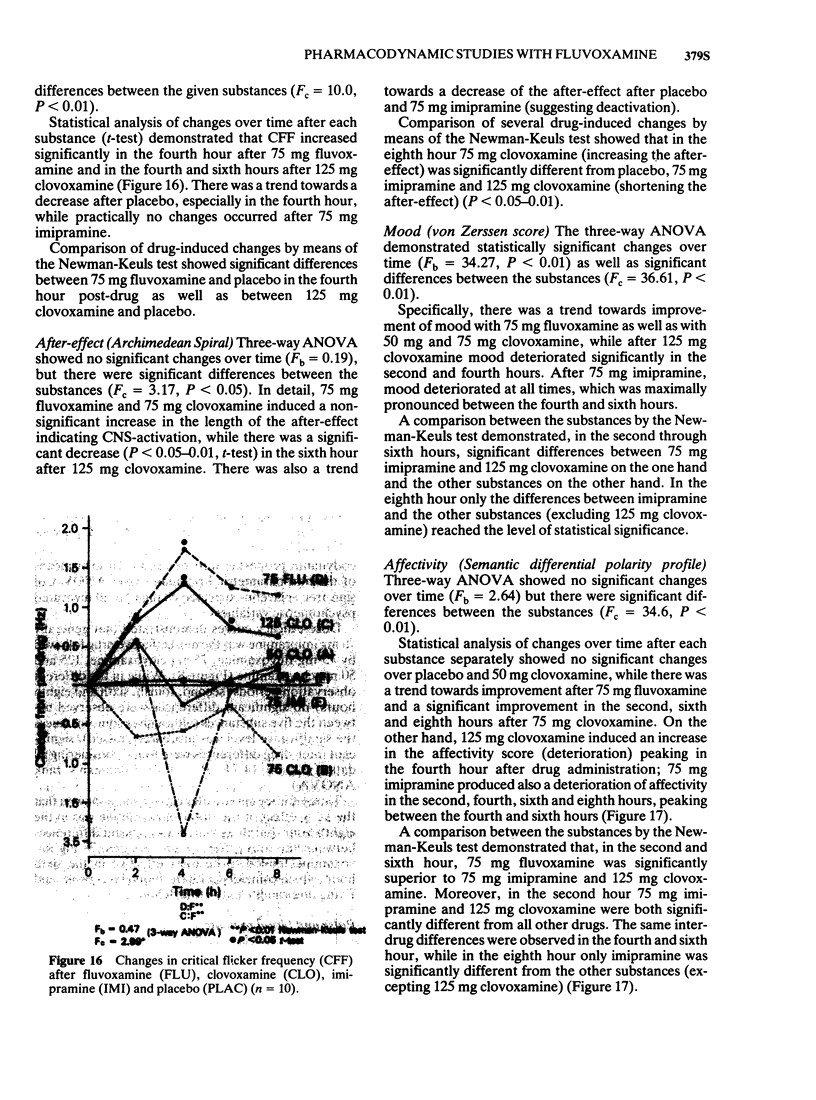
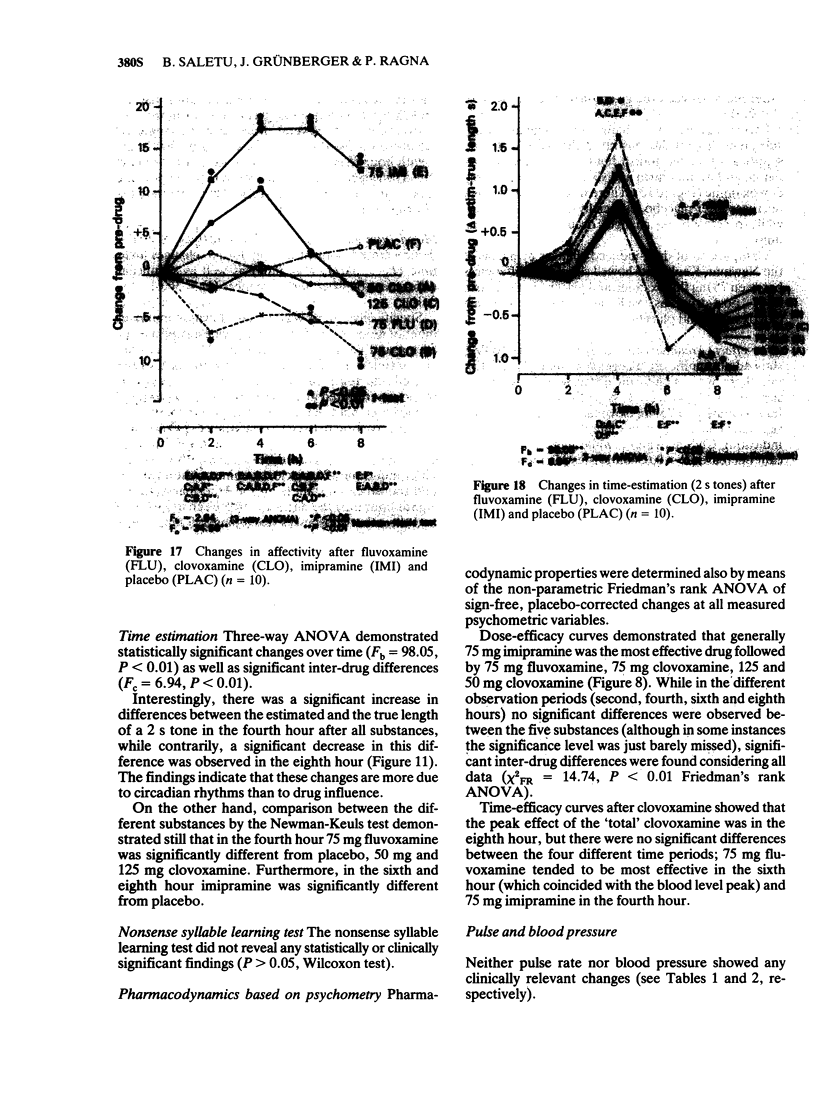
Abstract
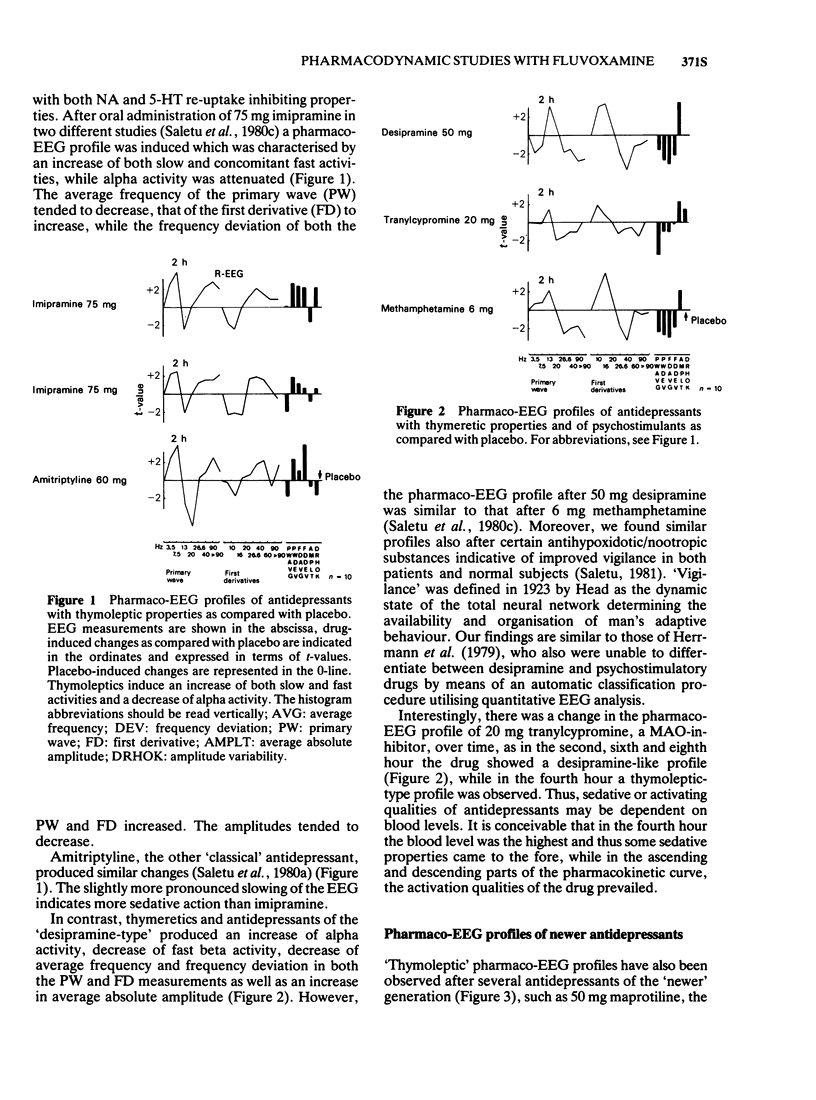
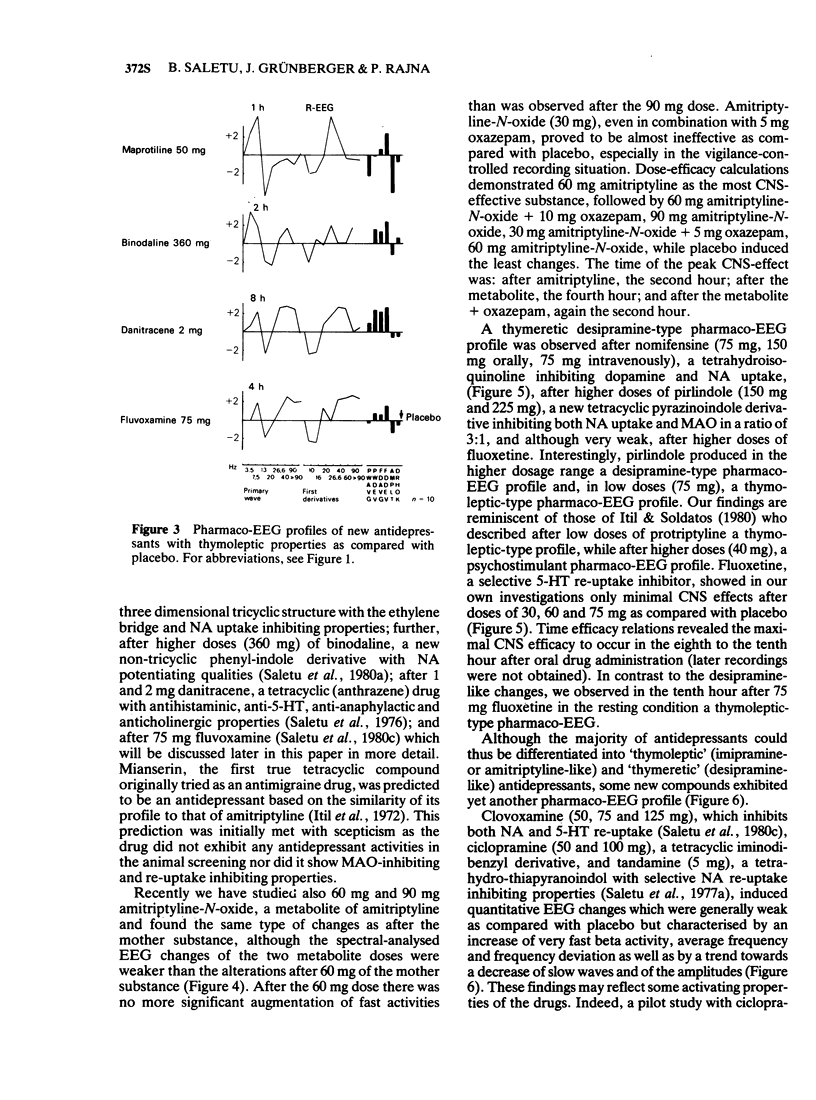
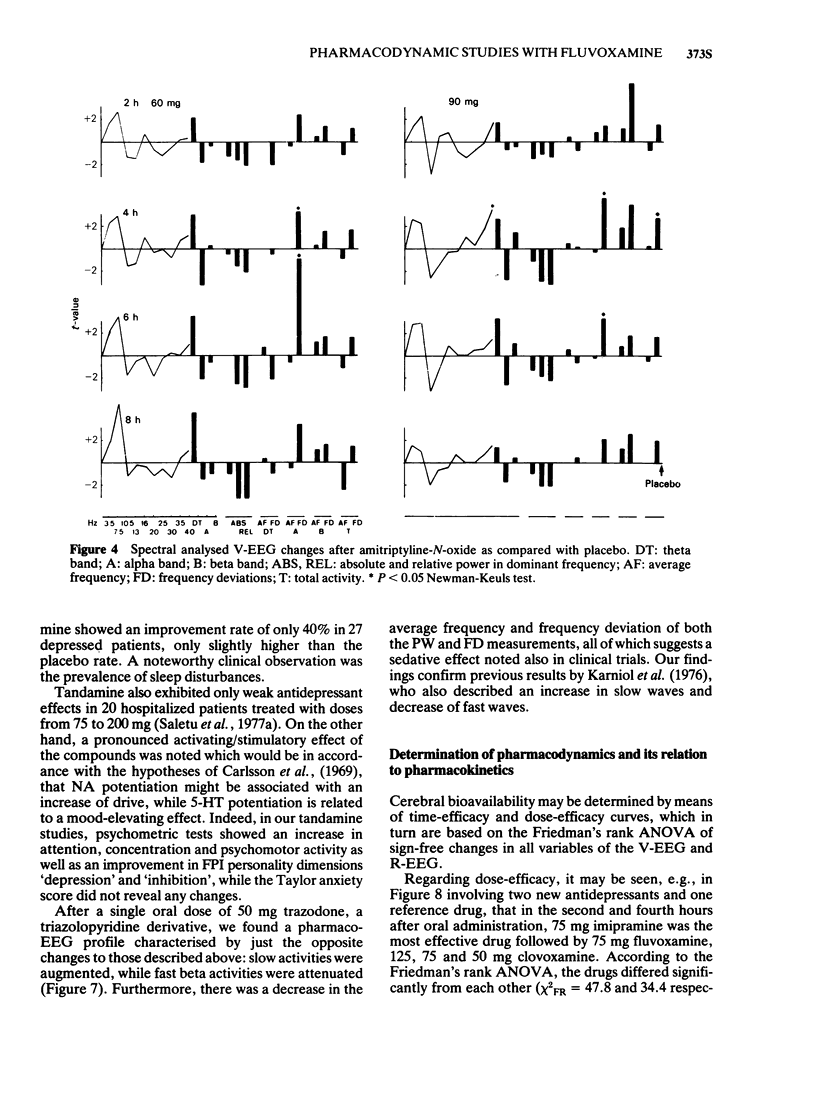
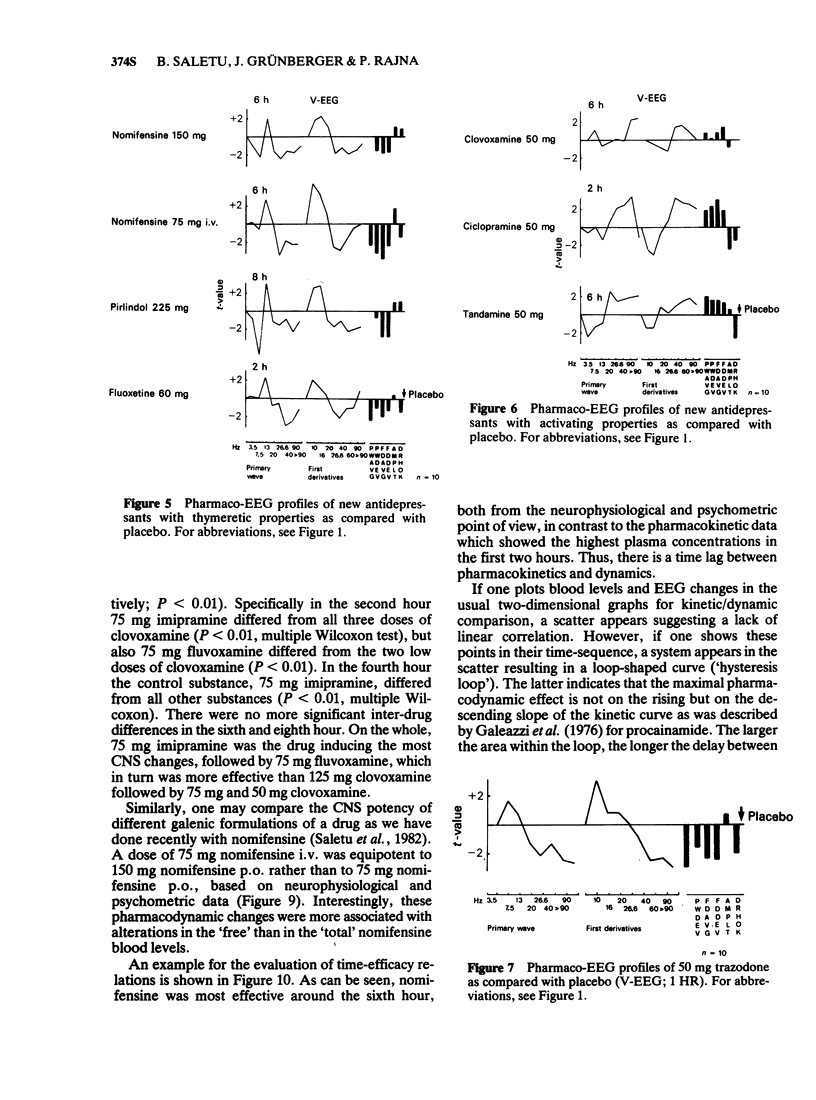
1 Antidepressant drugs produce significant changes in human brain function as reflected in the quantitatively analysed EEG. Two main types of pharmaco-EEG profiles may be differentiated: a thymeretic (desipramine-like) profile characterised mainly by an alpha increase suggesting activating properties and a thymoleptic (imipramine- or amitriptyline-like) profile showing a concomitant increase of slow and fast activities and a decrease in alpha activity indicating also sedative qualities. A small number of compounds exhibit still different profiles.
2 Aside from determining the type of EEG changes, the pharmaco-EEG method seems to be of value in determining time and dose efficacy relations at the target organ, the human brain. Moreover, the relationships between pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics may be determined.
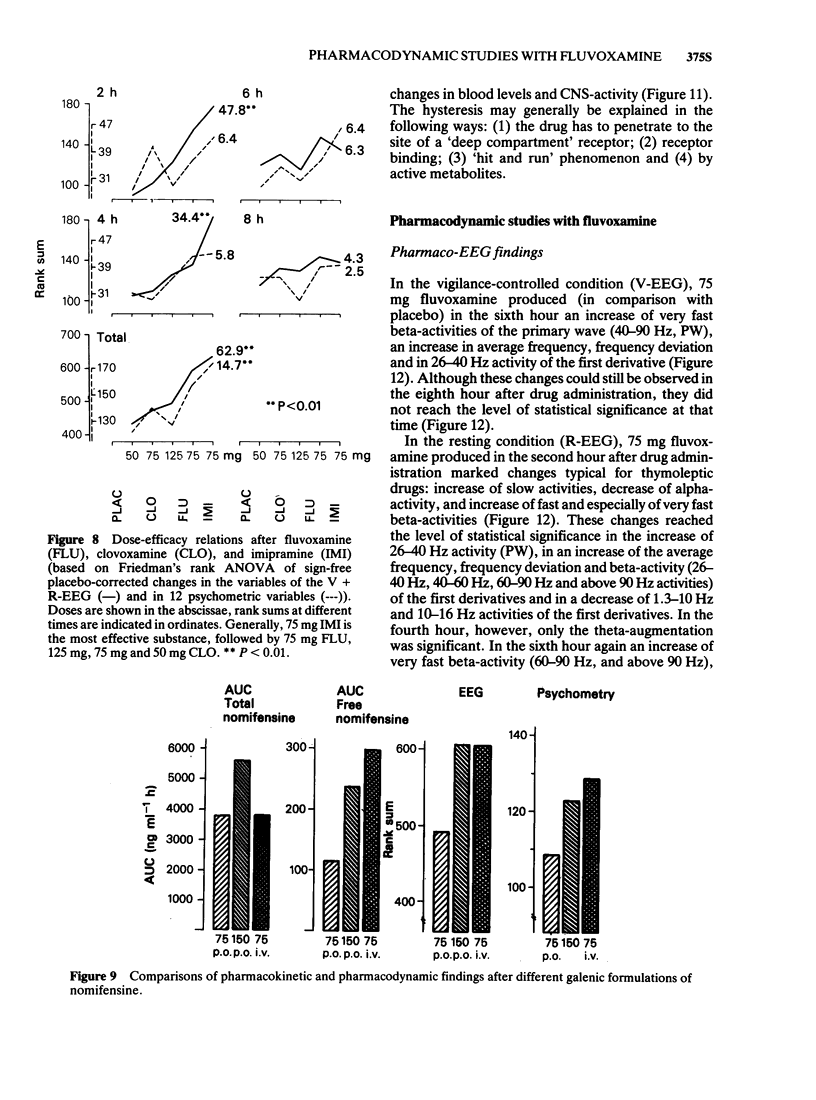
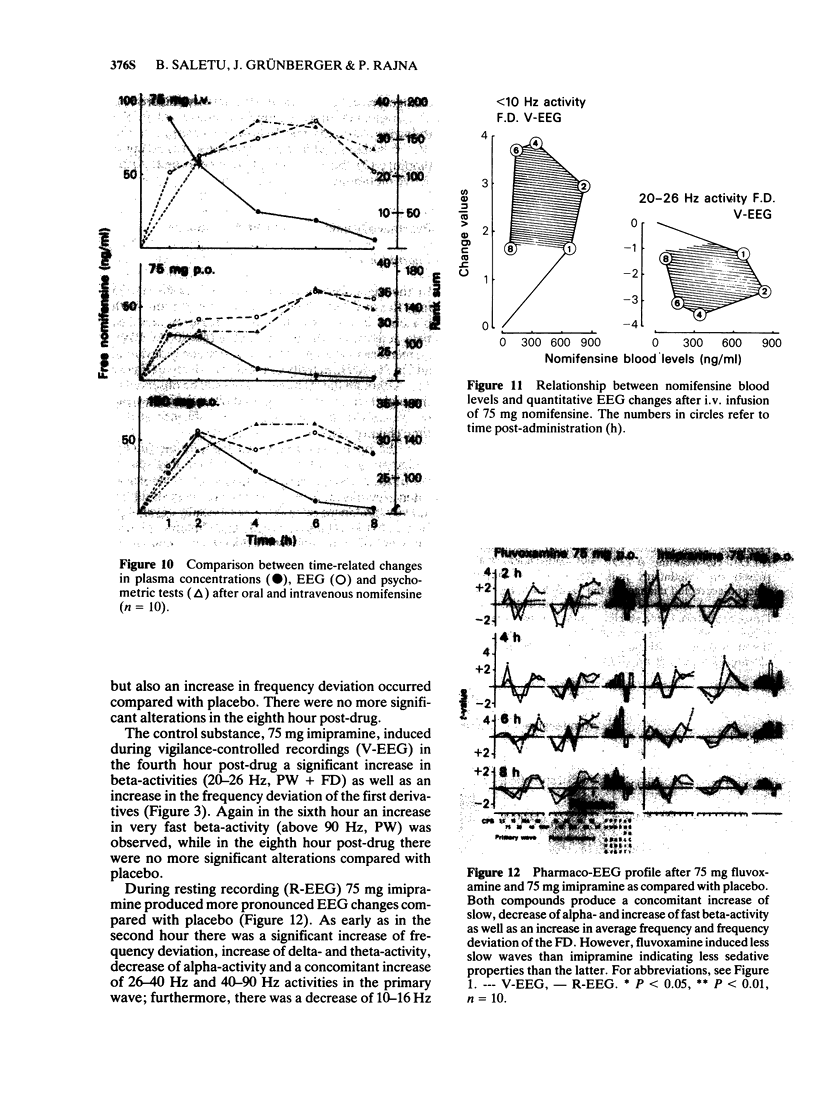
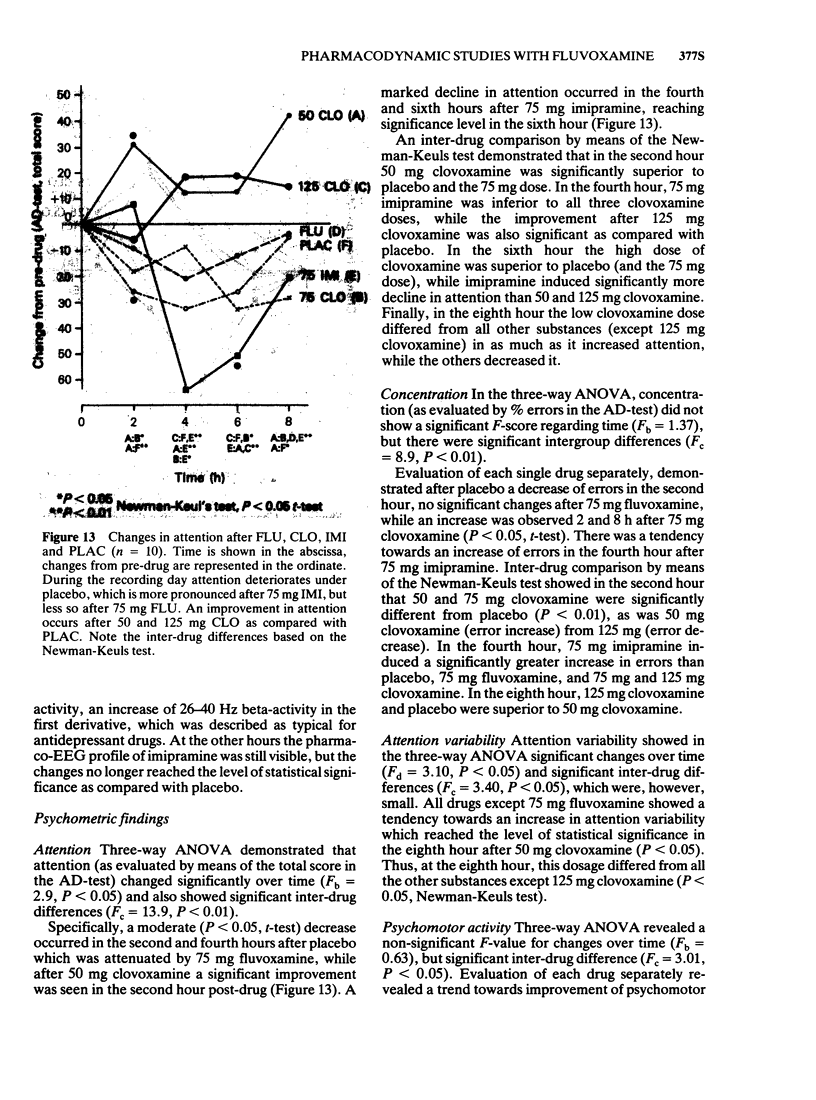
3 Fluvoxamine, a selective 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) re-uptake inhibitor from the new class of 2-aminoethyloximethers of aralkylketones, produced a typical thymoleptic pharmaco-EEG profile after oral doses of 75 mg in a double-blind placebo-controlled study involving 10 healthy volunteers. Fluvoxamine (75 mg) induced less augmentation of slow activity than 75 mg imipramine, indicating less sedative properties of fluvoxamine than imipramine.
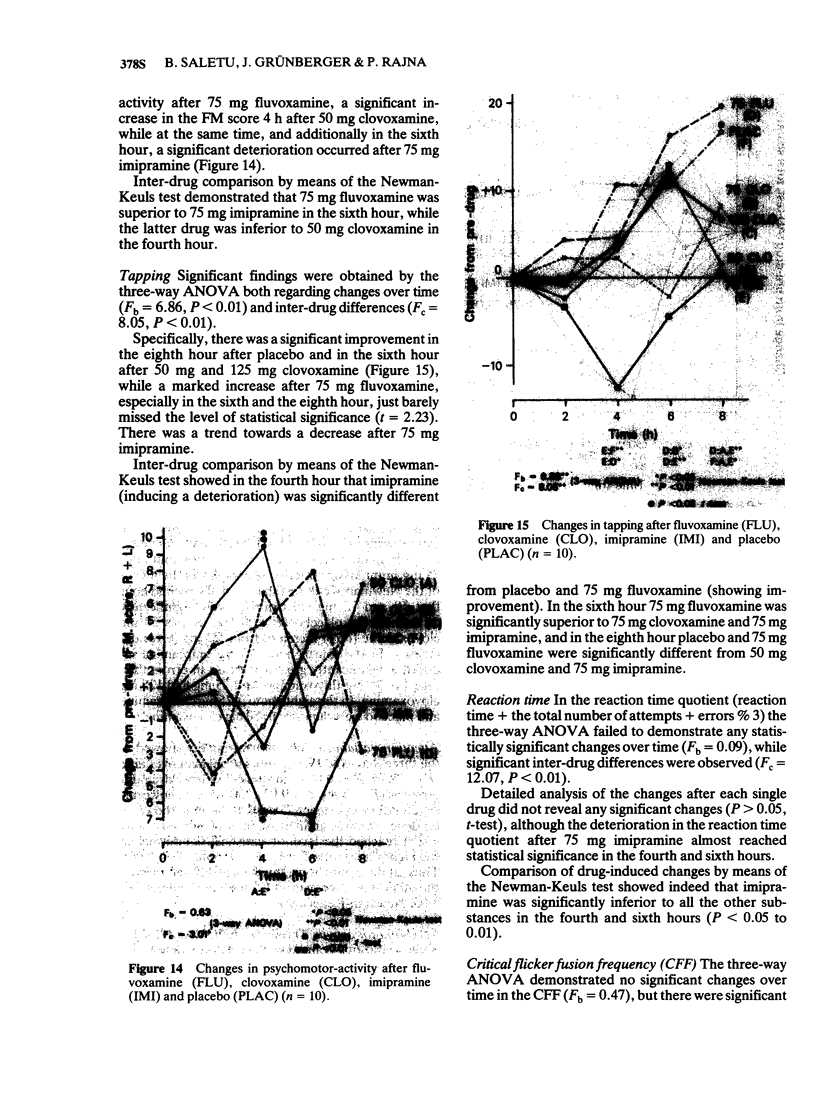
4 After 75 mg fluvoxamine psychometric tests demonstrated a tendency towards an improvement in attention, concentration, psychomotor activity, after-effect and mood and a significant increase in critical flicker fusion frequency as compared with placebo. Comparison with the reference drug, 75 mg imipramine, revealed a significant superiority of fluvoxamine regarding concentration, psychomotor activity, tapping, reaction time, mood and affectivity.
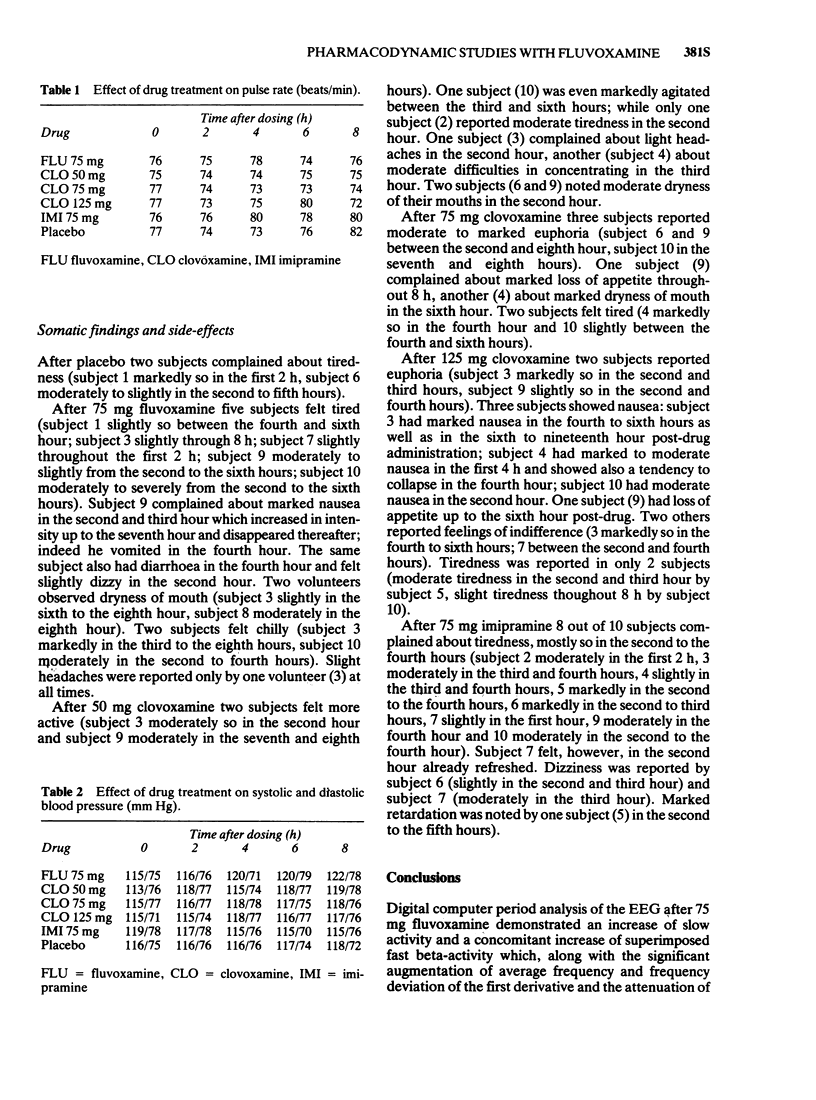
5 Side-effects (mostly tiredness) were seen in five out of 10 subjects after 75 mg fluvoxamine and in eight out of 10 subjects after 75 mg imipramine. There were no clinically relevant changes in pulse, systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carlsson A., Corrodi H., Fuxe K., Hökfelt T. Effect of antidepressant drugs on the depletion of intraneuronal brain 5-hydroxytryptamine stores caused by 4-methyl-alpha-ethyl-meta-tyramine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1969 Mar;5(4):357–366. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(69)90113-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink M. EEG and human psychopharmacology. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1969;9:241–258. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.09.040169.001325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galeazzi R. L., Benet L. Z., Sheiner L. B. Relationship between the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of procainamide. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1976 Sep;20(3):278–289. doi: 10.1002/cpt1976203278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grünberger J., Saletu B. Determination of pharmacodynamics of psychotropic drugs by psychometric analysis. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol. 1980;4(4-5):417–434. doi: 10.1016/0364-7722(80)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann W. M., Fichte K., Itil T. M., Kubicki S. Development of a classification rule for four clinical therapeutic psychotropic drug classes with EEG power-spectrum variables of human volunteers. Pharmakopsychiatr Neuropsychopharmakol. 1979 Jan;12(1):20–34. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1094591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itil T. M., Polvan N., Hsu W. Clinical and EEG effects of GB-94, a "tetracyclic" antidepressant (EEG model in discovery of a new psychotropic drug). Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 1972 Jul;14(7):395–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karniol I. G., Dalton J., Lader M. Comparative psychotropic effects of trazodone, imipramine and diazepam in normal subjects. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 1976 Sep;20(3):337–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saletu B., Grünberger J., Flener R., Linzmayer L., Sieroslawski H. Determination of psychoactivity and cerebral bioavailability of danitracene (WA 335) by quantitative pharmaco-EEG and psychometric investigations. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 1976 Dec;20(6):810–821. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saletu B., Krieger P., Grünberger J., Schanda H., Sletten I. Tandamine--a new norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor. Clinical, psychometric and quantitative EEG studies in depressed patients. Int Pharmacopsychiatry. 1977;12(3):137–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saletu B., Schjerve M., Grünberger J., Schanda H., Arnold O. H. Fluvoxamine-a new serotonin re-uptake inhibitor: first clinical and psychometric experiences in depressed patients. J Neural Transm. 1977;41(1):17–36. doi: 10.1007/BF01252962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Zerssen D., Koeller D. M., Rey E. R. Die Befindlichkeits-Skala (B-S)--ein einfaches Instrument zur Objektivierung von Befindlichkeitsstörungen, insbesondere im Rahmen von Längsschnittuntersuchungen. Arzneimittelforschung. 1970 Jul;20(7):915–918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


