Abstract
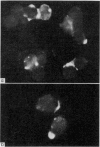
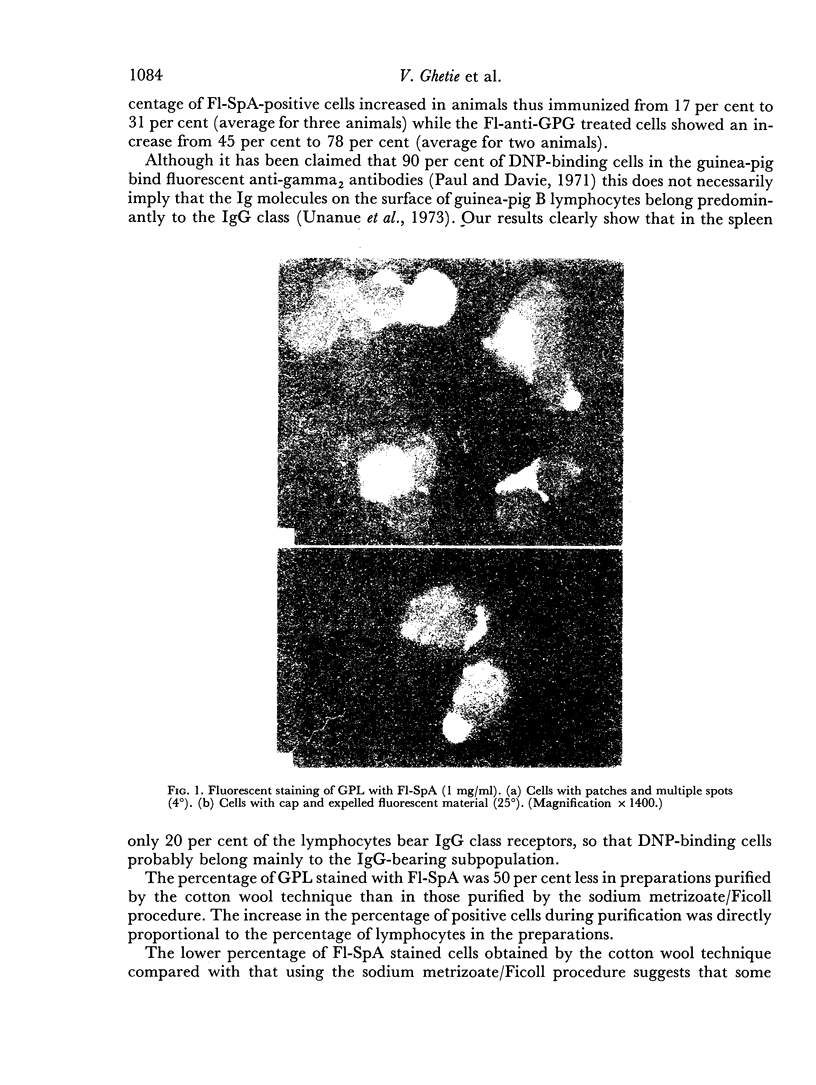
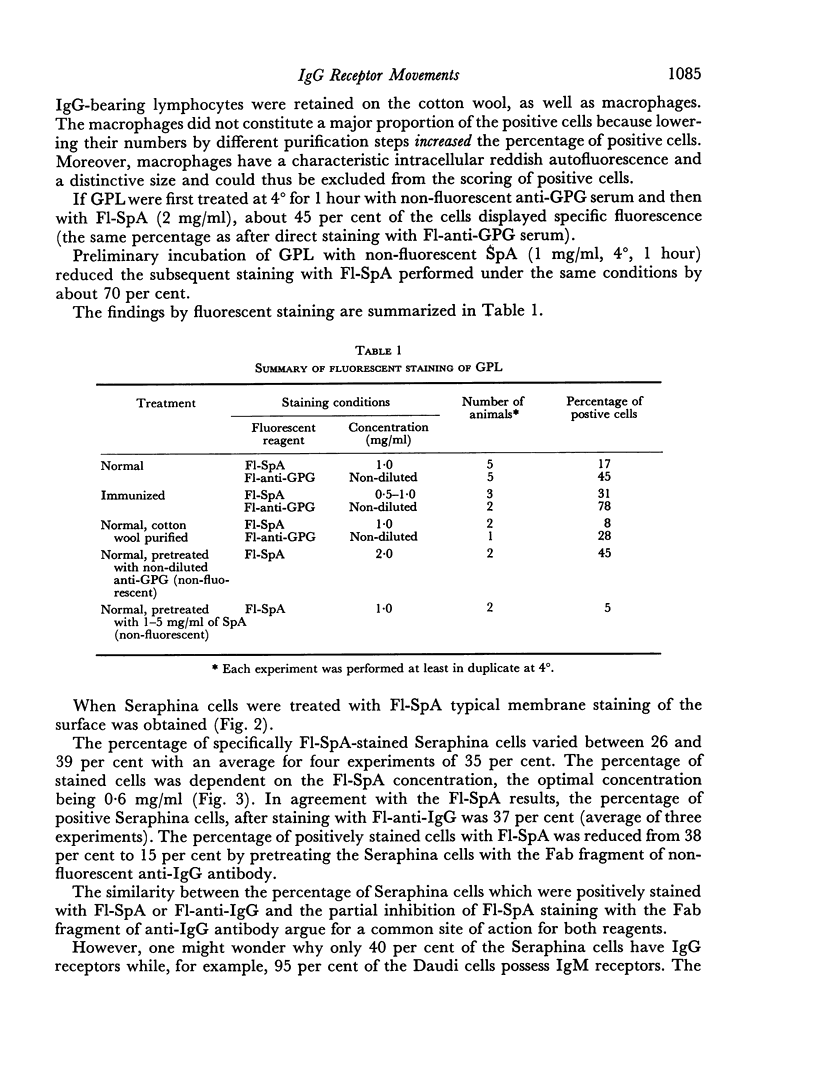
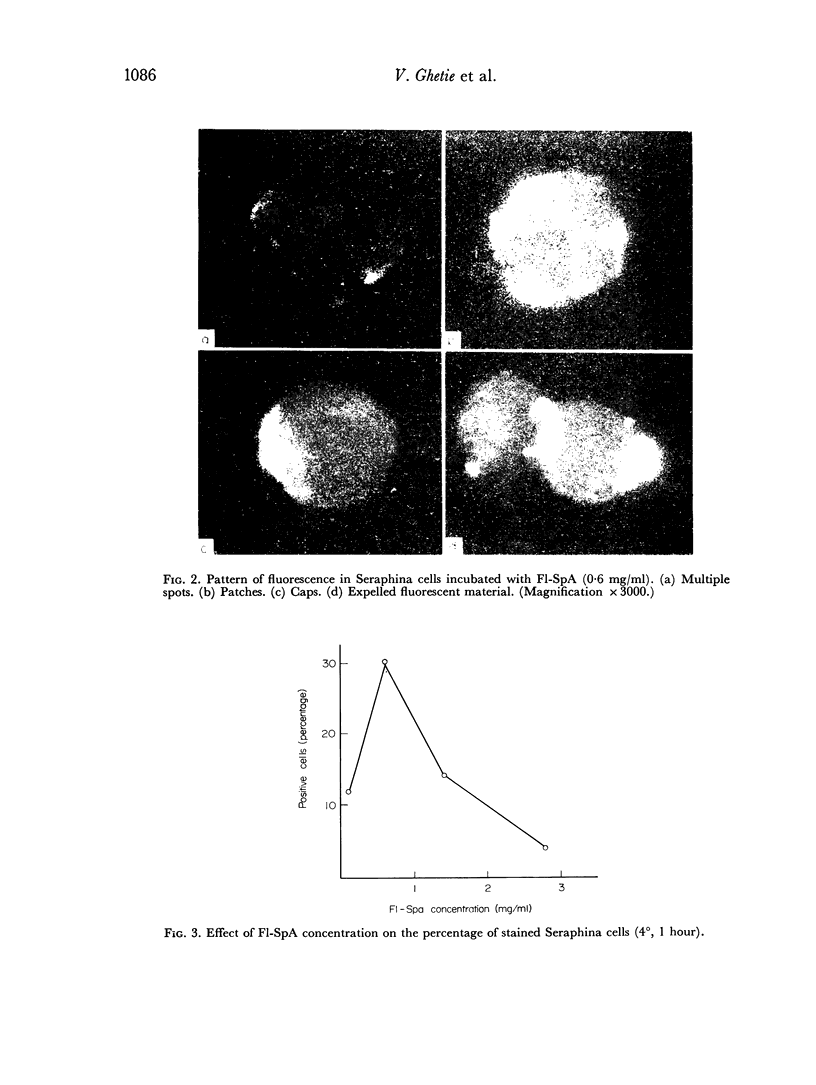
Fluorescent protein A of Staphylococcus aureus (F1-SpA) acts on the IgG receptors of guinea-pig lymphocytes (GPL) and human lymphoid cells (Seraphina) to induce a redistribution pattern (multiple spots, patches, expelled material, caps) similar to the membrane staining of some living cells with anti-IgG. No ring staining was observed, which implies that F1-SpA acts as a multivalent cross-linking agent on IgG receptors. A prozone effect dependent on F1-SpA concentration was observed.
F1-SpA staining was not abolished 2 hours after trypsinization of the cells, nor was it completely inhibited by pretreatment of the cells with non-fluorescent SpA. A low percentage of cap-like stained cells was recorded even at 4° or in the presence of sodium azide.
Seventeen per cent of GPL are specifically stained with F1-SpA whereas with fluorescent anti-guinea-pig gamma-globulin serum 45 per cent of the cells are fluorescent. After immunization of the animals with sheep red blood cells (SRBC) 31 per cent of the GPL became positive with F1-SpA.
Forty per cent of Seraphina cells were stained, whether fluorescent anti-human gamma chain serum or F1-SpA were used. It was also shown that the Fab fragment of an anti-human gamma chain preparation partially inhibited the specific staining of the Seraphina cells with F1-SpA. This suggests that both reagents have a common site of action (IgG receptors).
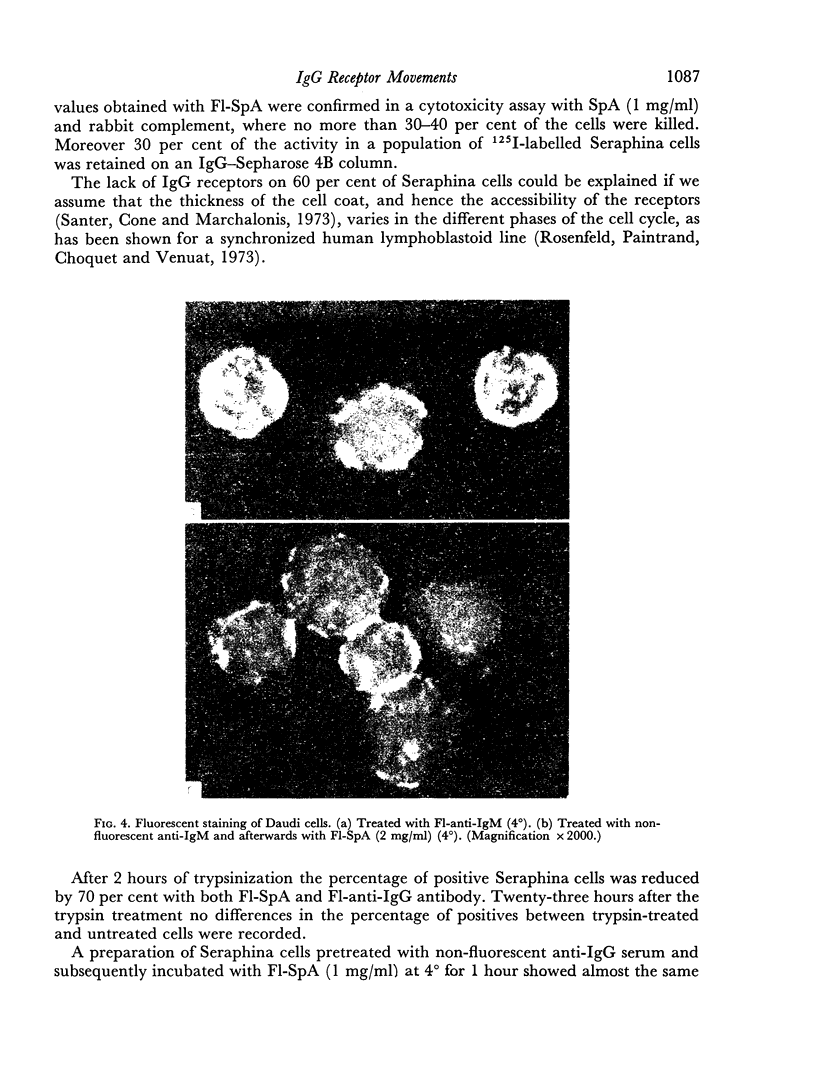
F1-SpA did not stain human lymphoid cells which bear IgM receptors (Daudi cells); SpA reacts only with the Fc region of IgG. However, by reacting Daudi cells with an anti-IgM serum (containing IgG antibodies) and afterwards with F1-SpA, specific staining was achieved. F1-SpA is therefore recommended as a fluorescent reagent for indirect immunofluorescent staining in which IgG antibodies are used.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Forsgren A., Sjöquist J. "Protein A" from S. aureus. I. Pseudo-immune reaction with human gamma-globulin. J Immunol. 1966 Dec;97(6):822–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjelm H., Hjelm K., Sjöquist J. Protein A from Staphylococcus aureus. Its isolation by affinity chromatography and its use as an immunosorbent for isolation of immunoglobulins. FEBS Lett. 1972 Nov 15;28(1):73–76. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80680-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein E., Eskeland T., Inoue M., Strom R., Johansson B. Surface immunoglobulin-moieties on lymphoid cells. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Sep;62(1):133–148. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90515-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Frommel D. Definition of staphylococcal protein A reactivity for human immunoglobulin G fragments. Immunochemistry. 1970 Jan;7(1):124–127. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(70)90036-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce C. W., Asofsky R., Solliday S. M. Immunoglobulin receptors on B lymphocytes: shifts in immunoglobulin class during immune responses. Fed Proc. 1973 Jan;32(1):41–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C. Two distinct populations of peripheral lymphocytes in mice distinguishable by immunofluorescence. Immunology. 1970 Oct;19(4):637–650. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santer V., Cone R. E., Marchalonis J. J. The glycoprotein surface coat on different classes of murine lymphocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Jun;79(2):404–416. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90460-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöquist J., Meloun B., Hjelm H. Protein A isolated from Staphylococcus aureus after digestion with lysostaphin. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Sep 25;29(3):572–578. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02023.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Engers H. D., Karnovsky M. J. Antigen receptors on lymphocytes. Fed Proc. 1973 Jan;32(1):44–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Petris S., Raff M. C. Normal distribution, patching and capping of lymphocyte surface immunoglobulin studied by electron microscopy. Nat New Biol. 1973 Feb 28;241(113):257–259. doi: 10.1038/newbio241257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]