Abstract
Treatment of bacteriophage with 3-iodo-4-hydroxy-5-nitrophenyl acetic acid chloride (NIP) in aqueous medium killed a proportion of the phage but the survivors were made susceptible to inactivation by rabbit immune sera to NIP-chicken globulin conjugate. The serum factor inactivating NIP-phage (T2) was eluted from a Sephadex G-200 column as 7S γ-globulin and was neutralized by a sheep antiserum against electrophoretically purified rabbit γ-globulin. The inactivation was strongly inhibited by the hapten and its derivatives. As little as 0.001 micromole per millilitre of NIP—ε-amino caproic acid was inhibitory.
Inactivation of NIP-phage was ascribed to anti-NIP antibody.
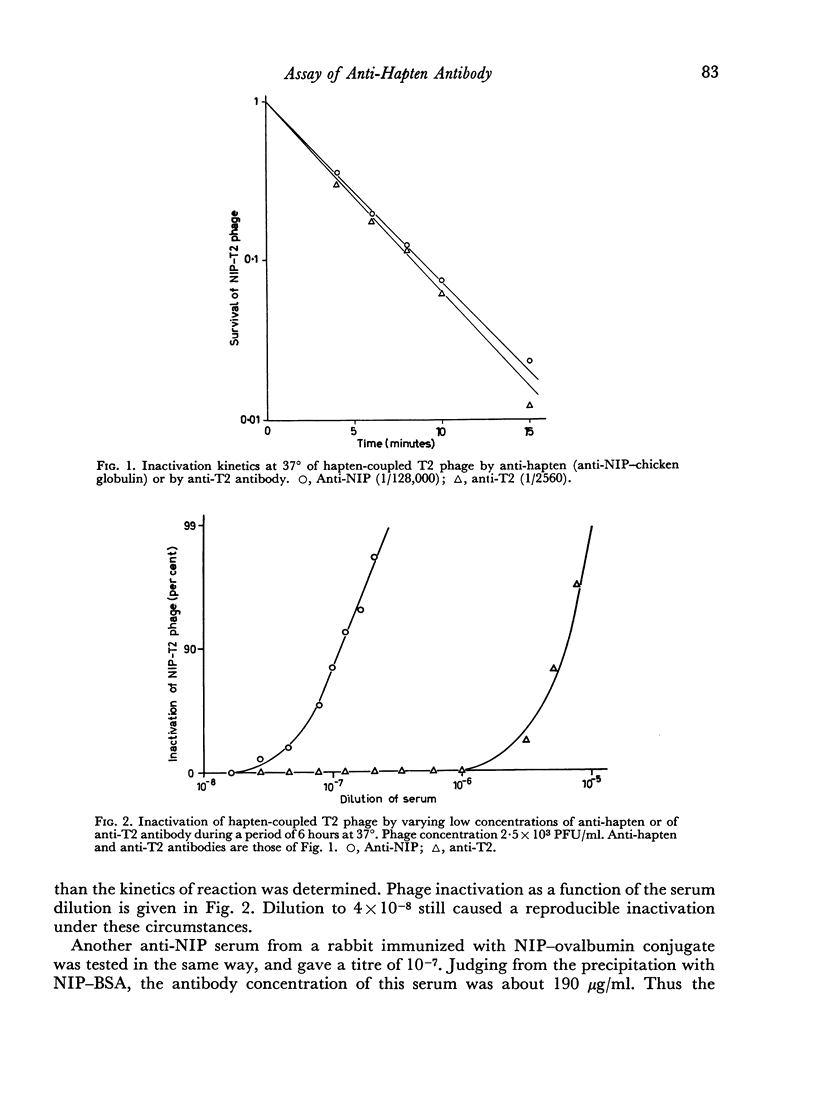
Inactivation of NIP-phage (T2) in strong anti-NIP sera approximately followed first-order reaction kinetics until 99 per cent of the phage became inactivated. When incubated with phage for 6 hours concentrations of antiserum as low as 10-7 (1.9×10-5 μg/ml) or less caused measurable inactivation of the phage. The threshold quantity of antibody was estimated to be less than 10-5 μg.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BULLOCK W. E., KANTOR F. S. HEMAGGLUTINATION REACTIONS OF HUMAN ERYTHROCYTES CONJUGATED COVALENTLY WITH DINITROPHENYL GROUPS. J Immunol. 1965 Mar;94:317–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKLIN N. C. Serological study of tail structure and function in coliphages T2 and T4. Virology. 1961 Aug;14:417–429. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90333-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


