Abstract
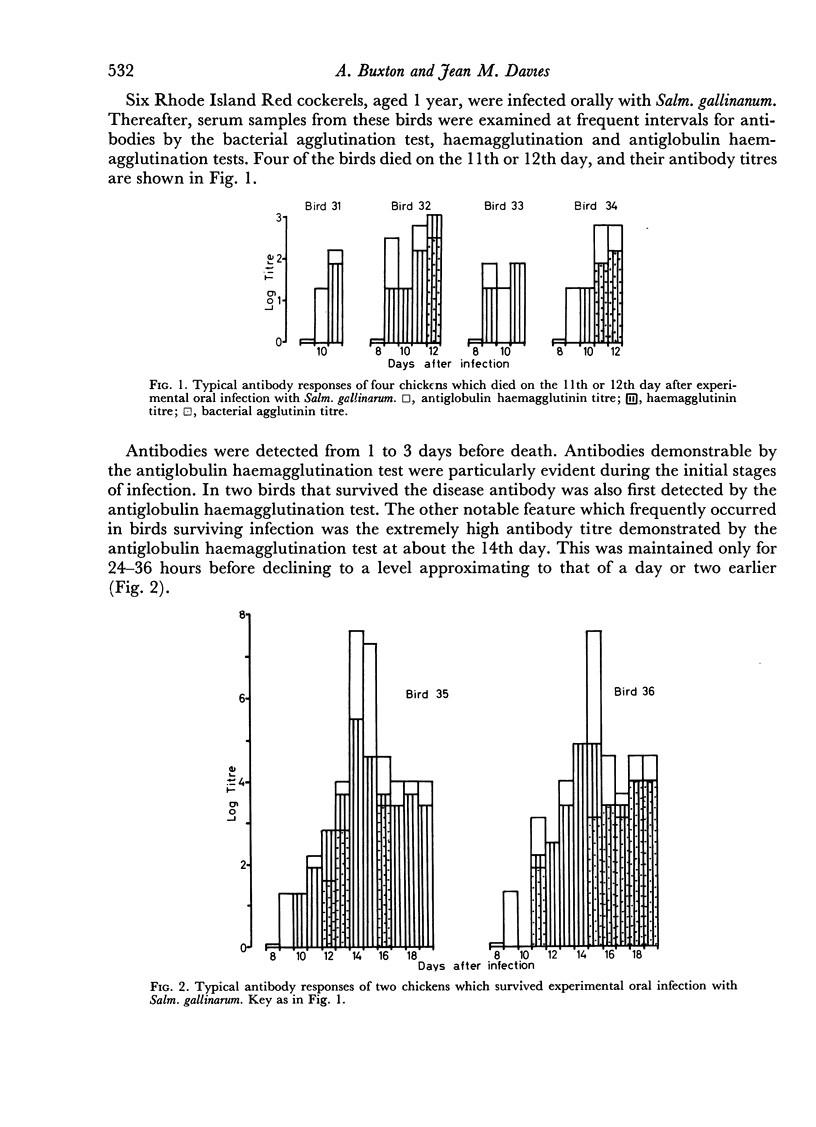
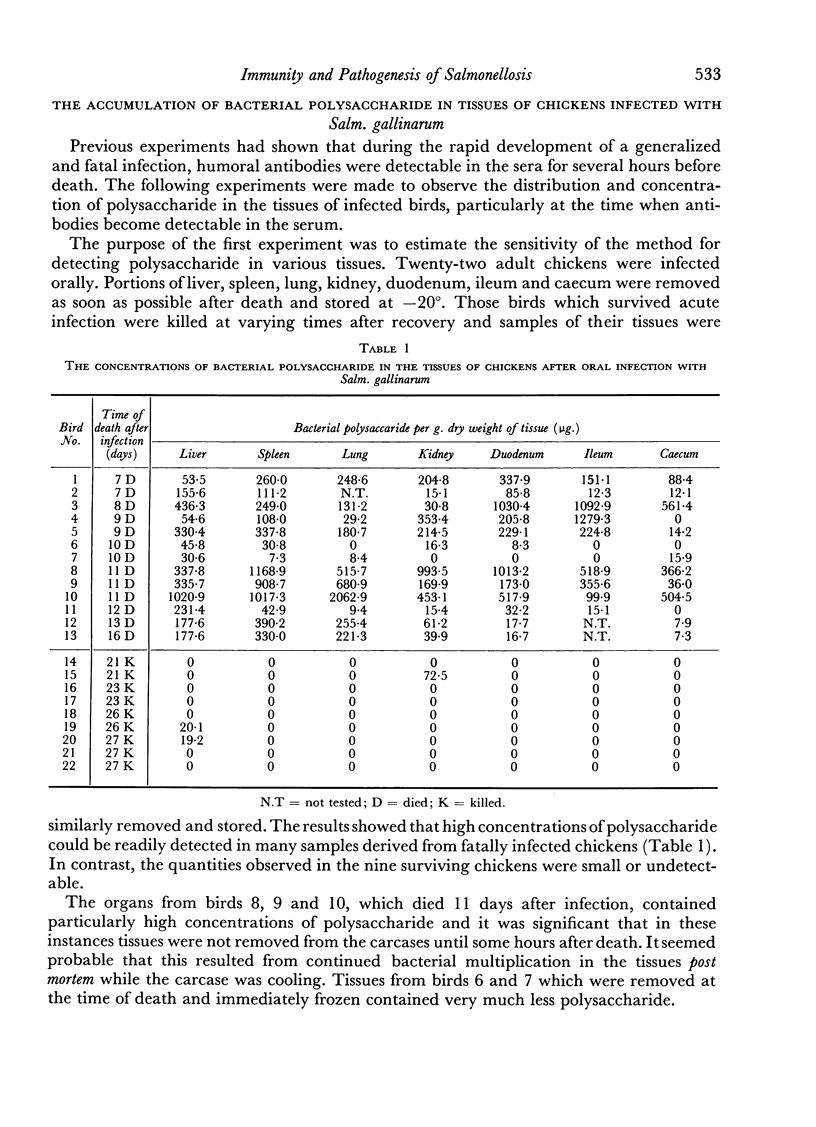
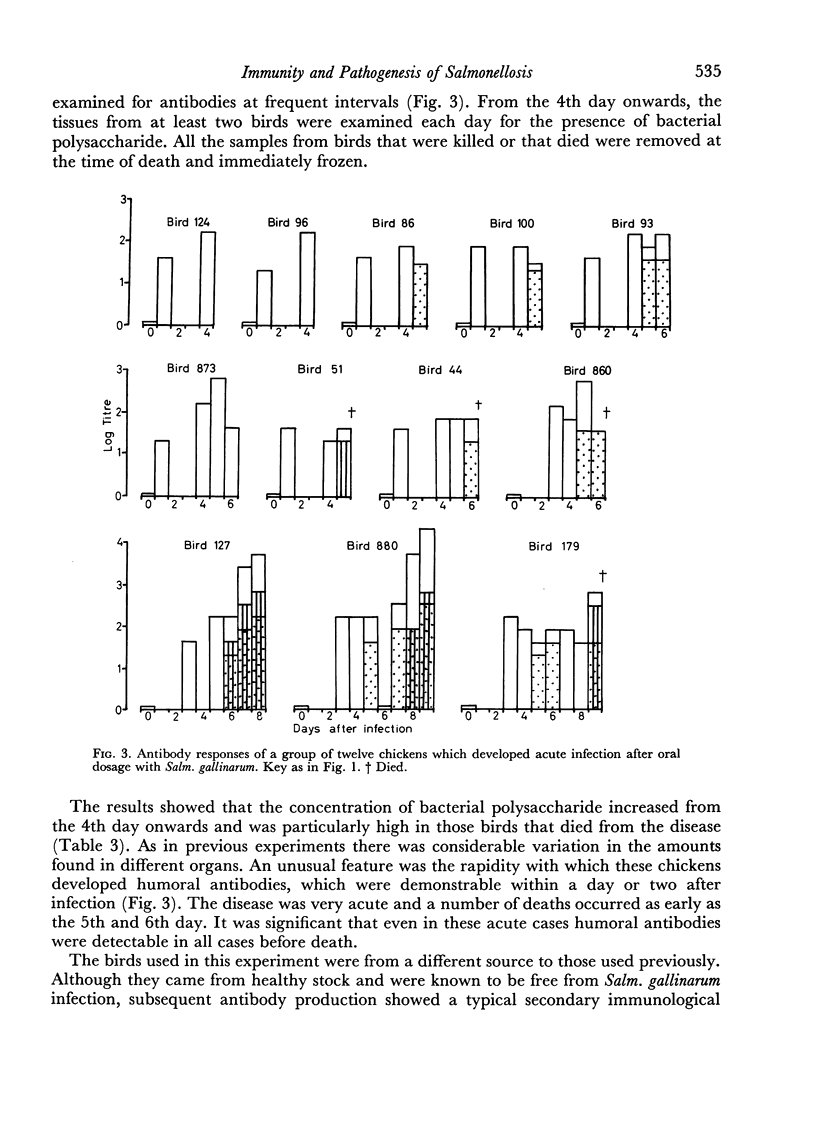
The bacterial agglutination, haemagglutination and antiglobulin haemagglutination tests have been used to detect antibody production during the development of Salmonella gallinarum infection in chickens. The latter test has detected serum antibodies as early as 1 day after oral infection in some cases of acute experimental disease, and antibodies were detected in the sera of all birds at the time of death.
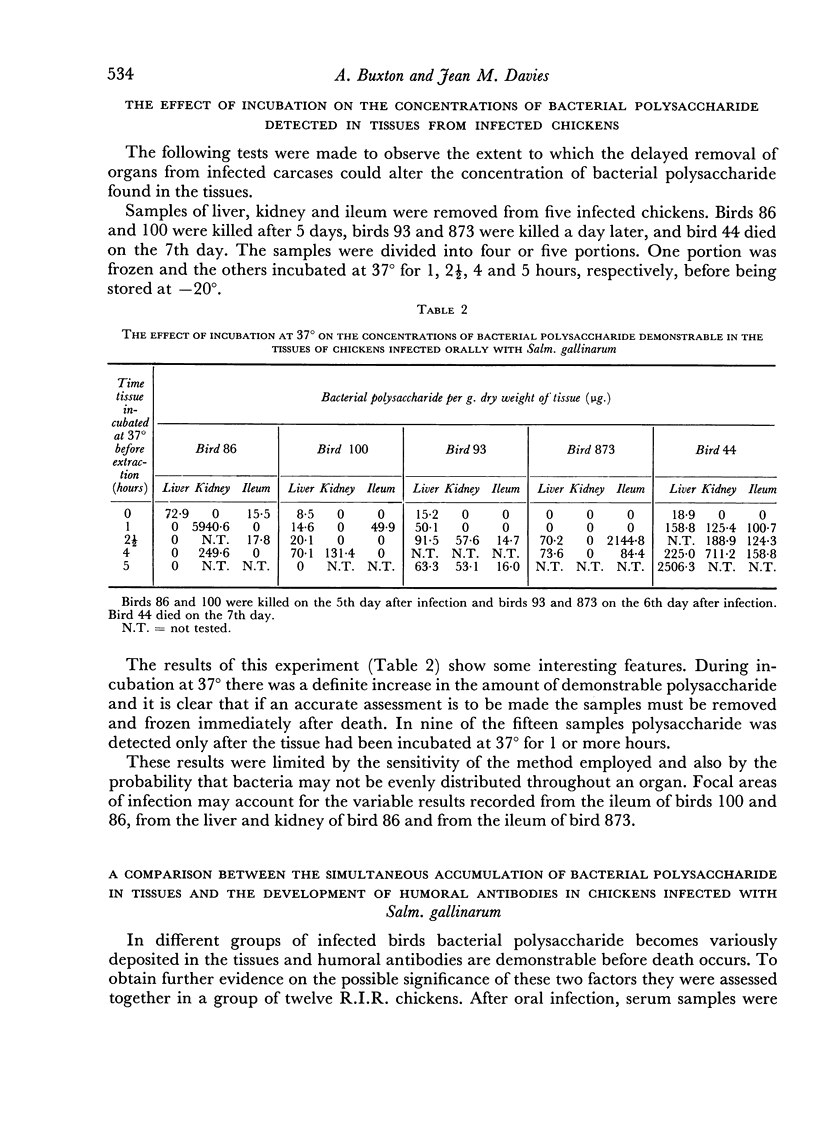
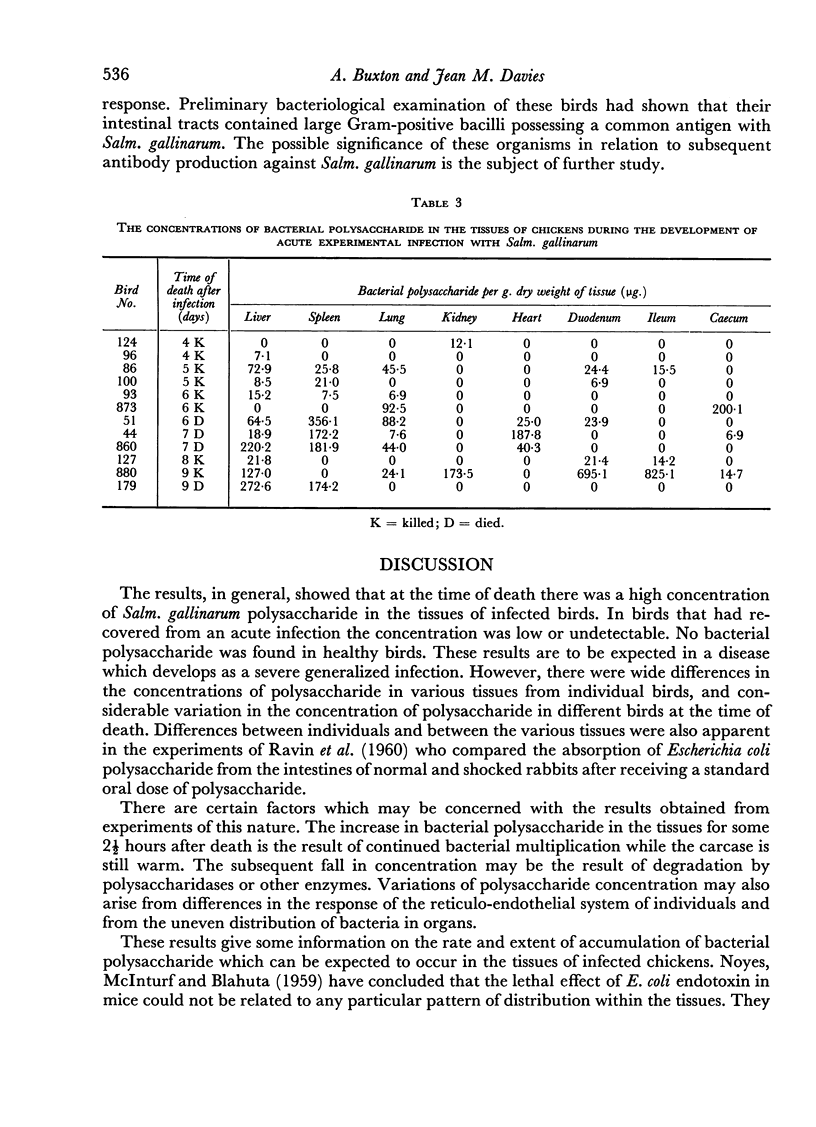
The accumulation of bacterial polysaccharide in the tissues of infected birds has been detected by a haemagglutination inhibition test. High but variable concentrations occurred in different organs of chickens which died from the disease.
The presence of bacterial antibody and bacterial polysaccharide in the tissues of infected birds at death is discussed in relation to the pathogenesis of this disease. It is postulated that an antigen—antibody reaction, developing as an anaphylactic type of hypersensitivity, may be closely associated with the production of symptoms and death of chickens infected with Salm. gallinarum.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BUXTON A., ALLAN D. STUDIES ON IMMUNITY AND PATHOGENESIS OF SALMONELLOSIS. I. ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY REACTIONS ON CIRCULATING LEUCOCYTES OF CHICKENS INFECTED WITH SALMONELLA GALLINARUM. Immunology. 1963 Nov;6:520–529. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRUMPTON M. J., DAVIES D. A., HUTCHISON A. M. The serological specificities of Pasteurella pseudotuberculosis somatic antigens. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Feb;18(1):129–139. doi: 10.1099/00221287-18-1-129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERMUTH F. G., Jr, MCKINNON G. E. Studies on the biological properties of antigen-antibody complexes. I. Anaphylatic shock induced by soluble antigen-antibody complexes in unsensitized normal guinea pigs. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1957 Jul;101(1):13–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMPHREY J. H., MOTA I. The mechanism of anaphylaxis: specificity of antigen-induced mast cell damage in anaphylaxis in the guinea pig. Immunology. 1959 Jan;2(1):31–43. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LECOMTE J., BEAUMARIAGE M. L. Le choc anaphylactique du coq; role de l'histamine dans son déterminisme. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1958;13(3-4):145–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAKINODAN T., WOLFE H. R., GOODMAN M., RUTH R. Precipitin production in chickens. VII. The relation between circulating antibody and anaphylactic shock. J Immunol. 1952 Mar;68(3):219–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOYES H. E., McINTURF C. R., BLAHUTA G. J. Studies on distribution of Escherichia coli endotoxin in mice. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Jan;100(1):65–68. doi: 10.3181/00379727-100-24525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAPPENHEIMER A. M., SALVIN S. B., UHR J. W. Delayed hypersensitivity. II. Induction of hypersensitivity in guinea pigs by means of antigen-antibody complexes. J Exp Med. 1957 Jan 1;105(1):11–24. doi: 10.1084/jem.105.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAVIN H. A., ROWLEY D., JENKINS C., FINE J. On the absorption of bacterial endotoxin from the gastro-intestinal tract of the normal and shocked animal. J Exp Med. 1960 Nov 1;112:783–792. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.5.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERRES G., WOLINS W. Enhanced immunological sensitization of mice by the simultaneous injection of antigen and specific antiserum. I. Effect of varying the amount of antigen used relative to the antiserum. J Immunol. 1961 Apr;86:361–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMLINSON J. R., BUXTON A. Anaphylaxis in pigs and its relationship to the pathogenesis of oedema disease and gastro-enteritis associated with Escherichia coli. Immunology. 1963 Mar;6:126–139. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIGLE W. O., COCHRANE C. G., DIXON F. J. Anaphylactogenic properties of soluble antigen-antibody complexes in the guinea pig and rabbit. J Immunol. 1960 Nov;85:469–477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


