Abstract
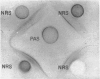
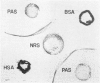
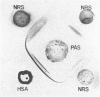
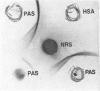
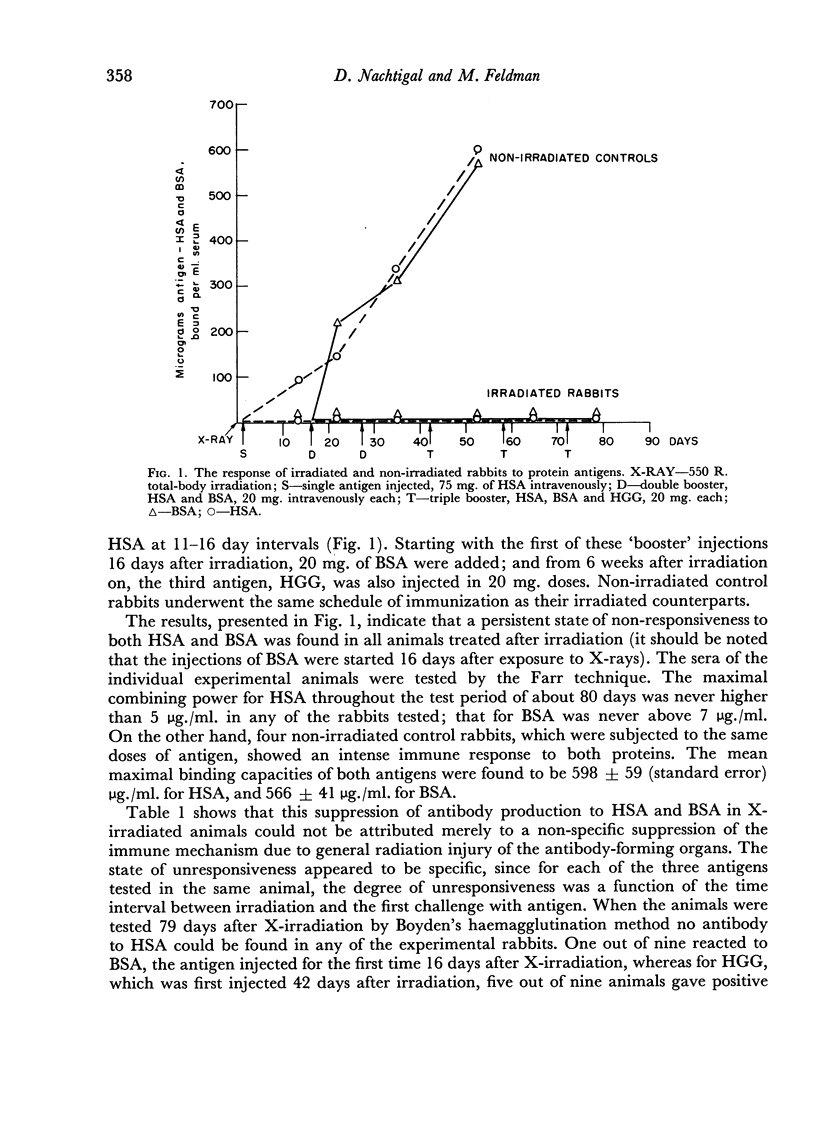
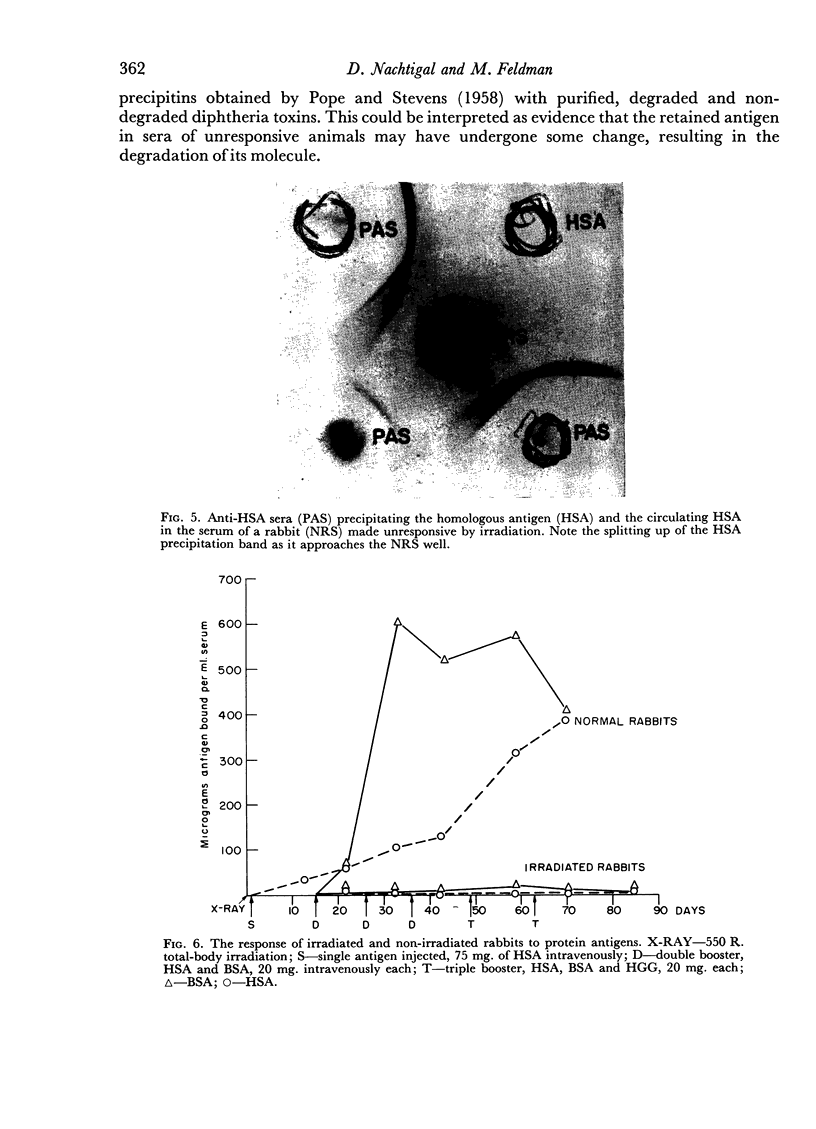
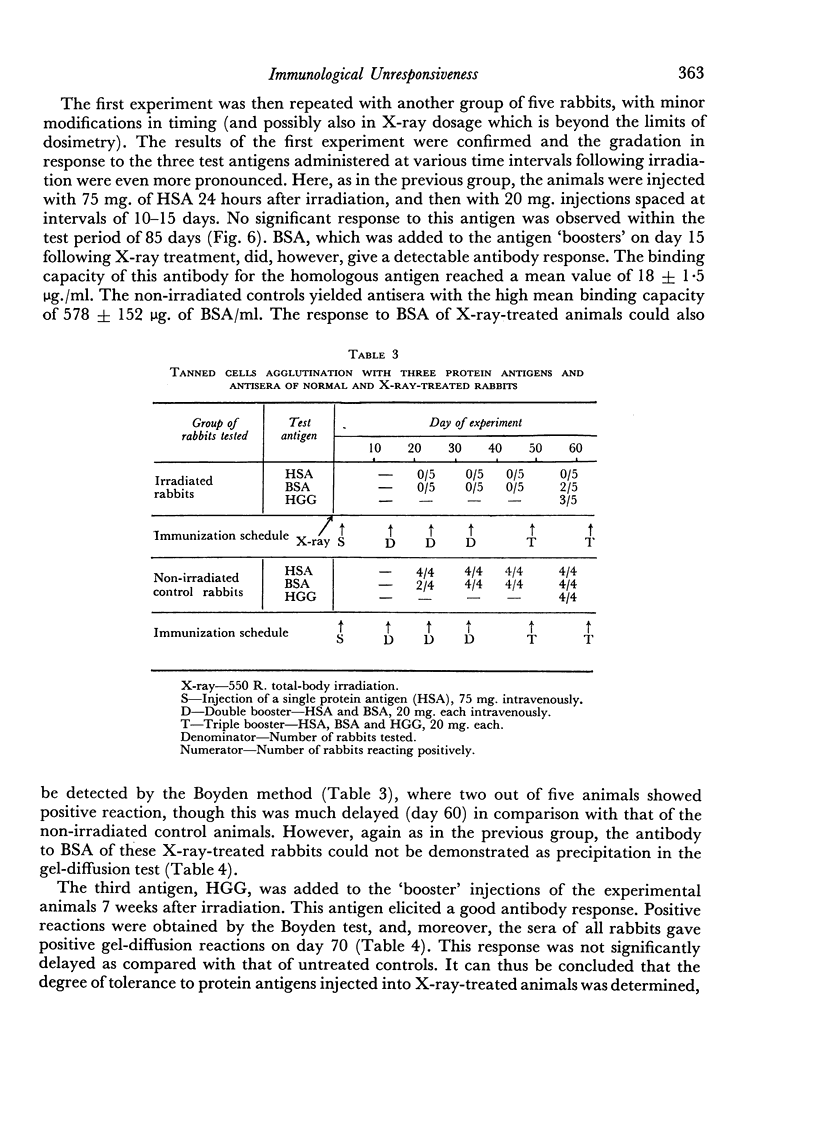
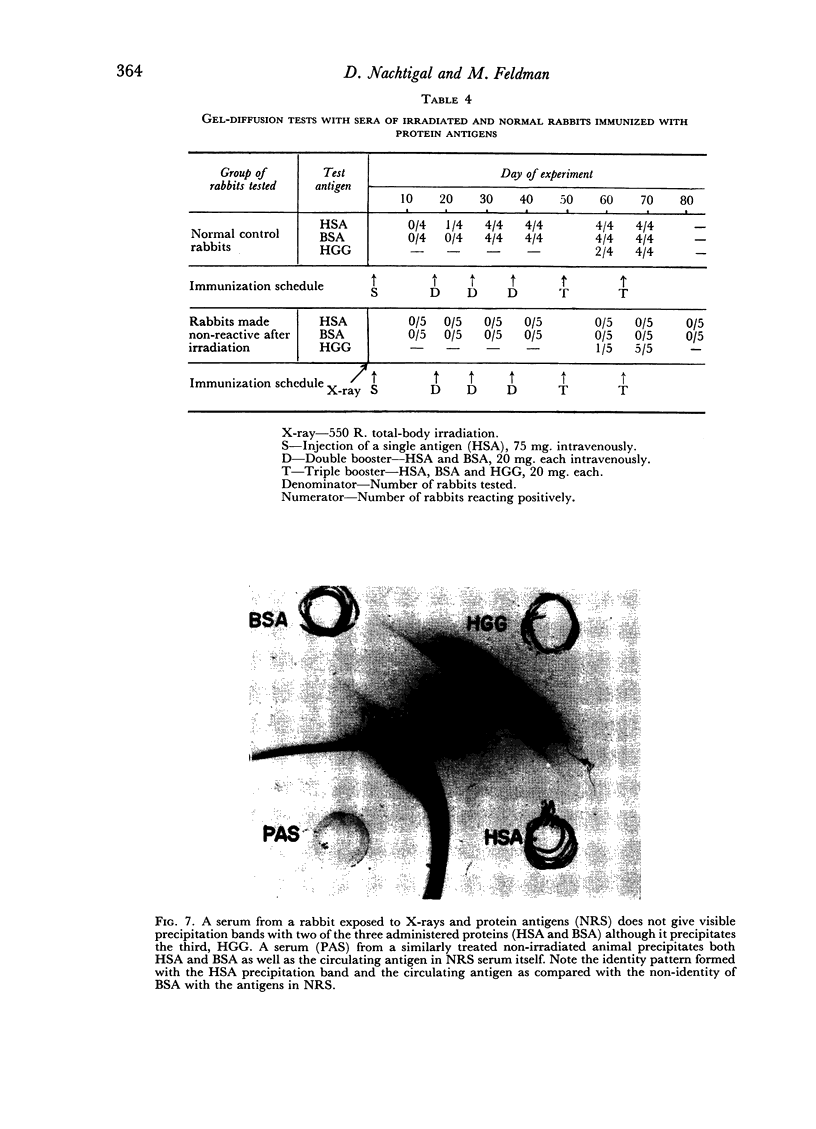
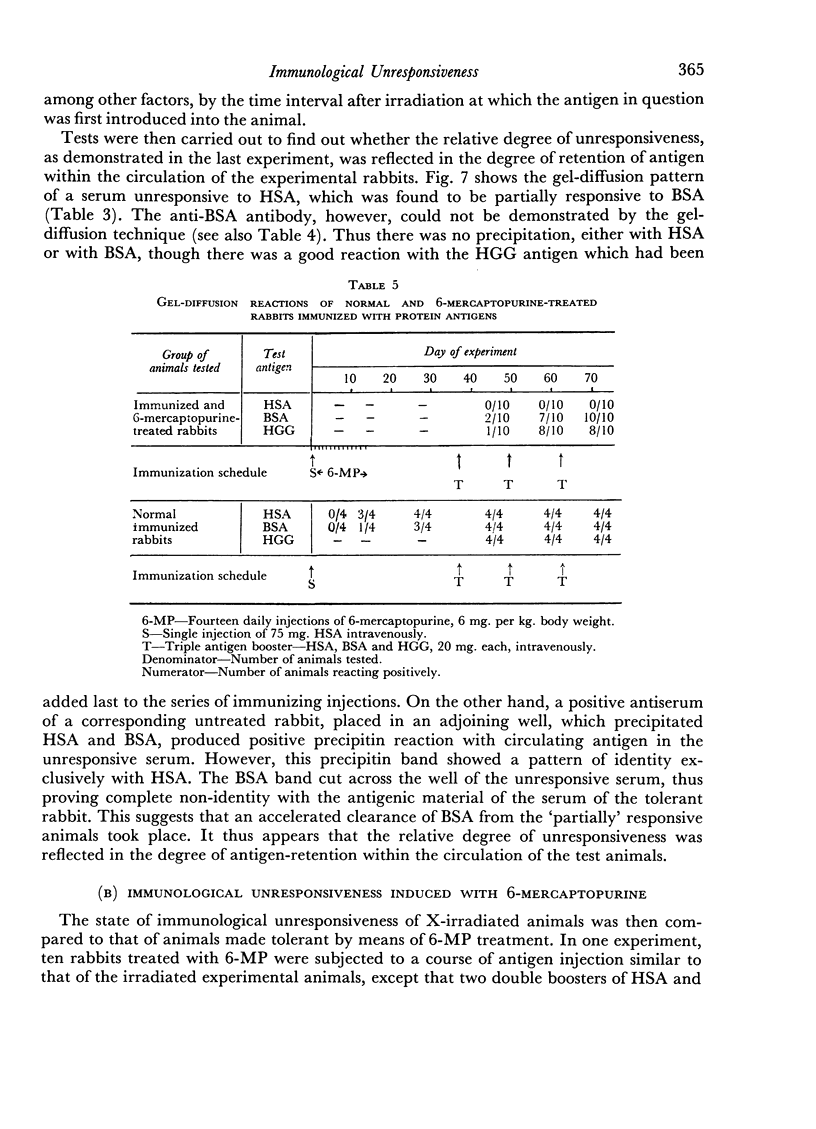
Immune unresponsiveness to HSA and BSA was induced in adult rabbits exposed to 550 R. total-body irradiation. Immunogenic doses of antigen, 20–75 mg., were found to be tolerogenic in this system. The degree of unresponsiveness was found to be a function of the time interval between X-irradiation and the beginning of antigen administration. The unresponsive animals retained the circulating antigen in quantities detectable by the gel-diffusion technique. These results were compared with the state of unresponsiveness induced by means of 6-mercaptopurine, and similar parameters were found to be operative. Some aspects of the significance of the ratio of antigen to competent cells, in the induction of immune unresponsiveness, are discussed.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BENEDICT A. A., BROWN R. J., AYENGAR R. Physical properties of antibody to bovine serum albumin as demonstrated by hemagglutination. J Exp Med. 1962 Jan 1;115:195–208. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.1.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CINADER B., DUBERT J. M. Acquired immune tolerance to human albumin and the response to subsequent injections of diazo human albumin. Br J Exp Pathol. 1955 Oct;36(5):515–529. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CINADER B., DUBERT J. M. Specific inhibition of response to purified protein antigens. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1956 Nov 13;146(922):18–33. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1956.0068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON F. J., MAUER P. H. Immunologic unresponsiveness induced by protein antigens. J Exp Med. 1955 Mar 1;101(3):245–257. doi: 10.1084/jem.101.3.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRESSER D. W. Specific inhibition of antibody production. II. Paralysis induced in adult mice by small quantities of protein antigen. Immunology. 1962 May;5:378–388. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOH K. O., MILLER D. G., DIAMOND H. D. An investigation into the use of 6-mercaptopurine to induce immunological tolerance. J Immunol. 1961 Jun;86:606–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANAN R., OYAMA J. Inhibition of antibody formation in mature rabbits by contact with the antigen at an early age. J Immunol. 1954 Jul;73(1):49–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NATHAN H. C., BIEBER S., ELION G. B., HITCHINGS G. H. Detection of agents which interfere with the immune response. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 Aug-Sep;107:796–799. doi: 10.3181/00379727-107-26758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POPE C. G., STEVENS M. F. The properties of crystalline diphtheria toxin-protein: its antigen composition as determined by gel-diffusion methods. Br J Exp Pathol. 1958 Apr;39(2):150–157. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ R., DAMESHEK W. Drug-induced immunological tolerance. Nature. 1959 Jun 13;183(4676):1682–1683. doi: 10.1038/1831682a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ R., STACK J., DAMESHEK W. Effect of 6-mercaptopurine on antibody production. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Oct;99(1):164–167. doi: 10.3181/00379727-99-24281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SERCARZ E., COONS A. H. Specific inhibition of antibody formation during immunological paralysis and unresponsiveness. Nature. 1959 Oct 3;184(Suppl 14):1080–1082. doi: 10.1038/1841080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH R. T., BRIDGES R. A. Immunological unresponsiveness in rabbits produced by neonatal injection of defined antigens. J Exp Med. 1958 Aug 1;108(2):227–250. doi: 10.1084/jem.108.2.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAVITSKY A. B. Micromethods for the study of proteins and antibodies. I. Procedure and general applications of hemagglutination and hemagglutination-inhibition reactions with tannic acid and protein-treated red blood cells. J Immunol. 1954 May;72(5):360–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERRES G., WOLINS W. Enhanced immunological sensitization of mice by the simultaneous injection of antigen and specific antiserum. I. Effect of varying the amount of antigen used relative to the antiserum. J Immunol. 1961 Apr;86:361–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]