Abstract
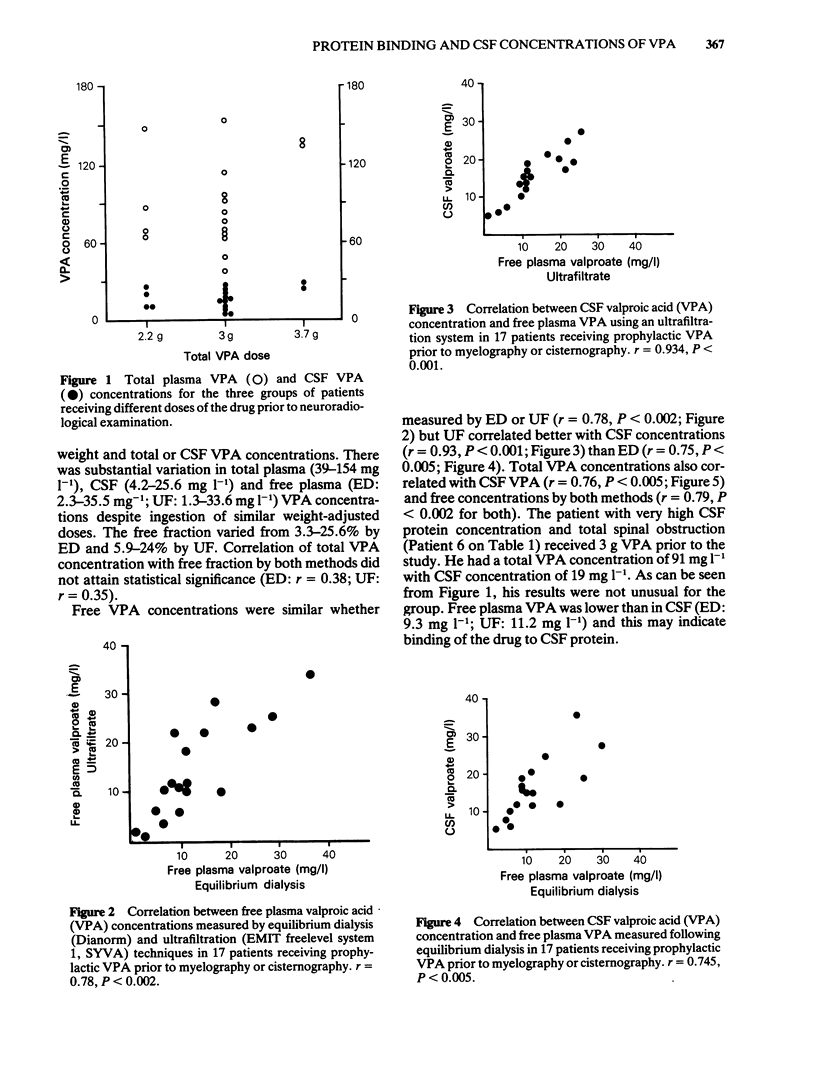
Simultaneous cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), total and free plasma valproic acid (VPA) concentrations were measured in 17 patients receiving two weight-adjusted VPA doses as seizure prophylaxis prior to diagnostic myelography or cisternography. Free drug concentrations were similar when measured by equilibrium dialysis (ED) at 37 degrees C for 24 h (Dianorm) or by a novel ultrafiltration (UF) method (EMIT freelevel system 1, SYVA) (ED:2.3-35.5 mg-1; UF:1.3-33.6 mg-1; r = 0.78, P less than 0.002). There was wide variation in total VPA concentration (39-154 mg-1) and in free fraction (ED: 3.3-25.6%; UF: 5.9-24%). Concentration dependent protein binding was not demonstrated. CSF VPA varied between 4.2 and 25.6 mg-1 and was accurately reflected by free plasma VPA concentrations (ED: r = 0.75, P less than 0.005: UF: r = 0.93, P less than 0.001). CSF concentration also correlated with the total plasma VPA (r = 0.76, P less than 0.005). The Emit freelevel system 1 provides a rapid measure of unbound VPA in the plasma which may be suitable for routine clinical use.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albani F., Riva R., Procaccianti G., Baruzzi A., Perucca E. Free fraction of valproic acid: in vitro time-dependent increase and correlation with free fatty acid concentration in human plasma and serum. Epilepsia. 1983 Feb;24(1):65–73. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1983.tb04867.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonati M., Kanto J., Tognoni G. Clinical pharmacokinetics of cerebrospinal fluid. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1982 Jul-Aug;7(4):312–335. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198207040-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowdle A. T., Patel I. H., Levy R. H., Wilensky A. J. Valproic acid dosage and plasma protein binding and clearance. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1980 Oct;28(4):486–492. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1980.192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gugler R., Mueller G. Plasma protein binding of valproic acid in healthy subjects and in patients with renal disease. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1978 May;5(5):441–446. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1978.tb01652.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gugler R., von Unruh G. E. Clinical pharmacokinetics of valproic acid. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1980 Jan-Feb;5(1):67–83. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198005010-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy R. H. Monitoring of free valproic acid levels? Ther Drug Monit. 1980;2(2):199–201. doi: 10.1097/00007691-198004000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macpherson P. Combined metrizamide ventriculogram and basal cisternogram via sub-occipital route. Br J Radiol. 1980 Jul;53(631):733–734. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-53-631-733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty J. J., Kilpatrick C. J., Moulds R. F. Intra-dose variation in plasma protein binding of sodium valproate in epileptic patients. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1982 Sep;14(3):399–404. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1982.tb01998.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQueen J. K., Blackwood D. H., Minns R. A., Brown J. K. Plasma levels of sodium valproate in childhood epilepsy. Scott Med J. 1982 Oct;27(4):312–317. doi: 10.1177/003693308202700410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowan A. J., Binnie C. D., Warfield C. A., Meinardi H., Meijer J. W. The delayed effect of sodium valproate on the photoconvulsive response in man. Epilepsia. 1979 Feb;20(1):61–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1979.tb04776.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowland M. Plasma protein binding and therapeutic drug monitoring. Ther Drug Monit. 1980;2(1):29–37. doi: 10.1097/00007691-198001000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schobben F., van der Kleijn E., Vree T. B. Therapeutic monitoring of valproic acid. Ther Drug Monit. 1980;2(1):61–71. doi: 10.1097/00007691-198001000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spero L. Epilepsy. Lancet. 1982 Dec 11;2(8311):1319–1322. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91522-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



