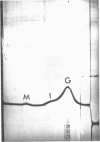
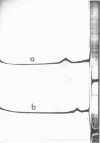
Abstract
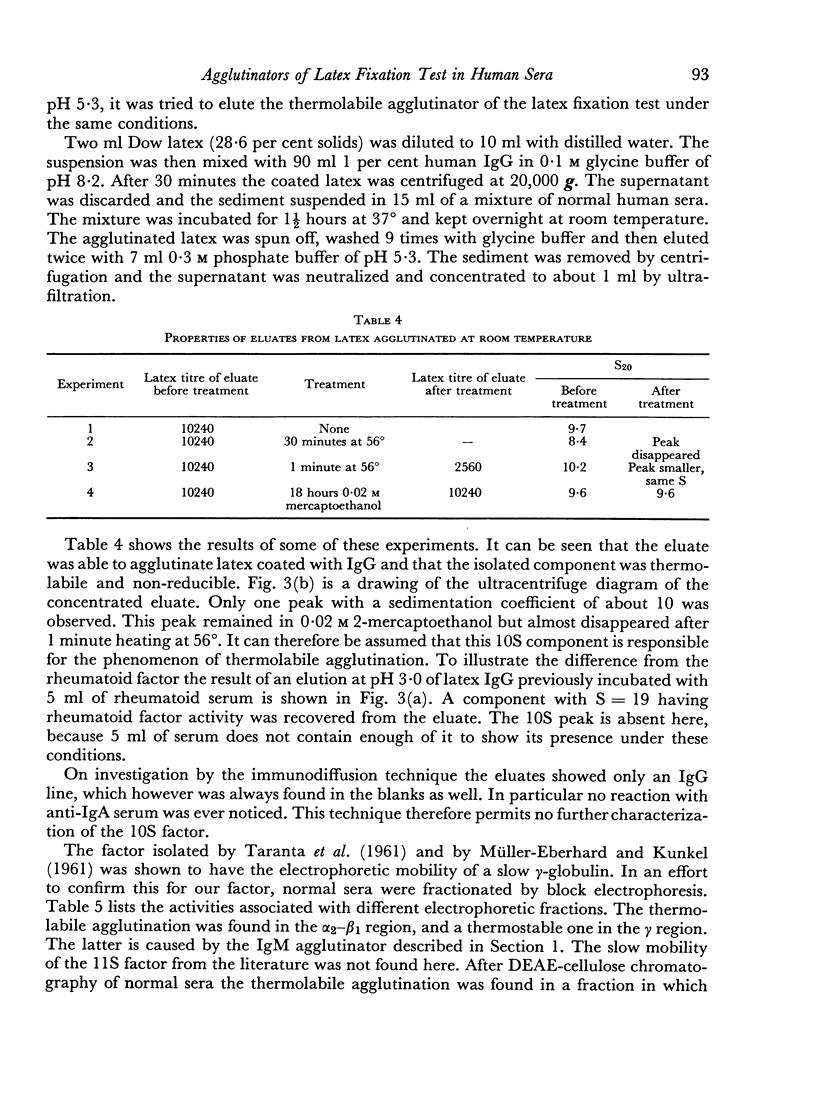
Using a sensitive modification of the latex fixation test it is possible to detect a small agglutinating effect in about 60 per cent of normal human sera, after these have been heated for 30 minutes at 56°. This was shown to be caused by an IgM globulin with the properties of a rheumatoid factor. The factor is able to react with human IgG globulin and may represent an antibody to the IgG part of circulating antigen—antibody complexes. The heat treatment probably inactivates an inhibitor of the latex fixation reaction.
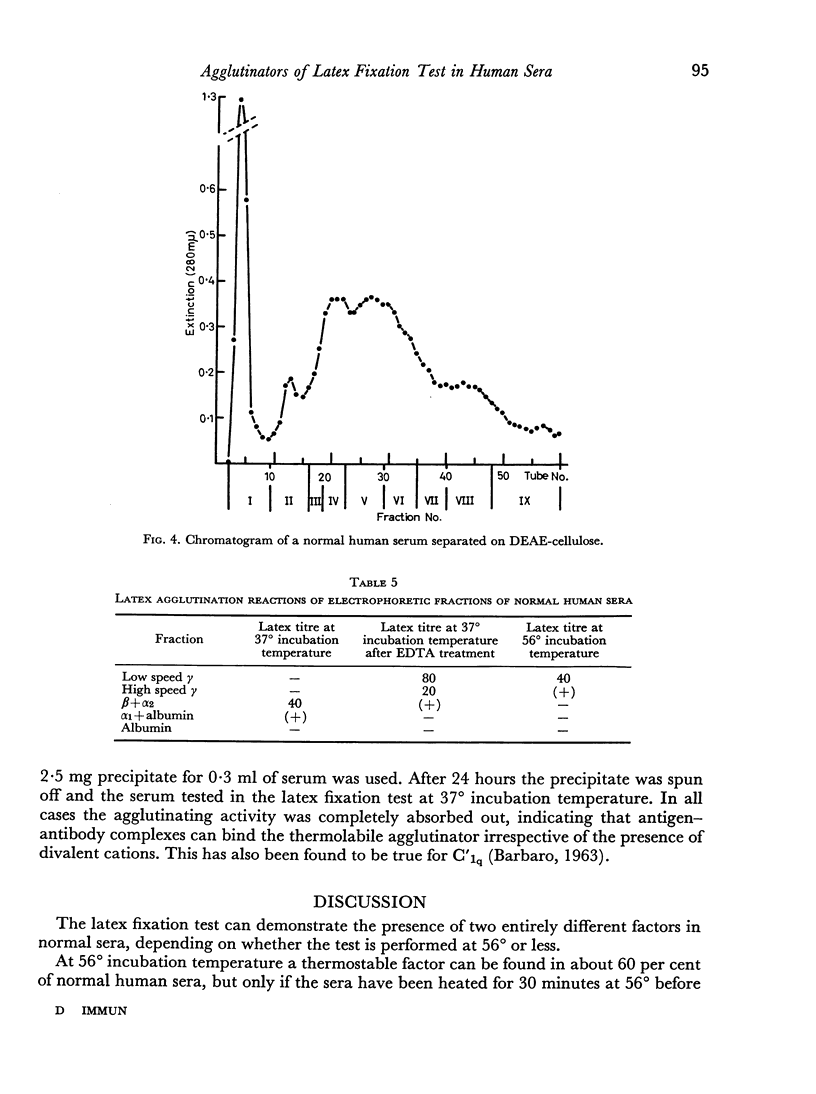
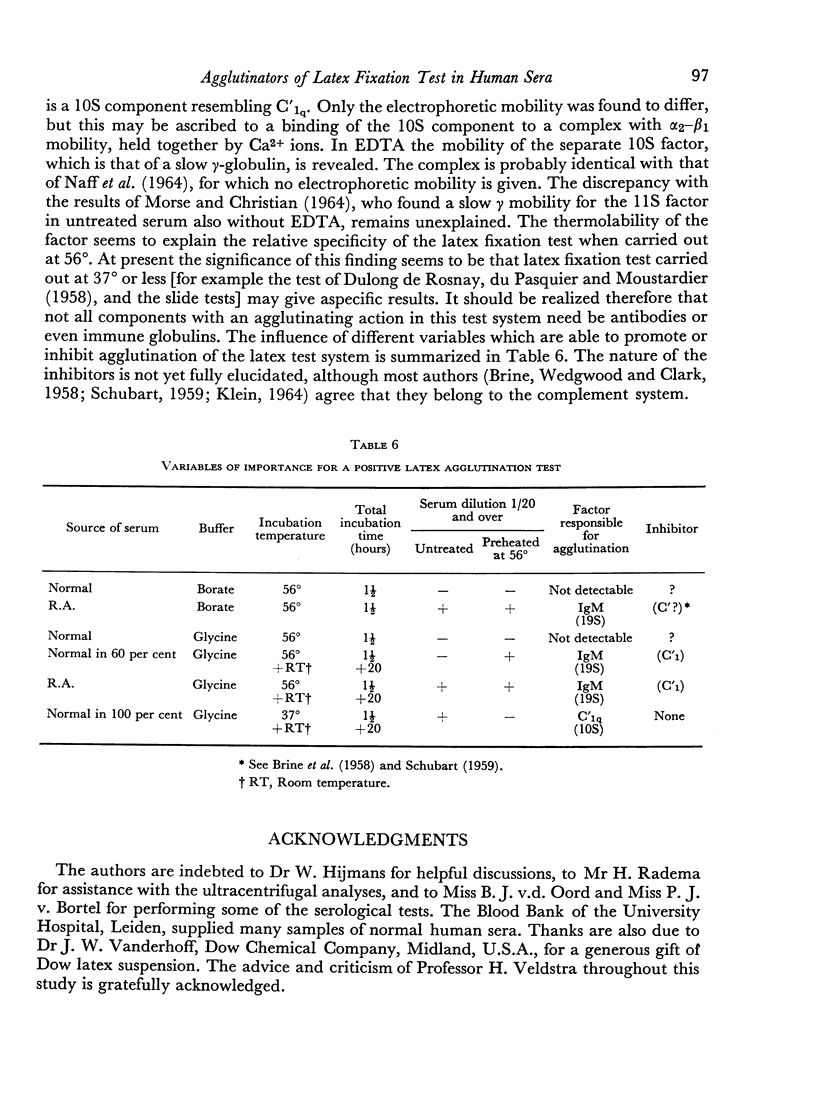
In addition all normal human sera give an agglutination reaction with IgG coated latex at incubation temperatures of 37° or lower. It was shown that these reactions are caused by a thermolabile, non-reducible component with a sedimentation constant of about 10. This component is probably identical with the complement component C'1q. The agglutinating activity was found in the α2—β1 region after electrophoresis of untreated serum, but in the slow γ region after treatment of the serum with EDTA. This kind of agglutination may cause false positive reactions in latex tests which are carried out at 37° or less.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABRUZZO J. L., CHRISTIAN C. L. The induction of a rheumatoid factor-like substance in rabbits. J Exp Med. 1961 Nov 1;114:791–806. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.5.791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARBARO J. F. DEMONSTRATION OF A HAEMOLYTICALLY ACTIVE 11 S COMPONENT OF RABBIT, GUINEA PIG AND HUMAN SERUM BY MEANS OF ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY PRECIPITATES. Nature. 1963 Aug 24;199:819–820. doi: 10.1038/199819a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRINE K. L., WEDGWOOD R. J., CLARK W. S. The effects of serum complement and its components on the rheumatoid latex fixation test. Arthritis Rheum. 1958 Jun;1(3):230–238. doi: 10.1002/art.1780010305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULONG DE ROSNAY C., DU PASQUIER P., MOUSTARDIER G. Nouvelle méthode de recherche du facteur agglutinant de la polyarthrite chronique évolutive. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1958 Jul;95(1):23–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EYQUEM A., GUYOT-JEANNIN N., PODLIACHOUK L. Présence dans les immunsérums anti-bactériens de facteurs antiglobuliniques analogues à ceux de la polyarthrite chronique évolutive. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1959 Mar;96(3):295–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAHEY J. L., McCOY P. F., GOULIAN M. Chromatography of serum proteins in normal and pathologic sera: the distribution of protein-bound carbohydrate and cholesterol, siderophilin, thyroxin-binding protein, B12-binding protein, alkaline and acid phosphatases, radio-iodinated albumin and myeloma proteins. J Clin Invest. 1958 Feb;37(2):272–284. doi: 10.1172/JCI103606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUDENBERG H. H., GOODMAN J. W., MILGROM F. IMMUNOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON RABBIT ANTI-ANTIBODY. J Immunol. 1964 Feb;92:227–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY J. D. The relationship between a serum and tissue inhibitor and the rheumatoid disease agglutinating factor. J Immunol. 1959 Jul;83(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEIMER R., LEVIN F. M., RUDD E. GLOBULINS RESEMBLING RHEUMATOID FACTOR IN SERUM OF THE AGED. Am J Med. 1963 Aug;35:175–181. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(63)90208-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORSE J. H., CHRISTIAN C. L. IMMUNOLOGICAL STUDIES OF THE 11S PROTEIN COMPONENT OF THE HUMAN COMPLEMENT SYSTEM. J Exp Med. 1964 Feb 1;119:195–209. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.2.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MULLER-EBERHARD H. J., KUNKEL H. G. Isolation of a thermolabile serum protein which precipitates gamma-globulin aggregates and participates in immune hemolysis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 Feb;106:291–295. doi: 10.3181/00379727-106-26313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAFF G. B., PENSKY J., LEPOW I. H. THE MACROMOLECULAR NATURE OF THE FIRST COMPONENT OF HUMAN COMPLEMENT. J Exp Med. 1964 Apr 1;119:593–613. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.4.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLOTZ C. M., SINGER J. M. The latex fixation test. I. Application to the serologic diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Med. 1956 Dec;21(6):888–892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TARANTA A., WEISS H. S., FRANKLIN E. C. Precipitating factor for aggregated gamma-globulins in normal human sera. Nature. 1961 Jan 21;189:239–240. doi: 10.1038/189239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON R. G. ANTIGLOBULINS IN NORMAL SERUM. II. DEMONSTRATION OF A HEAT-LABILE ANTIGLOBULIN IN NORMAL HUMAN SERA. J Immunol. 1963 Aug;91:243–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIFF M., BROWN P., LOSPALLUTO J., BADIN J., MCEWEN C. Agglutination and inhibition by serum globulin in the sensitized sheep cell agglutination reaction in rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Med. 1956 Apr;20(4):500–509. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(56)90134-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]