Abstract
The stringent response is a global bacterial response to nutritional stress mediated by (p)ppGpp. We previously found that both noninfectious Borrelia burgdorferi strain B31 and infectious B. burgdorferi strain N40 produced large amounts of (p)ppGpp during growth in BSK-H medium and suggested that the stringent response was triggered in B. burgdorferi under these conditions. Here we report that (p)ppGpp levels in B. burgdorferi growing in BSK-II or BSK-H medium are not further increased by nutrient limitation or by serine hydroxamate-induced inhibition of protein synthesis and that the presence of (p)ppGpp during growth of N40 in BSK-H medium is not associated with decreased 16S rRNA synthesis. Decreased 16S rRNA synthesis was associated with the decreased growth rate of N40 seen during coculture with tick cells, which are growth conditions that were previously shown to decrease (p)ppGpp levels. One-half as much of the mRNA of the gene encoding the Rel protein of B. burgdorferi (relBbu) was produced by B31 as by N40 during in vitro growth (2 ± 0.5 and 4 ± 0.8 fg of relBbu mRNA/ng of total Borrelia RNA, respectively). Although the amounts of N40 relBbu mRNA were identical during growth in vitro and in rat peritoneal chambers, they were markedly decreased during growth in nymphal ticks. In contrast to the lack of change in relBbu mRNA levels, larger amounts of a 78-kDa protein that was cross-reactive with antibodies to Bacillus subtilis RelBsu were detected in immunoblots of N40 lysates after growth in rat peritoneal chambers than after growth in vitro. Differences in the level of production of (p)ppGpp between B31 and N40 could not be explained by differences in relBbu promoters since identical transcriptional start sites 309 nucleotides upstream from the B31 and N40 relBbu ATG start codon and identical σ70-like promoters were identified by primer extension and sequencing analysis. relBbu complemented an Escherichia coli CF1693 relA spoT double mutant for growth on M9 minimal medium, and the transformed cells produced relBbu mRNA. These results indicate that relBbu is functional and that its transcription and translation and production of (p)ppGpp are affected by environmental conditions in strains N40 and B31. They also suggest that in B. burgdorferi, an organism with few rRNA operons that grows slowly, the role of (p)ppGpp may differ from the classic role played by this molecule in E. coli and that (p)ppGpp may not be responsible for growth rate control.
Alternating periods of starvation and surfeit characterize the life cycles of many bacteria. Borrelia burgdorferi does not escape this pattern while infecting, growing, and persisting in the microenvironments of its arthropod and mammalian hosts (9, 29). Some of these microenvironments favor multiplication of B. burgdorferi, while others are antagonistic to growth of this organism (18, 19). Differential gene expression and tight modulation appear to be essential for the ability of B. burgdorferi to survive in dissimilar host environments that may sometimes foster and at other times inhibit bacterial proliferation and persistence (2, 26, 30, 40). Variations in B. burgdorferi gene expression related to cycling between arthropod and mammalian hosts have been identified and characterized under both in vitro and in vivo conditions (1, 13, 22, 30, 33, 41).
For B. burgdorferi growing in vitro, changes in pH, cell concentration, temperature, or the presence of tick cells are accompanied by well-characterized changes in expression of different lipoproteins and other proteins (5, 24, 30, 40). Changes in expression of lipoproteins (e.g., a shift from OspA to OspC) are associated with passage of B. burgdorferi from ticks to the mammalian host (10, 33, 34). It has been postulated that these changes are secondary to differences in the nutritional milieus encountered by B. burgdorferi in these two hosts along with differences in pH, temperature, and bacterial cell concentration (40). Modulation of gene expression appears to be mediated at least in part by upregulation of σS by upregulated expression of σ54 (20, 23). The stimuli that trigger this loop and the manner in which σS mediates this regulation have not been characterized.
The stringent response is a global bacterial stress response to nutritional stress (7, 20, 37). It is classically characterized by a regulon-type response with extreme downregulation of stable RNA and protein synthesis and upregulation of protein degradation and amino acid synthesis. In Escherichia coli, the stringent response is triggered by uncharged tRNA and is mediated by production and degradation of the alarmon (p)ppGpp by the relA and spoT gene products (7). It was originally thought that the increased concentration of (p)ppGpp generated by RelA activated by stalled ribosomes in E. coli was the sole factor responsible for the metabolic changes of the stringent response and slow growth (7), but it was subsequently shown that rRNA synthesis in this organism is regulated by both stringent and growth rate-dependent controls (15).
Although a chromosomal gene encoding the Rel protein of B. burgdorferi (relBbu) has been identified in the B. burgdorferi genome (BB0198) which is orthologous to genes that encode other bacterial (p)ppGpp synthetases and hydrolases (14, 28), there is no evidence that the activity of the enzyme encoded by this gene mediates the stringent response in B. burgdorferi. relBbu has, however, been found to be upregulated in B. burgdorferi growing in BSK-H medium at 34°C and pH 7.6 compared with the response in B. burgdorferi growing in coculture with tick cells at the same temperature and pH (5). It is also upregulated in B. burgdorferi growing in BSK-H medium at 23°C and pH 7.5 compared with the response in organisms growing in BSK-H medium at 37°C and pH 6.8 or in rat peritoneal dialysis chambers (30).
Previously, infectious and noninfectious strains of B. burgdorferi have been shown to produce large amounts of (p)ppGpp and to transcribe relBbu during growth in BSK-H medium at 34°C and pH 7.6 (5). Under these conditions, 97% of B. burgdorferi N40 bmpD gene expression was associated with monocistronic mRNA from the bmpD promoter and only 3% of bmpD expression was associated with polycistronic messages with rpsL from the upstream promoter. In contrast, B. burgdorferi N40 cocultured with tick cells produced no (p)ppGpp and grew more slowly than it grew during culture in BSK-H medium, while total bmpD transcription decreased eightfold and only polycistronic rpsL-bmpD was transcribed. These observations suggested that the stringent response could modulate B. burgdorferi gene expression. The presence of a relBbu homologue in the genome of B. burgdorferi, production (p)ppGpp, and expression of B. burgdorferi relBbu mRNA encouraged us to continue our studies to characterize the putative stringent response and relBbu in B. burgdorferi.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Bacterial strains and growth conditions.
Unless otherwise specified, high-passage, noninfectious B. burgdorferi strain B31 (= ATCC 35210) was grown in BSK-II medium (32) or BSK-H medium (Sigma, St. Louis, Mo.) supplemented with 6% rabbit serum (Sigma). Low-passage infectious B. burgdorferi strain N40 (from Linda Bockenstadt, Yale University) and B. burgdorferi strain BL206, a recent clinical isolate from a human blood sample (from Ira Schwartz, New York Medical College), were grown in BSK-H medium at 34°C. E. coli CF1648 (wild type) and CF1693 (containing a double deletion of relA and spoT), obtained from Michael Cashel, National Institutes of Health (39), were grown with shaking at 37°C in Luria-Bertani (LB) medium (Life Technologies, Paisley, Scotland), in MOPS (morpholinepropanesulfonic acid) medium (6), or on M9 medium (31)-1.5% agar (Difco Laboratories, Detroit, Mich.) plates. Kanamycin and chloramphenicol (Sigma) were added at concentrations of 50 and 20 μg/ml, respectively, when E. coli CF1693 was grown (39).
(p)ppGpp detection.
B. burgdorferi cells from a log-phase culture (2 × 107 to 5 × 107 cells/ml) grown with 10 μCi of [32P]orthophosphate (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech, Piscataway, N.J.) per ml were centrifuged and were resuspended at a concentration of 7 × 106 cells/ml for B31 in complete medium or at a concentration of 0.7 × 106 cells/ml for N40 in media containing 10-fold-lower concentrations of rabbit serum, yeastolate (Difco), or neopeptone (Difco) or in complete medium containing 1 mg of dl-serine hydroxamate (Sigma) per ml. All of the resuspension media contained 10 μCi of uniformly labeled [32P]orthophosphate per ml. After various times of growth in these media, labeled cells were harvested from 1- to 5-ml cultures, (p)ppGpp was extracted with 50 μl of 2 M formic acid on ice for 30 min, and 5 μl of supernatant was loaded on a cellulose polyethyleneimine thin-layer chromatography plate (Selecto Scientific, Suwanee, Ga.). Samples were fixed in methanol (5 min) and dried. The thin-layer chromatography plates were developed in 1.5 M KH2PO4 (pH 3.4), air dried, and exposed to Hyperfilm MP (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech) for 18 to 48 h at −20°C or were counted by using a Molecular Dynamics Storm System 860 phosphorimager. To detect (p)ppGpp in E. coli, overnight colonies were inoculated into various media as described below, and (p)ppGpp was extracted from 200 μl of culture and detected as described above. B. burgdorferi spots were identified by comigration with E. coli (p)ppGpp and with ATP and GTP, which were used as standards (Sigma), as described previously (5, 6).
DNA isolation, sequencing, and cloning of B. burgdorferi relBbu.
DNAs of B. burgdorferi B31, N40, and BL206 cells from mid-log-phase cultures were isolated by using a High Pure PCR template preparation kit for isolation of genomic DNA (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany) according to the manufacturer's directions. DNA manipulations were performed by standard methods (31). The complete B. burgdorferi relBbu gene (BB0198), including nucleotides from position −546 upstream from the B. burgdorferi relBbu start codon to position 109 downstream from the B. burgdorferi relBbu stop codon, was cloned into pBluescript IISK+ as described previously (5). The B. burgdorferi N40 and BL206 relBbu DNA regions were sequenced by the dideoxy chain termination method by using a dye terminator Taq cycle sequencing kit and a model 377 DNA sequencer (Perkin-Elmer, Foster City, Calif.). Comparative analysis of B. burgdorferi B31 (14), BL206, and N40 relBbu regions was performed by using OMIGA 2.0 software (Oxford Molecular).
Infection of tick cell lines.
IDE8 tick cells (kindly provided by Ulrike Munderloh, University of Minnesota, St. Paul) were infected with a preparation containing 107 B. burgdorferi N40 cells/ml at a multiplicity of infection of 5 in L15BS medium at 32°C for 3 days as previously described (5).
Infection of ticks.
Four-week-old C3H/HeN mice were infected intradermally with B. burgdorferi N40 (104 bacteria/mouse). Two weeks after infection, ear punches were taken from the mice and checked for the presence of B. burgdorferi by culture in BSK-H medium containing 50 μg of rifampin (Merrel Dow Pharmaceuticals Inc., Cincinnati, Ohio) per ml and 2.5 μg of amphotericin B (Sigma) per ml. Ixodes scapularis larvae were fed to repletion on infected mice, collected, and allowed to molt into nymphs. Molted nymphs were engorged on mice or 2-month-old Sprague-Dawley rats (Harlan Sprague-Dawley Inc., Indianapolis, Ind.) for 48 to 72 h. Two groups of engorged nymphs were pooled for use in reverse transcription (RT)-PCR experiments. The first group contained 91 nymphs, and the second group contained 246 nymphs.
RNA isolation, RT-PCR, and competitive RT-PCR.
Total RNAs from infected engorged nymphal ticks, from B. burgdorferi, and from E. coli were isolated by the guanidine thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform method (8) and were treated with RQ1 RNase-free DNase (Promega) to eliminate DNA contamination. RT-PCR and competitive RT-PCR were performed by using the Access RT-PCR system (Promega, Madison, Wis.) as described previously (5, 12). The primers used for RT-PCR are described in Table 1. Constitutively expressed B. burgdorferi flaB (11) was used as a control to compare different RNA isolates in competitive RT-PCR experiments.
TABLE 1.
Primers used in this study
| Reaction | Gene | Primer | Sequence (5′-3′) | Size of amplified fragment (bp)
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wild type | Competitor | ||||
| Competitive RT-PCR | flaB | 49 | CTAGTGGGTACAGAATTAATCGAGC | 880 | 691 |
| 50 | TAACATAAAAATATCCTCCTTGC | ||||
| bmpA | 21 | CCAAGGTTGCGGCTCTTC | 307 | 219 | |
| 22 | CTTCTACCAGCTTCAAGGTCAG | ||||
| bmpB | 23 | TGGTGATGATGTTCAGATTCC | 339 | 241 | |
| 24 | TTTGCTGCCTCAATAACACC | ||||
| bmpC | 1 | GATGAGGCAATGACTGAGGATGC | 489 | 337 | |
| 2 | GCAGCGTCATAAACTCCAAGACC | ||||
| bmpD | 19 | CTGATGATGGCAAGTCGGAG | 610 | 506 | |
| 20a | CCTATACCAGAAAGCCCTGC | ||||
| rpsL-bmpD | 55 | GGAACAAAAAAGCCTAAAGC | 694 | 564 | |
| 52 | CGACTTGCCATCATCAGAGC | ||||
| relBbu | ST3 | CAAAAAAGCGGAATTGAAGCAG | 446 | 371 | |
| ST4 | GAATATTGACTTTTGTTGGCCG | ||||
| Real-time PCR | flaB | flaBd | TCATTGCCATTGCAGATTGTG | 278 | |
| flaBrc | ACCTTCTCAAGGCGGAGTTAA | ||||
| 16S rRNA | 16SrRNAd | GGCCCGAGAACGTATTCACC | 288 | ||
| 16SrRNArc | CGAGCGCAACCCTTGTTATC | ||||
| Primer extension | relBbu | SText1 | CTAGCTTTTTCAAGATCATTTATCTTG | —a | |
| SText2 | CCCAAAAGAGCTTTTGTGGGTTC | —a | |||
In the primer extension reaction the amplified fragment obtained with SText1 was 32 to 58 nucleotides downstream from the putative relBbu translation start site on the B. burgdorferi chromosome, and the amplified fragment obtained with SText2 was 207 to 229 nucleotides upstream from the putative relBbu translation start site.
RT and real-time PCR.
RNA from B. burgdorferi growing in BSK-H medium (2 × 107 to 5 × 107 cells/ml) or in a coculture with tick cells was isolated as described above. cDNA synthesis was performed with 1 μg of total B. burgdorferi RNA by using random primers and avian myeloblastosis virus (AMV) reverse transcriptase (Promega) according to the manufacturer's recommendations. To quantify flaB or 16S rRNA in B. burgdorferi growing in BSK-H medium or with tick cells, the resulting cDNAs were amplified and analyzed with a LightCycler real-time PCR instrument (Roche). The PCR was performed in glass capillaries by using a 10-μl (final volume) mixture containing 1× LightCycler master mixture (Roche), 3 mM MgCl2, each primer at a concentration of 1 μM (primers flaBd and flaBrc for flaB and primers 16SrRNAd and 16SrRNArc for 16S rRNA [Table 1]), and DNA template. The amplification program consisted of denaturation at 95°C for 2 min, followed by 35 cycles of 95°C for 1 s, 55°C (for flaB) or 57°C (for 16S rRNA) for 5 s, and 72°C for 10 s. Fluorescent product was detected at the last step of each cycle. Unless otherwise specified, the cooling or heating rate was 20°C/s. After amplification, a melting curve was acquired by heating the product to 95°C, cooling it to 60°C, and slowly heating it at a rate of 0.2°C/s to 95°C, with fluorescence collection at 0.2°C intervals. PCRs were performed twice for each RNA isolate. Each experimental sample was analyzed in triplicate. Data were analyzed with the Lightcycler software provided by the manufacturer. Only the log-linear portion of the amplification results was used for analysis. Background fluorescence was removed by setting a noise band, and a standard curve was prepared by plotting the crossing point versus the log of copy number based on standards included in each run. Copy numbers for the experimental samples were calculated by comparing the crossing points of the samples with those of the standards. Melting curves were used to determine the specificities of the PCR products. Genomic DNA from 103 to 106 B. burgdorferi cells was used as a standard to estimate the copy number of flaB or 16S rRNA. Samples with identical amounts of flaB were assumed to contain the same amount of B. burgdorferi total RNA (11).
Detection of B. burgdorferi in ticks.
DNA was isolated from ticks by using an Isoquick nucleic acid extraction kit (ORCA Research Inc., Bothell, Wash.) according to the manufacturer's protocol. B. burgdorferi DNA was detected by PCR performed with primers 49 and 50 for flaB (12) (Table 1).
Growth of B. burgdorferi in peritoneal chambers in rats.
Spectra/Por dialysis membrane chambers (Spectrum Medical Industries Inc., Los Angeles, Calif.) containing 103 B. burgdorferi N40 cells/ml in 5 ml of BSK-H medium were implanted in the peritonea of 4- to 6-week-old Sprague-Dawley rats (1). The chambers were removed on the eighth day after implantation. The concentration of B. burgdorferi at this time was approximately 107 cells/ml.
Immunoblot analysis.
B. burgdorferi N40 cell lysates were electrophoresed in 10 to 20% polyacrylamide gradient sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis gels, and the resolved proteins were transferred to Hybond ECL nitrocellulose membranes (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech) and screened with either mouse anti-B. burgdorferi FlaB monoclonal antibodies H9724 (4), mouse anti-B. burgdorferi OspA, monoclonal antibodies H5332 (3), or rabbit anti-Bacillus subtilis RelBsu polyclonal antibodies (38). Blots were developed with peroxidase-conjugated anti-mouse immunoglobulin G (Fc specific) (Sigma) or peroxidase-conjugated anti-rabbit immunoglobulin G (Sigma). Proteins were detected by using enhanced chemiluminescence technology (ECL Plus; Amersham Pharmacia Biotech).
Primer extension analysis.
B. burgdorferi B31 and N40 nucleic acids were isolated as described above. The relBbu transcription start was identified by a primer extension reaction performed with primer SText1 or SText2 (Table 1). Extension reactions were performed with the Primer Extension System-AMV Reverse Transcriptase (Promega). Extension products were resolved in a 6% denaturing polyacrylamide gel containing 8 M urea and were visualized by autoradiography. To generate a sequence ladder for the extension product, sequencing reactions with pBlue-ST DNA were performed with a T7 Sequenase Quick-Denature plasmid sequencing kit (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech) directed by the same primer that was used for primer extension.
Nucleotide sequence accession numbers.
The nucleotide sequences of the B. burgdorferi BL206 and N40 relBbu genes have been deposited in the GenBank database under accession numbers AY074789 and AY074790, respectively.
RESULTS
Detection of (p)ppGpp in B. burgdorferi during growth under different conditions.
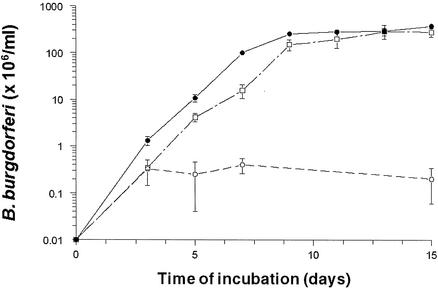
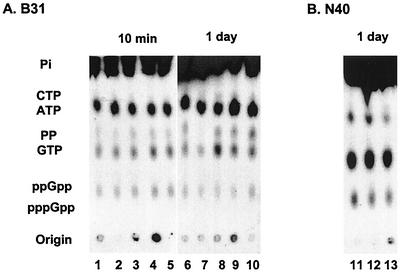
(p)ppGpp is produced by the noninfectious B31 and infectious N40 B. burgdorferi strains growing in BSK-H medium at 34°C and pH 7.6 (5). To determine if the levels of (p)ppGpp and the ATP/GTP/(p)ppGpp ratio changed under increased-starvation conditions, B31 and N40 were grown in BSK-II and BSK-H media containing 10-fold less rabbit sera than the complete media, in BSK-II medium containing10-fold less yeastolate and neopeptone than the complete medium, and in BSK-II and BSK-H media containing a competitive inhibitor of protein synthesis, serine hydroxamate (36). Serine hydroxamate (1 mg/ml) completely inhibited the growth of B. burgdorferi B31 in BSK-II medium (Fig. 1) and the growth of N40 in BSK-H medium (data not shown). These changes, while decreasing the growth rate, did not alter the observed high basal levels of ppGpp (Fig. 2) and the ATP/GTP/ppGpp ratio in either strain (1:4:1 for N40 and 8:2:1 for B31) compared to the basal levels of ppGpp and the ATP/GTP/ppGpp ratio in B. burgdorferi grown in complete BSK-II or BSK-H medium. Synthesis of ppGpp was constant for both B. burgdorferi strains in all growth media from 10 min to 5 days.
FIG. 1.
Inhibition of growth of B. burgdorferi B31 in BSK-II medium (•) by 0.1 mg of serine hydroxamate per ml (□) and by 1 mg of serine hydroxamate per ml (○). See Materials and Methods for details.
FIG. 2.
(p)ppGpp accumulation in B. burgdorferi under various culture conditions. (A) B. burgdorferi B31 was grown in BSK-II medium containing [32P]orthophosphate for 36 h and then centrifuged and resuspended in the same amount of BSK-II medium (lanes 1 and 6), in BSK-II medium containing 10-fold-lower levels of rabbit serum (final concentration, 0.6%) (lanes 2 and 7), yeastolate (lanes 3 and 8), or neopeptone (lanes 4 and 9), or in BSK-II medium containing 1 mg of dl-serine hydroxamate per ml (lanes 5 and 10) (all resuspension media contained [32P]orthophosphate) for 10 min or 1 day. (B) B. burgdorferi N40 was grown in BSK-H medium containing [32P]orthophosphate for 2 days, centrifuged, and resuspended in the same amount of BSK-H medium (lane 11), in BSK-H medium containing 10-fold-lower levels of rabbit serum (lane 12), or in BSK-H medium containing 1 mg of dl-serine hydroxamate per ml (lane 13) (all resuspension media contained [32P]orthophosphate) for 1 day. Cells were collected by centrifugation after growth for 10 min or 1 day, and (p)ppGpp was extracted as described in Materials and Methods.
Expression of B. burgdorferi relBbu mRNA, RelBbu protein, and genes of the bmp chromosomal cluster during in vitro and in vivo growth.
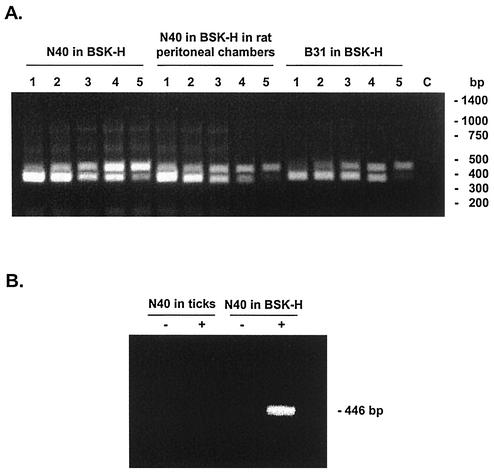
During growth in complete BSK-H medium containing 6% rabbit serum, N40 contained twice as much relBbu mRNA as B31 contained (4.0 ± 0.8 fg of relBbu mRNA/ng of total B. burgdorferi RNA for N40 versus 2.0 ± 0.5 fg/ng of total RNA for B31) (Table 2, Fig. 3A). The relBbu mRNA levels in B31 growing in BSK-II and BSK-H media were identical (data not shown). There was no difference in relBbu mRNA levels between N40 grown at 37°C in complete BSK-H medium and N40 grown in BSK-H medium containing only 0.6% rabbit serum (data not shown), nor was there any difference in relBbu mRNA levels between N40 grown in complete BSK-H medium at 37 and 23°C (data not shown). The N40 relBbu mRNA levels were the same (4.0 fg/ng of total RNA) during growth in rat peritoneal chambers as during growth in BSK-H medium at 37°C (Table 2, Fig. 3A). In contrast, relBbu mRNA was not detected during N40 growth in engorged nymphal ticks (Table 2, Fig. 3B).
TABLE 2.
Expression of mRNAs of selected B. burgdorferi genes under various culture conditions
| Gene(s) | mRNA expression (fg of mRNA/ng of total B. burgdorferi RNA)
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BSK-H medium
|
Nymphal ticks (strain N40) | Rat peritoneal chamber and BSK-H medium (strain N40) | ||
| Strain B31 | Strain N40 | |||
| relBbu | 2 | 4 | 4 | |
| bmpA | 6.5 | 6.5 | 6.5 | 6.5 |
| bmpB | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| bmpC | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | |
| bmpD | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| rpsL-bmpD | 0.4 | 0.06 | NDa | ND |
ND, not determined.
FIG. 3.
RT-PCR analysis of B. burgdorferi relBbu mRNA. (A) Relative concentrations of relBbu mRNA in B. burgdorferi N40 grown in BSK-H medium or in BSK-H medium in rat peritoneal chambers or in B. burgdorferi B31 grown in BSK-H medium. relBbu mRNA was detected by competitive RT-PCR. All reaction mixtures contained 1 ng of B. burgdorferi total RNA. The amounts of competitor were 16, 8, 4, 2, and 1 fg in lanes 1 to 5, respectively. Lane 3 for N40 and lane 4 for B31 showed equal signal intensities for relBbu mRNA (upper band) and the competitor (lower band), indicating that in these reaction mixtures they were present at equal concentrations. In lane C RNA was omitted. (B) relBbu mRNA in B. burgdorferi N40 in BSK-H medium and in ticks. −, reverse transcriptase omitted; +, complete reaction mixture for specific RNA detection.
Previous studies indicated that there is a correlation between attenuation of the stringent response in B. burgdorferi cocultured with tick cells [as manifested by undetectable levels of (p)ppGpp] and modulation of expression of rpsL-bmpD and bmpD messages (5). Moreover, the fact that expression of bmpD was linked to expression of the ribosomal protein gene rpsL suggested that bmpD expression might be indirectly regulated by the stringent response by the levels of rRNA synthesis (7). Therefore, expression of the entire bmp gene family under several in vivo growth conditions was examined (Table 2). B. burgdorferi-specific RNA and DNA were not detected in uninfected tick nymphs. Growth of B. burgdorferi N40 in engorged nymphs was accompanied by clear downmodulation of relBbu expression but not by changes in expression of bmpA, bmpB, or bmpD compared to the expression seen during in vitro growth in BSK-H medium (Table 2). The inability to detect bmpC mRNA in engorged ticks (Table 2) could have been a result of the relatively small amount of B. burgdorferi mRNA obtained under these conditions, as well as the generally limited expression of this gene (5, 12). The levels of transcription of the relBbu and bmp genes were identical during growth of N40 in rat peritoneal chambers and in BSK-H medium in vitro (Table 2).
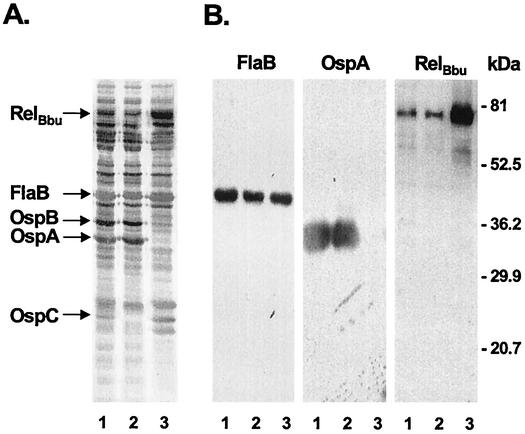
B. burgdorferi RelBbu (14) is 43% identical to B. subtilis RelBsu (38) over a 450-amino-acid span, suggesting that polyclonal anti-RelBsu antibodies could be used for immunoblot analysis of RelBbu in cell lysates. Immunoblot analysis with such antibodies of lysates of N40 grown in BSK-H medium detected a protein with an Mr of 78,000, which is similar to the Mr predicted for RelBbu (Fig. 4B, RelBbu panel, lanes 1 and 2). Despite identical relBbu transcription levels during N40 growth in rat peritoneal chambers and BSK-H medium in vitro (Table 2, Fig. 3A), the levels of RelBbu protein appeared to be much higher in host-adapted B. burgdorferi growing in rat peritoneal chambers than in an in vitro culture (Fig. 4B, RelBbu panel, compare lane 3 with lanes 1 and 2).
FIG. 4.
RelBbu protein in B. burgdorferi N40 grown in BSK-H medium at 37°C (lanes 1) or at 23°C (lanes 2) or in rat peritoneal chambers containing BSK-H medium (lanes 3). (A) Silver staining of B. burgdorferi proteins. Downmodulation of OspA and OspB and upregulation of OspC (lane 3) indicated that there was host adaptation of B. burgdorferi in rat peritoneal chambers. (B) Immunoblot analysis of B. burgdorferi proteins with anti-B. burgdorferi FlaB monoclonal antibodies (loading control), anti-B. burgdorferi OspA monoclonal antibodies (host adaptation control), and anti-B. subtilis RelBsu polyclonal antibodies. The positions of protein molecular mass standards are indicated on the right. In the FlaB panel the similar intensities of FlaB in lanes 1, 2, and 3 indicate that the amounts of total B. burgdorferi protein loaded in lanes 1, 2, and 3 were the same. In the OspA panel the absence of OspA in lane 3 is characteristic of host-adapted B. burgdorferi growing in rat peritoneal chambers (1; Caimano et al., unpublished).
Transcription of relBbu from a σ70-like promoter.
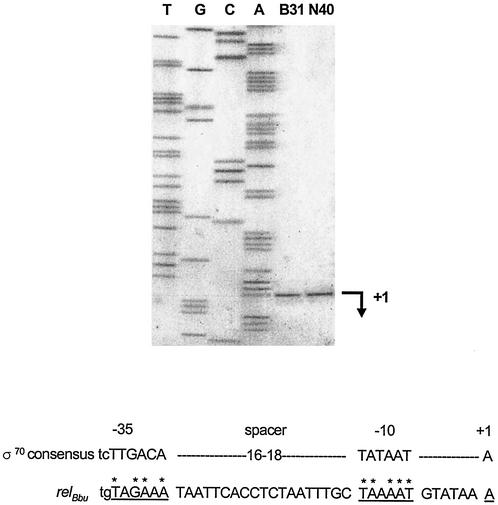
Primer extension analysis was used to determine whether differences in the levels of production of (p)ppGpp between noninfectious and infectious B. burgdorferi strains could be explained by differences in relBbu promoters. The relBbu promoter is located within the open reading frame (ORF) that is 5′ to relBbu (BB0197); this ORF encodes a putative protoporphyrinogen oxidase. Transcription of the relBbu gene began from a σ70-like promoter at a transcriptional start site located 308 nucleotides upstream from the relBbu ATG translational start in both B. burgdorferi B31 and N40 growing in BSK-H medium (Fig. 5). The putative relBbu promoter, like the putative bmpD promoter, has a 19-nucleotide space between the −10 and −35 elements (12). It is also possible that the putative relBbu promoter has an extended −10 element.
FIG. 5.
Primer extension analysis of B. burgdorferi B31 (lane B31) and N40 (lane N40) mRNAs and sequencing ladder of the homologous region of the B31 relBbu gene (lanes T, G, C, and A). Products having similar sizes were generated with AMV reverse transcriptase from B31 and N40. The arrow indicates the position of the primer extension products in relation to the sequencing ladder. +1, relBbu transcription site. The putative −10 promoter sequence and the putative −35 promoter sequence are underlined in the nucleotide sequence of the region upstream of relBbu. Homology of the deduced relBbu promoter with the E. coli σ70 promoter (21) is indicated by asterisks.
DNA sequence analysis of relBbu in B. burgdorferi B31, N40, and BL206.
Since the relBbu transcription start was the same in N40 and B31, an effort was made to determine if there might be differences in promoter sequences and other regulatory signals in regions upstream and downstream from the relBbu ORF. DNAs from infectious strains N40 and BL206 were amplified and sequenced in a region comprising 455 nucleotides upstream of the relBbu putative start codon and 55 nucleotides downstream of the putative termination codon, and the sequences were compared to the B31 sequence in this region (14). The DNA sequences of the entire relBbu region of BL206 and B31 were identical. There were no sequence differences among B31, BL206, and N40 in the 55 nucleotides downstream from the relBbu coding region. Compared to the B31 and BL206 DNA sequences, the N40 DNA sequence had 5 nucleotide substitutions in the 455 nucleotides upstream from the N40 relBbu start codon, all of which were outside the identified promoter, and 14 nucleotide substitutions in the 2,001 nucleotides of the coding sequence. Most substitutions in the coding region were silent, and only two led to amino acid changes. Substitution of an A (in N40) at position 1594 beginning from the translation start for a G (in B31) resulted in a change from Ala (B31) to Thr (N40) at amino acid 532 in the RelBbu protein, while substitution of an A at position 1708 (N40) for a C (B31) resulted in a change from Pro (B31) to Thr (N40) at amino acid 570.
Expression of B. burgdorferi relBbu in E. coli.
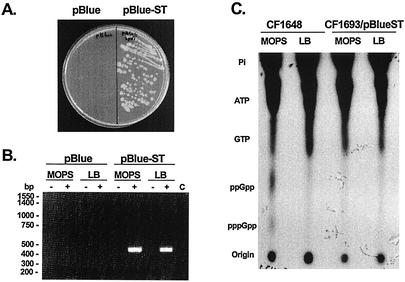
The functionality of the B. burgdorferi relBbu gene was confirmed by transformation of an E. coli CF1693 relA spoT double mutant with pBlue-ST containing the B. burgdorferi B31 relBbu gene, including 446 bp upstream from its start codon and 109 bp downstream from its stop codon. Untransformed E. coli CF1693 grew on LB agar but not on M9 minimal agar, while E. coli CF1693 transformed with the recombinant plasmid containing the B. burgdorferi relBbu gene grew well on both media (Fig. 6A). B. burgdorferi relBbu mRNA was detected in transformed E. coli CF1693 cells whether they were grown in MOPS starvation medium or in LB medium (Fig. 6B). The cross-reactivity of the polyclonal anti-RelBsu antibodies with a protein that has an Mr similar to that of RelBbu in E. coli lysates (CF1648 and CF1693) made it impossible to identify RelBbu expression in CF1693 cells transformed with pBlue-ST (data not shown). (p)ppGpp could not be detected in the double mutant or in cells transformed with B. burgdorferi relBbu (Fig. 6C), while both pppGpp and ppGpp were readily demonstrable in wild-type E. coli grown in MOPS starvation medium but not in LB medium.
FIG. 6.
Complementation of E. coli CF1693 (relA− spoT−) with B. burgdorferi relBbu homologue. (A) E. coli CF1693 was transformed with pBluescript IISK+ (left side) or pBlue-ST plasmid DNA (right side) and grown on a 1.5% agar-M9 medium plate. (B) B. burgdorferi relBbu mRNA synthesis by CF1693 containing pBlue-ST following growth in MOPS starvation medium or LB medium. −, reverse transcriptase omitted; +, complete reaction mixture for specific RNA detection. In lane C RNA was omitted. (C) (p)ppGpp accumulation in E. coli, as determined with wild-type strain CF1648 and the CF1693 relA− spoT− double mutant containing pBlue-ST in MOPS starvation medium or LB medium.
Influence of the stringent response on 16S rRNA synthesis.
Because rRNA gene number and organization in B. burgdorferi differ so markedly from rRNA gene number and organization in E. coli (14, 16, 25), because the mechanisms controlling rRNA transcription in B. burgdorferi are uncharacterized, and because slow growth of B. burgdorferi in the presence of tick cells was accompanied by an abrogation of the stringent response (5), the influence of the stringent response and slow growth on transcription of the single B. burgdorferi 16S rRNA gene was examined. This single gene and tRNAAla appear to be a single transcriptional unit (16). Real-time PCR indicated that B. burgdorferi N40 growing in BSK-H medium contained 294 ± 15 copies of 16S rRNA/pg of total B. burgdorferi RNA, while N40 cocultured with tick cells contained 102 ± 15 copies of 16S rRNA/pg of total B. burgdorferi RNA (means ± standard errors of the means, based on three independent experiments). The decreased synthesis of 16S rRNA in N40 cocultured with tick cells compared to the synthesis in BSK-H medium was highly significant (P < 0.01, as determined by a t test) and was correlated with slow growth of B. burgdorferi in the presence of tick cells rather than with the decrease in (p)ppGpp production seen under these conditions (5). Analysis of the regulatory DNA sequences of the 16S rRNA in B. burgdorferi failed to identify a GCGC discriminator motif immediately downstream from the −10 region for both putative 16S rRNA promoters in B. burgdorferi identified by sequence analysis (14, 16). In E. coli, this discriminator motif is associated with regulation of rRNA synthesis by the stringent response (42).
DISCUSSION
Limitation of intracellular amino acid availability and energy sources classically triggers the bacterial stringent response mediated by the alarmon (p)ppGpp (7). We previously detected production of (p)ppGpp in rapidly growing B. burgdorferi in BSK-H medium and the ablation of (p)ppGpp synthesis during slower growth of B. burgdorferi in the presence of tick cells (5). The changes in (p)ppGpp concentration were accompanied by changes in the transcription of chromosomally encoded genes, indicating the potential ability of (p)ppGpp to modulate transcription, as it does in the stringent response in other bacteria (7, 20, 37). The results described here extended our observations regarding the presence of (p)ppGpp and the functionality of B. burgdorferi relBbu by identification of the promoter, determination of the amounts of relBbu mRNA in B. burgdorferi strains grown under different conditions, detection the RelBbu protein, and demonstration of the ability of the RelBbu protein to complement an E. coli relA spoT double mutant.
Synthesis of larger amounts of ppGpp, expression of higher levels of relBbu mRNA, and slower growth of the infectious N40 strain compared to the results obtained with the noninfectious B31 strain during growth in BSK-II and BSK-H media could suggest that these strains respond differently to similar environmental stimuli. The identity of the relBbu regulatory regions in the noninfectious and infectious strains rules out the possibility that the observed quantitative differences in transcription between the noninfectious and infectious strains result from mutations in this region.
These results raise important questions regarding the role of (p)ppGpp in B. burgdorferi and its role in other bacteria as an indicator of nutritional and other stresses. The presence of (p)ppGpp, relBbu mRNA, and the RelBbu protein in B. burgdorferi growing in BSK-II medium and in BSK-H medium, which putatively are rich media, and our inability to upmodulate this response in these media by nutritional manipulations were unexpected, since in other bacteria the levels of (p)ppGpp produced during growth in culture media that do not fulfill nutritional requirements can be modulated by manipulation of medium nutrients (7, 28, 37). Equally unexpected was our observation that the presence of (p)ppGpp during N40 growth in BSK-H medium was associated with rapid growth but not with a decrease in 16S rRNA synthesis, while the decreased N40 growth rate seen during coculture with tick cells, growth conditions that decreased the levels of (p)ppGpp to undetectable levels (5), was associated with decreased 16S rRNA synthesis. However, these observations may not be as surprising as first supposed since even in the paradigmatic organism E. coli, rRNA synthesis can be regulated by a growth rate-dependent control system, as well as by the stringent response (15).
It is clearly possible that the B. burgdorferi stringent response involves as-yet-uncharacterized stimuli, regulatory mechanisms, and pathways that are different from those in other bacteria, so a model based on E. coli fails to predict the relevant changes in B. burgdorferi (20). The levels of (p)ppGpp and relBbu mRNA decreased compared to the levels seen during growth in BSK-H medium when N40 was grown with tick cells (5) or in engorged ticks (this study), suggesting that the latter conditions may modulate the production of (p)ppGpp in a similar manner. The coexistence of production of (p)ppGpp and increased transcription of relBbu in B. burgdorferi provides some support for the hypothesis that the environmental stimuli that trigger and regulate the stringent response in B. burgdorferi are different from the environmental stimuli that trigger and regulate the stringent response in other bacteria (6, 20, 37). This is not entirely unexpected as there appear to be differences among bacteria regarding the role of the stringent response in metabolism (28). The apparently different amounts of RelBbu protein encountered in B. burgdorferi growing in BSK-H medium and in rat peritoneal chambers (Fig. 4) in spite of the identical levels of relBbu mRNA (Table 2, Fig. 3A) suggests that the concentration of this protein may be regulated posttranscriptionally. The higher level of RelBbu expression in rat peritoneal chambers is consistent with data showing that B. burgdorferi strains are stressed under these conditions (30; M. J. Caimano, C. H. Eggers, J. E. Purser, S. J. Norris, and J. D. Radolf, unpublished data).
Further evidence that there are differences between the stringent response in B. burgdorferi and the stringent response in other bacteria came from our unexpected observation that synthesis of (p)ppGpp in B. burgdorferi was not associated with a decreased growth rate and decreased synthesis of the single 16S rRNA gene in the B. burgdorferi genome, a situation at variance with what occurs in E. coli or in other bacteria (7, 37). This suggests that there is dissociation between the effects of the stringent response mediated by (p)ppGpp and slow growth on synthesis of 16S rRNA in B. burgdorferi, as the latter condition, and not the increased levels of (p)ppGpp, was associated with downregulation of rRNA synthesis. A major limitation in the analysis of rRNA synthesis in these experiments was the lack of knowledge regarding the structure of the promoters of rRNA genes in B. burgdorferi and the organization of the transcription and processing (16). For example, we do not know whether in B. burgdorferi rRNA is expressed alternatively from two promoters, as it is in E. coli, and whether expression is influenced by upstream DNA sequences or DNA supercoiling; we also do not know the σ and other transcriptional factors, such as FIS and H-NS homologues, that regulate initiation of transcription of rRNA genes in other bacteria (25, 37). Analysis of the regulatory DNA sequences of the rRNA genes in B. burgdorferi did not identify a discriminator motif associated in E. coli with the regulation of rRNA synthesis by the stringent response (37, 42), and this finding potentially could explain the dissociation which we found between the presence of the stringent response and the lack of downregulation of 16S rRNA synthesis.
Production of (p)ppGpp could potentially have a central role in regulating growth, gene expression, and host adaptation in B. burgdorferi, an extracellular bacterium whose reduced genome contains few σ factors and few identified regulatory molecules (14). Under in vitro conditions that may correspond to those in flat ticks (BSK-H medium, pH 7.5, 23°C) and engorged ticks (BSK-H medium, pH 6.8, 37°C), DNA microarray analysis of B. burgdorferi gene expression revealed a twofold increase in relBbu transcription and few other changes in regulatory gene expression, while bmpD expression decreased sixfold at the lower temperature (30). In the present study, bmpD expression was the same in N40 growing in BSK-H medium (pH 7.6, 34°C) and in engorged ticks, while relBbu expression decreased under these conditions (Table 2). These findings in turn contrast with our previous findings which showed that downregulation of relBbu expression during coculture with tick cells was accompanied by decreases in the levels of (p)ppGpp and bmpD mRNA (5). However, our results are consistent with the results obtained with DNA microarrays regarding the changes in expression of relBbu and bmpD when B. burgdorferi is shifted between media simulating different environments (30). Unfortunately, absolute comparisons between our competitive RT-PCR data and the data from microarray studies are impossible due to differences in culture conditions, differences in the genetic makeup of the strains, such as plasmid composition, and differences in the methods of analysis of gene expression.
The deduced sequence of the B. burgdorferi RelBbu protein is similar to the sequences of E. coli SpoT and RelA, Mycobacterium tuberculosis RelMtu, Streptomyces coelicolor RelSco, and orthologues in other bacteria (28). The fact that the catalytic domains of these proteins are located within the N-terminal regions of the proteins (17, 27, 35) and the fact that we did not find any differences in the deduced amino acid sequence in this region in noninfectious and infectious B. burgdorferi strains suggest that any differences in the stringent response in these strains are not due to different enzymatic activities of their RelBbu proteins. The finding that the levels of relBbu mRNA paralleled the levels of (p)ppGpp suggests that expression of relBbu might be regulated by stress-related σS and σ54 promoters. Primer extension experiments ruled out transcription from a σ54 promoter but not transcription from a σS promoter, since σS recognizes promoters that are similar to those recognized by σ70 (21, 37). The location of the relBbu σ70 promoter within the ORF encoding protoporphyrinogen oxidase and the observation that many B. burgdorferi genes have their promoters within the structural DNA sequence of the preceding gene may simply be reflections of the compact and reduced nature of the B. burgdorferi genome (12, 14). The lack of detection of (p)ppGpp in the genetically complemented E. coli relA spoT double mutant could have been the result of low levels of expression of this gene in E. coli, degradation of foreign RelBbu in the E. coli environment, inadequate interaction with E. coli ribosomes, or, as is the case with Streptococcus equisimilis RelSeq, increased hydrolase activity of the enzyme (7, 27, 35). RelBbu may in fact not need to interact with ribosomes to be enzymatically active. For example, RelSeq is enzymatically active in the absence of ribosomes (27).
Despite the fact that increasing or decreasing the production of (p)ppGpp had no effect on 16S rRNA synthesis, changes in (p)ppGpp levels could modulate B. burgdorferi lipoprotein gene expression. It has been shown that growth of B. burgdorferi with cultured tick cells decreases the (p)ppGpp concentration (5) and is accompanied by upmodulation of polycistronic rpsL-bmpD transcription (as would be expected for a gene encoding a ribosomal protein released from stringent control [37]), downmodulation of monocistronic bmpD transcription, and a net decrease in bmpD expression. (p)ppGpp is likely to be a central regulator of the B. burgdorferi response to nutritional and other stresses encountered during growth in hosts and in culture. Our results suggest that the potential modulation of gene expression by (p)ppGpp and the resultant changes in composition of B. burgdorferi could increase the ability of this organism to survive in inimical environments and influence its virulence.
Acknowledgments
We thank M. Cashel, National Institutes of Health, for valuable advice and for providing E. coli strains CF1648 and CF1693, Thomas Wendrich, Institut für Biochemie, Marburg, Germany, for providing rabbit anti-B. subtilis RelBsu, Alan G. Barbour, University of California, Irvine, for providing anti-B. burgdorferi FlaB (H9724) and OspA (H5332) monoclonal antibodies, Linda Bockenstadt, Yale University, for providing B. burgdorferi N40, Ulrike Munderloh, University of Minnesota, St. Paul, for providing IDE8 tick cells, Aravinda de Silva, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, for valuable advice regarding tick infections, Ira Schwartz, New York Medical College, for providing B. burgdorferi BL206 and for repeated discussions, Guiqing Wang, Caroline Ojaimi, Stuart Newman, and Nadejda Mezenzeva, New York Medical College, for help with real-time PCR, and Harriett Harrison for manuscript preparation.
This work was supported by National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases grant AI43063 to Felipe C. Cabello and by the Lyme disease program of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (grant AI29735 to Justin D. Radolf and Melissa J. Caimano).
REFERENCES
- 1.Akins, D. R., K. W. Bourell, M. J. Caimano, M. V. Norgard, and J. D. Radolf. 1998. A new animal model for studying Lyme disease spirochetes in a mammalian host-adapted state. J. Clin. Investig. 101:2240-2250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Alban, P. S., P. W. Johnson, and D. R. Nelson. 2000. Serum-starvation-induced changes in protein synthesis and morphology of Borrelia burgdorferi. Microbiology 146:119-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Barbour, A. G., S. L. Tessier, and W. J. Todd. 1983. Lyme disease spirochetes and ixodid tick spirochetes share a common surface antigenic determinant defined by a monoclonal antibody. Infect. Immun. 41:795-804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Barbour, A. G., S. F. Hayes, R. A. Heiland, M. E. Schrumpf, and S. L. Tessier. 1986. A Borrelia-specific monoclonal antibody binds to a flagellar epitope. Infect. Immun. 52:549-554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bugrysheva, J., E. Y. Dobrikova, H. P. Godfrey, M. L. Sartakova, and F. C. Cabello. 2002. Modulation of Borrelia burgdorferi stringent response and gene expression during extracellular growth with tick cells. Infect. Immun. 70:3061-3067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cashel, M. 1994. Detection of (p)ppGpp accumulation patterns in Escherichia coli mutants. Methods Mol. Genet. 3:341-356. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Cashel, M., D. R. Gentry, V. J. Hernandez, and D. Vinella. 1996. The stringent response, p. 1458-1496. In F. C. Neidhardt, R. Curtiss III, J. L. Ingraham, E. C. C. Lin, K. B. Low, B. Magasanik, W. S. Reznikoff, M. Schaechter, and H. E. Umbarger (ed.), Escherichia coli and Salmonella: cellular and molecular biology, vol. 1. ASM Press, Washington, D.C.
- 8.Chomczynski, P., and N. Sacchi. 1987. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal. Biochem. 162:156-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.de Silva, A. M., and E. Fikrig. 1995. Growth and migration of Borrelia burgdorferi in ixodes ticks during blood feeding. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 53:397-404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.de Silva, A. M., and E. Fikrig. 1997. Perspectives series: host/pathogen interactions. Arthropod- and host-specific gene expression by Borrelia burgdorferi. J. Clin. Investig. 99:377-379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.de Silva, A. M., N. S. Zeidner, Y. Zhang, M. C. Dolan, J. Piesman, and E. Fikrig. 1999. Influence of outer surface protein A antibody in Borrelia burgdorferi within feeding ticks. Infect. Immun. 67:30-35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Dobrikova, E. Y., J. Bugrysheva, and F. C. Cabello. 2001. Two independent transcriptional units control the complex and simultaneous expression of the bmp paralogous chromosomal gene family in Borrelia burgdorferi. Mol. Microbiol. 39:370-378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Fikrig, E., M. Chen, S. W. Barthold, J. Anguita, W. Feng, S. R. Telford III, and R. A. Flavell. 1999. Borrelia burgdorferi erpT expression in the arthropod vector and murine host. Mol. Microbiol. 31:281-290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Fraser, C. M., S. Casjens, W. M. Huang, G. G. Sutton, R. Clayton, R. Lathigra, O. White, K. A. Ketchum, R. Dodson, E. K. Hickey, M. Gwinn, B. Dougherty, J. F. Tomb, R. D. Fleischmann, D. Richardson, J. Peterson, A. R. Kerlavage, J. Quackenbush, S. Salzberg, M. Hanson, R. van Vugt, N. Palmer, M. D. Adams, J. Gocayne, J. Weidman, T. Utterback, L. Watthey, L. McDonald, P. Artiach, C. Bowman, S. Garland, C. Fuji, M. D. Cotton, K. Horst, K. Roberts, B. Hatch, H. O. Smith, and J. C. Venter. 1997. Genomic sequence of a Lyme disease spirochaete, Borrelia burgdorferi. Nature 390:580-586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gaal, T., and R. L. Gourse. 1990. Guanosine 3′-diphosphate 5′-diphosphate is not required for growth rate-dependent control of rRNA synthesis in Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87:5533-5537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gazumyan, A., J. J. Schwartz, D. Liveris, and I. Schwartz. 1994. Sequence analysis of the ribosomal RNA operon of the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi. Gene 146:57-65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Gentry, D. R., and M. Cashel. 1996. Mutational analysis of the Escherichia coli spoT gene identifies distinct but overlapping regions involved in ppGpp synthesis and degradation. Mol. Microbiol. 19:1373-1384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Gern, L., Z. Zhu, and A. Aeschlimann. 1990. Development of Borrelia burgdorferi in Ixodes ricinus females during blood feeding. Ann. Parasitol. Hum. Comp. 65:89-93.2264691 [Google Scholar]
- 19.Gilmore, R. D., Jr., M. L. Mbow, and B. Stevenson. 2001. Analysis of Borrelia burgdorferi gene expression during life cycle phases of the tick vector Ixodes scapularis. Microbes Infect. 3:799-808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Godfrey, H. P., J. V. Bugrysheva, and F. C. Cabello. 2002. Role of the stringent response in the pathogenesis of bacterial infections. Trends Microbiol. 10:349-351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Harley, C. B., and R. P. Reynolds. 1987. Analysis of E. coli promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 15:2343-2361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hefty, P. S., S. E. Jolliff, M. J. Caimano, S. K. Wikel, J. D. Radolf, and D. R. Akins. 2001. Regulation of the OspE-related, OspF-related and Elp lipoproteins of Borrelia burgdorferi strain 297 by mammalian host-specific signals. Infect. Immun. 69:3618-3627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hubner, A., X. Yang, D. M. Nolen, T. G. Popova, F. C. Cabello, and M. V. Norgard. 2001. Expression of Borrelia burgdorferi OspC and DbpA is controlled by a RpoN-RpoS regulatory pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98:12724-12729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Indest, K. J., R. Ramamoorthy, M. Sole, R. D. Gilmore, B. J. B. Johnson, and M. T. Philipp. 1997. Cell-density-dependent expression of Borrelia burgdorferi lipoproteins in vitro. Infect. Immun. 65:1165-1171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Keener, J., and M. Nomura. 1996. Regulation of ribosome synthesis, p. 1417-1431. In F. C. Neidhardt, R. Curtiss III, J. L. Ingraham, E. C. C. Lin, K. B. Low, B. Magasanik, W. S. Reznikoff, M. Schaechter, and H. E. Umbarger (ed.), Escherichia coli and Salmonella: cellular and molecular biology, vol. 1. ASM Press, Washington, D.C.
- 26.Liang, F. T., F. K. Nelson, and E. Fikrig. 2002. Molecular adaptation of Borrelia burgdorferi in the murine host. J. Exp. Med. 196:275-280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Mechold, U., H. Murphy, L. Brown, and M. Cashel. 2002. Intramolecular regulation of the opposing (p)ppGpp catalytic activities of Relseq, the Rel/Spo enzyme from Streptococcus equisimilis. J. Bacteriol. 184:2878-2888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Mittenhuber, G. 2001. Comparative genomics and evolution of genes encoding bacterial (p)ppGpp synthetases/hydrolases (the Rel, RelA and SpoT proteins). J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 3:585-603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Nadelman, R. B., and G. P. Wormser. 1998. Lyme borreliosis. Lancet 352:557-565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Revel, A. T., A. M. Talaat, and M. V. Norgard. 2002. DNA microarray analysis of differential gene expression in Borrelia burgdorferi, the Lyme disease spirochete. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99:1562-1567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Sambrook, J., and D. W. Russell. 2001. Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd ed. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Plainview, N.Y.
- 32.Samuels, D. S. 1995. Electrotransformation of the spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi. Methods Mol. Biol. 47:253-259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Schwan, T. G., J. Piesman, W. T., Golde, M. C. Dolan, and P. A. Rosa. 1995. Induction of an outer surface protein on Borrelia burgdorferi during tick feeding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92:2909-2913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Schwan, T. G., and J. Piesman. 2000. Temporal changes in outer surface proteins A and C of the Lyme disease-associated spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi, during the chain of infection in ticks and mice. J. Clin. Microbiol. 38:382-388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Sun, J., A. Hesketh, and M. Bibb. 2001. Functional analysis of relA and rshA, two relA/spoT homologues of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J. Bacteriol. 183:3488-3498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Tosa, T., and L. I. Pizer. 1971. Biochemical bases for the antimetabolite action of l-serine hydroxamate. J. Bacteriol. 106:972-982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Wagner, R. 2000. Transcription regulation in prokaryotes, p. 275-281 and 288-303. Oxford University Press, New York. N.Y.
- 38.Wendrich, T. M., and M. A. Marahiel. 1997. Cloning and characterization of a relA/spoT homologue from Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Microbiol. 26:65-79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Xiao, H., M. Kalman, K. Ikehara, S. Zemel, G. Glaser, and M. Cashel. 1991. Residual guanosine 3′,5′-bispyrophosphate synthetic activity of relA null mutants can be eliminated by spoT null mutations. J. Biol. Chem. 266:5980-5990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Yang, X., M. S. Goldberg, T. G. Popova, G. B. Schoeler, S. K. Wikel, K. E. Hagman, and M. V. Norgard. 2000. Interdependence of environmental factors influencing reciprocal patterns of gene expression in virulent Borrelia burgdorferi. Mol. Microbiol. 37:1470-1479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Yang, X., T. G. Popova, M. S. Goldberg, and M. W. Norgard. 2001. Influence of cultivation media on genetic regulatory patterns in Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect. Immun. 69:4159-4163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Zacharias, M., H. U. Goringer, and R. Wagner. 1989. Influence of the GCGC discriminator motif introduced into ribosomal RNA P2- and tac promoter on growth-rate control and stringent sensitivity. EMBO J. 8:3357-3363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]