Abstract
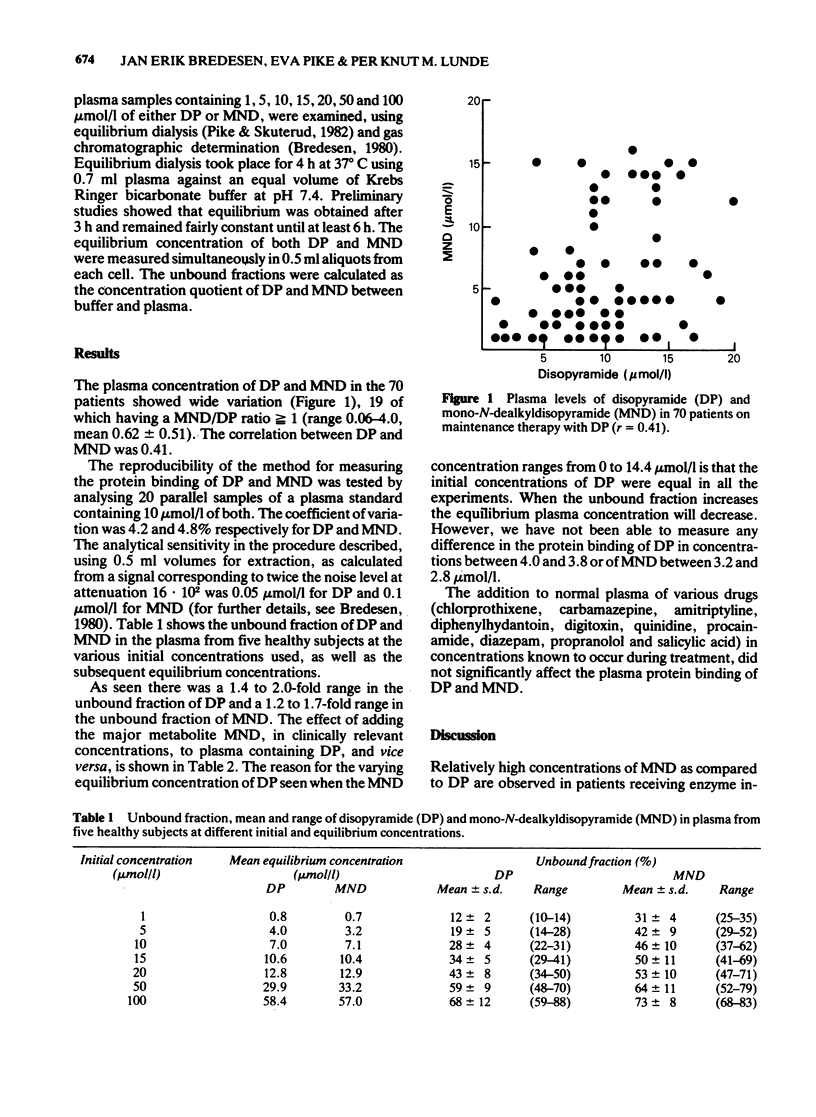
1 Measuring total plasma levels of disopyramide (DP) and the main metabolite mono-N-dealkyldisopyramide (MND) in patients on maintenance therapy with DP has shown concentrations of MND comparable with those of DP, with wide intersubject variations. 2 A method which permits simultaneous measurement of unbound fraction of DP and MND has been developed. 3 In healthy subjects the unbound fraction of both DP and MND was concentration dependent, i.e. increased with higher concentrations of DP or MND. 4 The plasma protein binding of DP is altered by varying concentrations of MND. Clinically relevant concentrations of MND may increase the unbound fraction of DP approximately twofold. 5 The plasma protein binding of MND is also altered by varying concentrations of DP. Variation in the concentration of DP from the lower to the upper part of the therapeutic range may cause a 1.5-fold increase in the unbound fraction of MND. 6 In the assumed therapeutic range of 6-15 mumol DP/L, the interpatient variance of unbound DP concentration might be ten-fold or even higher. The present findings indicate the need for monitoring unbound drug concentrations in any attempt to establish plasma concentration/effect relationship.
Full text
PDF
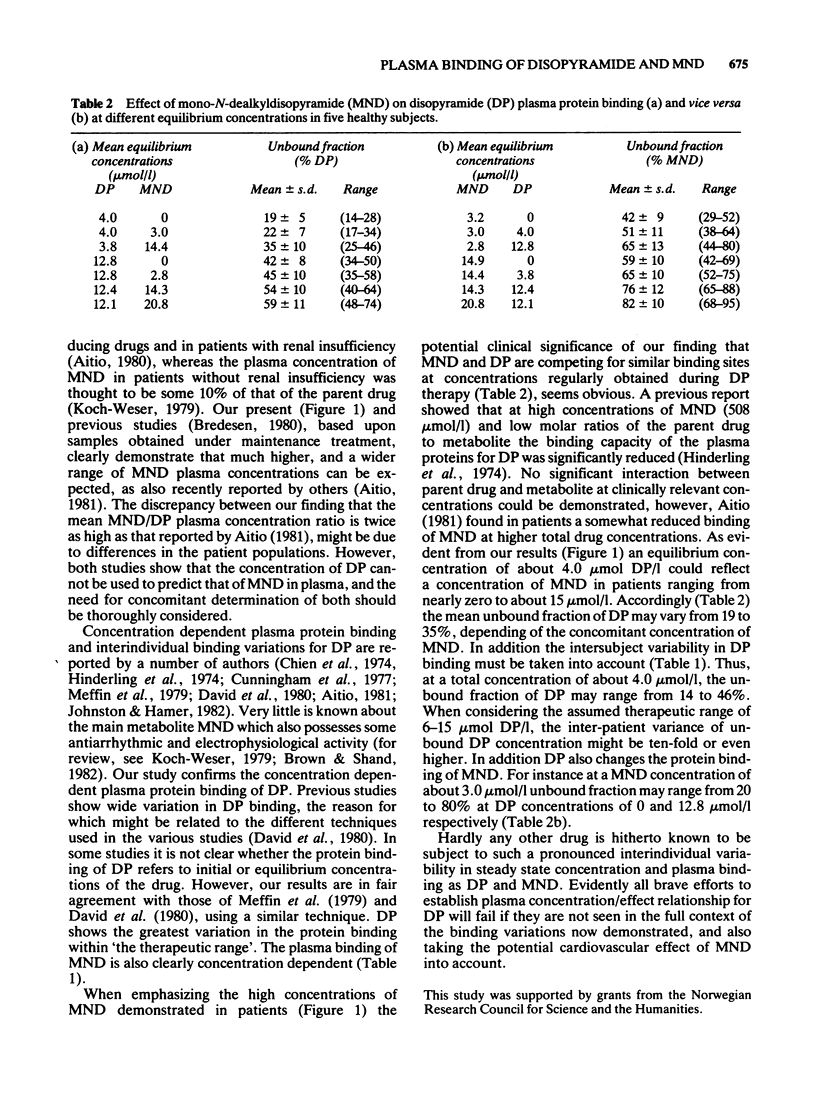

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aitio M. L. Plasma concentrations and protein binding of disopyramide and mono-N-dealkyldisopyramide during chronic oral disopyramide therapy. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1981 Apr;11(4):369–375. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1981.tb01134.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aitio M. L., Vuorenmaa T. Enhanced metabolism and diminished efficacy of disopyramide by enzyme induction? Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1980 Feb;9(2):149–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1980.tb05825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredesen J. E. Gas-chromatographic determination of disopyramide and its mono-N-dealkylated metabolite in serum with use of a nitrogen-selective detector. Clin Chem. 1980 Apr;26(5):638–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. E., Shand D. G. Therapeutic drug monitoring of antiarrhythmic agents. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1982 Mar-Apr;7(2):125–148. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198207020-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien Y. W., Lambert H. J., Karim A. Comparative binding of disopyramide phosphate and quinidine sulfate to human plasma proteins. J Pharm Sci. 1974 Dec;63(12):1877–1879. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600631210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham J. L., Shen D. D., Shudo I., Azarnoff D. L. The effects of urine pH and plasma protein binding on the renal clearance of disopyramide. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1977 Sep-Oct;2(5):373–383. doi: 10.2165/00003088-197702050-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David B. M., Madsen B. W., Ilett K. F. Plasma binding of disopyramide. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1980 Jun;9(6):614–618. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1980.tb01090.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinderling P. H., Bres J., Garrett E. R. Protein binding and erythrocyte partitioning of disopyramide and its monodealkylated metabolite. J Pharm Sci. 1974 Nov;63(11):1684–1690. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600631103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch-Weser J. Disopyramide. N Engl J Med. 1979 Apr 26;300(17):957–962. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197904263001705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lima J. J., Boudoulas H., Blanford M. Concentration-dependence of disopyramide binding to plasma protein and its influence on kinetics and dynamics. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Dec;219(3):741–747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meffin P. J., Robert E. W., Winkle R. A., Harapat S., Peters F. A., Harrison D. C. Role of concentration-dependent plasma protein binding in disopyramide disposition. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1979 Feb;7(1):29–46. doi: 10.1007/BF01059439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


