Abstract
FliN is a major constituent of the C ring in the flagellar basal body of many bacteria. It is present in >100 copies per flagellum and together with FliM and FliG forms the switch complex that functions in flagellar assembly, rotation, and clockwise-counterclockwise switching. FliN is essential for flagellar assembly and switching, but its precise functions are unknown. The C-terminal part of the protein is best conserved and most important for function; a crystal structure of this C-terminal domain of FliN from Thermotoga maritima revealed a saddle-shaped dimer formed mainly from β strands (P. N. Brown, M. A. A. Mathews, L. A. Joss, C. P. Hill, and D. F. Blair, J. Bacteriol. 187:2890-2902, 2005). Equilibrium sedimentation studies showed that FliN can form stable tetramers and that a FliM1FliN4 complex is also stable. Here, we have examined the organization of FliN subunits by using targeted cross-linking. Cys residues were introduced at various positions in FliN, singly or in pairs, and disulfide cross-linking was induced by oxidation. Efficient cross-linking was observed for certain positions near the ends of the dimer and for some positions in the structurally uncharacterized N-terminal domain. Certain combinations of two Cys replacements gave a high yield of cross-linked tetramer. The results support a model in which FliN is organized in doughnut-shaped tetramers, stabilized in part by contacts involving the N-terminal domain. Electron microscopic reconstructions show a bulge at the bottom of the C-ring whose size and shape are a close match for the hypothesized FliN tetramer.
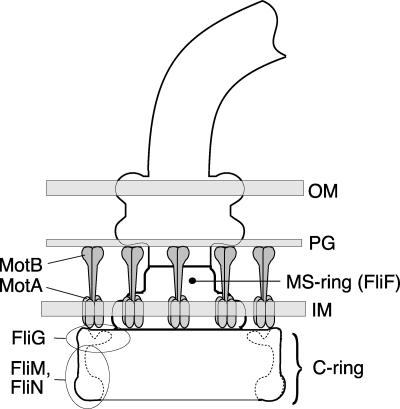
Many species of bacteria are propelled by rotating flagella (2) that obtain energy from the membrane ion gradient (16, 23; for reviews, see references 1 and 21) The flagella are built from about 25 different proteins, most of which have roles in forming the flagellar basal body, hook, and filament (22, 26). Only a few proteins function in rotation and switching. The membrane proteins MotA and MotB form ion-conducting complexes that function as the stator (3, 8-11, 33). The proteins FliN, FliM, and FliG form the rotor-mounted switch complex that functions in flagellar assembly, rotation, and clockwise-counterclockwise (CW/CCW) direction control (44, 45). The switch complex contains >100 copies of FliN (47), about 34 copies of FliM (47), and 25 copies of FliG (13, 18, 35, 36, 47). Together, these form the C ring, a 45-nm-diameter, drum-shaped structure at the bottom (the cytoplasm-proximal end) of the basal body (Fig. 1) (14, 19, 40).
FIG. 1.
Cartoon of the flagellar basal body indicating the approximate locations of the proteins that form the stator (MotA and MotB) and the switch complex (FliG, FliM, and FliN). OM, outer membrane; PG, peptidoglycan; IM, inner membrane.
FliG functions directly in rotation of the flagellum (17, 24). It interacts with the FliF protein that forms the MS ring (13, 15, 20, 30) and with the membrane-associated stator protein MotA (48) and must presumably be located in the upper (membrane-proximal) part of the C ring (Fig. 1). FliM and FliN have not been located precisely but are probably more distant from the membrane because they do not function as directly in rotation (24) and are not believed to interact directly with FliF or MotA. FliM is closely involved in direction switching (34) and contains a binding site for the CW-signaling protein CheY (28, 41, 43). FliN has been implicated in CW/CCW switching (17) and in the export process that occurs during flagellar assembly (42), but its exact functions are unknown.
The FliN protein of Escherichia coli or Salmonella contains 137 residues (27). The C-terminal part of the protein, from about residue 58 to the end, is best conserved and most important for function (37). A FliN protein lacking 57 N-terminal residues is sufficient for flagellar assembly and rotation, but the cells swarm at about one-third of the wild-type rate in soft agar (37) and show relatively slow, erratic motility in liquid (K. Paul and D. Blair, unpublished data). In the flagellum, FliN interacts with the C-terminal domain of FliM (FliMC) (28, 41). Portions of FliMC show sequence homology to FliN (28) and may therefore show some similarity in folding. FliN might also bind to FliG, but the evidence for this is less strong (39).
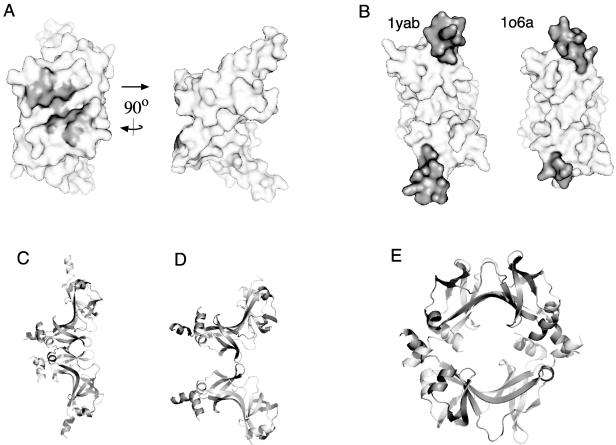
Two crystal structures were recently solved for most of the FliN protein from Thermotoga maritima (Protein Data Bank [PDB] entries 1o6a and 1yab) (5). Both structures show a saddle-shaped dimer formed mainly from β strands, with short α helices at the ends (Fig. 2). The two structures differ somewhat in the position of α-helix 1, which packs near the body of the dimer in one crystal (1o6a) but extends to contact an adjacent dimer in the other (1yab). The FliN dimer exhibits a sizable surface hydrophobic patch, formed from the side chains of 5 residues (10 residues in the dimer) with a strongly conserved nonpolar character. A mutation in the hydropobic patch (Val113→Asp) affects both flagellar assembly and switching (5).
FIG. 2.
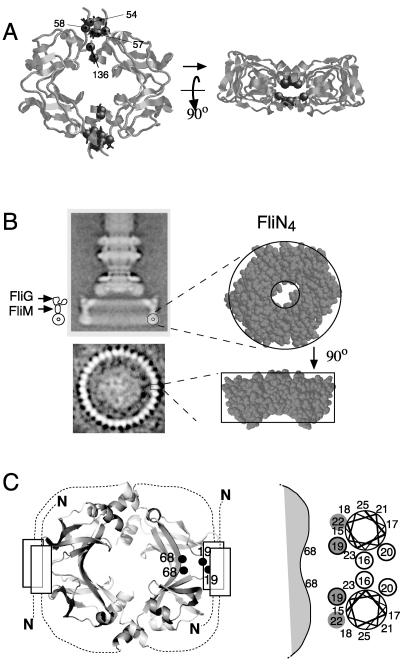
(A) Crystal structure of FliN (PDB accession no. 1yab), with the hydrophobic patch indicated by gray coloring. (B) Differing positions of helix 1 (colored gray) in the two FliN crystal structures. In the 1o6a structure, the two helices of the dimer have different apparent lengths because the structural model begins at residue 68 of one subunit and residue 74 of the other. (C) Model for the FliN tetramer based upon the subunit organization seen in the crystal structure of HrcQBC (12). (D) Example of a dimer-dimer contact occurring in the FliN crystal structure 1o6a. (E) Ring-shaped tetramer of FliN subunits seen in the crystal structure 1yab. Panels A and B were prepared using Pymol, and panels C and D were prepared using Rasmol.
Equilibrium sedimentation experiments showed that the FliN protein of E. coli forms a stable tetramer in solution and that the FliN and FliM proteins of T. maritima form a stable complex with the composition FliM1FliN4 (5). (Sedimentation experiments with FliM used the T. maritima proteins because E. coli FliM is prone to aggregation.) Accordingly, we proposed that FliM1FliN4 complexes might be structural units of the C ring (5). The subunit composition of the C ring is not yet firmly established, however; an estimate of subunit stoichiometry in purified basal bodies of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium gave a FliM:FliN ratio closer to 1:3 (47). Because FliMC shows sequence similarity to FliN, it might be capable of replacing a FliN subunit to form a FliM-FliN heterodimer, and such heterodimers in combination with FliN dimers could account for a 1:3 subunit composition. The location and arrangement of the FliN subunits in the C ring are also unknown. The related protein HrcQBC crystallized as an elongated tetramer in which the dimers are joined end to end (12). Patterns of residue conservation indicate that FliN dimers might associate in a similar end-to-end fashion (5), but the subunit associations seen in FliN crystals indicate that other arrangements are also possible, including some with the shape of a ring (Fig. 2C to E).
Here, we have used targeted cross-linking to test various models for the organization of FliN. Cys residues were introduced in various positions on the surface of FliN, singly or in pairs; disulfide cross-linking was induced; and the products were analyzed on immunoblots. The subunit replacement model was tested by making Cys replacements at predicted interfacial positions in FliN and FliMC. The results indicate that FliN is organized in tetramers and does not form subunit-exchanged heterodimers with FliMC. The FliN tetramer is not organized like the tetramer seen in the HrcQBC crystal structure but has a doughnut shape similar to the subunit organization seen in one of the FliN crystal structures. The FliN doughnut seen in the crystal structure is puckered and as a result is predicted to be bistable (to exist in two equally stable conformations). In the flagellum, the two conformations would be nonequivalent and might be relevant for CW/CCW switching. Some Cys replacements were also made in the structurally uncharacterized N-terminal domain of FliN. Occurrences of efficient cross-linking show that the N-terminal segments of two FliN subunits are in proximity to each other and are near the hydrophobic patch of another dimer. These interactions appear to stabilize the tetramer, because a protein lacking the N-terminal domain formed mainly dimers. Electron microscopic reconstructions (40, 46) show a bulge at the bottom of the C ring of the appropriate size and shape to fit the FliN tetramers.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Strains and media.
The E. coli strains and plasmids used are listed in Table 1. Procedures for transformation and plasmid isolation were described previously (38). TB contained 10 g tryptone and 5 g NaCl per liter. SB contained, per liter, 12-g tryptone, 24-g yeast extract, 5-ml glycerol, 3.8-g KH2PO4, and 12.5-g K2HPO4. Ampicillin (Amp) was used at 125 μg/ml in liquid medium and at 50 μg/ml in swarm plates. Chloramphenicol was used at 50 μg/ml in liquid and 12.5 μg/ml in swarm plates. IPTG (isopropyl-β-d-thiogalactopyranoside) was prepared as a 0.1 M stock in water.
TABLE 1.
Strains and plasmids
| Strain or plasmid | Relevant genotype or property | Reference or source |
|---|---|---|
| DFB223 | fliN-null strain | 37 |
| RP3098 | flhDC deletion strain; expresses no chromosomal flagellar genes | J. S. Parkinson |
| pTBM30 | Ptac expression vector(Apr); parent of pHT39 | 29 |
| pLS4 | fliN in pAlter-1(Apr); used for site-directed mutagenesis of fliN | 37 |
| pSB4 | Expresses fliN codons 58-137 in pTBM30 | 37 |
| pHT39 | fliN in pTBM30; used to express FliN proteins with Cys replacements | 24 |
| pHT41 | fliM in pAlter-1; used for site-directed mutagenesis and expression of fliM | 24 |
| pDB94 | Ptac expression vector for fliM; Cmr | 38 |
Site-directed mutagenesis and assays of swarming.
Single-stranded DNA preparation and site-directed mutagenesis were carried out according to the Altered Sites procedure (Promega), with fliN cloned in plasmid pLS4 (24) or with fliM cloned in pHT41 (38). The mutations were confirmed by DNA sequencing. The mutated fliN and fliM genes were transferred into plasmids (pHT39 and pDFB97, respectively) that allow IPTG-regulated expression from the tac promoter. Swarming in soft agar, swimming in liquid, and flagellation were assayed as described previously (38) by using the fliN deletion strain DFB223 transformed with wild-type or mutant plasmids. Swarm plates contained TB, 0.27% agar, and an appropriate antibiotic(s).
Cross-linking.
Initial cross-linking experiments used the catalyst Cu[1,10-phenanthroline]3 (Cu-phenanthroline) and were performed as described previously (4), with minor modifications. fliN deletion strain DFB223 or flhDC deletion strain RP3098 was transformed with wild-type or mutant plasmids. RP3098 expresses no flagellar genes, except those expressed from plasmids, and thus does not assemble flagella. Cells were cultured overnight in TB and antibiotics at 32°C, then diluted 100 fold into TB containing appropriate antibiotics, and grown for 1 h at 32°C. The culture was then induced with 25 μM IPTG, and growth was continued for an additional 3.5 h. The absorbance of each culture was measured at 600 nm. The least-dense culture was transferred to a centrifuge tube in its entirety, and the other cultures were transferred in volumes adjusted (by using A600 readings) to give equal numbers of cells. The cells were pelleted (3,000 × g; 10 min) and resuspended in 200 μl lysis buffer (50 mM Tris [pH 8], 0.5 M sucrose, 10 mM EDTA, 0.2-mg/ml lysozyme). The cells were incubated on ice for 1 h and then rapidly diluted by the addition of 1.8 ml of ice-cold water. Samples were divided into two 1-ml fractions, and 110 μl of cross-linking reagent was added to one of the tubes and 110 μl of 50% ethanol was added to the other. The cross-linking reagent contained 4 mM CuSO4 and 16 mM 1,10-phenanthroline in 50% ethanol and was freshly prepared from a 1 M stock of 1,10-phenanthroline in 95% ethanol and a 400 mM stock of CuSO4 in water. Samples were incubated at room temperature with gentle rotation for 5 min, sonicated for 15 s (50% duty cycle, power level 2; Branson model 450 sonifier), and incubated an additional 5 min. Reactions were quenched by the addition of N-ethylmaleimide (22 μl of a 1 M stock in 95% ethanol) and EDTA (126 μl of a 0.5 M stock). A total of 100 μl of each sample was mixed with 100 μl of nonreducing gel-loading buffer, boiled, and used for electrophoresis.
For some cross-linking experiments using iodine, cells were cultured, collected as described above, and then treated with 0.2 mM I2 added from a 2 mM stock in 95% ethanol. N-Ethylmaleimide was added after 5 min, and then cells were mixed with gel loading buffer (lacking reducing agent), boiled, loaded on gels, and analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and immunoblotting, as described below.
SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting.
Protein samples were separated on 10% or 12% SDS-PAGE minigels (Bio-Rad MiniProtean system). Proteins were transferred to nitrocellulose using a semidry transfer apparatus (Bio-Rad). Rabbit polyclonal antibody against FliN was prepared as described previously (37) and was used at an ∼1,000-fold dilution. Bands were visualized using the Super Signal West Picoluminol system (Pierce) and X-ray film. Bands were quantified by video densitometry using the public domain image-processing program NIH Image (developed at the U.S. National Institutes of Health and available online at http://rsb.info.nih.gov/nih-image/).
Gel filtration chromatography.
The fliN deletion strain DFB223 was transformed with plasmids encoding either full-length FliN or FliN lacking 57 N-terminal residues. Cells were grown at 37°C in 500 ml SB-Amp broth to an absorbance of 0.7 at 600 nm, then IPTG was added to 400 μM, and growth was continued for 3 h. Cells were pelleted and resuspended in 40 ml of buffer containing 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 500 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, and 1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride. Cells were lysed by passage through a French pressure cell, and the lysate was centrifuged (23,000 × g; 45 min) to pellet the membranes. The supernatant was collected in a fresh tube. A 2-ml sample of the supernatant was filtered and loaded onto a Superdex-300 size exclusion column in a fast-performance liquid chromatography apparatus (ÄKTA; Amersham). The column was run in 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0)-200 mM NaCl, and fractions were collected and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting.
RESULTS
Shape of the FliN tetramer.
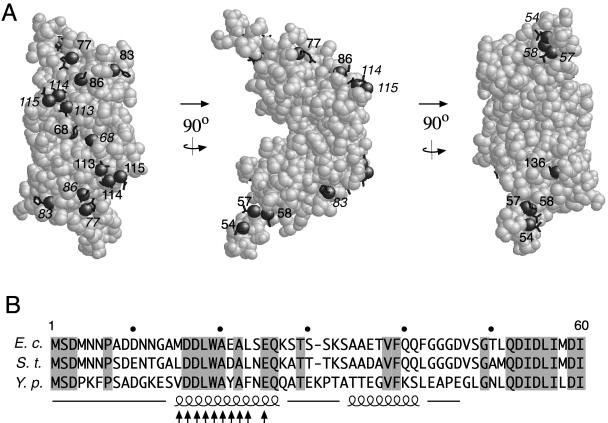
The crystal structure is known for residues 68 to 154 of T. maritima FliN (5) (PDB accession numbers 1yab and 1o6a), corresponding to residues 51 to 137 of the E. coli protein. The cross-linking experiments used the protein from E. coli. The wild-type protein contains no Cys residues. In the part of FliN of known structure, 10 Cys replacements were made on the surface and 1 was made at a more interior position near the dimer twofold axis. Several Cys replacements were also made in the N-terminal domain, which has not yet been crystallized. The positions of the mutations are shown in Fig. 3, either on the crystal structure (for positions 54 and higher) or on a sequence alignment of the N-terminal segment (for the replacements in the N-terminal domain). A secondary-structure prediction for the N-terminal part of the protein is also shown. The Cys replacements in the N-terminal domain were in a segment that is relatively well conserved and predicted to form an α helix.
FIG. 3.
(A) Positions of Cys replacements on the FliN dimer. The structure shown is 1yab (5). Labels in roman type are for subunit B and those in italic type are for subunit A. (B) Positions of the Cys replacements in the N-terminal domain (arrows). The structure of this domain is not known; secondary structures predicted by a neural-net algorithm (32) are shown on a sequence alignment of the N-terminal segments from some closely related species, with springs indicating α helices and lines indicating coil. S.t., Salmonella typhimurium; Y.p., Yersinia pestis.
First, we examined cross-linking of proteins with single Cys residues on the surface of the domain of known structure. One double mutant (77C/83C) was also studied, because these positions are predicted to be near each other in the HrcQBC-based model for the FliN tetramer (5, 12). The Cys-substituted FliN proteins were expressed in the fliN deletion strain DFB223, cells were lysed, and copper phenanthroline was added to catalyze oxidative cross-linking. The deletion in strain DFB223 is fully complemented by plasmid-encoded fliN (37), and so the cells in these experiments were flagellate. Parallel experiments were also conducted with an flhDC strain (RP3098) that does not express any chromosomal flagellar genes and that does not assemble flagella to determine whether similar subunit contacts occur when the protein is not assembled into motors. Proteins were resolved on SDS-PAGE gels, and the products of cross-linking were characterized on FliN immunoblots.
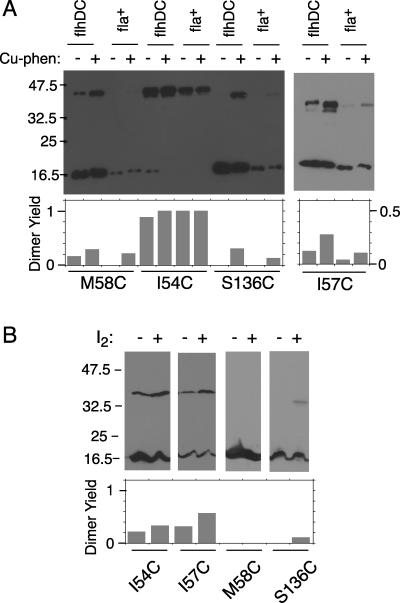
Wild-type FliN and most of the Cys-replacement proteins showed no cross-linking when treated with Cu-phenanthroline. Just four of the mutant proteins, with Cys replacements at positions 54, 57, 58, and 136, showed cross-linking upon oxidation (Fig. 4). (Numbers are for the E. coli protein; T. maritima numbers are higher by 17.) Each showed a single major cross-linked product with an apparent molecular weight of 42 kDa. Although this was larger than expected for a normally migrating FliN dimer (predicted mass, 31 kDa), cross-linked species often exhibit aberrant mobility, and other evidence described below supports its assignment as a FliN dimer. These four positions are near the ends of the FliN dimer (Fig. 3), in a region that is the major site of contact between dimers in the 1yab FliN crystal structure (Fig. 2E) (5). This region did not contribute to the dimer-dimer interface in the HrcQBC-based model for the FliN tetramer (see Fig. S1A in the supplemental material). Cross-linking results were similar for the flagellum-forming strain and the flhDC strain (Fig. 4). Thus, the cross-linked product did not contain any flagellar proteins besides FliN, and the contacts through positions 54, 57, 58, and 136 did not require the protein to be assembled into flagella. Given the location of these residues at the ends of the (crystallographic) FliN dimer, the cross-linking was not between the two subunits of this dimer but must occur within a larger assembly—presumably, the FliN tetramer known from sedimentation equilibrium experiments (5).
FIG. 4.
Efficient cross-linking by four Cys replacements on the FliN domain of known structure. (A) Cross-linking by Cu[1,10-phenanthroline]3. The experiments used either the fliN-null strain DFB223 or the flhDC strain RP3098, as indicated. DFB223 is flagellate when it expresses the FliN protein from the plasmid, whereas strain RP3098 is nonflagellate, and so the FliN is not present in flagellar motors. Experiments used either a 10% gel (57C) or 12% gels (58C, 54C, and 136C). Products of cross-linking, here and in panel B, are visualized on anti-FliN immunoblots. (B) Cross-linking of the same proteins by iodine. The experiment used the fliN-null strain DFB223 and 10% polyacrylamide gels. Iodine was used at 0.4 mM for the 54C and 57C proteins and 0.2 mM for the 58C and 136C proteins. (These were chosen as those showing the highest yield, in a series of experiments using 0.2, 0.4, or 0.6 mM.)
Fluctuations in protein position or orientation might allow cross-linking between sites that are somewhat separated in the lowest-energy configuration (7). Previous studies found that such motional effects are minimized when iodine rather than copper phenanthroline is used for oxidation (4, 6); so to place tighter constraints on residue proximity, we examined cross-linking by iodine. Although yields were lower than those with copper phenanthroline, the proteins with Cys replacements at position 54, 57, or 136 showed a readily detectable cross-linked product upon treatment with iodine. Position 58, which showed a lower yield than the others with copper phenanthroline, did not show any cross-linking using iodine.
FliN and FliMC do not form a subunit-exchanged heterodimer.
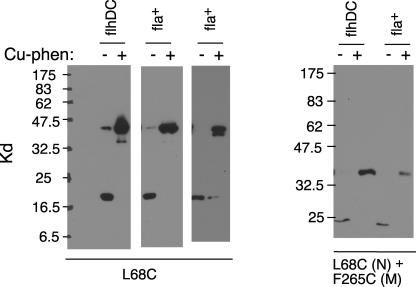
As discussed above, sequence similarities between FliN and FliMC raise the possibility that FliM-FliN heterodimers form by replacement of a FliN subunit by FliMC. To test this subunit-replacement model, we introduced a Cys replacement at a position that is near the twofold axis of the FliN dimer seen in the crystal structures (Leu 68 in E. coli, corresponding to Leu 85 in T. maritima). The L68C protein gave cross-linked FliN dimer in very high yield (Fig. 5), again with an apparent mass of approximately 42 kDa. We conclude that position 68 of each FliN subunit is close to position 68 of the other subunit in the dimer, as is seen in the crystal structures. Although the yield of cross-linking showed some variability between experiments, it was typically >80% and appeared to be quantitative (i.e., with no detectable monomer remaining) in some experiments. Such complete conversion into dimer would not be possible if a significant fraction of the FliN were present in FliM-FliN heterodimers formed by a subunit replacement. As a further test, we looked for cross-linking between FliN with Cys at position 68 and FliM with Cys at position 265, the residue that corresponds with FliN-Leu68 in a FliM-FliN sequence alignment. No FliM-FliN cross-linking was detected using either FliN or FliM immunoblots, and the major product was again FliN dimer (Fig. 5; the FliN blot is shown). We conclude that subunit-exchanged FliM-FliN heterodimers do not occur or are present as only a minor species. These data support a tetrameric FliN complex and argue against a complex with composition FliN3FliM1.
FIG. 5.
(Left) Efficient cross-linking of the FliN protein with Cys at position 68, near the twofold axis of the dimer. Cross-linking was induced by Cu[1,10-phenanthroline]3. The experiment used either the nonflagellate flhDC strain RP3098 (flhDC), or the fliN-null strain DFB223 (fla+), as indicated. Two representative experiments in strain DFB223 are shown. Proteins were resolved on 12% polyacrylamide gels, and the blot used anti-FliN antibody. (Right) Absence of cross-linking between FliN (L68C) and FliM (F265C). FliM has a molecular weight of approximately 38 kDa, and a FliM-FliN heterodimer would have a molecular weight of 52.7 kDa. Phe265 is the residue of FliM that aligns with Leu68 in a FliM:FliN sequence comparison (28). The cross-linked dimer shows closer-to-normal mobility in this experiment, which used a lower acrylamide concentration (10%). A FliN immunoblot is shown; FliM blots (not shown) exhibited only the FliM monomer.
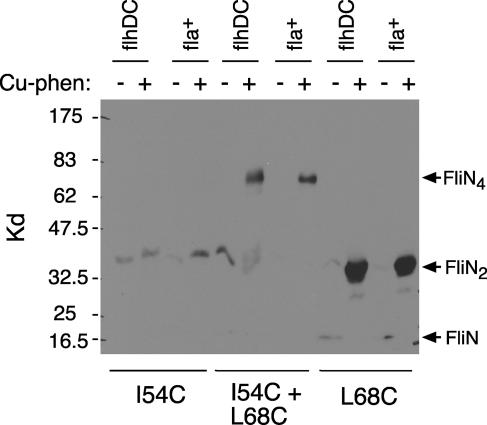
To probe FliN tetramer organization further, we examined cross-linking of a FliN protein with one Cys replacement at position 68 near the twofold axis of the dimer and another at position 54 near the end(s) of the dimer. Cross-linking was induced with copper phenanthroline, and products were examined using immunoblots, as before. Representative results are shown in Fig. 6. In the flagellate strain, cross-linking of the 54C/68C double mutant gave a species with an apparent mass of about 70 kDa as the only major product. In the nonflagellate strain, the results were similar, except that a small amount of dimer was also observed. Because the 54C and 68C replacements individually showed very efficient cross-linking (Fig. 4 and 6), we assigned the 70-kDa band as a FliN tetramer cross-linked through both positions. The apparent mass was close to that expected (predicted tetramer mass, 62 kDa). Although the tetramer formed in very high yield, larger products were not observed in significant amounts.
FIG. 6.
Cross-linking of the FliN protein with Cys residues at both positions 54 and 68 (and corresponding single-Cys controls). Cross-linking was induced by Cu[1,10-phenanthroline]3. Proteins were resolved on a 10% polyacrylamide gel and visualized with anti-FliN immunoblots. The experiment used either the flagellate strain (fliN-null strain complemented with fliN on a plasmid) or the nonflagellate flhDC strain, as indicated.
Organization of a segment in the N-terminal domain.
As discussed above, the N-terminal domain of FliN contributes to optimal swarming motility but is not essential for flagellar assembly. We hypothesized that the N-terminal segment might contribute to the stability of the FliN tetramer. To test this, we used gel filtration to examine the state of association of a FliN protein deleted for residues 1 to 57. The FliN(Δ1-57) protein ran with an apparent mass of about 20 kDa in the sizing column (Fig. 7), close to that expected for a dimer (predicted dimer mass, 16 kDa) and too small to be a tetramer. The full-length FliN protein, by contrast, exhibited a broad peak centered at around 100 kDa, consistent with previous sedimentation experiments indicating a tetramer with nonglobular shape (5). Thus, the N-terminal domain appears necessary for the formation of a stable FliN tetramer.
FIG. 7.
Size exclusion chromatography of full-length FliN and FliN lacking residues 1 to 57. Cell lysates were chromatographed on a Superdex-300 column, and eluted fractions were examined on FliN immunoblots, as described in Materials and Methods. Positions of the elution peaks for three molecular mass standards are indicated at the top.
To examine further the organization of the N-terminal domain, we studied cross-linking of proteins with single Cys replacements in a relatively well-conserved, predicted α-helical segment (Fig. 3). An initial experiment used Cu-phenanthroline with Cys replacements positions 16, 19, 22, and 25. In each case, treatment with Cu-phenanthroline gave cross-linked dimer in high yield (Fig. 8A), indicating that the N-terminal segments of different FliN subunits are in proximity to each other. The protein cross-linked through these positions migrated with an apparent mass of 35 kDa in gels, close to the mass expected for a FliN dimer.
FIG. 8.
(A) Cross-linking of FliN proteins with Cys replacements at four positions in the N-terminal domain, using Cu[1,10-phenanthroline]3. Experiments used either the nonflagellate flhDC strain or the flagellate strain, as indicated. (B) Cross-linking of FliN proteins with Cys replacements in 10 positions in the N-terminal segment, using 0.4 mM iodine. This experiment used strain DB223. Experiments for both panels used 10% polyacrylamide gels and anti-FliN immunoblots.
To place tighter constraints on the arrangement of the N-terminal segment, we examined iodine-induced cross-linking of FliN proteins with Cys in 10 positions in the predicted helical segment (Fig. 3). Although yields were relatively low, the proteins with Cys at position 16, 19, or 20 produced cross-linked dimer at readily detectable levels (Fig. 8B). If this segment of FliN were α helical, then these positions would lie on one face, and the pattern of cross-linking would suggest that the N-terminal segments of two FliN subunits approach most closely through this face.
Next, we examined cross-linking of FliN proteins with a Cys replacement at position 19 in the N-terminal domain and a second replacement at position 68 near the dimer twofold axis. Oxidation using copper phenanthroline gave two major products, both in the range expected for a tetramer. Two products in the range expected for a dimer and one in the range expected for a trimer were also seen, but in smaller amounts (Fig. 9). Species larger than a tetramer did not occur in significant amounts. Results were similar in the flagellate strain and the nonflagellate flhDC strain, and so the cross-linked products did not contain any flagellar proteins besides FliN. Because FliN in solution is known to form a stable tetramer and patterns of cross-linking were similar whether or not flagella were assembled, we concluded that the cross-linking occurred within rather than between FliN tetramers. Given the results with the individual Cys replacements at positions 19 and 68, one interpretation might be that FliN dimers joined by a 68-68 disulfide can cross-link into tetramers through position 19. Such tetramers could contain either three or four disulfide bonds (i.e., be either linear or closed), which could account for the occurrence of two major products. An alternative possibility is that the N-terminal segment is positioned near the hydrophobic patch, and cross-linking between positions 19 and 68 gives rise to tetramers and other products.
FIG. 9.
(A) Cross-linking of the FliN protein with Cys residues at both positions 19 and 68 and single-Cys controls. Cross-linking used Cu[1,10-phenanthroline]3. (B) Cross-linking of the 19-68 double mutant and other double mutants, using iodine (0.2 mM). In all experiments, proteins were resolved on 10% polyacrylamide gels and visualized on FliN immunoblots. (C) Testing alternative models for the disposition of the N-terminal segment. Two alternative topologies are pictured. The four lines (two thick and two thin) represent the four subunits in the FliN tetramer. Cross-linking of the 19C-54C double mutant with Cu-phenanthroline is predicted to give only dimer in one case but tetramer in the other. The experiment, shown on the right, gave a high yield of tetramer.
To distinguish between these possibilities, we first examined cross-linking of the 19C-68C double mutant by using iodine. The 19C replacement by itself showed only very weak cross-linking with iodine, and so iodine treatment should give little or no tetramer if tetramer formation requires the 19-19 disulfide. Iodine treatment of the 19C-68C double mutant gave both dimer and tetramer in high yield, as well as species at a higher molecular weight (Fig. 9B). Because iodine was not expected to induce efficient 19-19 cross-linking, this suggested that the tetramer and larger species were formed by cross-linking between positions 19 and 68. Some tetramer was also formed upon iodine treatment of the 16C-68C, 22C-68C, and 25C-68C double mutants (Fig. 9B). Positions 22 and 25, like 19, showed no iodine-induced cross-linking by themselves, and so the production of tetramer in the 22C-68C and 25C-68C mutants reinforces the conclusion that position 68 can cross-link to positions in the N-terminal segment.
Tetramer formation might still be due to 68-68 cross-linking in combination with 19-19 cross-linking, if we postulate that the Cys replacement at position 68 affects the position or mobility of the N-terminal segment to increase the efficiency of 19-19 cross-linking. Thus, as a further means of distinguishing the models, we examined cross-linking of FliN with one Cys replacements at position 19 and another at position 54. Cu-phenanthroline was used for this experiment, because unlike iodine it allows efficient cross-linking through positions in the N-terminal segment, including position 19. One model predicts formation of tetramer upon treatment with copper phenanthroline, while the other predicts formation of only dimer (Fig. 9C). Some cross-linked dimer was present prior to treatment with the oxidation catalyst, as was also observed with the 54C single replacement. Treatment with Cu-phenanthroline gave an additional dimer form and a high yield of tetramer. This supports the model in which the N-terminal segments are in proximity to the hydrophobic patch of another dimer (Fig. 9C).
Function of the Cys mutant proteins.
The FliN proteins that displayed efficient cross-linking were tested by swarming assays to determine whether their function was altered by the Cys replacements. The proteins with Cys replacements at positions 16, 19, 22, 25, 54, 57, and 136 allowed cells to swarm at approximately wild-type rates. The replacement at position 58 caused a roughly twofold reduction in swarming rate. The replacement at position 68, either alone or in combination with other Cys replacements, allowed flagellar assembly and vigorous swimming, but the cells swarmed at <1/10 of the wild-type rate in soft agar and exhibited aberrantly smooth motility in liquid, indicating a CCW motor bias.
DISCUSSION
Based on patterns of sequence conservation, we suggested previously (5) that FliN might be organized similarly to the tetramer of HrcQBC (a FliN paralog) seen in a crystal structure (12). However, a subunit organization like that in the HrcQBC crystal cannot account for the pattern of disulfide cross-linking observed here with FliN (see Fig. S1 in the supplemental material). The positions of high-yield cross-linking instead indicate a doughnut-like arrangement, substantially similar to the organization seen in one of the FliN crystal structures (1yab) (Fig. 10A) (5). The subunits contacts in this arrangement are provided largely by α-helix 1, particularly positions 54 and 57. An alignment of FliN sequences (not shown) shows that hydrophobic character is very well conserved at these positions. Although helix 1 participates in close dimer-dimer contacts in one of the crystals (1yab) (5), it does not preserve these contacts in the other crystal form (1o6a), which might account for its different positioning in the two structures (Fig. 2B).
FIG. 10.
Model for FliN subunit arrangement and location. (A) Doughnut-like arrangement seen in the FliN crystal structure 1yab (5). Positions that gave a high yield of cross-linked dimer are indicated. At each dimer-dimer interface, the structure shows interpretable density for residue 136 of only one subunit, extending only to residue 135 in the other subunit. Residue 136 occurs in an α helix; to obtain a rough estimate of its position, this helix from the first subunit was overlaid on the (shorter) helix of the second. (B) Proposed location of the FliN tetramers in the flagellar basal body. The location and orientation of one FliN tetramer are indicated; the flagellum would contain approximately 34 FliN tetramers in all. The side view of the basal body is from reference 40 (with permission of the publisher), and the end view is from reference 46 (with permission of the publisher). Given this location for FliN and evidence that FliG must lie near the top (15, 20, 25, 30, 48), it follows that FliM is located in the middle of the C-ring wall, as indicated. (C, left) Arrangement of N-terminal segments that can account for the cross-linking results and for the contribution of the segment to stability of the tetramer. The segment containing residues 15 to 25 is hypothesized to form an α helix. Two such helices are in proximity to each other and to the hydrophobic patch of the other FliN dimer, bringing residues 19 and 68 into proximity. Although the arrangement pictured is stable enough to allow high-yield cross-linking between positions 19 and 68, the results also indicate that the segments are dynamic (see Discussion). (Right) Detailed view of the hypothesized interface between the N-terminal segments and the body of the dimer. The view is along the segments, one pointing toward the viewer and the other pointing away. Positions that cross-link most efficiently to position 68 are shaded, and positions that allow some cross-linking between the two N-terminal segments are circled.
Our results show that little if any of the FliN in the cell occurs in the form of subunit-exchanged FliMC/FliN heterodimers. A Cys residue near the twofold axis of the FliN dimer gave disulfide-linked dimer in very high yield, and no FliM-FliN cross-linking was observed when a second Cys residue was introduced at the corresponding position in FliMC (Fig. 5). We therefore favor a model in which FliM1FliN4 units, rather than FliM1FliN3 units, are constituents of the C ring. Sedimentation equilibrium studies have established the stability of a FliM1FliN4 complex of the T. maritima proteins (5). The FliM protein of E. coli is less amenable to such studies, owing to its tendency to aggregate, but we are attempting to identify better-behaved fragments that might allow further tests of this model for the complex.
The shape and dimensions of the hypothesized FliN tetramer provide strong constraints on its location in the C ring. Electron microscopic reconstructions of the basal body at approximately 20-Å resolution (14, 40) show that a ring with these dimensions would not fit in the part of the C ring just under FliG but is a close match for the bulge at the bottom edge of the ring. The FliN tetramer appears a good fit for this location in both side and end views of the basal body (Fig. 10B). Given this location for FliN at the bottom and the previously inferred location for FliG at the top of the C ring (13, 15, 20, 25, 30, 48), we conclude that FliM must be situated in the middle of the C-ring wall (Fig. 10B). Although the crystal structure of FliM has not been reported, a crystal structure is known for the related chemotaxis protein CheC (31). The structure shows an ellipsoidal protein with dimensions (approximately 2.5 nm by 3.5 nm by 5 nm) that are a good fit for this location.
Although we still lack detailed structural information on the N-terminal part of FliN, the present results cast some light on its function and organization. This domain contributes to the stability of the tetramer, because a truncated FliN lacking residues 1 to 57 formed primarily dimers. The cross-linking results establish that the N-terminal segments of two FliN subunits are in fairly close contact (Fig. 8) and that this assembly of two N-terminal segments, most likely two α helices, is positioned near the hydrophobic patch of another FliN dimer (Fig. 9). If residues 15 to 25 form an α helix, as predicted, then the observed pattern of cross-linking can be accounted for in a simple model for the segment organization (Fig. 10C).
In E. coli, the N-terminal segment is joined to the rest of FliN by a Gly-rich segment (GGG43-45) that should allow considerable conformational flexibility. The cross-linking experiments give two indications that the N-terminal segments are not rigidly fixed but can undergo some movement relative to each other and to the patch: yields of intersegment cross-linking were much higher when Cu-phenanthroline was used instead of iodine (Fig. 8A), and several different positions in the N-terminal segment showed some ability to cross-link to the same position (residue 68) in the main body of the protein (Fig. 9B). Given this dynamic character, we predict that the N-terminal segments could be displaced from the hydrophobic patch readily, to allow interactions with other proteins, such as FliH (K. Paul and D. F. Blair, unpublished data). Flexibility of the N-terminal segment might also allow it to reach between different tetramers; such bridging could account for the occurrence of products larger than tetramer in some of the cross-linking experiments with double Cys proteins (Fig. 9B).
Studies of spontaneous mutants showed that FliN has some role in CW/CCW switching (17). In this context, we note that the FliN tetramer in the 1yab crystal structure is puckered, as can be seen in side views (Fig. 10A and B; see Fig. S2 in the supplemental material). If such puckering occurs in the FliN tetramer in the flagellum, then the tetramer would be capable of existing in two conformations (puckered in one direction or the other). The two conformations would be equivalent in an isolated tetramer and thus equally stable, but in the context of the C-ring they would be nonequivalent and might correspond to CW and CCW states of the switch (see Fig. S2 in the supplemental material).
Finally, we note that the subunit arrangement we propose is likely to be relevant for other species that contain FliN but might be different in species that use the much larger protein FliY. These include most gram-positive species and spirochaetes. The organization of FliY and the shape of the C ring in those species remain to be examined.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank Sandy Parkinson for strains; Jonathan McMurry, Bertha Gonzáles-Pedrajo, Dennis Thomas, Perry Brown, Bryan Lowder, and Jacob Harmon for discussions and advice; Moises Terrazas for assistance with swarming-rate measurements; Stan Williams and Marian Price-Carter for assistance with FPLC experiments; and Marian Price-Carter for critical reading of the manuscript.
This work was supported by grants R01-GM64664 and R01-GM64663 from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences and grant R01-EB2041 from the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering. The Protein-DNA Core Facility at the University of Utah receives support from the National Cancer Institute (5P30 CA42014).
Footnotes
Supplemental material for this article may be found at http://jb.asm.org/.
REFERENCES
- 1.Berg, H. C. 2003. The rotary motor of bacterial flagella. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 72:19-54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Berg, H. C., and R. A. Anderson. 1973. Bacteria swim by rotating their flagellar filaments. Nature 245:380-382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Blair, D. F., and H. C. Berg. 1990. The MotA protein of E. coli is a proton-conducting component of the flagellar motor. Cell 60:439-449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Braun, T. F., and D. F. Blair. 2001. Targeted disulfide cross-linking of the MotB protein of Escherichia coli: evidence for two H+ channels in the stator complex. Biochemistry 40:13051-13059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Brown, P. N., M. A. A. Mathews, L. A. Joss, C. P. Hill, and D. F. Blair. 2005. Crystal structure of the flagellar rotor protein FliN from Thermotoga maritima. J. Bacteriol. 187:2890-2902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Butler, S. L., and J. J. Falke. 1998. Cysteine and disulfide scanning reveals two amphiphilic helices in the linker region of the aspartate chemoreceptor. Biochemistry 37:10746-10756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Careaga, C. L., and J. J. Falke. 1992. Thermal motions of surface alpha-helices in the d-galactose chemosensory receptor. Detection by disulfide trapping. J. Mol. Biol. 226:1219-1235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chun, S. Y., and J. S. Parkinson. 1988. Bacterial motility: membrane topology of the Escherichia coli MotB protein. Science 239:276-278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Dean, G. E., R. M. Macnab, J. Stader, P. Matsumura, and C. Burke. 1984. Gene sequence and predicted amino acid sequence of the MotA protein, a membrane-associated protein required for flagellar rotation in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 143:991-999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.DeMot, R., and J. Vanderleyden. 1994. The C-terminal sequence conservation between OmpA-related outer membrane proteins and MotB suggests a common function in both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, possibly in the interaction of these domains with peptidoglycan. Mol. Microbiol. 12:333-334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Enomoto, M. 1966. Genetic studies of paralyzed mutants in Salmonella. II. Mapping of three mot loci by linkage analysis. Genetics 54:1069-1076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Fadouloglou, V. E., A. P. Tampakaki, N. M. Glykos, M. N. Bastaki, J. M. Hadden, S. E. Phillips, N. J. Panopoulos, and M. Kokkinidis. 2004. Structure of HrcQB-C, a conserved component of the bacterial type III secretion systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101:70-75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Francis, N. R., V. M. Irikura, S. Yamaguchi, D. J. DeRosier, and R. M. Macnab. 1992. Localization of the Salmonella typhimurium flagellar switch protein FliG to the cytoplasmic M-ring face of the basal body. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:6304-6308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Francis, N. R., G. E. Sosinsky, D. Thomas, and D. J. DeRosier. 1994. Isolation, characterization and structure of bacterial flagellar motors containing the switch complex. J. Mol. Biol. 235:1261-1270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Grünenfelder, B., S. Gehrig, and U. Jenal. 2003. Role of the cytoplasmic C terminus of the FliF motor protein in flagellar assembly and rotation. J. Bacteriol. 185:1624-1633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hirota, N., M. Kitada, and Y. Imae. 1981. Flagellar motors of alkalophilic Bacillus are powered by an electrochemical potential gradient of Na+. FEBS Lett. 132:278-280. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Irikura, V. M., M. Kihara, S. Yamaguchi, H. Sockett, and R. M. Macnab. 1993. Salmonella typhimurium fliG and fliN mutations causing defects in assembly, rotation, and switching of the flagellar motor. J. Bacteriol. 175:802-810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Jones, C. J., R. M. Macnab, H. Okino, and S.-I. Aizawa. 1990. Stoichiometric analysis of the flagellar hook-(basal-body) complex of Salmonella typhimurium. J. Mol. Biol. 212:377-387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Khan, I. H., T. S. Reese, and S. Khan. 1992. The cytoplasmic component of the bacterial flagellar motor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:5956-5960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kihara, M., G. U. Miller, and R. M. Macnab. 2000. Deletion analysis of the flagellar switch protein FliG of Salmonella. J. Bacteriol. 182:3022-3028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kojima, S., and D. F. Blair. 2004. The bacterial flagellar motor: structure and function of a complex molecular machine. Int. Rev. Cytol. 233:93-134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kubori, T., N. Shimamoto, S. Yamaguchi, K. Namba, and S.-I. Aizawa. 1992. Morphological pathway of flagellar assembly in Salmonella typhimurium. J. Mol. Biol. 226:433-446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Larsen, S. H., J. Adler, J. J. Gargus, and R. W. Hogg. 1974. Chemomechanical coupling without ATP: the source of energy for motility and chemotaxis in bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 71:1239-1243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lloyd, S. A., H. Tang, X. Wang, S. Billings, and D. F. Blair. 1996. Torque generation in the flagellar motor of Escherichia coli: evidence of a direct role for FliG but not for FliM or FliN. J. Bacteriol. 178:223-231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Lowder, B. J., M. D. Duyvesteyn, and D. F. Blair. 2005. FliG subunit arrangement in the flagellar rotor probed by targeted cross-linking. J. Bacteriol. 187:5640-5647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Macnab, R. M. 2003. How bacteria assemble flagella. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 57:77-100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Malekooti, J., Y. Komeda, and P. Matsumura. 1989. DNA sequence analysis, gene product identification, and localization of flagellar motor components of Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 171:2728-2734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Mathews, M. A. A., H. L. Tang, and D. F. Blair. 1998. Domain analysis of the FliM protein of Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 180:5580-5590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Morrison, T. B., and J. S. Parkinson. 1994. Liberation of an interaction domain from the phosphotransfer region of CheA, a signaling kinase of Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91:5485-5489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Oosawa, K., T. Ueno, and S.-I. Aizawa. 1994. Overproduction of the bacterial flagellar switch proteins and their interactions with the MS ring complex in vitro. J. Bacteriol. 176:3683-3691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Park, S. Y., X. Chao, G. Gonzalez-Benet, B. D. Beel, A. M. Bilwes, and B. R. Crane. 2004. Structure and function of an unusual family of protein phosphatases: the bacterial chemotaxis proteins CheC and CheX. Mol. Cell 16:563-574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Rost, B., and C. Sander. 1993. Combining evolutionary information and neural networks to predict protein secondary structure. Proteins 19:55-72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Silverman, M., and M. Simon. 1976. Operon controlling motility and chemotaxis in E. coli. Nature 264:577-580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sockett, H., S. Yamaguchi, M. Kihara, V. M. Irikura, and R. M. Macnab. 1992. Molecular analysis of the flagellar switch protein FliM of Salmonella typhimurium. J. Bacteriol. 174:793-806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Sosinsky, G. E., N. R. Francis, D. J. DeRosier, J. S. Wall, M. N. Simon, and J. Hainfeld. 1992. Mass determination and estimation of subunit stoichiometry of the bacterial hook-basal body flagellar complex of Salmonella typhimurium by scanning transmission electron microscopy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:4801-4805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Suzuki, H., K. Yonekura, and K. Namba. 2004. Structure of the rotor of the bacterial flagellar motor revealed by electron cryo-microscoy and single-particle image analysis. J. Mol. Biol. 337:105-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Tang, H., S. Billings, X. Wang, L. Sharp, and D. F. Blair. 1995. Regulated underexpression and overexpression of the FliN protein of Escherichia coli and evidence for an interaction between FliN and FliM in the flagellar motor. J. Bacteriol. 177:3496-3503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Tang, H., and D. F. Blair. 1995. Regulated underexpression of the FliM protein of Escherichia coli and evidence for a location in the flagellar motor distinct from the MotA/MotB torque generators. J. Bacteriol. 177:3485-3495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Tang, H., T. F. Braun, and D. F. Blair. 1996. Motility protein complexes in the bacterial flagellar motor. J. Mol. Biol. 261:209-221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Thomas, D., D. G. Morgan, and D. J. DeRosier. 2001. Structures of bacterial flagellar motors from two FliF-FliG gene fusion mutants. J. Bacteriol. 183:6404-6412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Toker, A. S., and R. M. Macnab. 1997. Distinct regions of bacterial flagellar switch protein FliM interact with FliG, FliN and CheY. J. Mol. Biol. 273:623-634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Vogler, A. P., M. Homma, V. M. Irikura, and R. M. Macnab. 1991. Salmonella typhimurium mutants defective in flagellar filament regrowth and sequence similarity of FliI to F0F1, vacuolar, and archaebacterial ATPase subunits. J. Bacteriol. 173:3564-3572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Welch, M., K. Oosawa, S.-I. Aizawa, and M. Eisenbach. 1993. Phosphorylation-dependent binding of a signal molecule to the flagellar switch of bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90:8787-8791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Yamaguchi, S., S.-I. Aizawa, M. Kihara, M. Isomura, C. J. Jones, and R. M. Macnab. 1986. Genetic evidence for a switching and energy-transducing complex in the flagellar motor of Salmonella typhimurium. J. Bacteriol. 168:1172-1179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Yamaguchi, S., H. Fujita, A. Ishihara, S.-I. Aizawa, and R. M. Macnab. 1986. Subdivision of flagellar genes of Salmonella typhimurium into regions responsible for assembly, rotation, and switching. J. Bacteriol. 166:187-193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Young, H. S., H. Dang, Y. Lai, D. J. DeRosier, and S. Khan. 2003. Variable symmetry in Salmonella typhimurium flagellar motors. Biophys. J. 84:571-577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Zhao, R., N. Pathak, H. Jaffe, T. S. Reese, and S. Khan. 1996. FliN is a major structural protein of the C-ring in the Salmonella typhimurium flagellar basal body. J. Mol. Biol. 261:195-208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Zhou, J., S. A. Lloyd, and D. F. Blair. 1998. Electrostatic interactions between rotor and stator in the bacterial flagellar motor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95:6436-6441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.