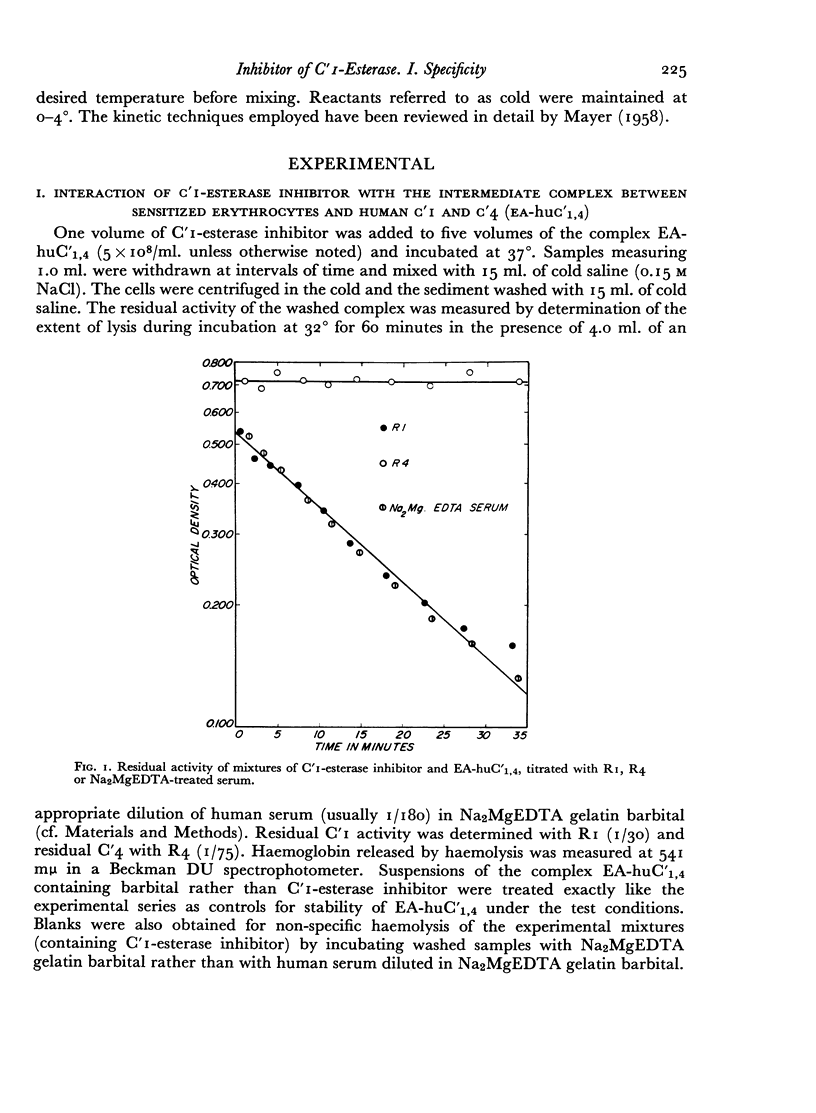
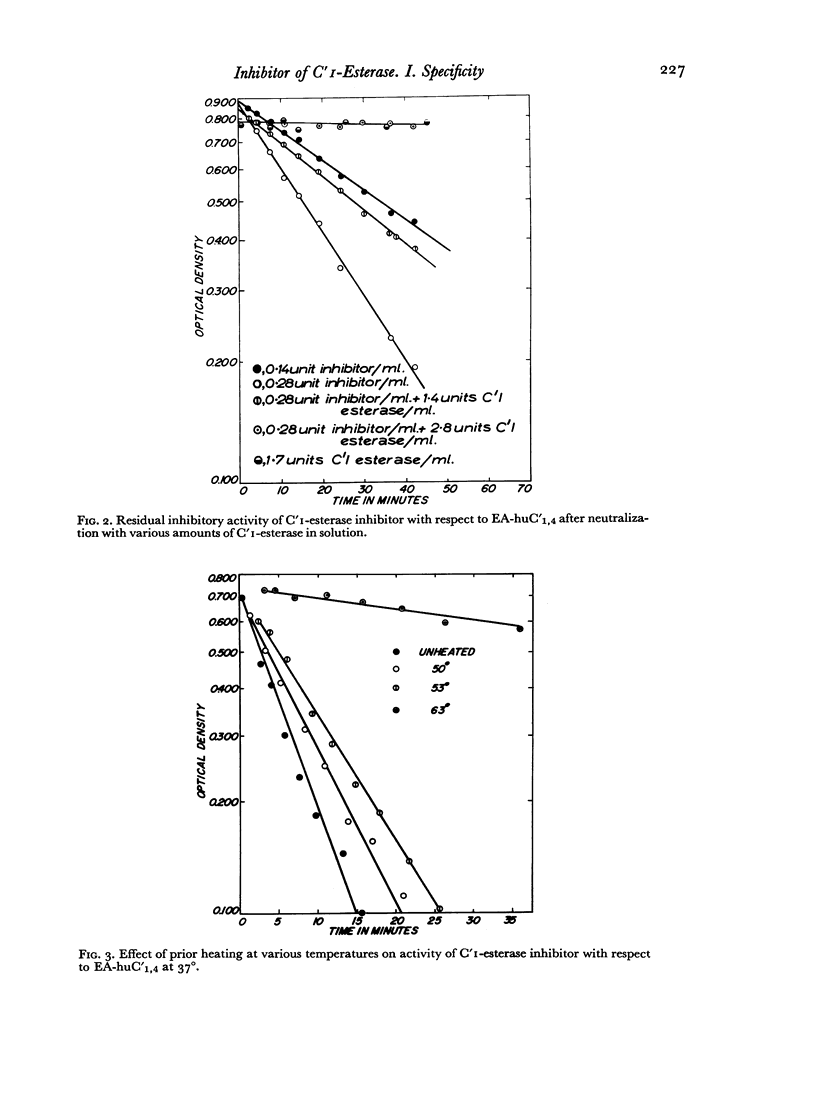
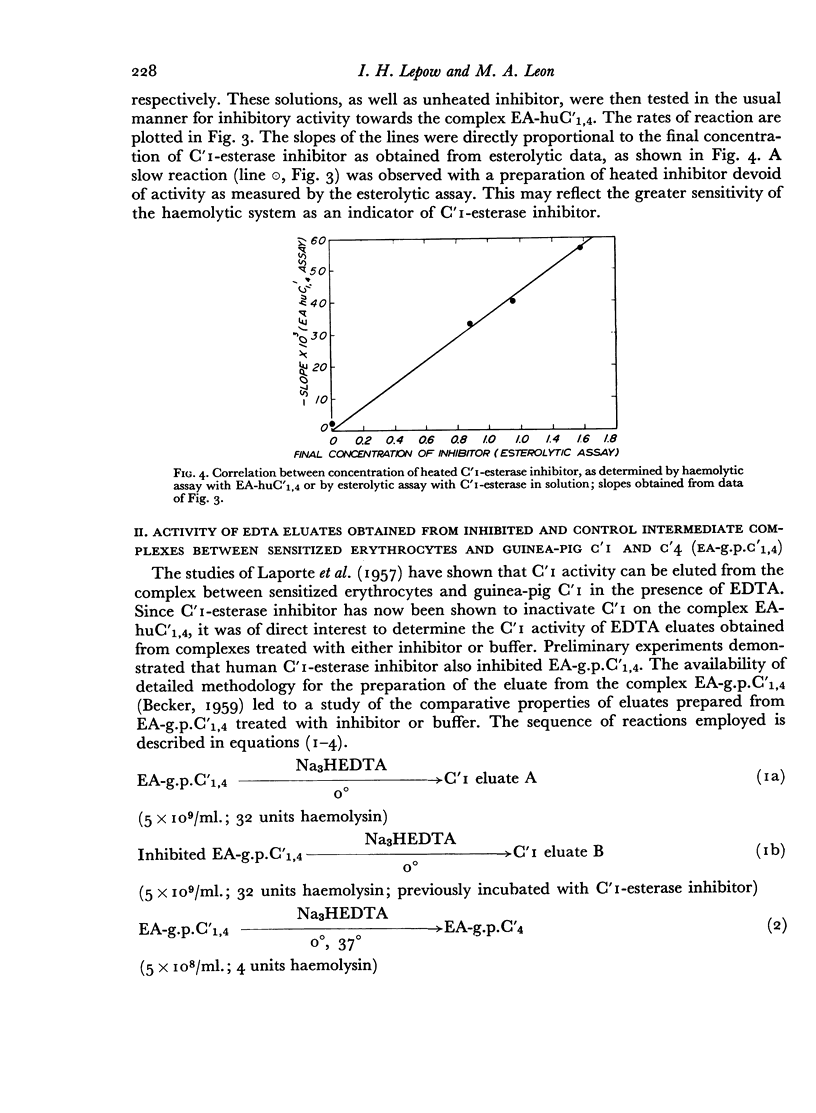
Abstract
An investigation is described of the interaction of a highly purified human serum inhibitor of C′1-esterase with various intermediate complexes of sensitized sheep erythrocytes and human or guinea-pig complement. The inhibitor reacted with and blocked specifically the activity of C′1 on these complexes. There was a direct correlation, by several criteria, between the ability of the inhibitor to block esterolytic activity of C′1-esterase in solution and its ability to inhibit C′1 activity on the intermediate complexes, implying the participation of C′1-esterase in immune haemolysis. Prior interaction of the inhibitor with complexes between sensitized erythrocytes and C′1 and C′4 prevented subsequent reaction of these complexes with C′2. However, once the complex between sensitized erythrocytes and C′1, C′4 and C′2 had been formed, the inhibitor was no longer effective in preventing haemolysis. These data suggested a biochemical function for C′1-esterase in reactions involving C′4 and C′2 but not in further steps leading to immune haemolysis.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BECKER E. L. Concerning the mechanism of complement action. IV. The properties of activated first component of guinea pig complement. J Immunol. 1959 Jan;82(1):43–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BECKER E. L. Concerning the mechanism of complement action. V. The early steps in immune hemolysis. J Immunol. 1960 Mar;84:299–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BECKER E. L. Inhibition of complement activity by di-isopropyl fluorophosphate. Nature. 1955 Dec 3;176(4492):1073–1073. doi: 10.1038/1761073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARDRE DE LOOZE L., LAPORTE R., SILLARD R. Contribution à l'étude du complément. II. Premiers stades de l'action hémolytique du complément; rôle particulier du premier composant. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1957 Jan;92(1):15–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENT J. F., OTERO A. G., HARRIGAN R. E. Relative specificity of serologic tests for syphilis in Mycobacterium leprae infection. Am J Clin Pathol. 1957 May;27(5):539–545. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/27.5.539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEON M. A. Kinetics of human complement. III. Intermediates in the reaction between human complement and sensitized cells. J Immunol. 1957 Dec;79(6):480–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEON M. A. Kinetics of human complement. V. Decay of the intermediate complex EAhuC'A. J Immunol. 1959 Sep;83:291–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEON M. A. Quantitative studies on the properdin-complement system. II. Kinetics of the reaction between properdin and zymosan. J Exp Med. 1957 May 1;105(5):403–415. doi: 10.1084/jem.105.5.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEPOW I. H., PILLEMER L. Studies on the mechanism of inactivation of human complement by plasmin and by antigen-antibody aggregates. II. Demonstration of two distinct reaction stages in complement fixation. J Immunol. 1955 Jul;75(1):63–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEPOW I. H., WURZ L., RATNOFF O. D., PILLEMER L. Studies on the mechanism of inactivation of human complement by plasmin and by antigen-antibody aggregates. I. The requirement for a factor resembling C'1 and the role of Ca++. J Immunol. 1954 Sep;73(3):146–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE L., OSLER A. G., MAYER M. M. Studies on the role of Ca++ and Mg++ in complement fixation and immune hemolysis. III. The respective roles of Ca++ and Mg++ in immune hemolysis. J Immunol. 1953 Nov;71(5):374–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAYER M. M. Studies on the mechanism of hemolysis by antibody and complement. Prog Allergy. 1958;5:215–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PENSKY J., LEVY L. R., LEPOW I. H. Partial purification of a serum inhibitor of C'1-esterase. J Biol Chem. 1961 Jun;236:1674–1679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RATNOFF O. D., LEPOW I. H. Some properties of an esterase derived from preparations of the first component of complement. J Exp Med. 1957 Aug 1;106(2):327–343. doi: 10.1084/jem.106.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


