Abstract
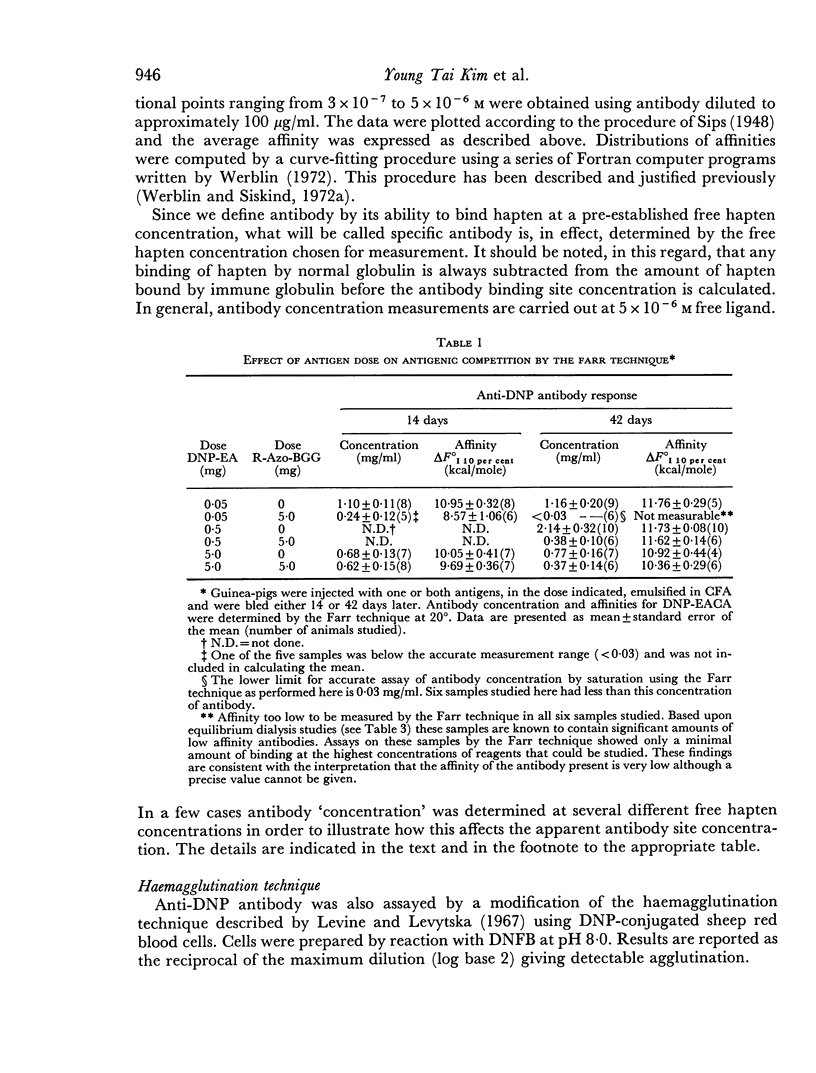
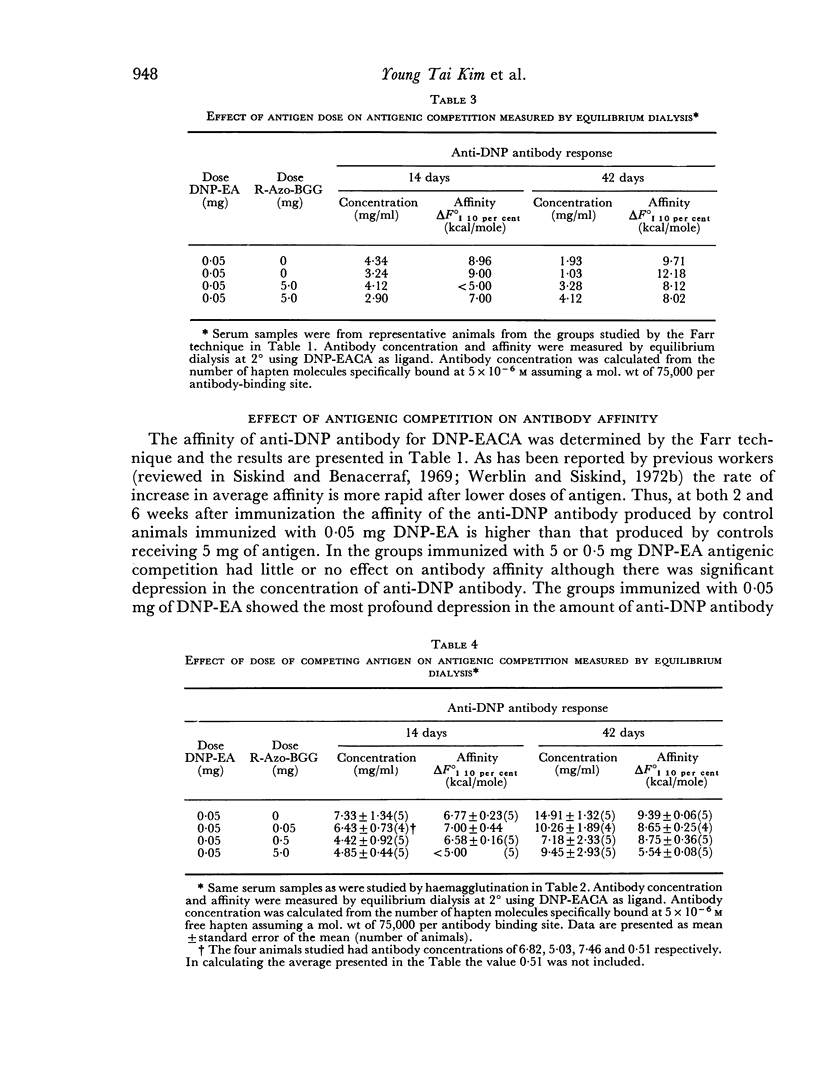
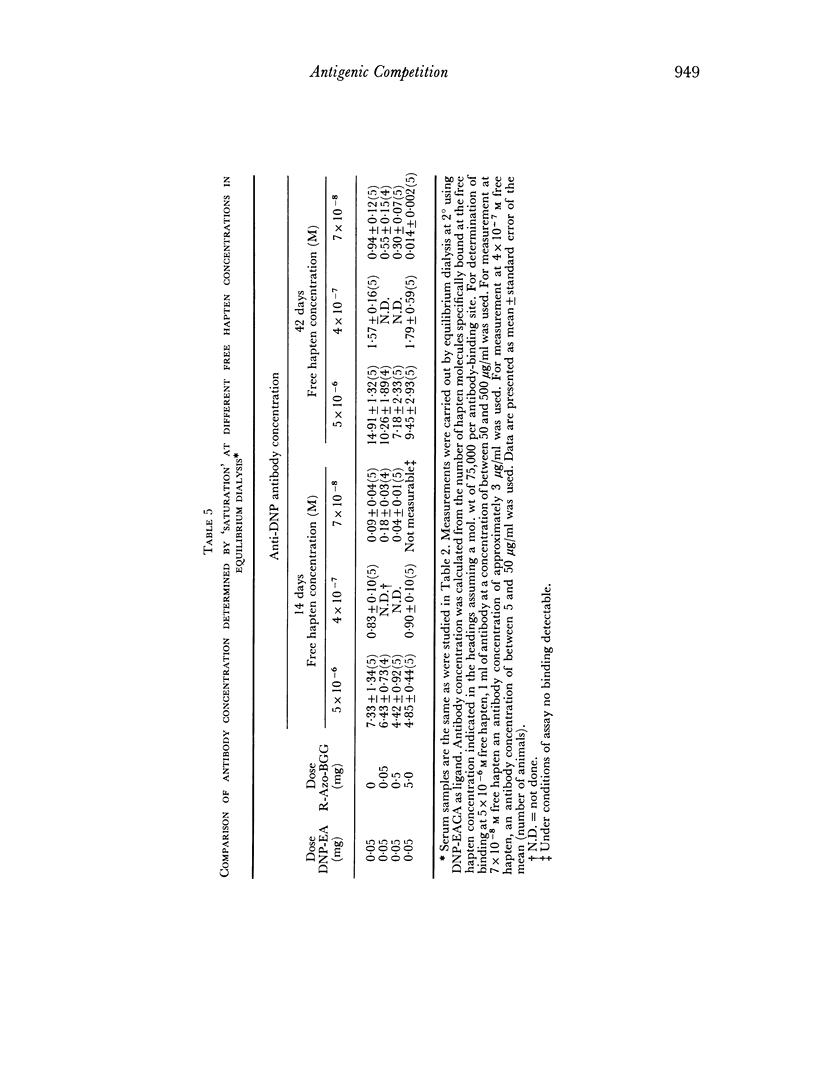
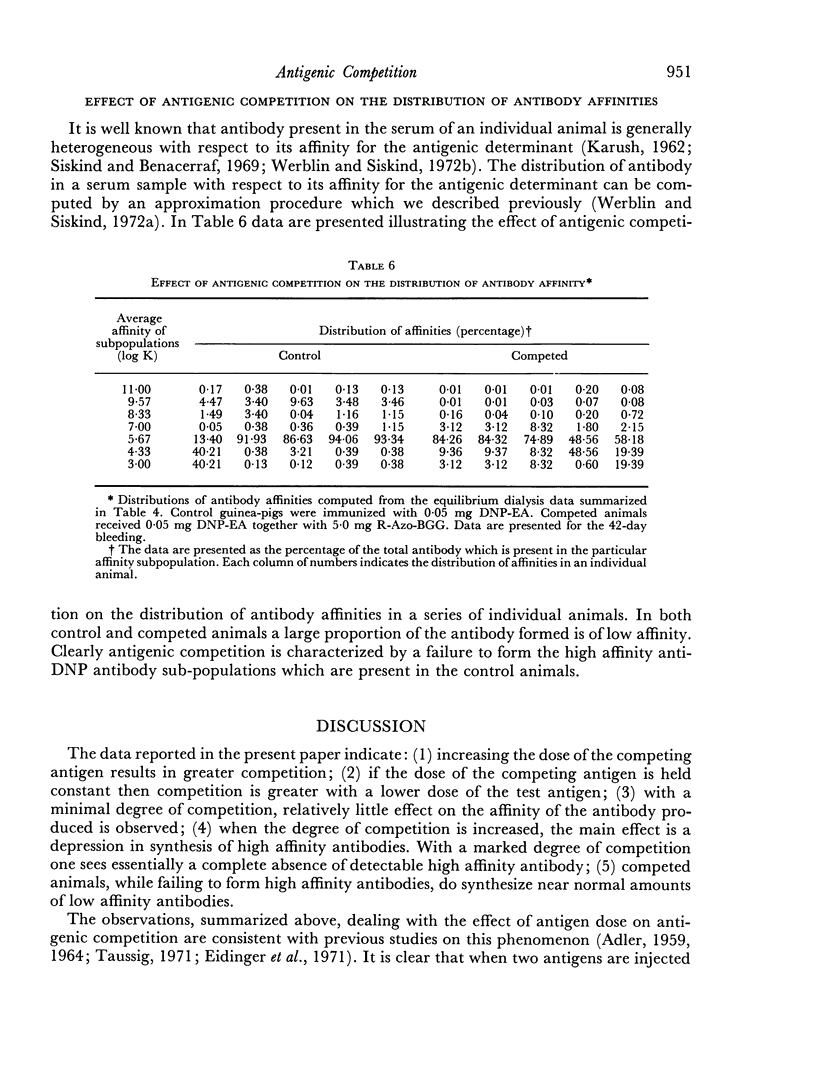
The effect of antigenic competition on antibody affinity was studied using a haptenic system in guinea-pigs. A moderate depression in the amount of antibody formed, as a result of antigenic competition, had relatively little effect on affinity. Increasing the dose of the competing antigen resulted in a greater degree of competition. Under these conditions a large amount of low affinity antibody was produced by the animals while essentially no high affinity antibody was detectable. Thus, marked competition appeared to result in a failure to select for high affinity antibody synthesis.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-Efraim S., Liacopoulos P. The competitive effect of DNP-poly-L-lysine in responder and non-responder guinea pigs. Immunology. 1969 May;16(5):573–580. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody N. I., Siskind G. W. Studies on antigenic competition. II. Evidence for effect at level of antigen 'processing'. Immunology. 1972 Jan;22(1):75–85. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody N. I., Siskind G. W. Studies on antigenic competition. J Exp Med. 1969 Oct 1;130(4):821–832. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.4.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody N. I., Walker J. G., Siskind G. W. Studies on the control of antibody synthesis. Interaction of antigenic competition and suppression of antibody formation by passive antibody on the immune response. J Exp Med. 1967 Jul 1;126(1):81–91. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davie J. M., Paul W. E., Katz D. H., Benacerraf B. Hapten-specific tolerance. Preferential depression of the high affinity antibody response. J Exp Med. 1972 Sep 1;136(3):426–438. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.3.426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eidinger D., Pross H. F., Kerbel R. S., Baines M. G., Ackerman A., Khan S. A. Further studies of competition of antigens. I. Variation in immunosuppression induced by alterations of dosage, route of injection, nature of antigen, and immunological status of host. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Jun;17(6):803–812. doi: 10.1139/m71-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARR R. S. A quantitative immunochemical measure of the primary interaction between I BSA and antibody. J Infect Dis. 1958 Nov-Dec;103(3):239–262. doi: 10.1093/infdis/103.3.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann M., Nossal G. J. Tolerance, enhancement and the regulation of interactions between T cells, B cells and macrophages. Transplant Rev. 1972;13:3–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1972.tb00058.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon R. K., Kondo K. Antigenic competition between heterologous erythrocytes. I. Thymic dependency. J Immunol. 1971 Jun;106(6):1524–1531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harel S., Ben-Efraim S., Liacopoulos P. The production and affinity of anti-hapten antibody under the influence of various inhibitory conditions. Immunology. 1970 Aug;19(2):319–327. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz D. H., Paul W. E., Benacerraf B. Carrier function in anti-hapten antibody responses. VI. Establishment of experimental conditions for either inhibitory or enhancing influences of carrier-specific cells on antibody production. J Immunol. 1973 Jan;110(1):107–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerbel R. S., Eidinger D. Further studies of antigenic competition. 3. A model to account for the phenomenon based on a deficiency of cell-to-cell interaction in immune lymphoid cell populations. J Exp Med. 1971 May 1;133(5):1043–1060. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.5.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine B. B., Levytska V. A sensitive hemagglutination assay method for dinitrophenyl-specific antibodies. The effect of antibody binding affinity on titers. J Immunol. 1967 Mar;98(3):648–652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monier J. C., Salussola D. La compétition antigénique chez des souris thymectomisées à la naissance. Experientia. 1971 Jun;27(6):698–699. doi: 10.1007/BF02136970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal G. J., Abbot A., Mitchell J., Lummus Z. Antigens in immunity. XV. Ultrastructural features of antigen capture in primary and secondary lymphoid follicles. J Exp Med. 1968 Feb 1;127(2):277–290. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.2.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radovich J., Talmage D. W. Antigenic competition: cellular or humoral. Science. 1967 Oct 27;158(3800):512–514. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3800.512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SISKIND G. W. QUANTITATIVE STUDIES ON THE PRECIPITATION OF ANTI-2,4DINITROPHENYL ANTIBODY IN ANTIGEN EXCESS. J Immunol. 1964 May;92:702–708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siskind G. W., Benacerraf B. Cell selection by antigen in the immune response. Adv Immunol. 1969;10:1–50. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60414-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöberg O., Britton S. Antigenic competition in vitro between heterologous erythrocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1972 Jun;2(3):282–288. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830020318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stupp Y., Yoshida T., Paul W. E. Determination of antibody-hapten equilibrium constants by an ammonium sulfate precipitation technique. J Immunol. 1969 Sep;103(3):625–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taussig M. J. Antigenic competition. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1973;60:125–174. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-65502-9_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taussig M. J., Lachmann P. J. Studies on antigenic competition. II. Abolition of antigenic competition by antibody against or tolerance to the dominant antigen: a model for antigenic competition. Immunology. 1972 Feb;22(2):185–197. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taussig M. J. Studies on antigenic competition. I. Antigenic competition between the Fc and Fab fragments of rabbit IgG in mice. Immunology. 1971 Jul;21(1):51–60. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. B., Iverson G. M. Hapten competition and the nature of cell-cooperation in the antibody response. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1971 Jan 12;176(1045):393–418. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1971.0003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theis G. A., Siskind G. W. Selection of cell populations in induction of tolerance: affinity of antibody formed in partially tolerant rabbits. J Immunol. 1968 Jan;100(1):138–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterston R. H. Antigen competition: a paradox. Science. 1970 Dec 4;170(3962):1108–1110. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werblin T. P., Kim Y. T., Quagliata F., Siskind G. W. Studies on the control of antibody synthesis. 3. Changes in heterogeneity of antibody affinity during the course of the immune response. Immunology. 1973 Mar;24(3):477–492. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werblin T. P., Siskind G. W. Distribution of antibody affinities: technique of measurement. Immunochemistry. 1972 Oct;9(10):987–1011. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(72)90110-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werblin T. P., Siskind G. W. Effect of tolerance and immunity on antibody affinity. Transplant Rev. 1972;8:104–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1972.tb01566.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


