Abstract
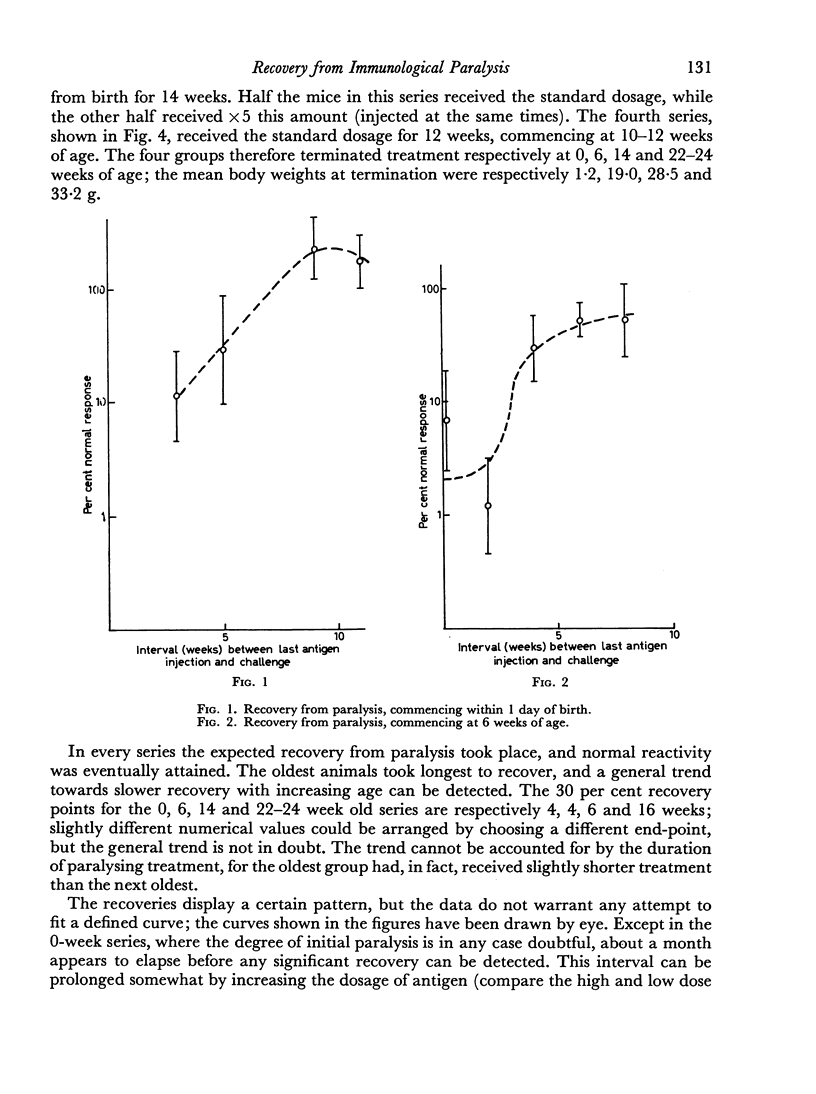
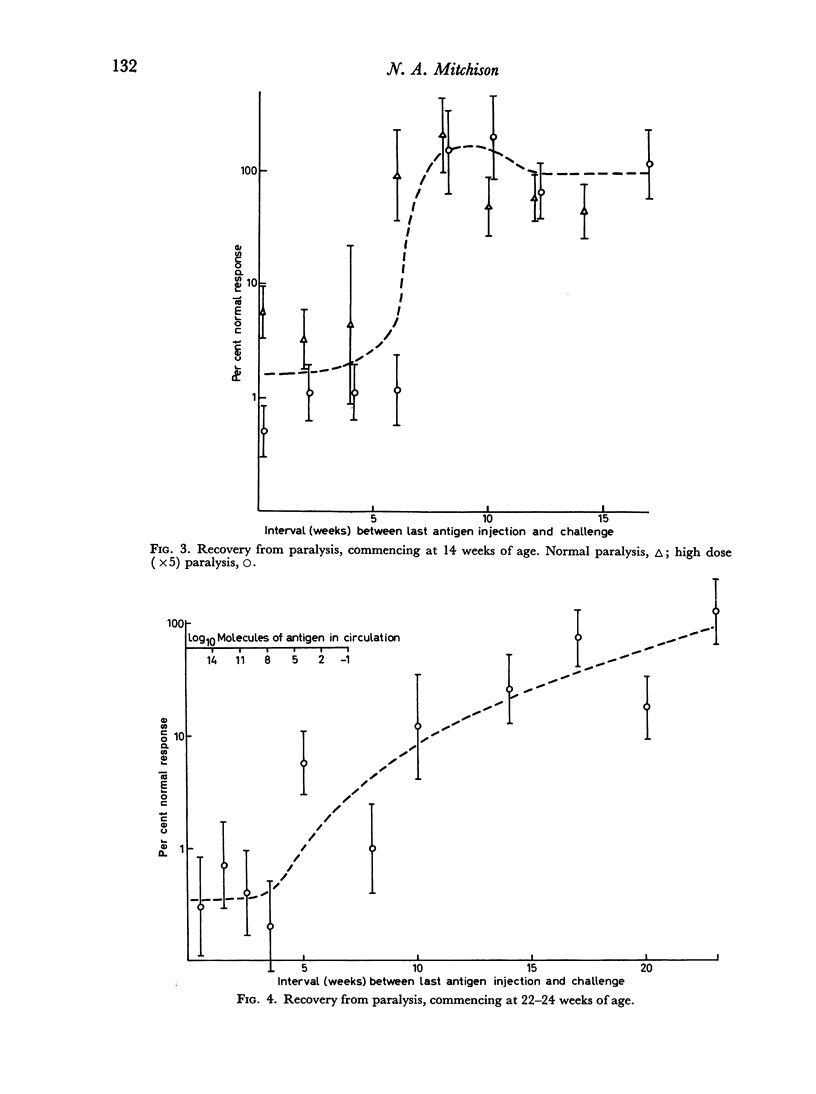
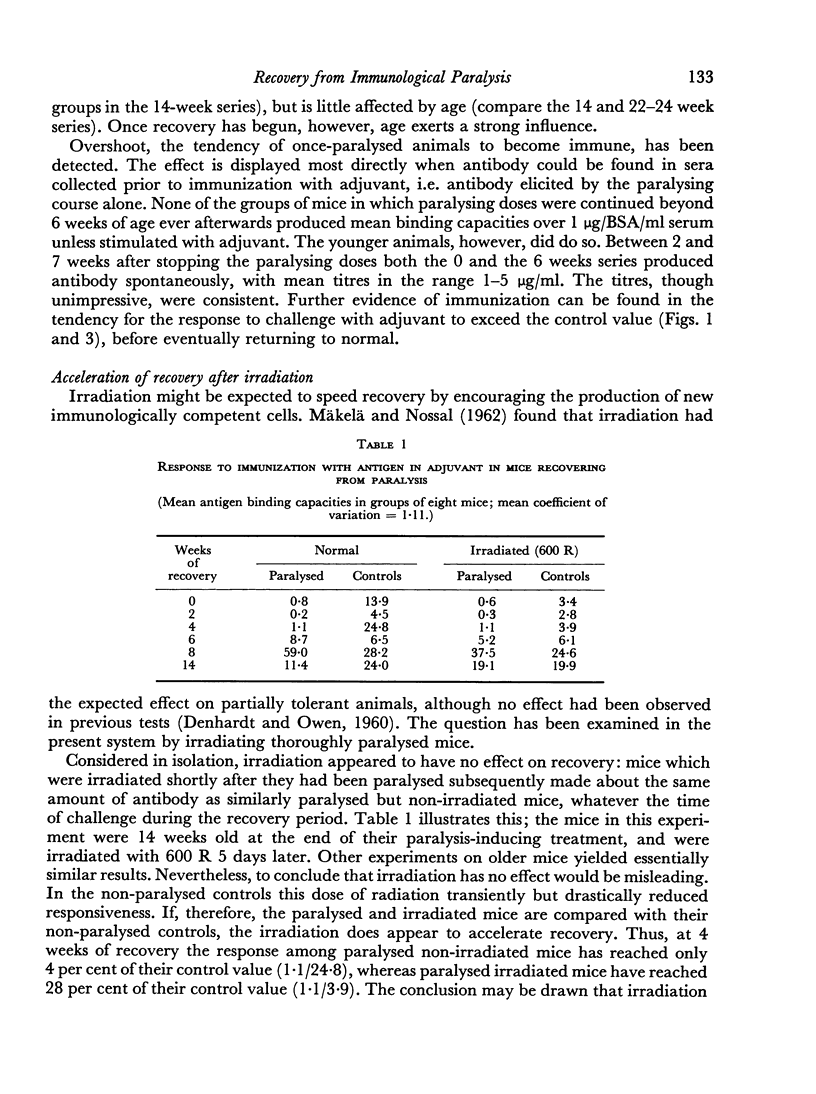
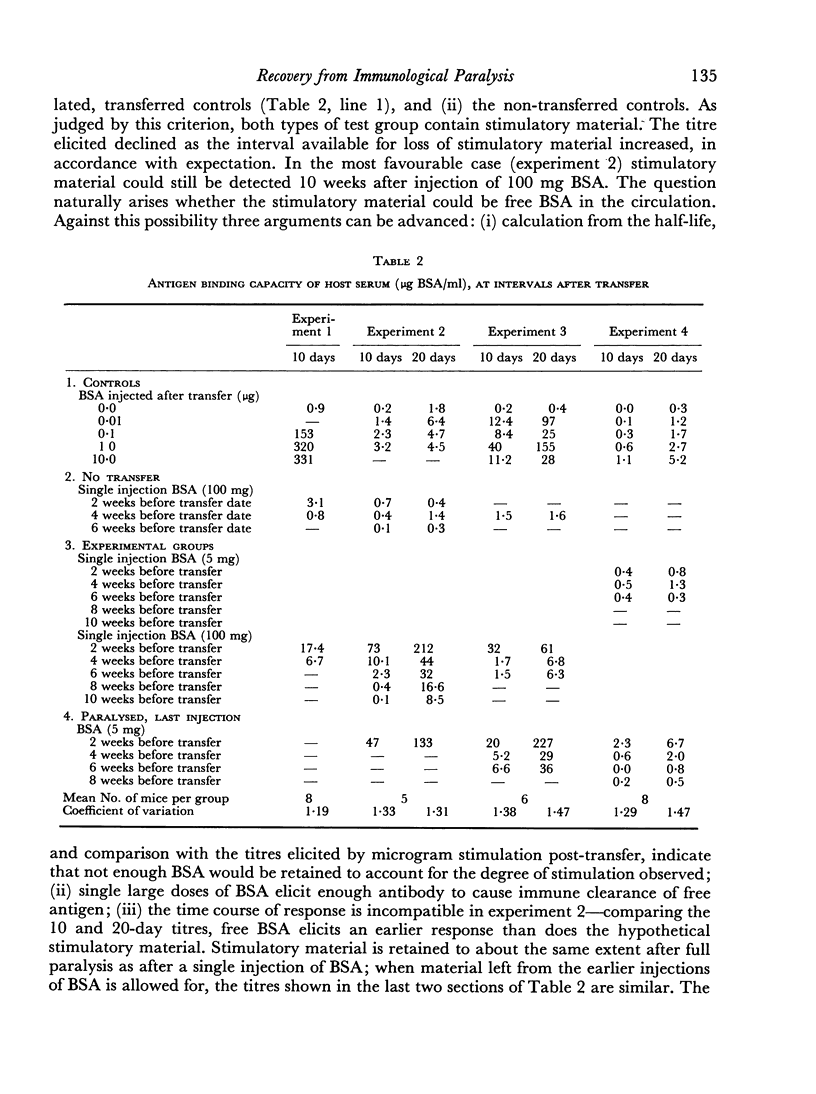
Mice paralysed by bovine serum albumin gradually recover immunological reactivity. Recovery has been mapped at various ages by challenge with antigen in Freund's adjuvant, and comparing the resulting antigen binding capacity of the serum with that of normal controls. Recovery proceeds more rapidly in young than in old animals, irrespective of the duration of previous exposure to antigen. This is considered to confirm the importance of cell turnover in recovery. In harmony with this hypothesis, irradiation proved capable of deleting an existing state of paralysis without appreciably enhancing recovery. A cell transfer test has been used to detect antigen in paralysed animals, supplemented by measurement of radioactivity from [131I]labelled antigen. Antigen can be detected throughout the lag period preceding the start of recovery in quantities probably sufficient to account for the lag.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CAFFREY R. W., RIEKE W. O., EVERETT N. B. Radioautographic studies of small lymphocytes in the thoracic duct of the rat. Acta Haematol. 1962;28:145–154. doi: 10.1159/000207257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLAMAN H. N., TALMAGE D. W. THYMECTOMY: PROLONGATION OF IMMUNOLOGICAL TOLERANCE IN THE ADULT MOUSE. Science. 1963 Sep 20;141(3586):1193–1194. doi: 10.1126/science.141.3586.1193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DENHARDT D. T., OWEN R. D. The resistance of the tolerant state to x-irradiation. Transplant Bull. 1960 Apr;7:394–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIETRICH F. M., WEIGLE W. O. Induction of tolerance to heterologous proteins and their catabolism in C57BL/6 mice. J Exp Med. 1963 Apr 1;117:621–631. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.4.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELTON L. D., KAUFFMANN G., PRESCOTT B., OTTINGER B. Studies on the mechanism of the immunological paralysis induced in mice by pneumococcal polysaccharides. J Immunol. 1955 Jan;74(1):17–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMPHREY J. H. IMMUNOLOGICAL UNRESPONSIVENESS TO PROTEIN ANTIGENS IN RABBITS. I. THE DURATION OF UNRESPONSIVENESS FOLLOWING A SINGLE INJECTION AT BIRTH. Immunology. 1964 Jul;7:449–461. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN M. E., COONS A. H., DEANE H. W. Localization of antigen in tissue cells; cellular distribution of pneumococcal polysaccharides types II and III in the mouse. J Exp Med. 1950 Jan 1;91(1):15-30, 4 pl. doi: 10.1084/jem.91.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAKELA O., NOSSAL G. J. Accelerated breakdown of immunological tolerance following whole body irradiation. J Immunol. 1962 May;88:613–620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHISON N. A. INDUCTION OF IMMUNOLOGICAL PARALYSIS IN TWO ZONES OF DOSAGE. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1964 Dec 15;161:275–292. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1964.0093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHISON N. A. Tolerance of erythrocytes in poultry: loss and abolition. Immunology. 1962 May;5:359–369. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä O., Mitchison N. A. The effect of antigen dosage on the response of adoptively transferred cells. Immunology. 1965 Jun;8(6):549–556. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä O., Mitchison N. A. The role of cell number and source in adoptive immunity. Immunology. 1965 Jun;8(6):539–548. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SERCARZ E., COONS A. H. Specific inhibition of antibody formation during immunological paralysis and unresponsiveness. Nature. 1959 Oct 3;184(Suppl 14):1080–1082. doi: 10.1038/1841080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SISKIND G. W., PATERSON P. Y., THOMAS L. INDUCTION OF UNRESPONSIVENESS AND IMMUNITY IN NEWBORN AND ADULT MICE WITH PNEUMOCOCCAL POLYSACCHARIDE. J Immunol. 1963 Jun;90:929–934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR R. B. AN EFFECT OF THYMECTOMY ON RECOVERY FROM IMMUNOLOGICAL PARALYSIS. Immunology. 1964 Sep;7:595–602. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERRES G., HUGHES W. L. Acquired immune tolerance in mice to crystalline bovine serum albumin. J Immunol. 1959 Nov;83:459–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


