Abstract
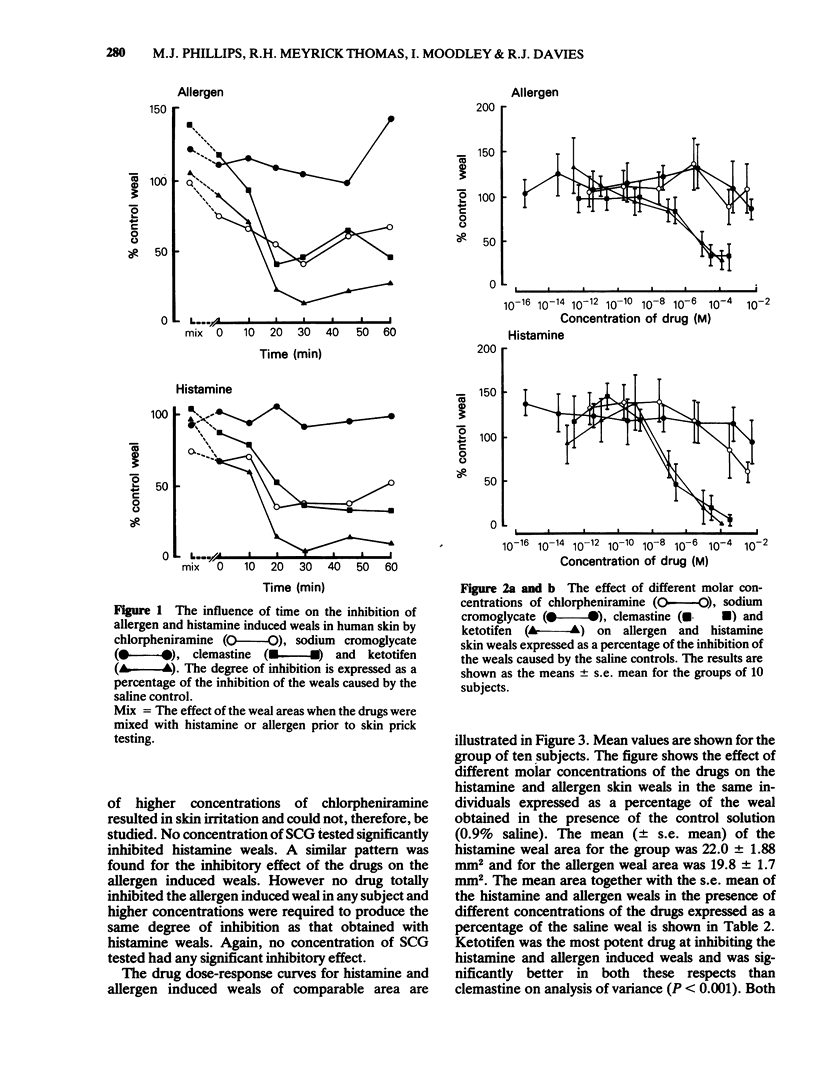
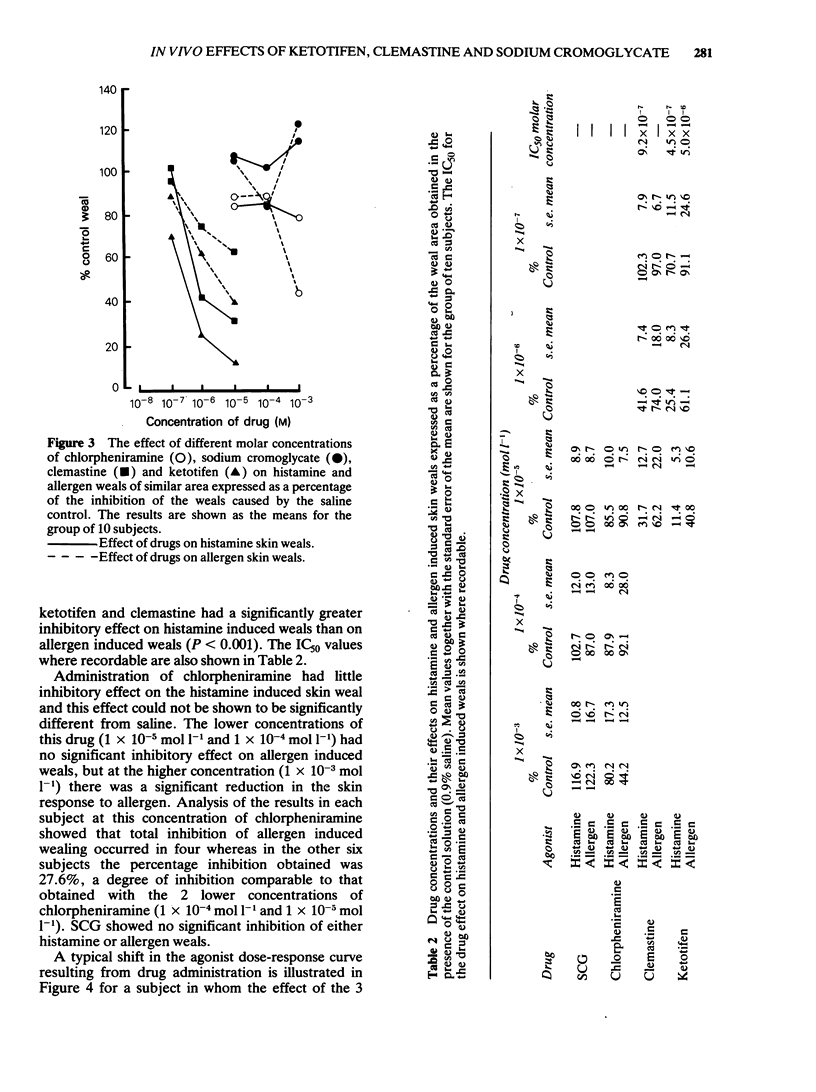
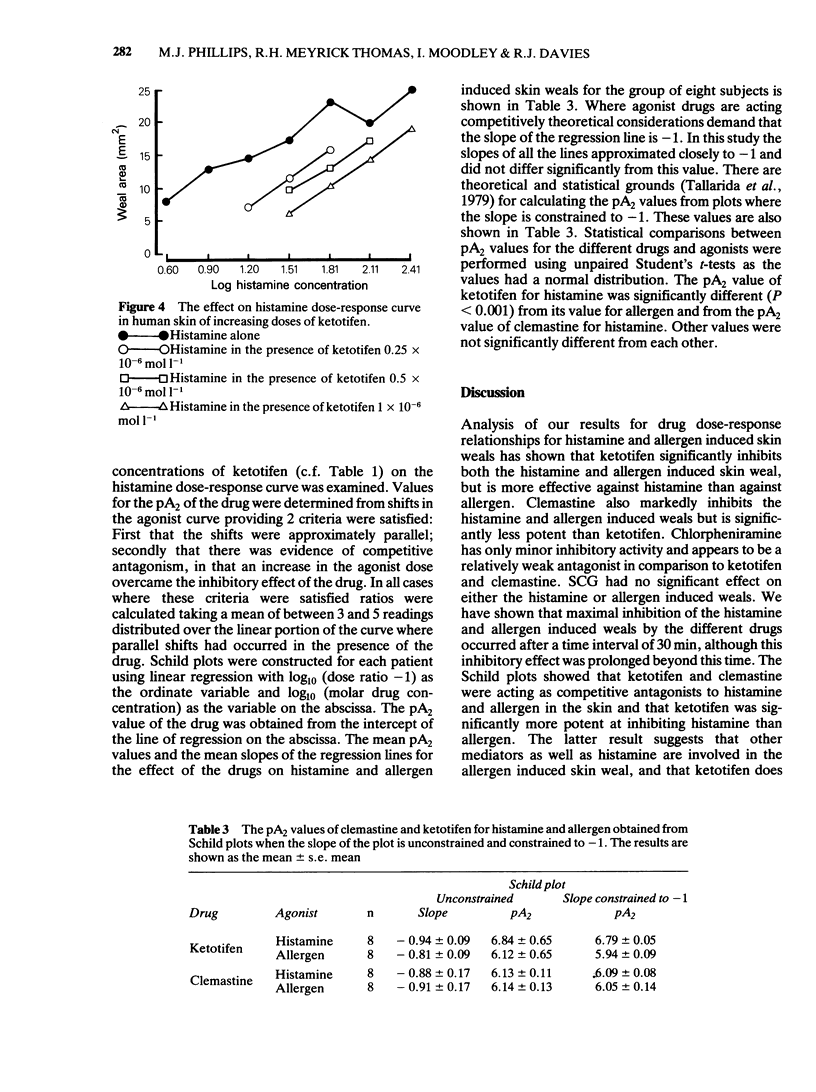
The effect of ketotifen was compared with that of clemastine and chlorpheniramine, known antihistamines, and sodium cromoglycate, a drug considered to have mast cell "stabilizing' properties on histamine and allergen wealing reactions in human skin, in random order, double-blind, placebo controlled studies. Ketotifen was significantly more potent in the inhibition of both histamine (P less than 0.001) and allergen (P less than 0.001) skin wealing reactions than either clemastine or chlorpheniramine. Sodium cromoglycate had no significant effect on either histamine or allergen skin wealing reactions in any of the concentrations tested. However ketotifen, like clemastine, had a significantly greater inhibitory effect on histamine than on allergen induced weals (P less than 0.001) and both drugs were shown to act as competitive antagonists of histamine. Ketotifen has been shown to be a potent anti-histamine but there is no evidence from these in vivo studies to suggest that it has any additional inhibitory activity on release of mediators from mast cells in human skin.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assem E. S., Mongar J. L. Inhibition of allergic reactions in man and other species by cromoglycate. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1970;38(1):68–77. doi: 10.1159/000230260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church M. K., Gradidge C. F. Inhibition of histamine release from human lung in vitro by antihistamines and related drugs. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Aug;69(4):663–667. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb07919.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook T. J., MacQueen D. M., Wittig H. J., Thornby J. I., Lantos R. L., Virtue C. M. Degree and duration of skin test suppression and side effects with antihistamines. A double blind controlled study with five antihistamines. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1973 Feb;51(2):71–77. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(73)80002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. S. Disodium cromoglycate (FPL 670) ('Intal'): a specific inhibitor of reaginic antibody-antigen mechanisms. Nature. 1967 Dec 30;216(5122):1328–1329. doi: 10.1038/2161328a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galant S. P., Bullock J., Wong D., Maibach H. I. The inhibitory effect of antiallergy drugs on allergen and histamine induced wheal and flare response. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1973 Jan;51(7):11–21. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(73)90003-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garland L. G. Effect of cromoglycate on anaphylactic histamine release from rat peritoneal mast cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Sep;49(1):128–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08275.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goose J., Blair A. M. Passive cutaneous anaphylaxis in the rat, induced with two homologous reagin-like antibodies and its specific inhibition with disodium cromoglycate. Immunology. 1969 Jun;16(6):749–760. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. P., Schocket A. L. The effect of H1 and H2 blockade on cutaneous histamine response in man. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1980 Feb;65(2):136–139. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(80)90198-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedges A., Maclay W. P., Newman-Taylor A. J., Turner P. Some central and peripheral effects of meclastine, a new antihistaminic drug, in man. J Clin Pharmacol New Drugs. 1971 Mar-Apr;11(2):112–119. doi: 10.1177/009127007101100206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. J. A steroid sparing effect of ketotifen in steroid-dependent asthmatics. Clin Allergy. 1980 Sep;10(5):519–525. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1980.tb02132.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenstein L. M., Gillespie E. The effects of the H1 and H2 antihistamines on "allergic" histamine release and its inhibition by histamine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975 Feb;192(2):441–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOTA I., da SILVA W. The anti-anaphylactic and histamine-releasing properties of the antihistamines. Their effect on the mast cells. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1960 Sep;15:396–404. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1960.tb01262.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks R., Greaves M. W. Vascular reactions to histamine and compound 48/80 in human skin: suppression by a histamine H2-receptor blocking agent. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1977 Jun;4(3):367–369. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1977.tb00725.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin U., Römer D. The pharmacological properties of a new, orally active antianaphylactic compound: ketotifen, a benzocycloheptathiophene. Arzneimittelforschung. 1978;28(5):770–782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moodley I., Davies R. J. The mechanism of ketotifen-induced histamine release from human peripheral leucocytes. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1982;68(2):176–178. doi: 10.1159/000233090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce C. A., Greaves M. W., Plummer V. M., Yamamoto S. Effect of disodium cromoglycate on antigen-evoked histamine release from human skin. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Jul;17(3):437–440. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheard P., Killingback P. G., Blair A. M. Antigen induced release of histamine and SRS-A from human lung passively sensitized with reaginic serum. Nature. 1967 Oct 21;216(5112):283–284. doi: 10.1038/216283a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes T. C., Morley J. Prospects for an oral Intal. Br J Dis Chest. 1981 Jan;75(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/s0007-0971(81)80002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tallarida R. J., Cowan A., Adler M. W. pA2 and receptor differentiation: a statistical analysis of competitive antagonism. Life Sci. 1979 Aug 20;25(8):637–654. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90505-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor W. A., Sheldon D. Effect of lung tissue on the inhibitory actions of isoprenaline, theophylline, disodium cromoglycate and PGE1 on antigen-induced mast cell degranulation. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1977;54(4):322–328. doi: 10.1159/000231844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


