Abstract
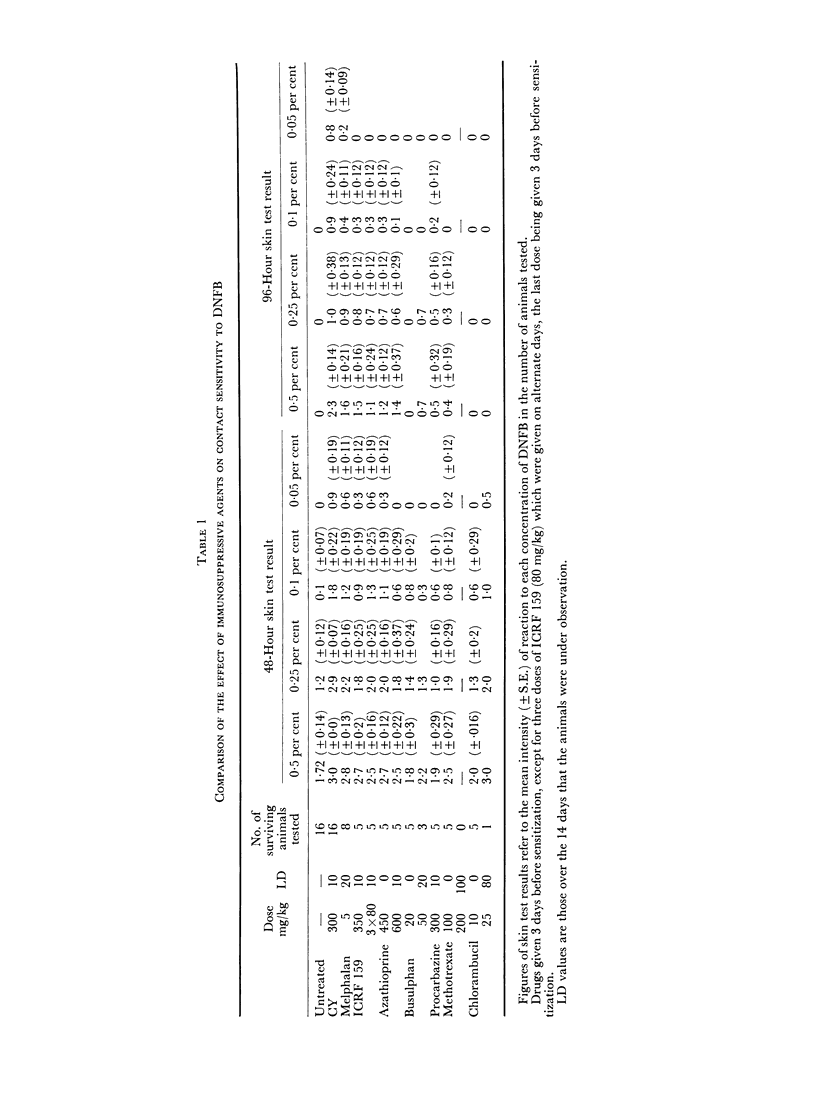
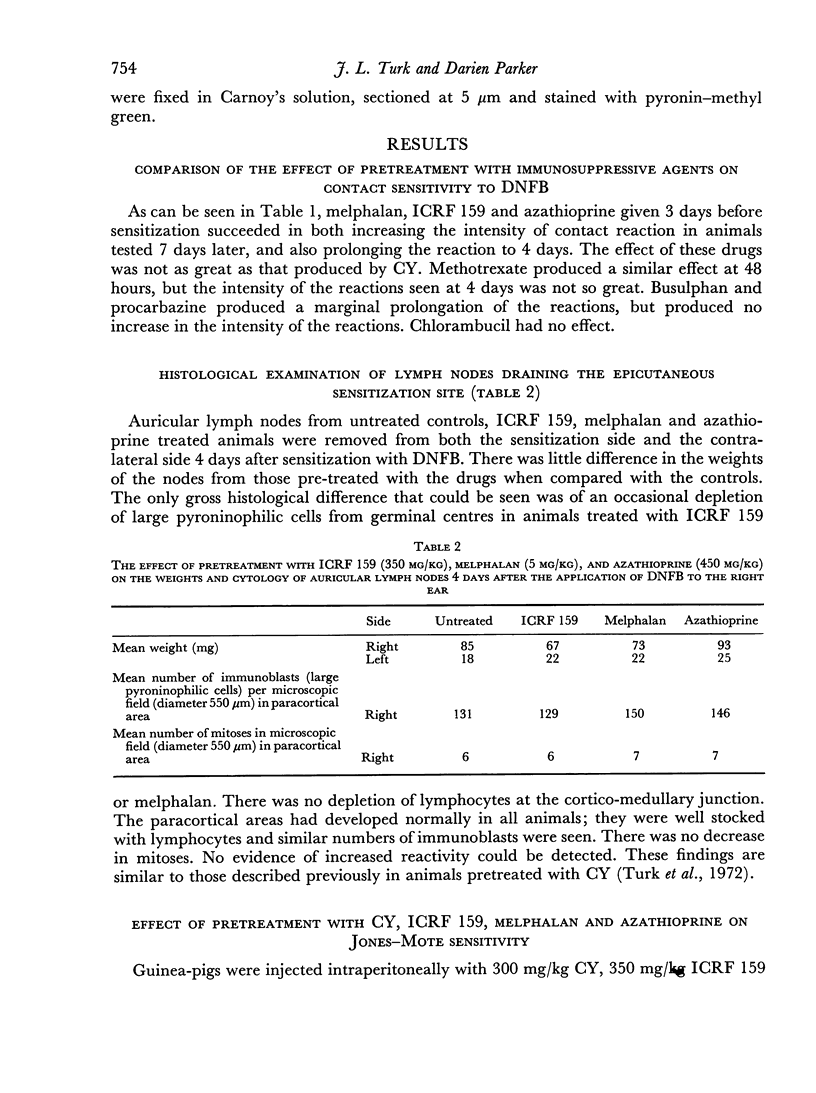
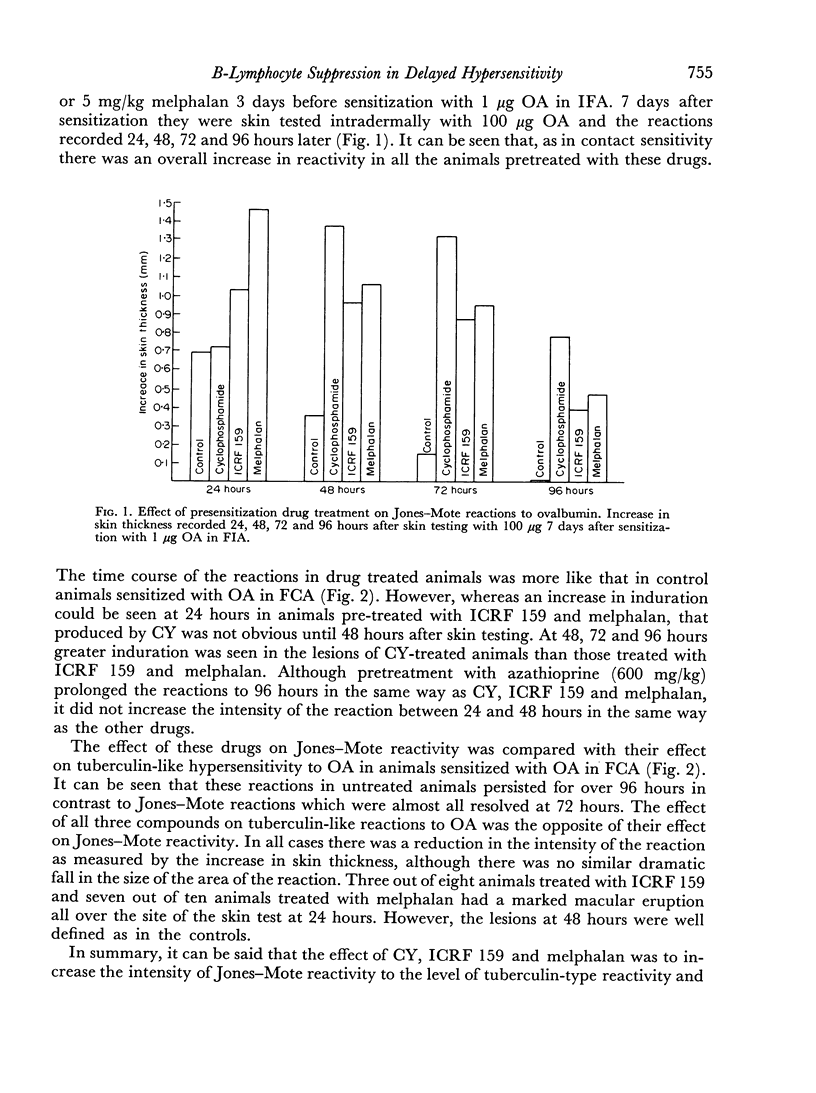
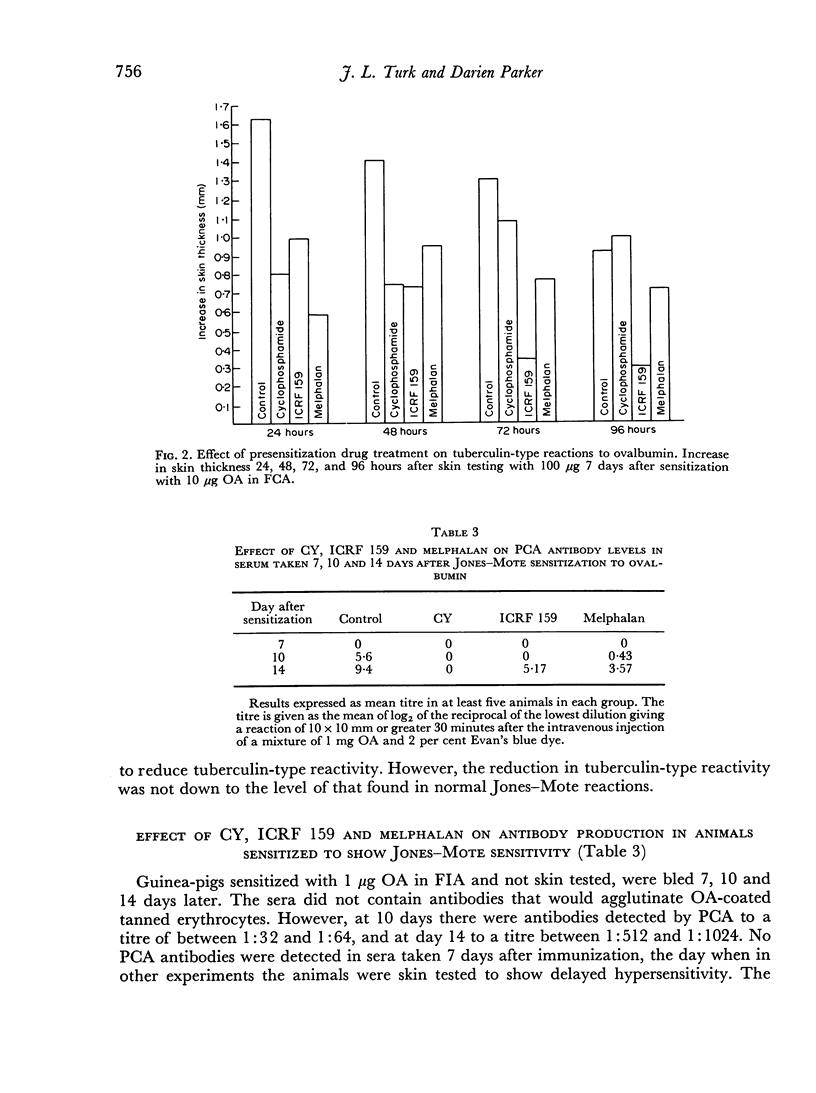
A previous report of increased intensity and prolongation of contact hypersensitivity in animals pre-treated with cyclophosphamide (CY) has been confirmed using other immunosuppressive agents. Melphalan, ICRF 159 and azathioprine caused a similar increase in contact sensitivity reactions, whereas busulphan, procarbazine and chlorambucil were inactive in this respect. The increased contact hypersensitivity was not associated with increased lymph node activity. Pre-treatment with CY, ICRF 159 and melphalan also caused increased intensity and prolonged Jones—Mote type reactions so that they resembled tuberculin-type reactions. This was associated with a marked reduction in γ1 antibody production. It is therefore suggested that Jones—Mote hypersensitivity is a further example of a T-lymphocyte reaction modulated by a B-lymphocyte response.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blazkovec A. A., Sorkin E., Turk J. L. A study of the passive cellular transfer of local cutaneous hypersensitivity. I. Passive transfer of delayed hypersensitivity in inbred and outbred guinea-pigs. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1965;27(5):289–303. doi: 10.1159/000229624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak H. F., Simpson B. A., Bast R. C., Jr, Leskowitz S. Cutaneous basophil hypersensitivity. 3. Participation of the basophil in hypersensitivity to antigen-antibody complexes, delayed hypersensitivity and contact allergy. Passive transfer. J Immunol. 1971 Jul;107(1):138–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellmann K. Effect of ICRF 159 on immune responses. Proc R Soc Med. 1972 Mar;65(3):264–265. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richerson H. B. Cutaneous basophil (Jones-Mote) hypersensitivity after "tolerogenic" doses of intravenous ovalbumin in the guinea pig. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 1):630–641. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.3.630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richerson H. B., Dvorak H. F., Leskowitz S. Cutaneous basophil hypersensitivity. I. A new look at the Jones-Mote reaction, general characteristics. J Exp Med. 1970 Sep 1;132(3):546–557. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.3.546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk J. L., Parker D., Poulter L. W. Functional aspects of the selective depletion of lymphoid tissue by cyclophosphamide. Immunology. 1972 Oct;23(4):493–501. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk J. L., Poulter L. W. Selective depletion of lymphoid tissue by cyclophosphamide. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Feb;10(2):285–296. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


