Abstract
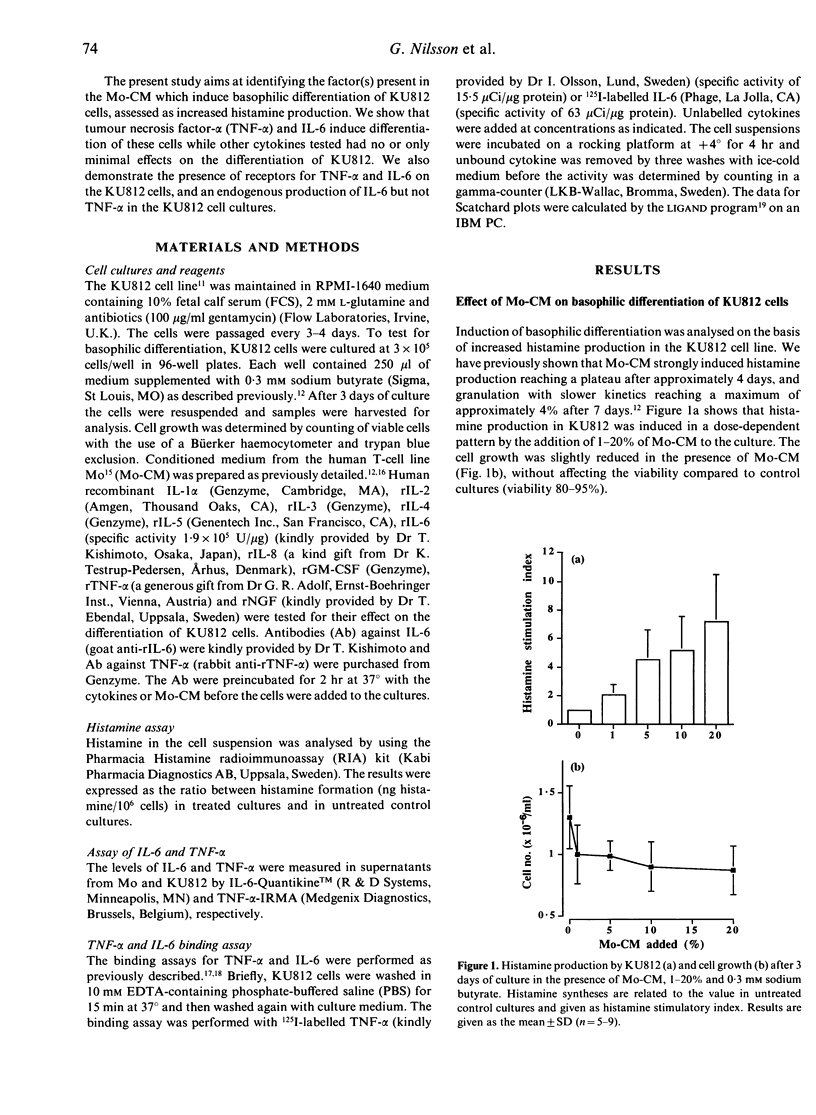
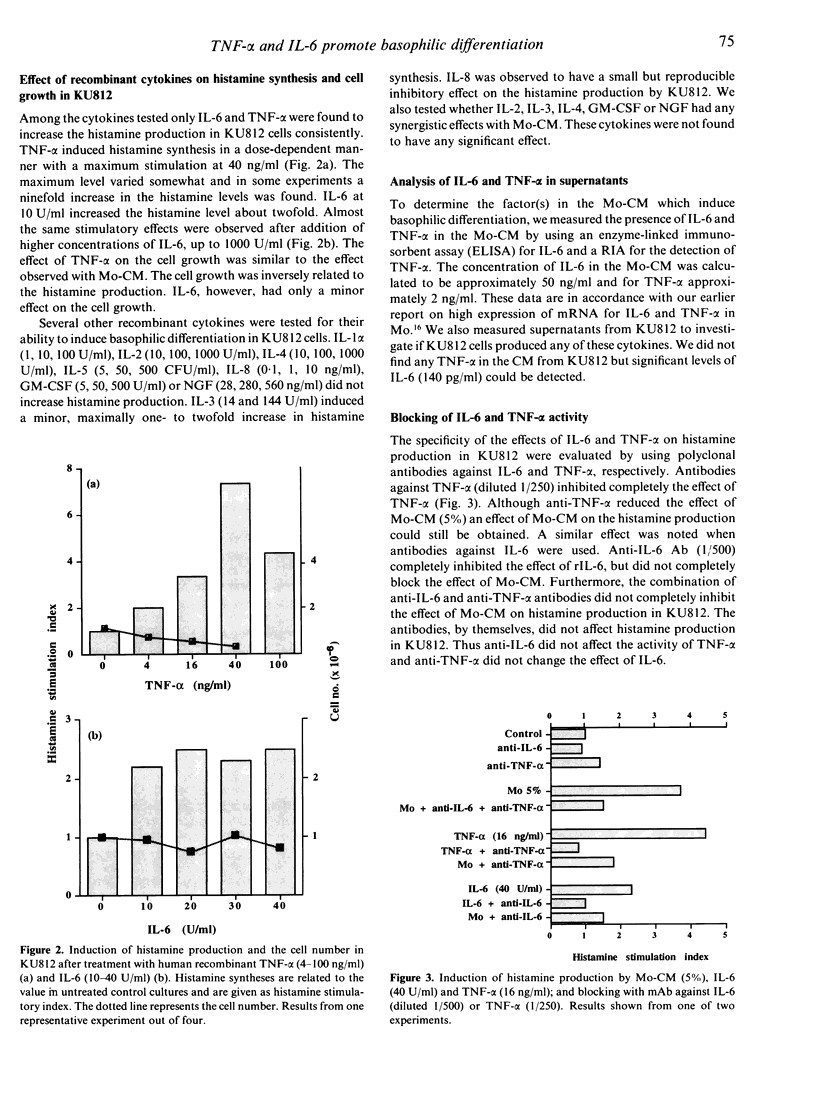
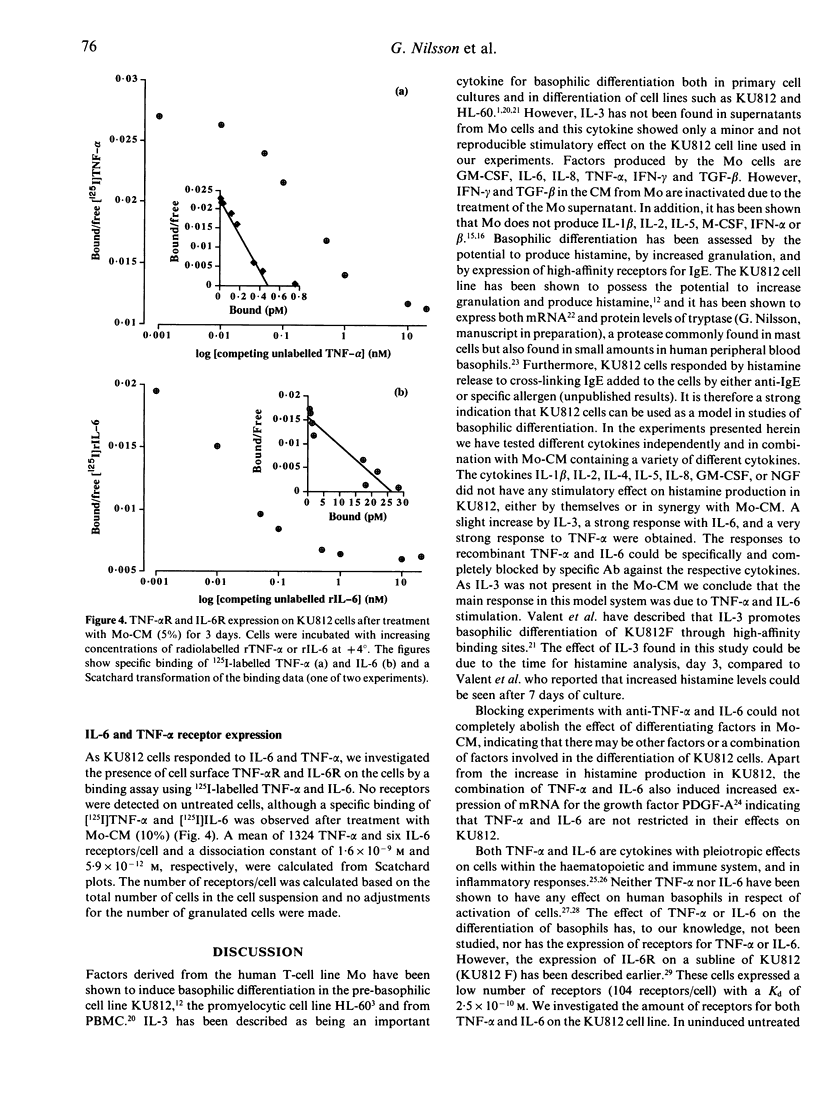
The basophilic leukaemia cell line KU812 can be induced to differentiate into basophil-like cells in vitro when exposed to supernatant from the Mo T-cell line. KU812 cells express affinity receptors for IgE, produce histamine and tryptase and have the capacity for IgE-mediated histamine release. In this study we have examined the cytokines, produced by the Mo cell line, which are responsible for the observed differentiation-inducing effect in the KU812 cell line. It was shown that interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) induced differentiation in the KU812 cells and that these cytokines were responsible for the differentiation-inducing effect of the Mo supernatant. Other cytokines tested, IL-1 beta, IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, IL-8, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and nerve growth factor (NGF) were without effect on the KU812 cells. KU812 was also shown to express receptors for both TNF-alpha and IL-6 after 3 days cultivation with conditioned media from the Mo T-cell line. Untreated cells showed no detectable levels of TNF-alpha or IL-6 receptors indicating induction of these receptors during differentiation. Spontaneous differentiation was shown to occur under serum-free conditions which may be the result of endogenous IL-6 production through an autocrine loop. The activity of TNF-alpha and IL-6 could be blocked by specific monoclonal antibodies (mAb) to the respective cytokine.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almlöf I., Nilsson K., Johansson V., Akerblom E., Slotte H., Ahlstedt S., Matsson P. Induction of basophilic differentiation in the human basophilic cell line KU812. Scand J Immunol. 1988 Sep;28(3):293–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1988.tb01451.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. The biology of cachectin/TNF--a primary mediator of the host response. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:625–655. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff S. C., Dahinden C. A. c-kit ligand: a unique potentiator of mediator release by human lung mast cells. J Exp Med. 1992 Jan 1;175(1):237–244. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.1.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blom T., Huang R., Aveskogh M., Nilsson K., Hellman L. Phenotypic characterization of KU812, a cell line identified as an immature human basophilic leukocyte. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Aug;22(8):2025–2032. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockhaus M., Schoenfeld H. J., Schlaeger E. J., Hunziker W., Lesslauer W., Loetscher H. Identification of two types of tumor necrosis factor receptors on human cell lines by monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3127–3131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broide D. H., Lotz M., Cuomo A. J., Coburn D. A., Federman E. C., Wasserman S. I. Cytokines in symptomatic asthma airways. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1992 May;89(5):958–967. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(92)90218-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner T., de Weck A. L., Dahinden C. A. Platelet-activating factor induces mediator release by human basophils primed with IL-3, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, or IL-5. J Immunol. 1991 Jul 1;147(1):237–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterfield J. H., Weiler D., Dewald G., Gleich G. J. Establishment of an immature mast cell line from a patient with mast cell leukemia. Leuk Res. 1988;12(4):345–355. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(88)90050-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castells M. C., Irani A. M., Schwartz L. B. Evaluation of human peripheral blood leukocytes for mast cell tryptase. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2184–2189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J., Gallo R. C., Gallagher R. E. Continuous growth and differentiation of human myeloid leukaemic cells in suspension culture. Nature. 1977 Nov 24;270(5635):347–349. doi: 10.1038/270347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denburg J. A., Silver J. E., Abrams J. S. Interleukin-5 is a human basophilopoietin: induction of histamine content and basophilic differentiation of HL-60 cells and of peripheral blood basophil-eosinophil progenitors. Blood. 1991 Apr 1;77(7):1462–1468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg K., Nilsson G., Ren Z. P., Hellman L., Westermark B., Nistér M. Constitutive and inducible expression of PDGF in the human basophilic cell line, KU 812. Growth Factors. 1993;9(3):231–241. doi: 10.3109/08977199309010835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda T., Kishi K., Ohnishi Y., Shibata A. Bipotential cell differentiation of KU-812: evidence of a hybrid cell line that differentiates into basophils and macrophage-like cells. Blood. 1987 Sep;70(3):612–619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golde D. W., Quan S. G., Cline M. J. Human T lymphocyte cell line producing colony-stimulating activity. Blood. 1978 Nov;52(5):1068–1072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosset P., Tsicopoulos A., Wallaert B., Joseph M., Capron A., Tonnel A. B. Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-6 production by human mononuclear phagocytes from allergic asthmatics after IgE-dependent stimulation. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 Sep;146(3):768–774. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/146.3.768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irani A. M., Nilsson G., Miettinen U., Craig S. S., Ashman L. K., Ishizaka T., Zsebo K. M., Schwartz L. B. Recombinant human stem cell factor stimulates differentiation of mast cells from dispersed human fetal liver cells. Blood. 1992 Dec 15;80(12):3009–3021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jernberg-Wiklund H., Pettersson M., Carlsson M., Nilsson K. Increase in interleukin 6 (IL-6) and IL-6 receptor expression in a human multiple myeloma cell line, U-266, during long-term in vitro culture and the development of a possible autocrine IL-6 loop. Leukemia. 1992 Apr;6(4):310–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishi K. A new leukemia cell line with Philadelphia chromosome characterized as basophil precursors. Leuk Res. 1985;9(3):381–390. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(85)90060-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T. The biology of interleukin-6. Blood. 1989 Jul;74(1):1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson L. G., Carlsson M., Schena M., Lantz M., Caligaris-Cappio F., Nilsson K. Interleukin-2 enhances the production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in activated B-type chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) cells. Leukemia. 1993 Feb;7(2):226–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsson P., Almlöf I., Nilsson K., Ahlstedt S. Conditioned media from cultured blood cells of atopic individuals can induce differentiation in the human basophilic leukemia cell line KU812. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1989;88(1-2):122–125. doi: 10.1159/000234762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsui H., Furitsu T., Dvorak A. M., Irani A. M., Schwartz L. B., Inagaki N., Takei M., Ishizaka K., Zsebo K. M., Gillis S. Development of human mast cells from umbilical cord blood cells by recombinant human and murine c-kit ligand. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):735–739. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navarro S., Louache F., Debili N., Vainchenker W., Doly J. Autocrine regulation of terminal differentiation by interleukin-6 in the pluripotent KU812 cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 May 31;169(1):184–191. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91452-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson G., Jernberg H., Hellman L., Ahlstedt S., Nilsson K. Enhancement of IgE synthesis in the human myeloma cell line U-266 with an IgE binding factor from a human T-cell line. Scand J Immunol. 1991 Dec;34(6):721–726. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1991.tb01596.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peetre C., Gullberg U., Nilsson E., Olsson I. Effects of recombinant tumor necrosis factor on proliferation and differentiation of leukemic and normal hemopoietic cells in vitro. Relationship to cell surface receptor. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1694–1700. doi: 10.1172/JCI112764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Hatake K., Dvorak A. M., Leiferman K. M., Donnenberg A. D., Arai N., Ishizaka K., Ishizaka T. Selective differentiation and proliferation of hematopoietic cells induced by recombinant human interleukins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2288–2292. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon K. Genetic alterations in leukemia: events on a grand scale. Blood. 1992 Jul 1;80(1):1–2. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valent P., Besemer J., Kishi K., Kaltenbrunner R., Kuhn B., Maurer D., Lechner K., Bettelheim P. IL-3 promotes basophilic differentiation of KU812 cells through high affinity binding sites. J Immunol. 1990 Sep 15;145(6):1885–1889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valent P., Schmidt G., Besemer J., Mayer P., Zenke G., Liehl E., Hinterberger W., Lechner K., Maurer D., Bettelheim P. Interleukin-3 is a differentiation factor for human basophils. Blood. 1989 May 15;73(7):1763–1769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valent P., Spanblöchl E., Sperr W. R., Sillaber C., Zsebo K. M., Agis H., Strobl H., Geissler K., Bettelheim P., Lechner K. Induction of differentiation of human mast cells from bone marrow and peripheral blood mononuclear cells by recombinant human stem cell factor/kit-ligand in long-term culture. Blood. 1992 Nov 1;80(9):2237–2245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki K., Taga T., Hirata Y., Yawata H., Kawanishi Y., Seed B., Taniguchi T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. Cloning and expression of the human interleukin-6 (BSF-2/IFN beta 2) receptor. Science. 1988 Aug 12;241(4867):825–828. doi: 10.1126/science.3136546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


