Abstract
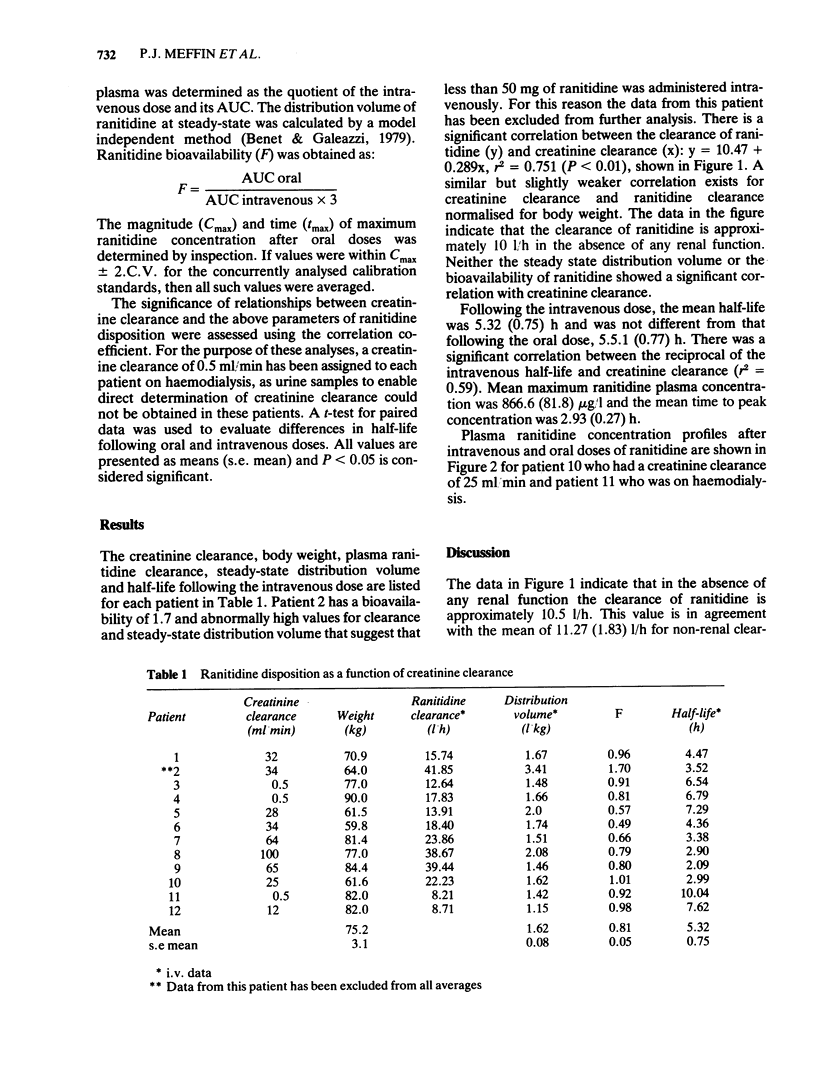
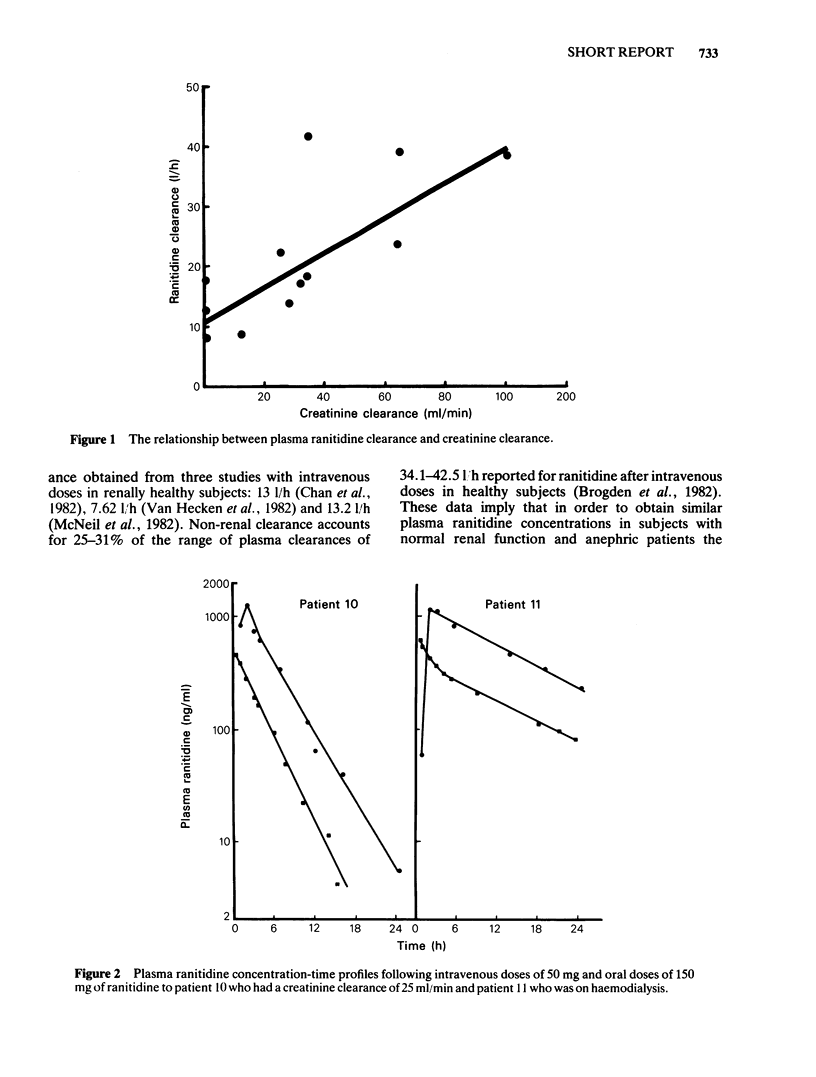
Ranitidine disposition has been studied in 12 patients with renal impairment following 50 mg given intravenously and 150 mg given by mouth on separate occasions. The clearance of ranitidine from plasma (y) was correlated with creatinine clearance (x): y = 10.47 + 0.289x,r2 = 0.751, but there was no significant correlation of creatinine clearance with distribution volume or bioavailability. The mean (s.e. mean) distribution volume was 1.62 (0.08) 1/kg and the mean bioavailability 0.81 (0.05). These data suggest that in order to obtain similar ranitidine plasma concentrations in anephric patients and patients with normal renal function, the maintenance dose in the anephric patients should be 25-30% of that for patients with normal renal function.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benet L. Z., Galeazzi R. L. Noncompartmental determination of the steady-state volume of distribution. J Pharm Sci. 1979 Aug;68(8):1071–1074. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600680845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brogden R. N., Carmine A. A., Heel R. C., Speight T. M., Avery G. S. Ranitidine: a review of its pharmacology and therapeutic use in peptic ulcer disease and other allied diseases. Drugs. 1982 Oct;24(4):267–303. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198224040-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey P. F., Martin L. E., Owen P. A method for the determination of ranitidine and its metabolites in urine by h.p.l.c. and its application to study the metabolism and pharmacokinetics of ranitidine in man. Biochem Soc Trans. 1981 Feb;9(1):112–112. doi: 10.1042/bst0090112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finley P. R., Williams R. J., Lichti D. A., Thies A. C. Evaluation of a new multichannel analyzer, "Astra-8". Clin Chem. 1978 Dec;24(12):2125–2131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil J. J., Mihaly G. W., Anderson A., Marshall A. W., Smallwood R. A., Louis W. J. Pharmacokinetics of the H2- receptor antagonist ranitidine in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1981 Sep;12(3):411–415. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1981.tb01236.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mihaly G. W., Drummer O. H., Marshall A., Smallwood R. A., Louis W. J. High-pressure liquid chromatographic determination of ranitidine, a new H2-receptor antagonist, in plasma and urine. J Pharm Sci. 1980 Oct;69(10):1155–1157. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600691008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Hecken A. M., Tjandramaga T. B., Mullie A., Verbesselt R., de Schepper P. J. Ranitidine: single dose pharmacokinetics and absolute bioavailability in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1982 Aug;14(2):195–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1982.tb01961.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


