Abstract
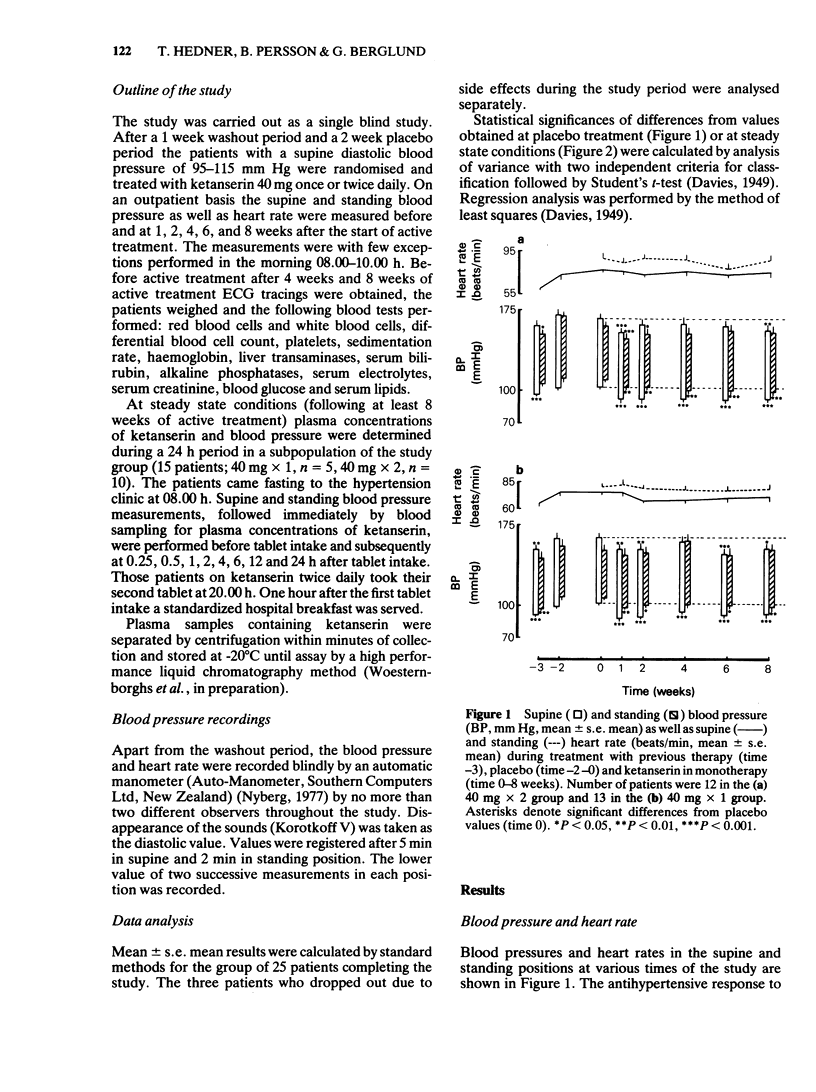
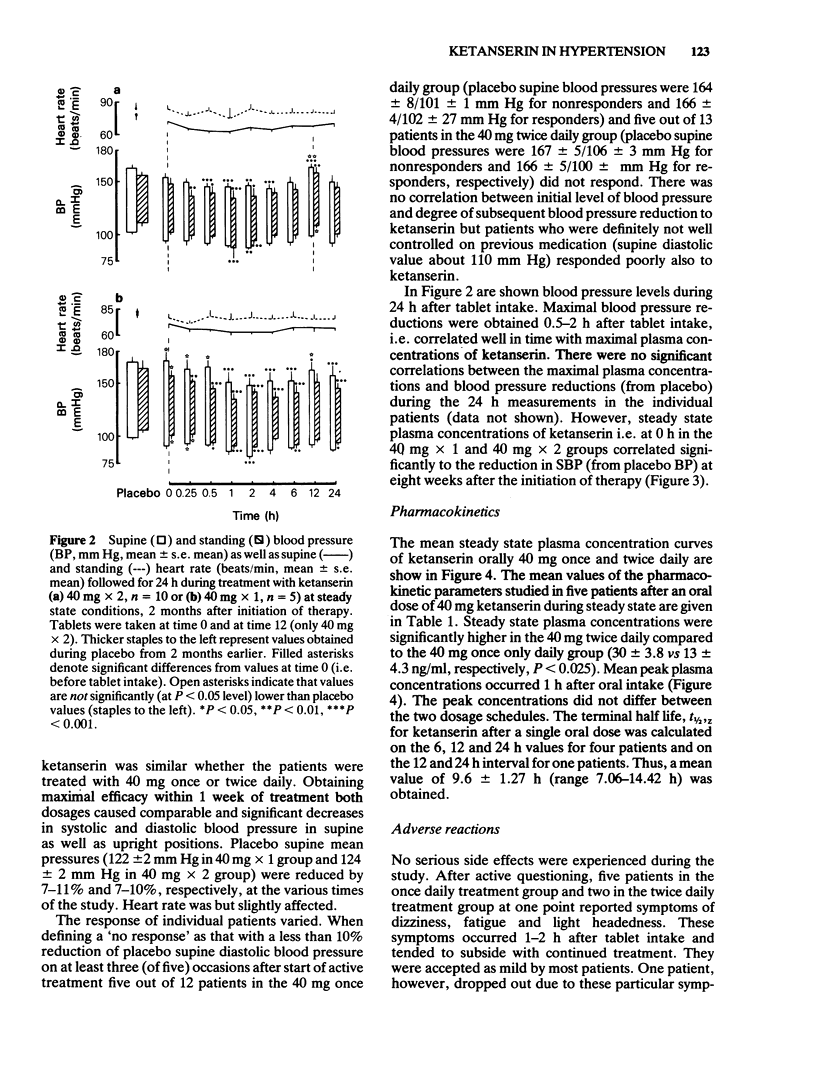
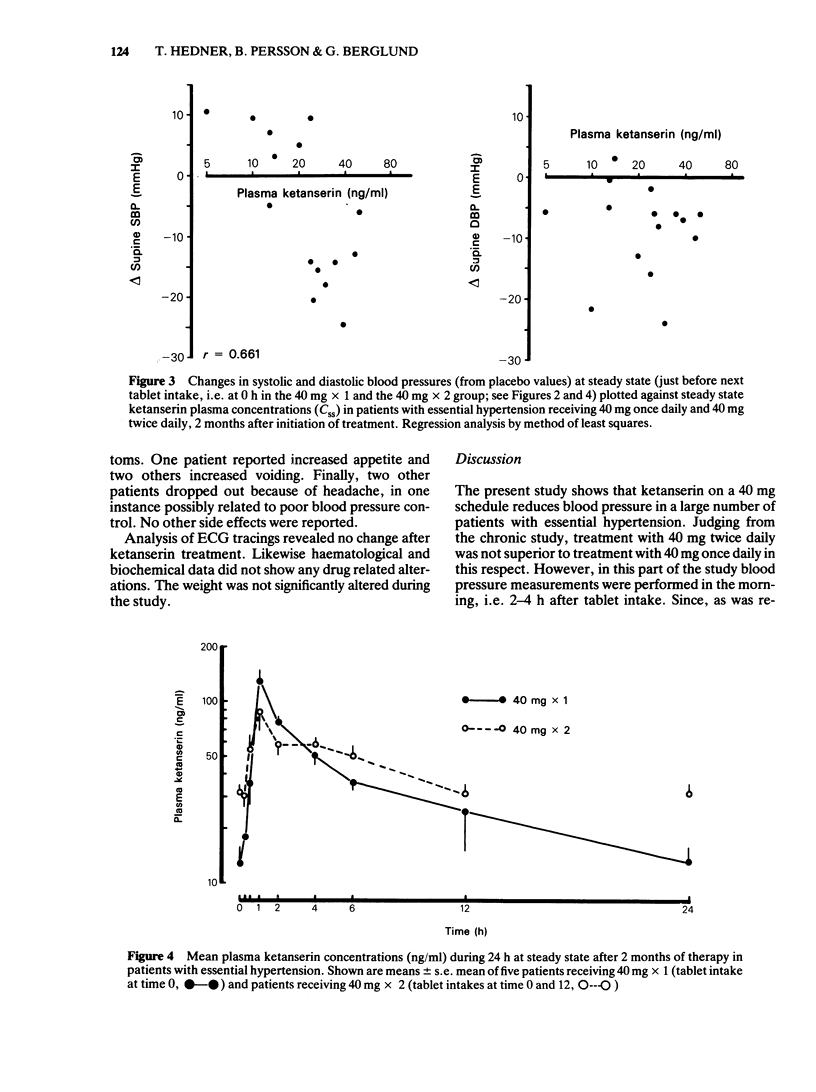
Blood pressure and heart rate, supine and standing, were studied in patients with essential hypertension during 8 weeks of oral therapy with two dosage schedules of ketanserin, 40 mg once and twice daily. Ketanserin caused significant reductions in both supine and standing blood pressure but no significant alterations in heart rate in both groups of patients. Measurements of blood pressure and heart rate over a 24 h period during steady state conditions revealed that maximal blood pressure reduction was correlated with time to peak plasma concentrations. Steady state plasma concentrations of ketanserin were significantly higher in the patients receiving 40 mg twice daily compared to 40 mg once daily. In the group with once daily treatment, tmax was 1.2 +/- 0.17 h, Css 13 +/- 4.3 ng/ml, Cmax 137 +/- 19.6 ng/ml and t1/2, z h. 9.6 +/- 1.27 h.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cohen M. L., Fuller R. W., Wiley K. S. Evidence for 5-HT2 receptors mediating contraction in vascular smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Aug;218(2):421–425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Cree J., Leempoels J., De Cock W., Geukens H., Verhaegen H. The antihypertensive effects of a pure and selective serotonin-receptor blocking agent (R 41 468) in elderly patients. Angiology. 1981 Feb;32(2):137–144. doi: 10.1177/000331978103200206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn D. M., Wolf W. A., Lovenberg W. Review of the role of the central serotonergic neuronal system in blood pressure regulation. Hypertension. 1980 May-Jun;2(3):243–255. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.2.3.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leysen J. E., Awouters F., Kennis L., Laduron P. M., Vandenberk J., Janssen P. A. Receptor binding profile of R 41 468, a novel antagonist at 5-HT2 receptors. Life Sci. 1981 Mar 2;28(9):1015–1022. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90747-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyberg G. Indirect blood pressure and heart rate measured quickly without observer bias using a semi-automatic machine (auto-manometer)--response to isometric exercise in normal healthy males and its modification by beta-adrenoceptor blockade. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1977 Jun;4(3):275–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1977.tb00712.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson B., Hedner T., Henning M. Cardiovascular effects in the rat of ketanserin, a novel 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor blocking agent. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1982 Jul;34(7):442–445. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1982.tb04753.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Nueten J. M., Janssen P. A., Van Beek J., Xhonneux R., Verbeuren T. J., Vanhoutte P. M. Vascular effects of ketanserin (R 41 468), a novel antagonist of 5-HT2 serotonergic receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Jul;218(1):217–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenting G. J., Man in 't Veld A. J., Woittiez A. J., Boomsma F., Schalekamp M. A. Treatment of hypertension with ketanserin, a new selective 5-HT2 receptor antagonist. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Feb 20;284(6315):537–539. doi: 10.1136/bmj.284.6315.537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


