Abstract
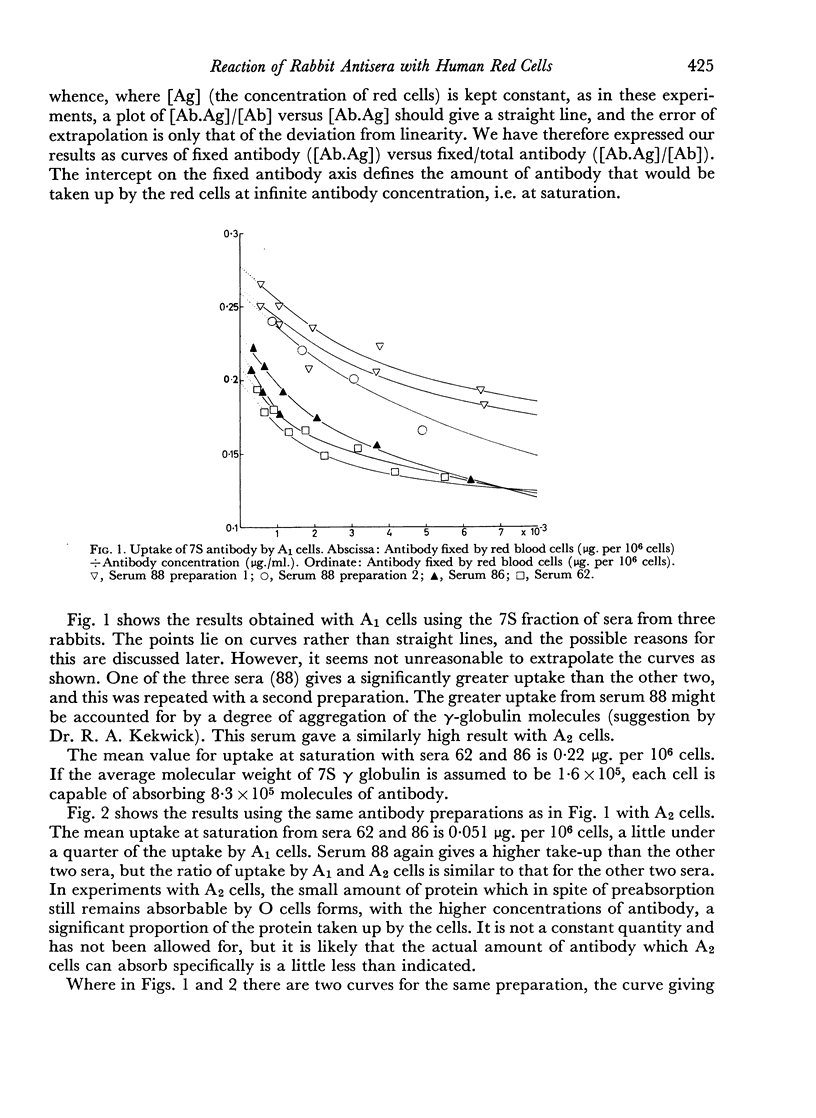
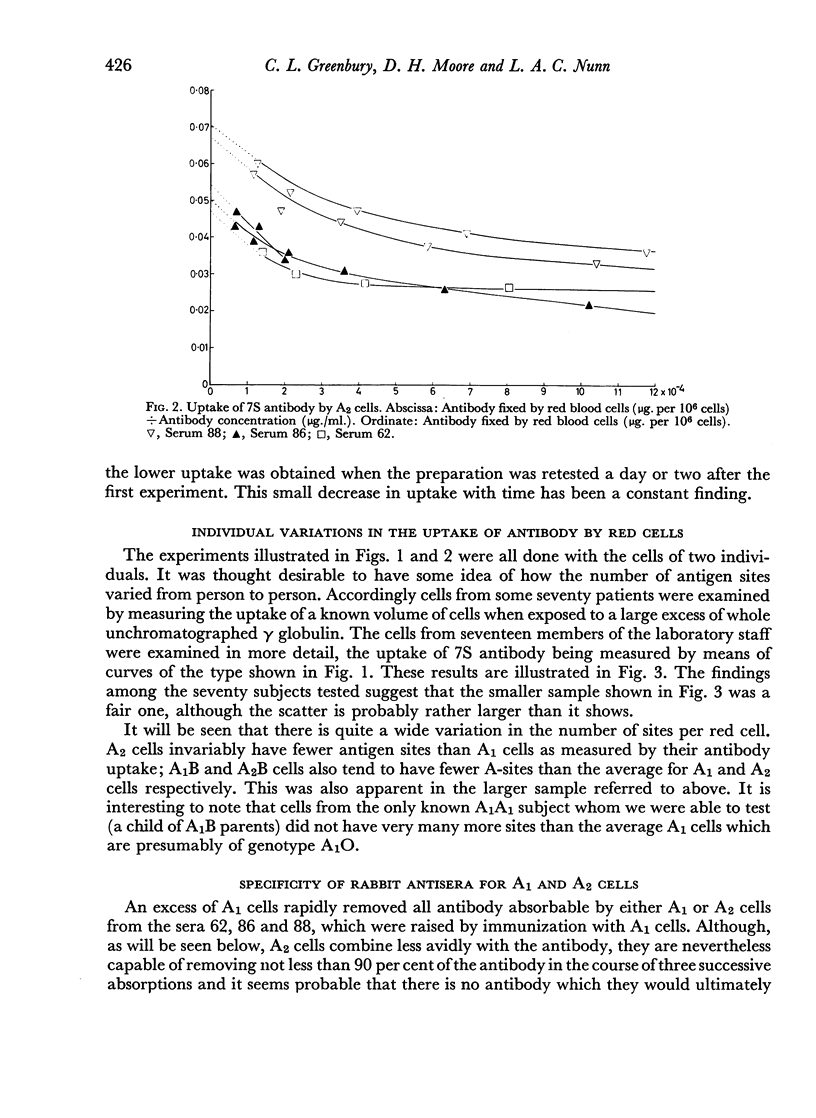
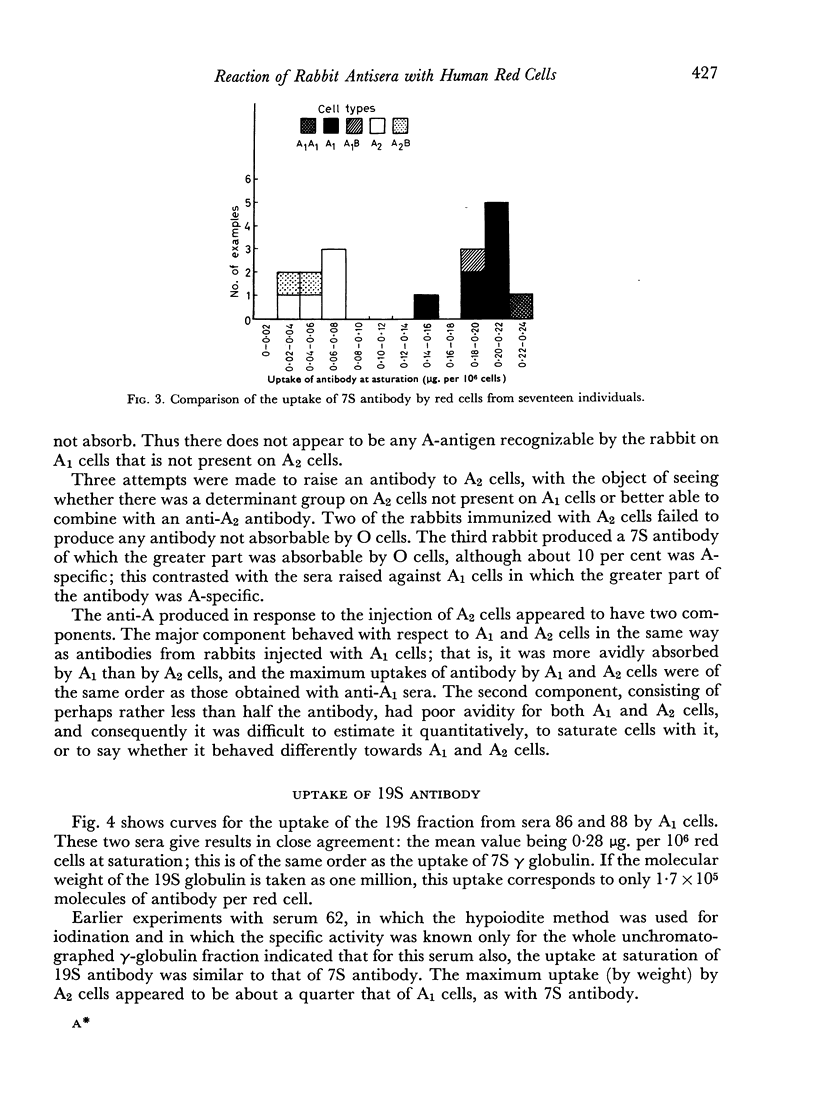
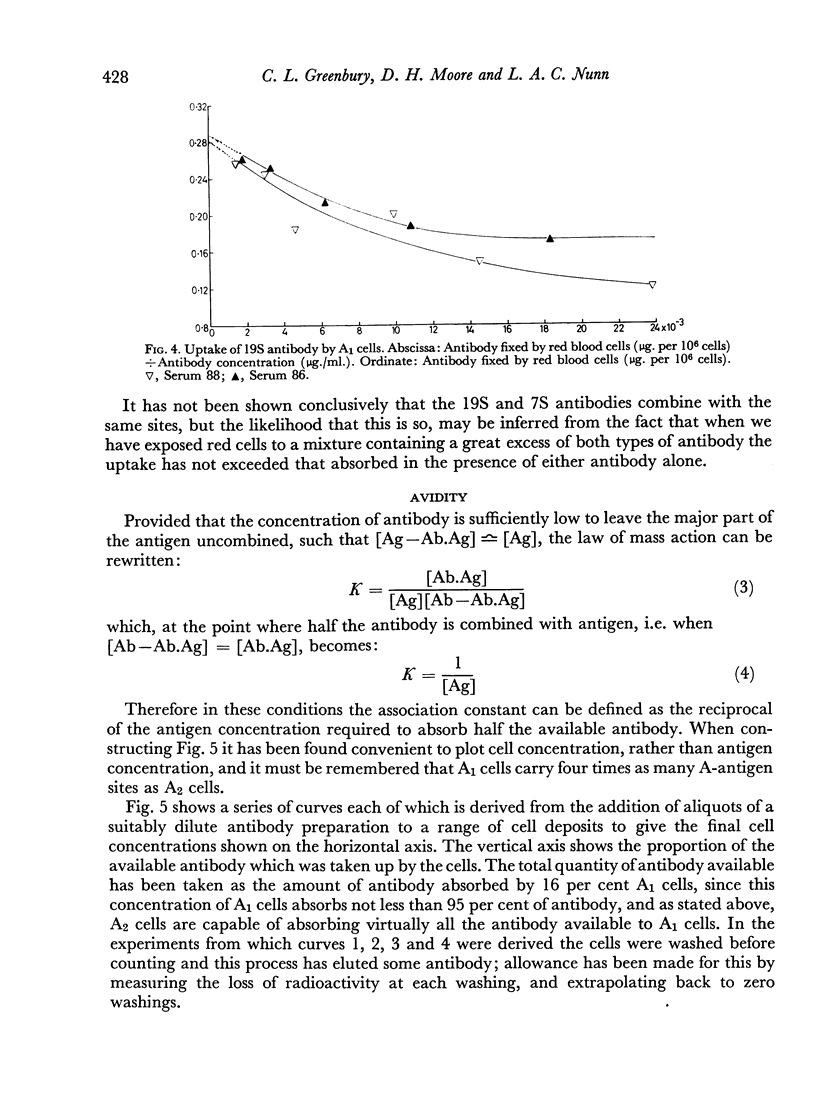
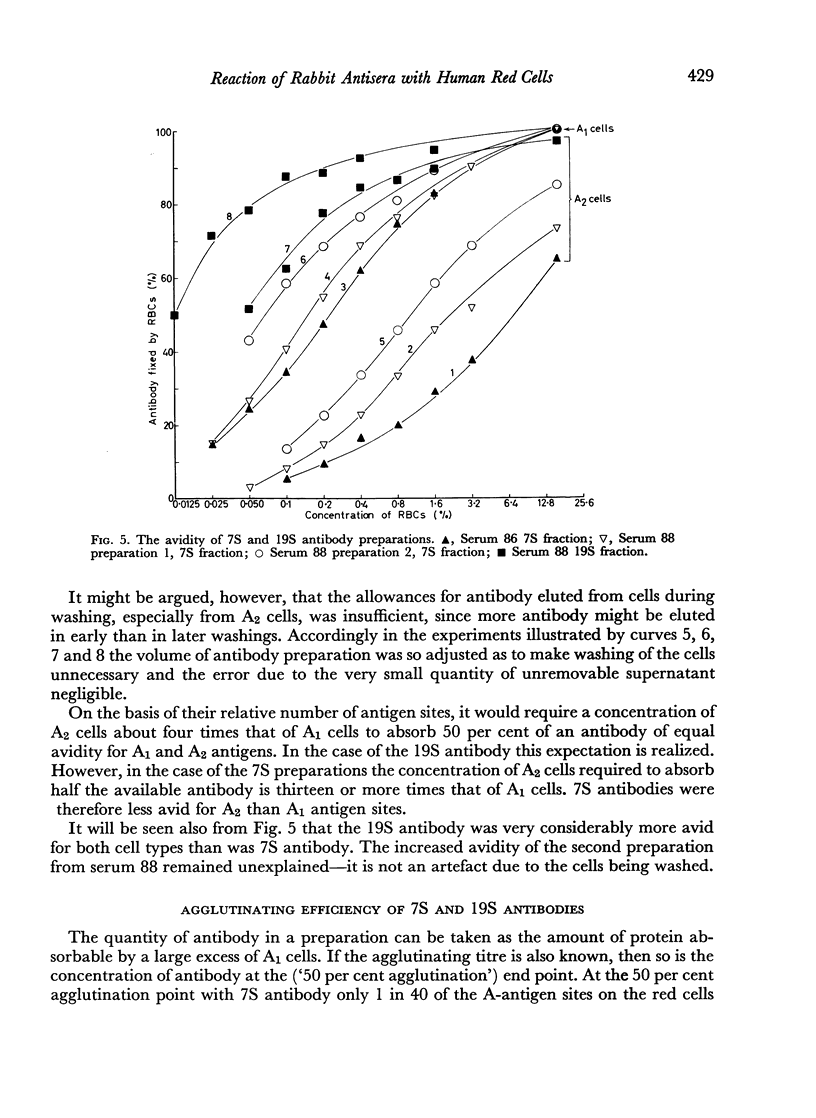
7S and 19S components of rabbit anti-A antibody, labelled with 131I have been separated by chromatography on DEAE-cellulose. The reactions of these components with human group A1, A2 and AB red cells have been investigated. At saturation point A1 cells combine with 0.22 μg. of 7S antibody per million cells, this corresponds to a minimum of 8.3×105 A-antigen sites per cell. A2 cells can take up only one quarter as much antibody, and combine much less avidly with it than do A1 cells. Cells can take up only about one-fifth as many 19S as 7S antibody molecules. 19S antibody is more avid and, on a molecular basis, is 750 times more efficient at agglutinating red cells than 7S antibody. The significance of these findings is discussed with regard to the differences between A1 and A2 antigens, and the valency and mode of attachment to the red cells of the antibodies.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASKONAS B. A., FARTHING C. P., HUMPHREY J. H. The significance of multiple antibody components in serum of immunized rabbits. Immunology. 1960 Oct;3:336–351. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COSTEA N., SCHWARTZ R., CONSTANTOULAKIS M., DAMESHEK W. The use of radioactive antiglobulin for the detection of erythrocyte sensitization. Blood. 1962 Aug;20:214–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FILITTI-WURMSER S., JACQUOT-ARMAND Y., AUBEL-LESURE G., WURMSER R. Physico-chemical study of human isohaemagglutination. Ann Eugen. 1954 Jan;18(3):183–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1952.tb02511.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODMAN H. S. Antigen- and antibody-combining properties and their influence on the immune reaction of red cells. Nature. 1962 Jun 9;194:934–937. doi: 10.1038/194934a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES-JONES N. C., GARDNER B., TELFORD R. The kinetics of the reaction between the blood-group antibody anti-c and erythrocytes. Biochem J. 1962 Dec;85:466–474. doi: 10.1042/bj0850466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASOUREDIS S. P., MELCHER L. R., KOBLICK D. C. Specificity of radioiodinated (I131) immune globulin as determined by quantitative precipitin reaction. J Immunol. 1951 Mar;66(3):297–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFARLANE A. S. Efficient trace-labelling of proteins with iodine. Nature. 1958 Jul 5;182(4627):53–53. doi: 10.1038/182053a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER R. R. The hydrolysis of rabbit y-globulin and antibodies with crystalline papain. Biochem J. 1959 Sep;73:119–126. doi: 10.1042/bj0730119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petermann M. L., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr THE ACTION OF CRYSTALLINE PEPSIN ON HORSE ANTI-PNEUMOCOCCUS ANTIBODY. Science. 1941 May 9;93(2419):458–458. doi: 10.1126/science.93.2419.458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROCKEY J. H., KUNKEL H. G. Studies of the rabbit antibodies which sensitize red blood cells for agglutination by rheumatoid factors. Arthritis Rheum. 1961 Oct;4:449–462. doi: 10.1002/art.1780040502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATKINS W. M., MORGAN W. T. The A and H character of the blood group substances secreted by persons belonging to group A2. Acta Genet Stat Med. 1956;6(4):521–526. doi: 10.1159/000150892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


