Abstract
Circulating antibodies to Eimeria stiedae have been demonstrated in rabbit serum using precipitation in gel and liquid media and complement fixation tests.
Sera prepared by subcutaneous injections of antigen were similar to those obtained after oral infection with oocysts of E. stiedae.
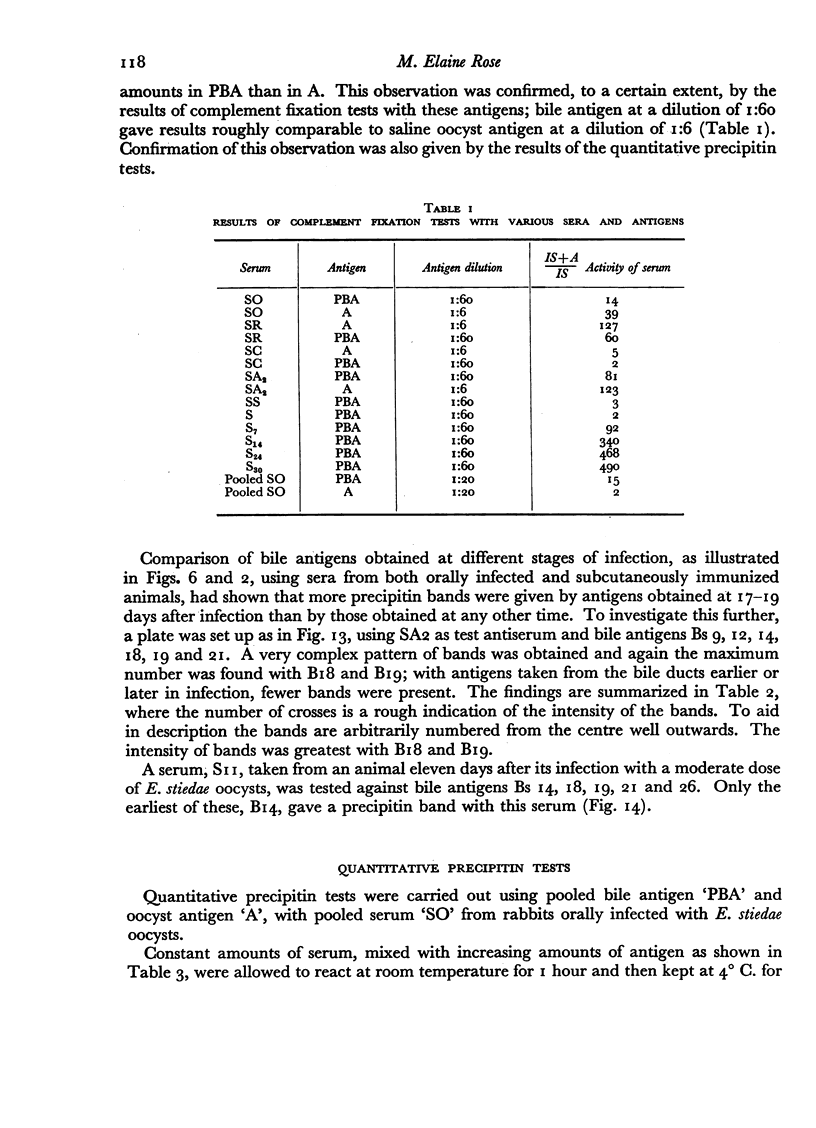
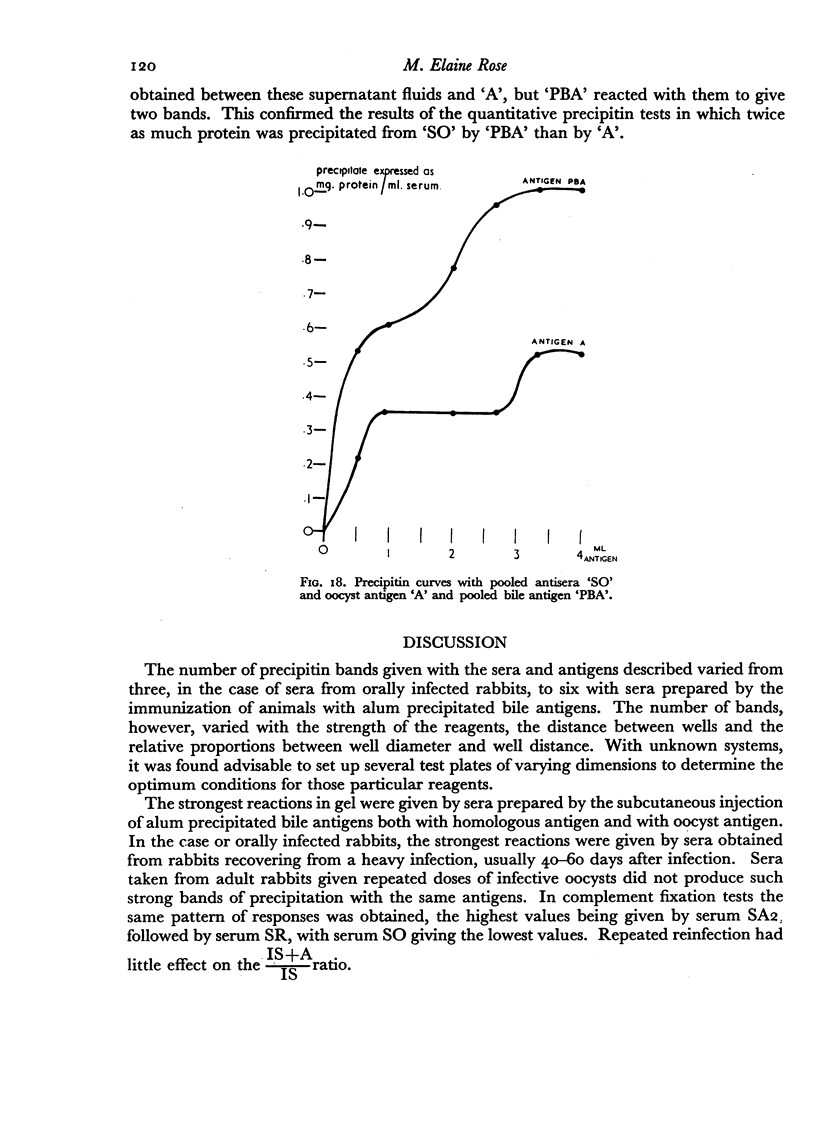
Antigens prepared from crushed oocysts and the exudate of infected bile ducts had similar properties, although a constituent of the bile duct antigen was absent or only present in very small amounts in the oocyst antigen.
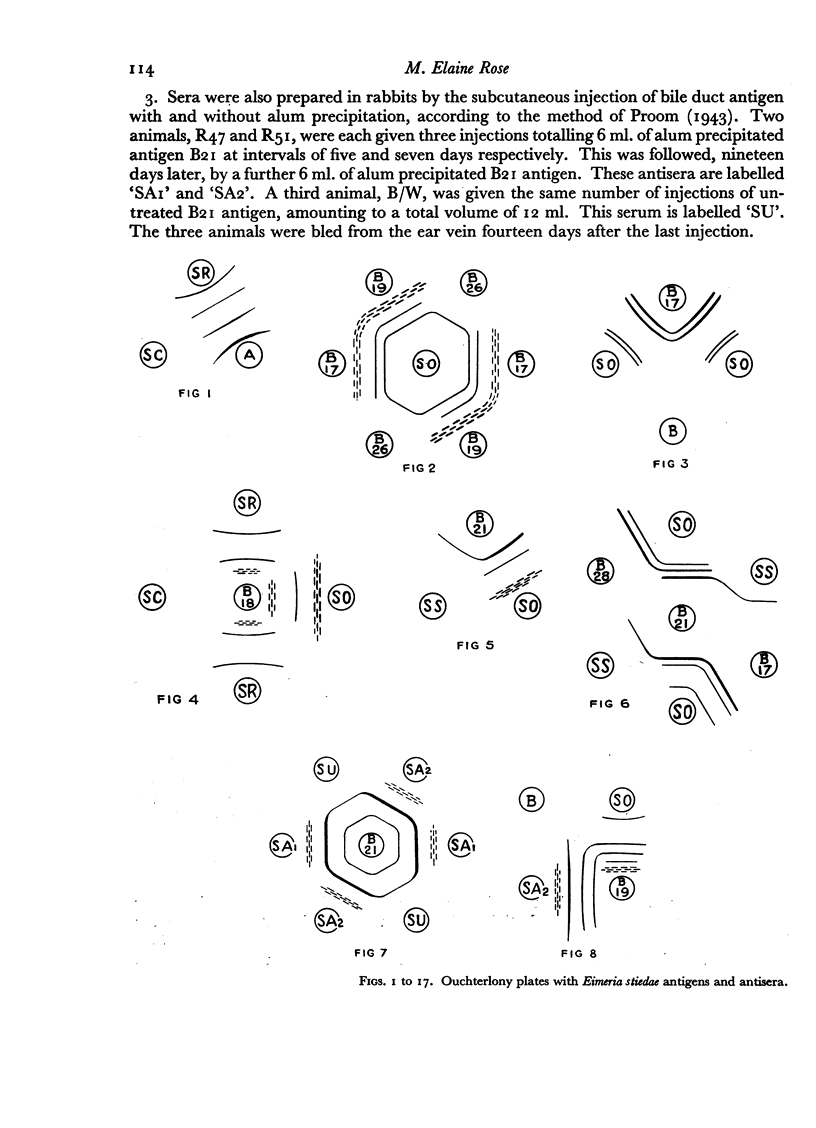
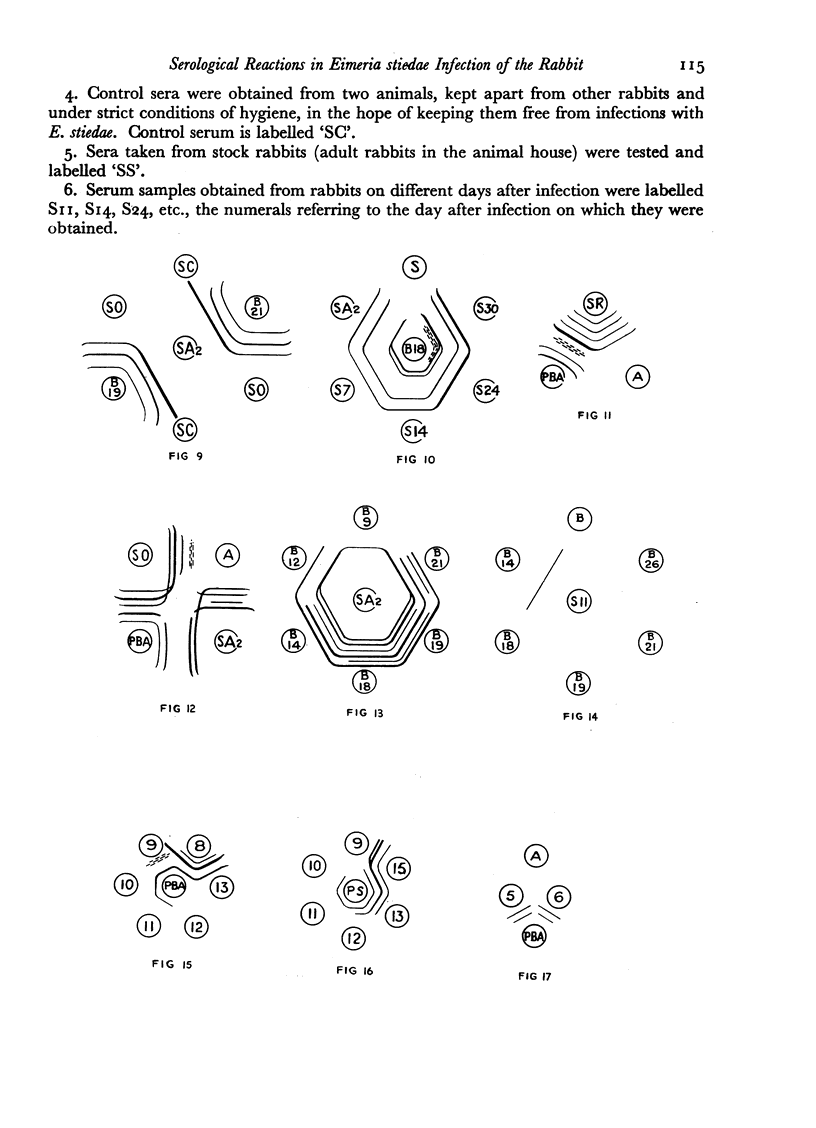
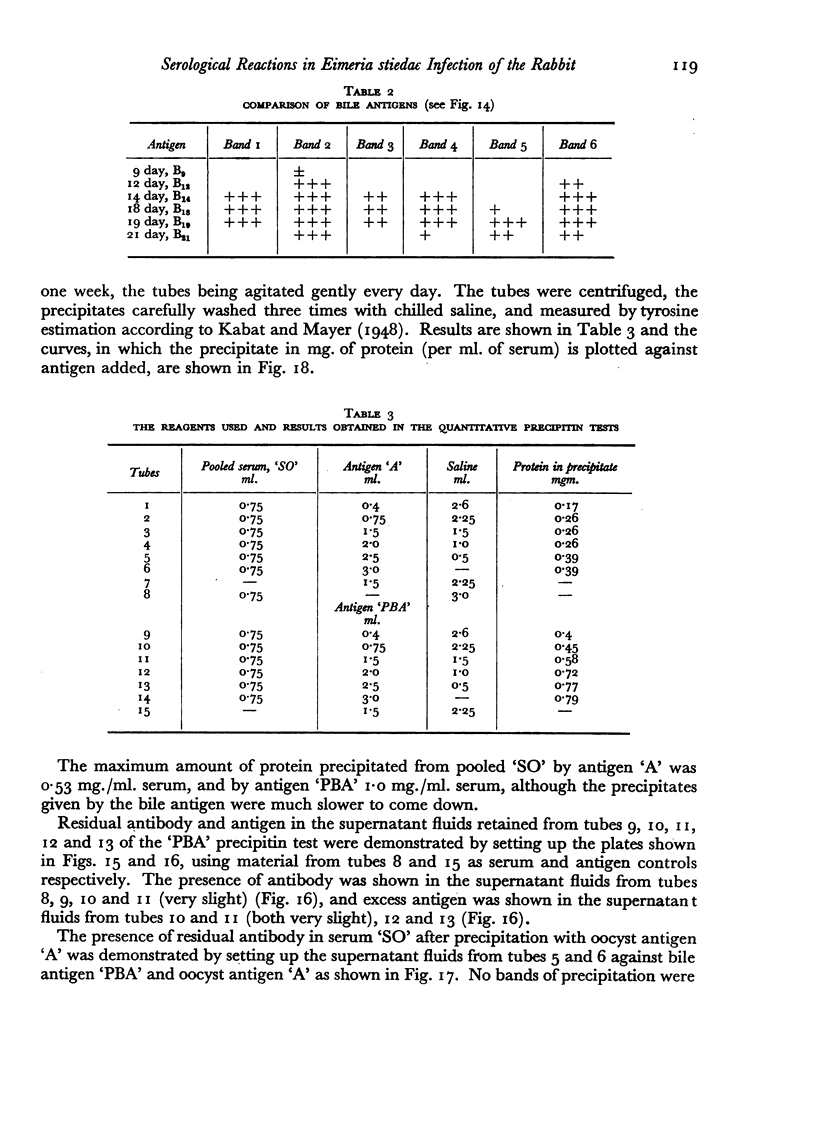
Antigens obtained on different days after infection from bile ducts showed differing precipitation patterns in gel; the maximum number of bands was given by antigens obtained 17–19 days after infection, antigens taken before and after this period reacted to give fewer precipitation bands.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- OUDIN J. B. Specific precipitation in gels and its application to immunochemical analysis. Methods Med Res. 1952;5:335–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


