Abstract
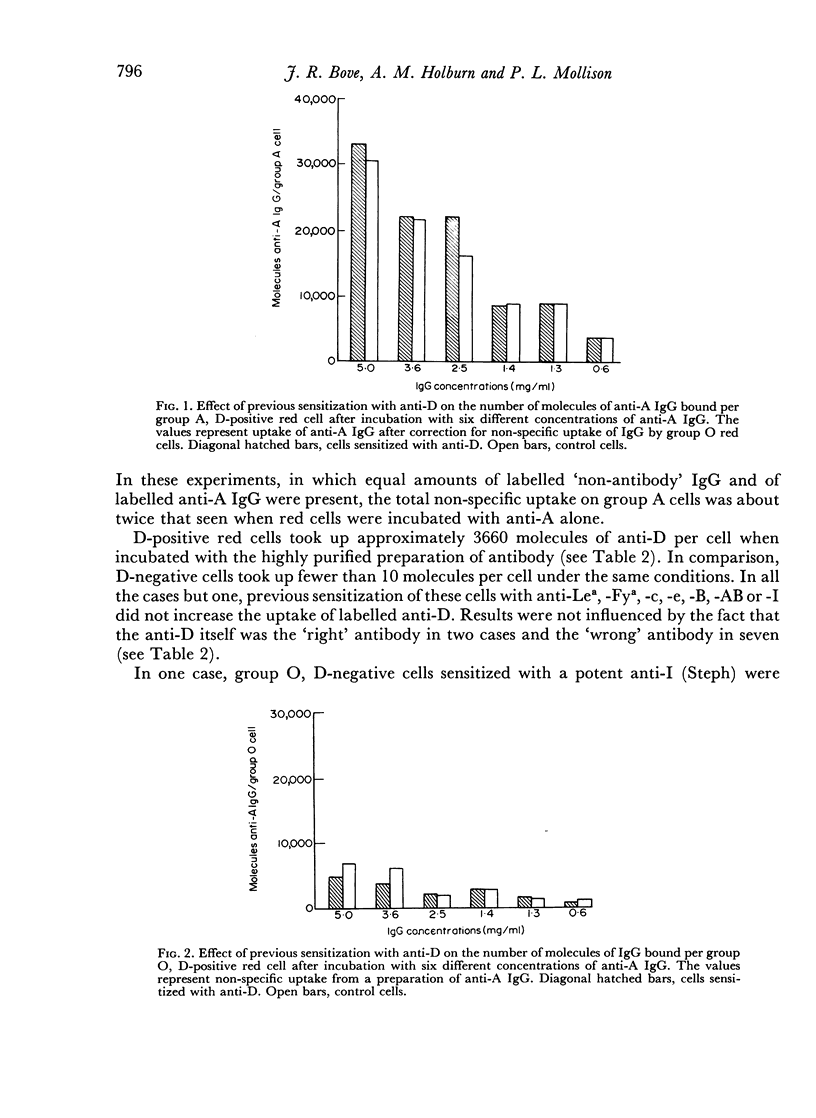
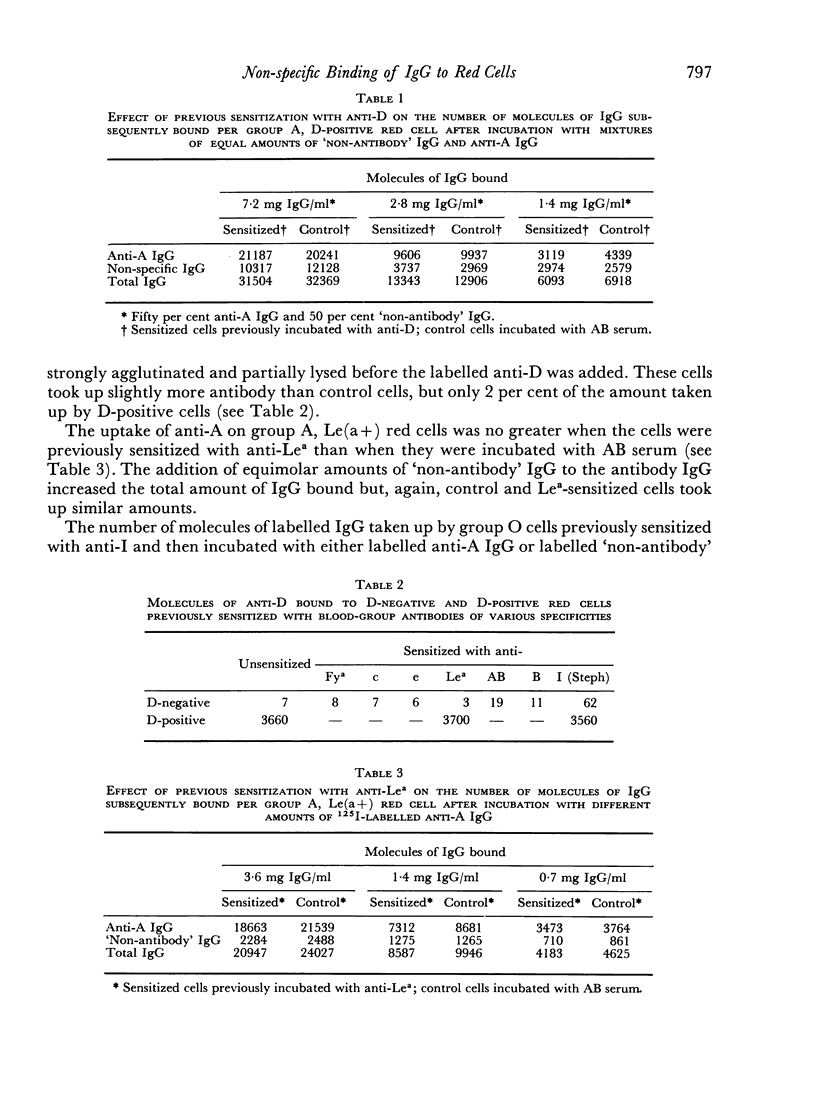
Several observers have reported that red cells coated with a specific blood-group antibody may take up a second blood-group antibody non-specifically, an effect known as the `Matuhasi—Ogata phenomenon'. In the present work, this effect was investigated using either 125I-labelled antibodies of various specificities or a 131I-labelled preparation of IgG lacking relevant antibodies. In confirmation of much previous work, it was found that red cells took up appreciable amounts of IgG non-specifically; however, this uptake was not increased by previous coating of the red cells with specific antibody. When the IgG taken up non-specifically included a blood-group antibody in relatively high concentration, an eluate subsequently prepared from the red cells contained sufficient of the antibody to be detectable. Thus, the finding of unexpected antibodies in eluates may be due to non-specific uptake of IgG rather than to adherence of antibodies to antigen—antibody complexes.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- HARSHMAN S., NAJJAR V. A. The binding of autologous gamma-globulin with isohemagglutinin activity to human red blood cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 May 28;11:411–415. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90132-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONES N. C., GARDNER B. The exchange of 131-I-labelled lipid and 131-I-labelled protein between red cells and serum. Biochem J. 1962 May;83:404–413. doi: 10.1042/bj0830404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFARLANE A. S. Efficient trace-labelling of proteins with iodine. Nature. 1958 Jul 5;182(4627):53–53. doi: 10.1038/182053a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OGATA T., MATUHASI T. FURTHER OBSERVATIONS ON THE PROBLEMS OF SPECIFIC AND CROSS REACTIVITY OF BLOOD GROUP ANTIBODIES. Bibl Haematol. 1964;19:528–531. doi: 10.1159/000426599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUBIN H. Antibody elution from red blood cells. J Clin Pathol. 1963 Jan;16:70–73. doi: 10.1136/jcp.16.1.70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romano E. L., Hughes-Jones N. C., Mollison P. L. Direct antiglobulin reaction in ABO-haemolytic disease of the newborn. Br Med J. 1973 Mar 3;1(5852):524–526. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5852.524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voak D., Williams M. A. An explanation of the failure of the direct antiglobulin test to detect erythrocyte sensitization in ABO haemolytic disease of the newborn and observations on pinocytosis of IgG anti-A antibodies by infant (cord) red cells. Br J Haematol. 1971 Jan;20(1):9–23. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1971.tb00782.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


