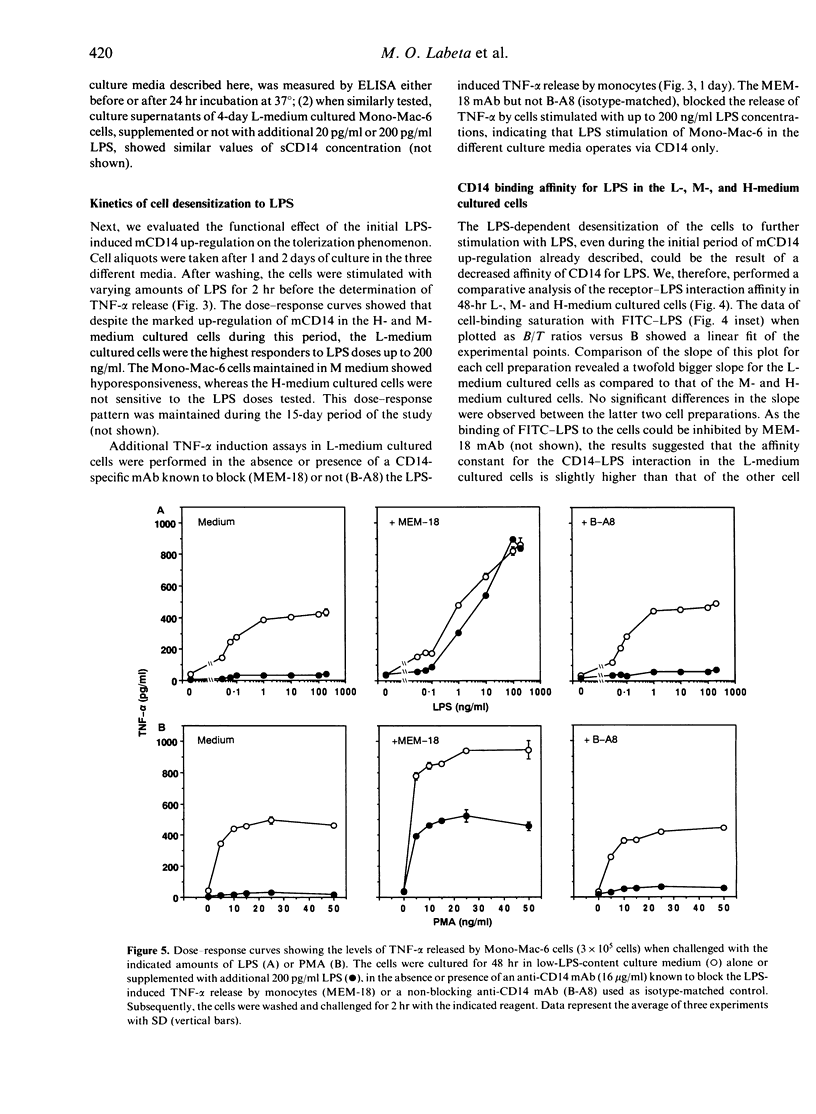
To evaluate the role of the high-affinity monocyte receptor for lipopolysaccharide (LPS), CD14, in the process of tolerance to LPS, the human monocytic cell line Mono-Mac-6 was cultured in the absence or presence of different amounts of LPS. The kinetics of CD14 modulation in these cells showed an initial 4-day period characterized by increased cell-surface expression, rate of biosynthesis (peaking at 48 hr) and release of its soluble forms (sCD14) which correlated with the amount of LPS in the culture. At this time, tolerance to LPS was already established, as measured by tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) induction, it was LPS dose dependent and persisted up to 15 days. LPS also reduced the cell proliferation rate in a dose-dependent manner. After 8 days and up to 15 days, the CD14 biosynthesis, cell-surface expression and release of sCD14 inversely correlated with the level of LPS in the culture. The 48-hr LPS-pretreated cells showed a slightly decreased CD14 affinity for LPS, a relative high number of CD14 molecules per cells, and desensitization also to a phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) challenge. An anti-CD14 monoclonal antibody (mAb) protected the cells from tolerization when added at the beginning of culture, as revealed by challenge with LPS and PMA. The data indicate that in this model tolerization to LPS (1) precedes CD14 down-modulation, (2) operates by alteration of the receptor affinity for LPS and by a mechanism which affects a protein kinase C (PKC)-dependent signalling pathway, and (3) that CD14 plays a critical role in the establishment of tolerance to LPS. In addition, analysis of the data suggests the existence of a PKC-independent signalling pathway for LPS tolerization and a CD14-independent mechanism for establishing tolerance.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bazil V., Horejsí V., Baudys M., Kristofová H., Strominger J. L., Kostka W., Hilgert I. Biochemical characterization of a soluble form of the 53-kDa monocyte surface antigen. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Dec;16(12):1583–1589. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830161218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazil V., Strominger J. L. Shedding as a mechanism of down-modulation of CD14 on stimulated human monocytes. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 1;147(5):1567–1574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Krochin N., Milsark I. W., Luedke C., Cerami A. Control of cachectin (tumor necrosis factor) synthesis: mechanisms of endotoxin resistance. Science. 1986 May 23;232(4753):977–980. doi: 10.1126/science.3754653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfeld A. E., Doyle C., Maniatis T. Human tumor necrosis factor alpha gene regulation by virus and lipopolysaccharide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9769–9773. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas J. G., Baeuerle P. A., Riethmüller G., Ziegler-Heitbrock H. W. Molecular mechanisms in down-regulation of tumor necrosis factor expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9563–9567. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas J. G., Thiel C., Blömer K., Weiss E. H., Riethmüller G., Ziegler-Heitbrock H. W. Downregulation of tumor necrosis factor expression in the human Mono-Mac-6 cell line by lipopolysaccharide. J Leukoc Biol. 1989 Jul;46(1):11–14. doi: 10.1002/jlb.46.1.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horejsí V., Hilgert I., Kristofová H., Bazil V., Bukovský A., Kulhánková J. Monoclonal antibodies against human leucocyte antigens. I. Antibodies against beta-2-microglobulin, immunoglobulin kappa light chains, HLA-DR-like antigens, T8 antigen, T1 antigen, a monocyte antigen, and a pan-leucocyte antigen. Folia Biol (Praha) 1986;32(1):12–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard A. L., Cohn Z. A. The enzymatic iodination of the red cell membrane. J Cell Biol. 1972 Nov;55(2):390–405. doi: 10.1083/jcb.55.2.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikewaki N., Inoko H. Induction of CD14 antigen on the surface of U937 cells by an interleukin-6 autocrine mechanism after culture with formalin-killed gram-negative bacteria. Tissue Antigens. 1991 Sep;38(3):117–123. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1991.tb02024.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitchens R. L., Ulevitch R. J., Munford R. S. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) partial structures inhibit responses to LPS in a human macrophage cell line without inhibiting LPS uptake by a CD14-mediated pathway. J Exp Med. 1992 Aug 1;176(2):485–494. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.2.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labeta M. O., Fernandez N., Reyes A., Ferrara P., Marelli O., Le Roy E., Houlihan J., Festenstein H. Biochemical analysis of a novel H-2 class I-like glycoprotein expressed in five AKR-(Gross virus) derived spontaneous T cell leukemias. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 15;143(4):1245–1253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labeta M. O., Landmann R., Obrecht J. P., Obrist R. Human B cells express membrane-bound and soluble forms of the CD14 myeloid antigen. Mol Immunol. 1991 Jan-Feb;28(1-2):115–122. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(91)90094-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen N. E., Sullivan R. Interaction between endotoxin and human monocytes: characteristics of the binding of 3H-labeled lipopolysaccharide and 51Cr-labeled lipid A before and after the induction of endotoxin tolerance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3491–3495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauener R. P., Goyert S. M., Geha R. S., Vercelli D. Interleukin 4 down-regulates the expression of CD14 in normal human monocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Nov;20(11):2375–2381. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830201103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maliszewski C. R., Ball E. D., Graziano R. F., Fanger M. W. Isolation and characterization of My23, a myeloid cell-derived antigen reactive with the monoclonal antibody AML-2-23. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):1929–1936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maliszewski C. R. CD14 and immune response to lipopolysaccharide. Science. 1991 May 31;252(5010):1321–1322. doi: 10.1126/science.1718034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathison J. C., Virca G. D., Wolfson E., Tobias P. S., Glaser K., Ulevitch R. J. Adaptation to bacterial lipopolysaccharide controls lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor production in rabbit macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1990 Apr;85(4):1108–1118. doi: 10.1172/JCI114542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathison J. C., Wolfson E., Ulevitch R. J. Participation of tumor necrosis factor in the mediation of gram negative bacterial lipopolysaccharide-induced injury in rabbits. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jun;81(6):1925–1937. doi: 10.1172/JCI113540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matic M., Simon S. R. Tumor necrosis factor release from lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human monocytes: lipopolysaccharide tolerance in vitro. Cytokine. 1991 Nov;3(6):576–583. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(91)90484-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Ryan J. L. Endotoxins and disease mechanisms. Annu Rev Med. 1987;38:417–432. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.38.020187.002221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F. Secretory products of macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1987 Feb;79(2):319–326. doi: 10.1172/JCI112815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raetz C. R. Biochemistry of endotoxins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:129–170. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.001021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumann R. R., Leong S. R., Flaggs G. W., Gray P. W., Wright S. D., Mathison J. C., Tobias P. S., Ulevitch R. J. Structure and function of lipopolysaccharide binding protein. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1429–1431. doi: 10.1126/science.2402637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherry B., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor exerts endocrine, paracrine, and autocrine control of inflammatory responses. J Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;107(4):1269–1277. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.4.1269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley D. R., Lefkowitz R. J. Molecular mechanisms of receptor desensitization using the beta-adrenergic receptor-coupled adenylate cyclase system as a model. Nature. 1985 Sep 12;317(6033):124–129. doi: 10.1038/317124a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virca G. D., Kim S. Y., Glaser K. B., Ulevitch R. J. Lipopolysaccharide induces hyporesponsiveness to its own action in RAW 264.7 cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21951–21956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Ramos R. A., Tobias P. S., Ulevitch R. J., Mathison J. C. CD14, a receptor for complexes of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and LPS binding protein. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1431–1433. doi: 10.1126/science.1698311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler-Heitbrock H. W., Thiel E., Fütterer A., Herzog V., Wirtz A., Riethmüller G. Establishment of a human cell line (Mono Mac 6) with characteristics of mature monocytes. Int J Cancer. 1988 Mar 15;41(3):456–461. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910410324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]