Abstract
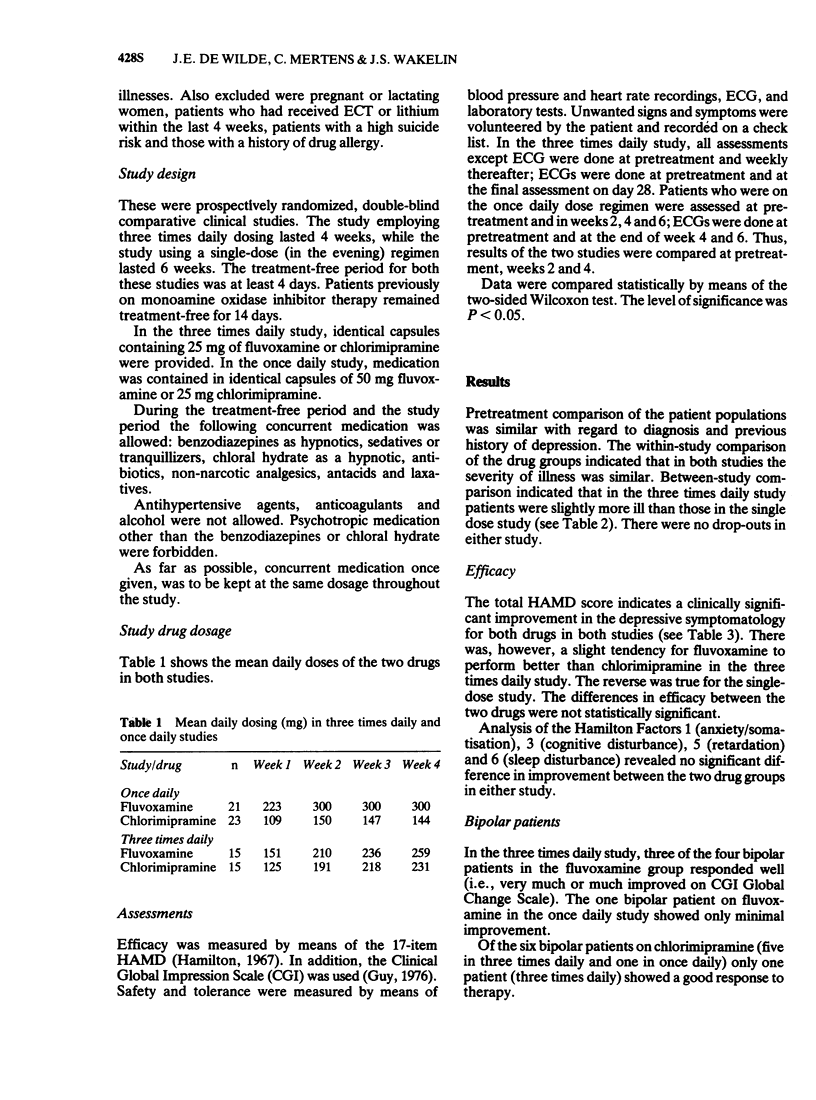
1 Two double-blind, randomised studies were performed to compare the efficacy of fluvoxamine and chlorimipramine in depressed patients. In the first study the effects of a single daily dosage of between 100 and 300 mg of fluvoxamine were compared with those of chlorimipramine at a dosage of 50-150 mg daily in 43 out-patients with endogenous depression.
2 In a second study using three times daily dosing with a daily dosage of 150-300 mg for both fluvoxamine and chlorimipramine, 30 in-patients with unipolar or bipolar depression were assessed.
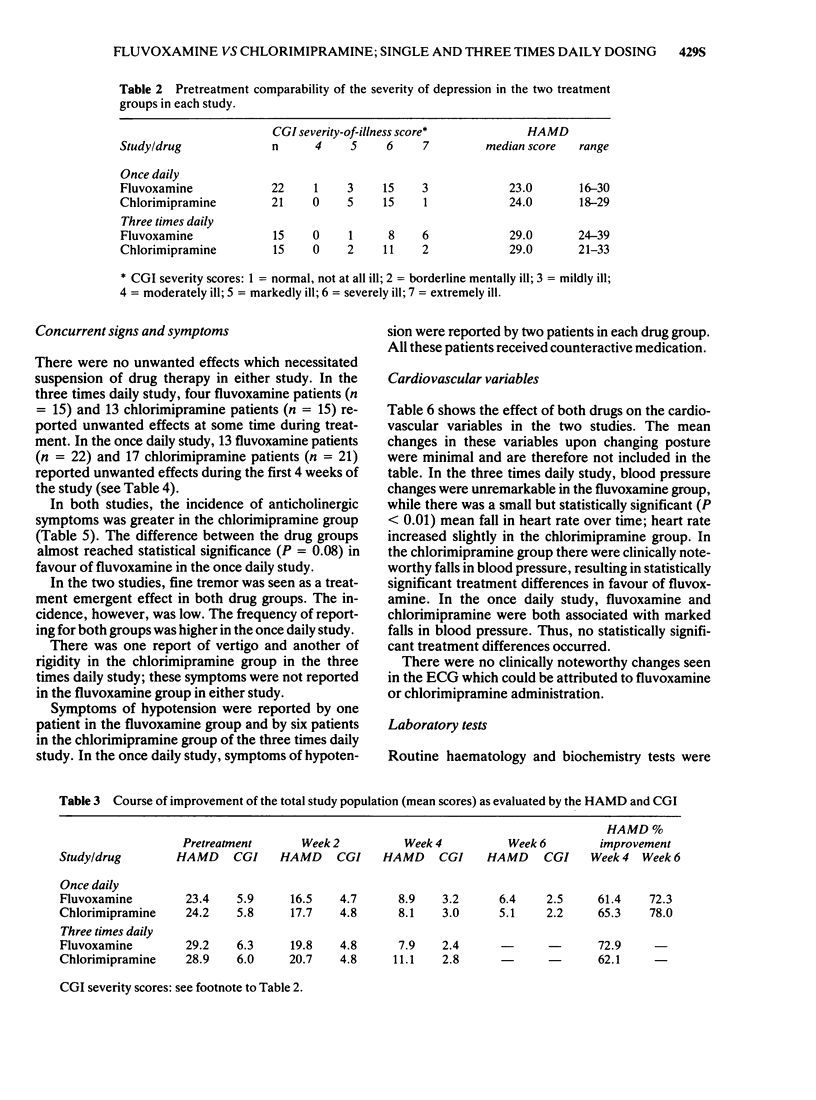
3 Four weeks of treatment with single daily dosing resulted in a mean improvement of 61.4% (± s.d. 31.7) on the Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression (HAMD) for fluvoxamine and of 65.3% (± s.d. 25.8) for chlorimipramine. In the study with three times daily dosing the mean results were 72.9% (± s.d. 22.3) improvement for fluvoxamine and 62.1% (± s.d. 28.5) for chlorimipramine.
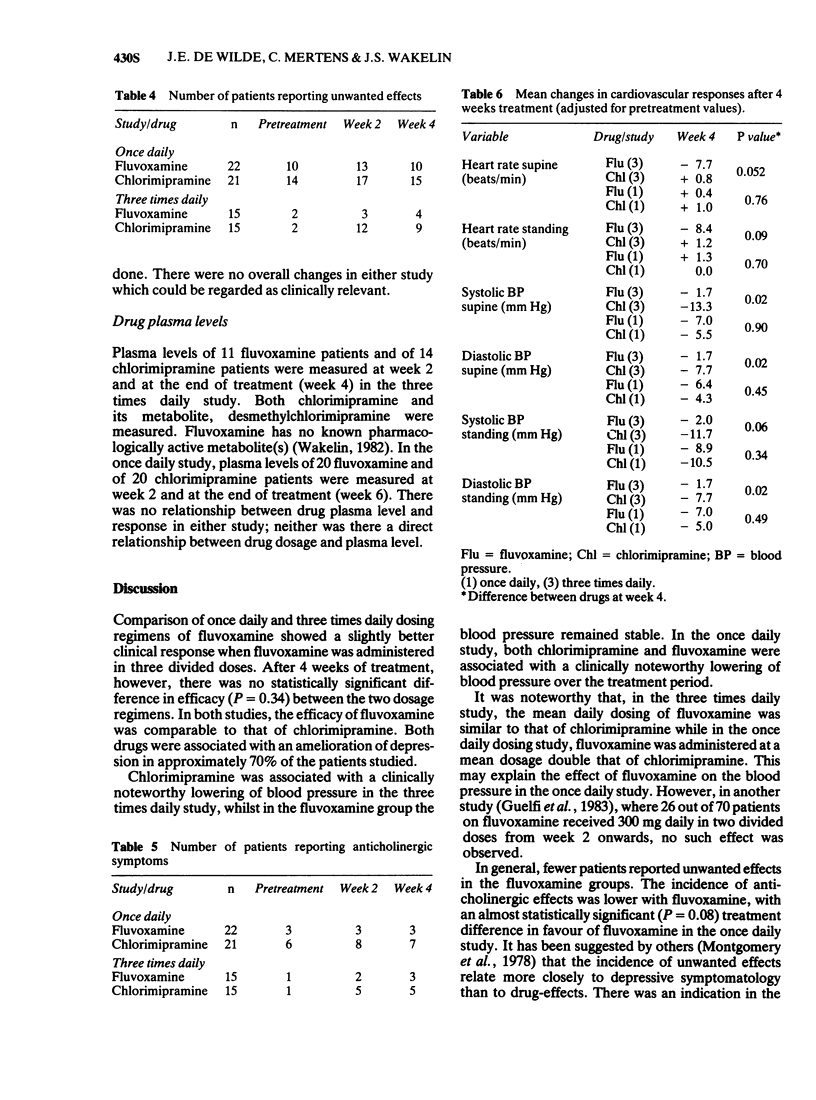
4 At similar dosages, fluvoxamine had significantly less untoward effects on blood pressure than chlorimipramine. Anticholinergic effects were also fewer in the fluvoxamine group, as were nervous system symptoms, with the latter difference reaching statistical significance (P = 0.02).
5 We conclude that fluvoxamine, given in a single daily dose of 150-250 mg, provides antidepressant efficacy similar to chlorimipramine. At this dosage it may be expected to produce less anticholinergic effects and have less influence on blood pressure than chlorimipramine.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braithwaite R. A., Nakra B. R., Gaind R. Steady-state plasma concentrations during single and multiple dosage schedules of amitriptyline. Psychol Med. 1974 Aug;4(3):338–341. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700043038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claassen V., Davies J. E., Hertting G., Placheta P. Fluvoxamine, a specific 5-hydroxytryptamine uptake inhibitor. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Aug;60(4):505–516. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb07528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Wilde J. E., Doogan D. P. Fluvoxamine and chlorimipramine in endogenous depression. J Affect Disord. 1982 Sep;4(3):249–259. doi: 10.1016/0165-0327(82)90009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feighner J. P., Robins E., Guze S. B., Woodruff R. A., Jr, Winokur G., Munoz R. Diagnostic criteria for use in psychiatric research. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1972 Jan;26(1):57–63. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1972.01750190059011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton M. Development of a rating scale for primary depressive illness. Br J Soc Clin Psychol. 1967 Dec;6(4):278–296. doi: 10.1111/j.2044-8260.1967.tb00530.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klok C. J., Brouwer G. J., van Praag H. M., Doogan D. Fluvoxamine and clomipramine in depressed patients. A double-blind clinical study. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1981 Jul;64(1):1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1981.tb00756.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery S., McAuley R., Montgomery D. B. Relationship between mianserin plasma levels and antidepressant effect in a double-blind trial comparing a single night-time and divided daily dose regimens. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1978;5 (Suppl 1):71S–76S. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmeier P. C., Baumann P., Greengrass P. M., Maître L. Effects of clomipramine and other tricyclic antidepressants on biogenic amine uptake and turnover. Postgrad Med J. 1976;52(3 Suppl):33–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


