Abstract
1 The effects of 1.0 mg and 2.5 mg lorazepam on learning performance were examined in a double-blind cross-over study using student volunteers. 2 Test conditions were manipulated to prevent rehearsal and to vary the subjects' motivation to perform well. Self-ratings of alertness, motivation to perform well and state anxiety were obtained prior to each test. 3 Performance in arithmetic tasks of varying difficulty was also studied. 4 Lorazepam produced dose-related deficits in verbal and nonsense-syllable learning tasks. A greater proportion of errors in the number of problems attempted in the arithmetic tests reflected an impairment in cognitive function. Lorazepam reduced the number of arithmetic problems that were correctly solved as well as increasing the percentage of errors in the problems attempted. 5 Lorazepam did not significantly decrease motivation to perform well and the lorazepam impairment was found even when the test conditions were manipulated so as to prevent rehearsal. Therefore the learning deficits cannot be explained solely by changes in motivation or impairments in rehearsal. 6 Performance in the learning tasks correlated with ratings of alertness and therefore the deficits observed after administration of lorazepam seem likely to result from the non-specific sedative effect of the drug.
Full text
PDF

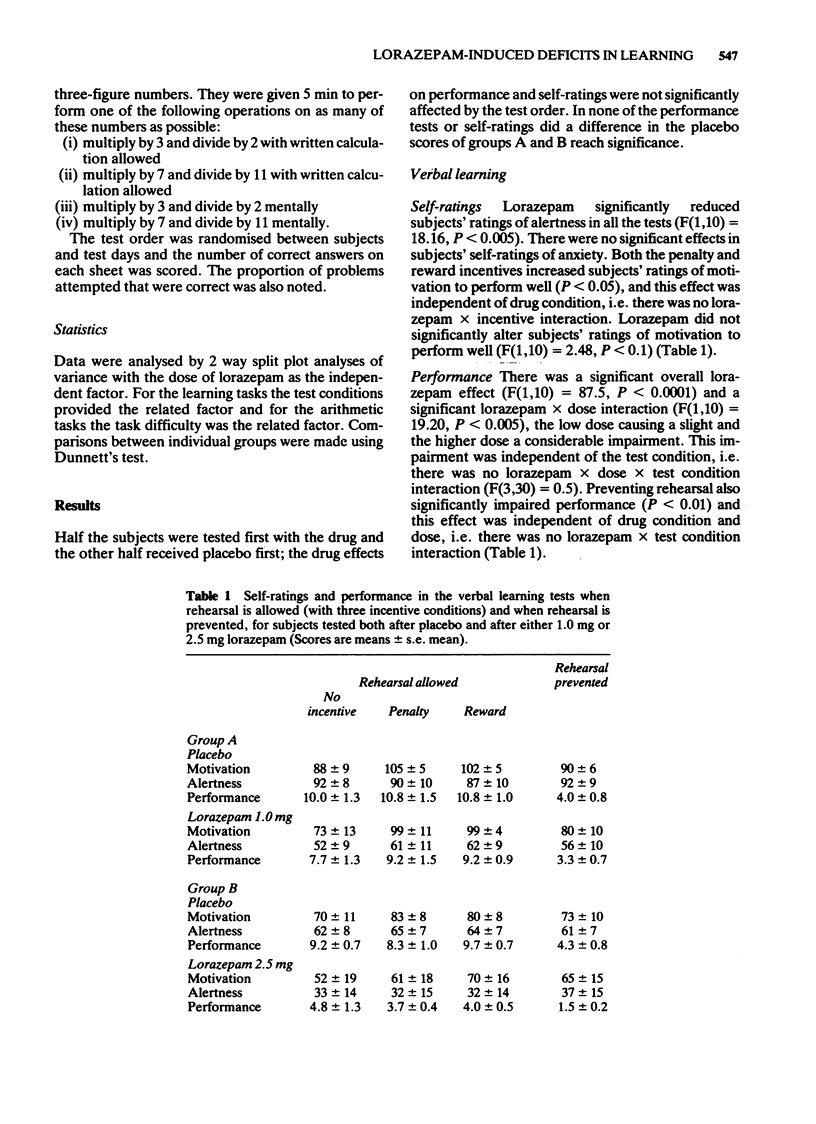
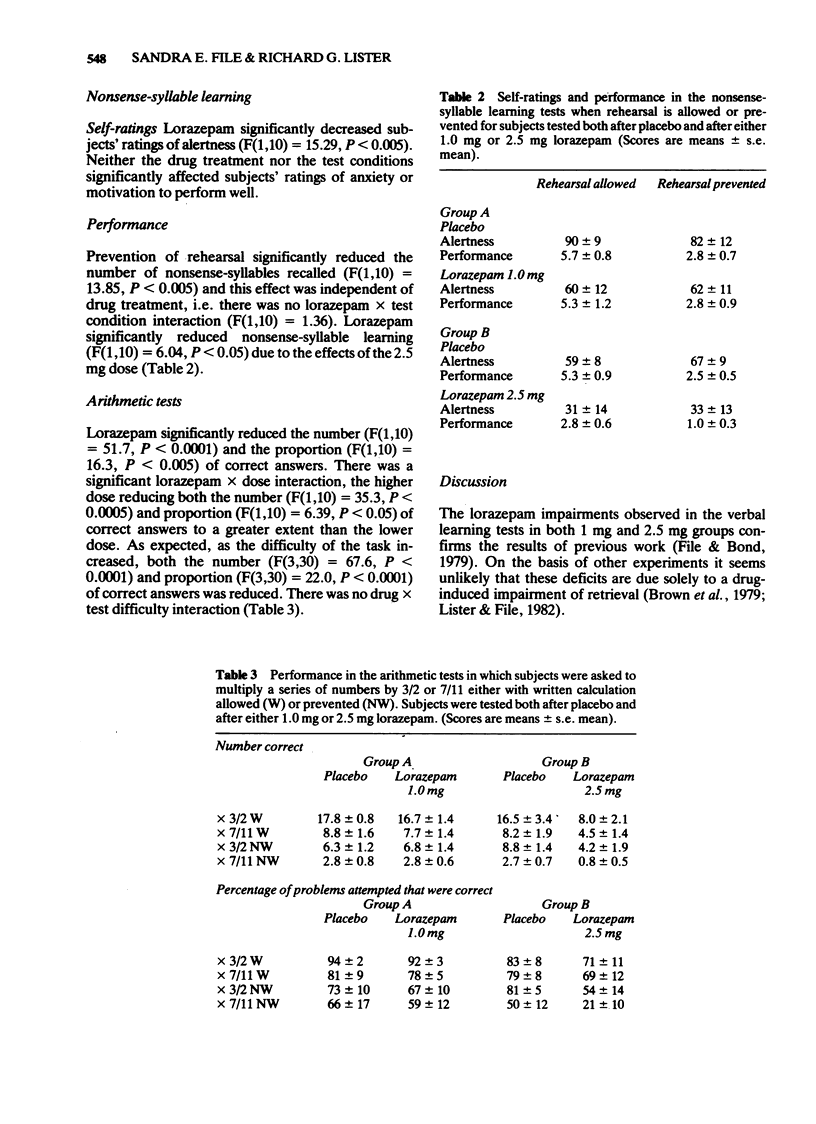


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown J., Lewis V., Brown M. W., Horn G., Bowes J. B. Amnesic effects of intravenous diazepam and lorazepam. Experientia. 1978 Apr 15;34(4):501–502. doi: 10.1007/BF01935954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- File S. E., Bond A. J. Impaired performance and sedation after a single dose of lorazepam. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1979;66(3):309–313. doi: 10.1007/BF00428325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- File S. E., Bond A. J., Lister R. G. Interaction between effects of caffeine and lorazepam in performance tests and self-ratings. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1982 Apr;2(2):102–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt D. J., Shader R. I. Dependence, tolerance, and addiction to benzodiazepines: clinical and pharmacokinetic considerations. Drug Metab Rev. 1978;8(1):13–28. doi: 10.3109/03602537808993775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARLESTON B. W. Test anxiety and performance in problem solving situations. J Pers. 1962 Dec;30:557–573. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-6494.1962.tb01689.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart J., Hill H. M., Bye C. E., Wilkinson R. T., Peck A. W. The effects of low doses of amylobarbitone sodium and diazepam on human performance. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1976 Apr;3(2):289–298. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1976.tb00606.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jochemsen R., van der Graaff M., Boeijinga J. K., Breimer D. D. Influence of sex, menstrual cycle and oral contraception on the disposition of nitrazepam. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1982 Mar;13(3):319–324. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1982.tb01381.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEINSMITH L. J., KAPLAN S. Paired-associate learning as a function of arousal and interpolated interval. J Exp Psychol. 1963 Feb;65:190–193. doi: 10.1037/h0040288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORCHIN S. J., LEVINE S. Anxiety and verbal learning. J Abnorm Psychol. 1957 Mar;54(2):234–240. doi: 10.1037/h0049282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leherissey B. L., O'Neil H. F., Jr, Heinrich D. L., Hansen D. N. Effect of anxiety, response mode, subject matter familiarity, and program length on achievement in computer-assisted learning. J Educ Psychol. 1973 Jun;64(3):310–324. doi: 10.1037/h0034601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljequist R., Palva E., Linnoila M. Effects on learning and memory of 2-week treatments with chlordiazepoxide lactam, N-desmethyldiazepam, oxazepam and methyloxazepam, alone or in combination with alcohol. Int Pharmacopsychiatry. 1979;14(4):190–198. doi: 10.1159/000468381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR J. A. A personality scale of manifest anxiety. J Abnorm Psychol. 1953 Apr;48(2):285–290. doi: 10.1037/h0056264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


