Abstract
1 The long-term effects of the oral angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor captopril with the addition of a diuretic (chlorthalidone) were examined in 16 patients with moderate or grave hypertension. Of these, 14 had essential hypertension and two renovascular hypertension.
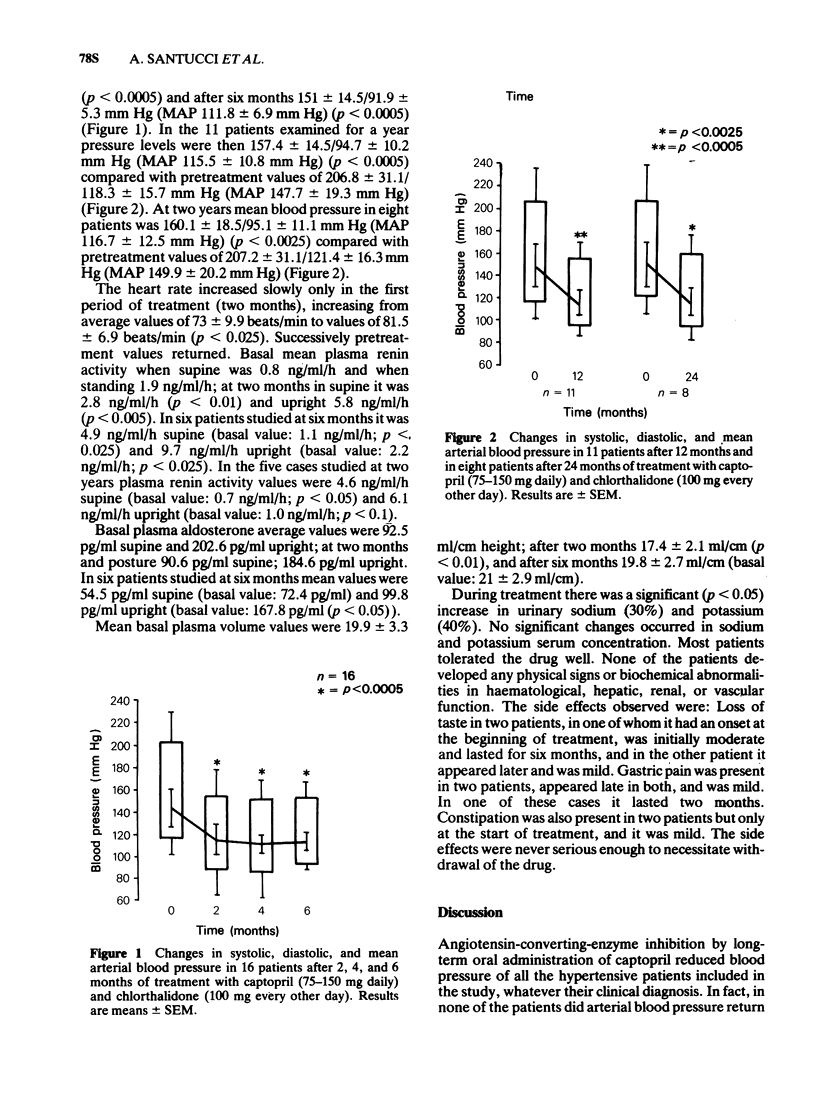
2 Blood pressure fell sharply in all patients and this antihypertensive effect was maintained during 2, 4, 6, 12, and 24-month follow-up periods. The efficacy of treatment was not predicted by basal values of plasma renin activity.
3 Urinary excretion of sodium and potassium increased, but the increases were never such as to modify significantly sodium and potassium serum concentration.
4 The long-term treatment was generally well tolerated.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brunner H. R., Gavras H., Turini G. A., Waeber B., Cappuis P., McKinstry D. N. Long-term treatment of hypertension in man by an orally active angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor. Clin Sci Mol Med Suppl. 1978 Dec;4:293s–295s. doi: 10.1042/cs055293s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner H. R., Gavras H., Waeber B., Kershaw G. R., Turini G. A., Vukovich R. A., McKinstry D. N., Gavras I. Oral angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor in long-term treatment of hypertensive patients. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Jan;90(1):19–23. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-1-19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell B. C., Shepherd A. N., Reid J. L. Effects of the angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor, captopril, in essential hypertension. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1982 Feb;13(2):213–217. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1982.tb01359.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elijovisch F., Krakoff L. R. Captopril associated granulocytopenia in hypertension after renal transplantation. Lancet. 1980 Apr 26;1(8174):927–928. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)90854-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber E., Koerner T., Page L. B., Kliman B., Purnode A. Application of a radioimmunoassay for angiotensin I to the physiologic measurements of plasma renin activity in normal human subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1969 Oct;29(10):1349–1355. doi: 10.1210/jcem-29-10-1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoorntje S. J., Kallenberg C. G., Weening J. J., Donker A. J., The T. H., Hoedemaeker P. J. Immune-complex glomerulopathy in patients treated with captopril. Lancet. 1980 Jun 7;1(8180):1212–1215. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91677-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staessen J., Fagard R., Lijnen P., Amery A. Captopril and agranulocytosis. Lancet. 1980 Apr 26;1(8174):926–927. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)90853-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vetter W., Vetter H., Siegenthaler W. Radioimmunoassay for aldosterone without chromatography. 2. Determination of plasma aldosterone. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1973 Nov;74(3):558–567. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0740558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


