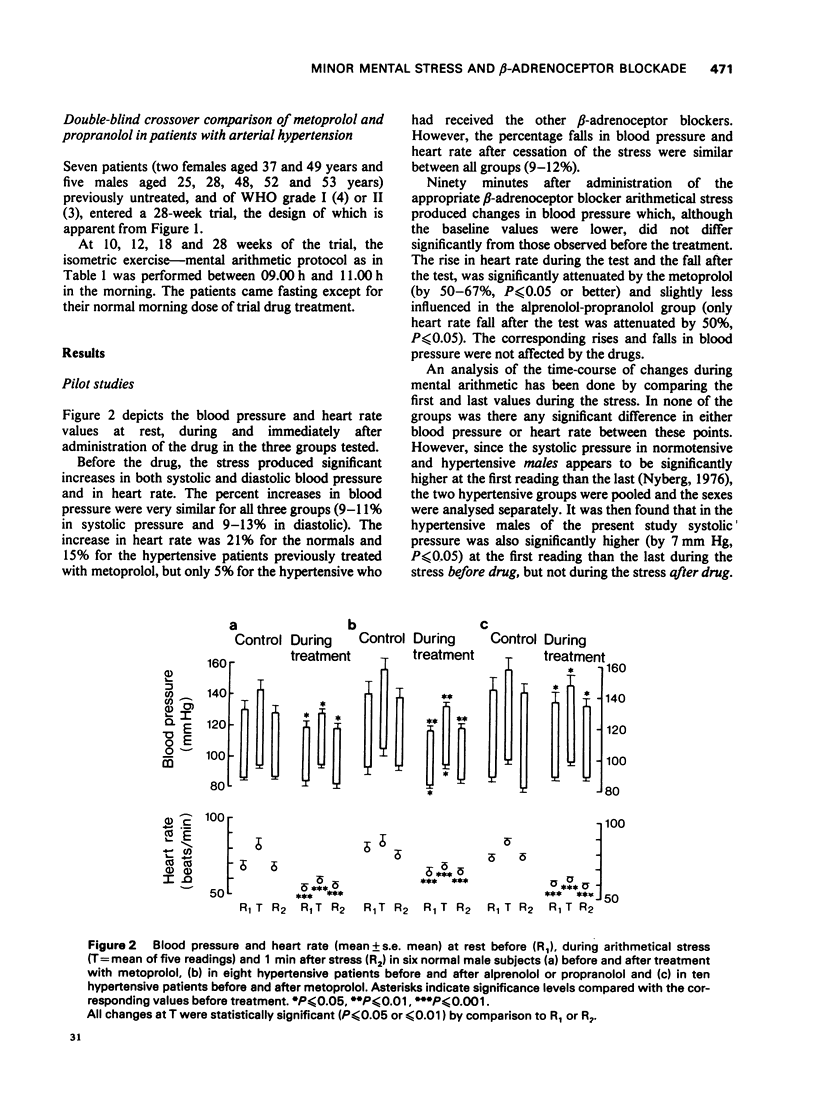
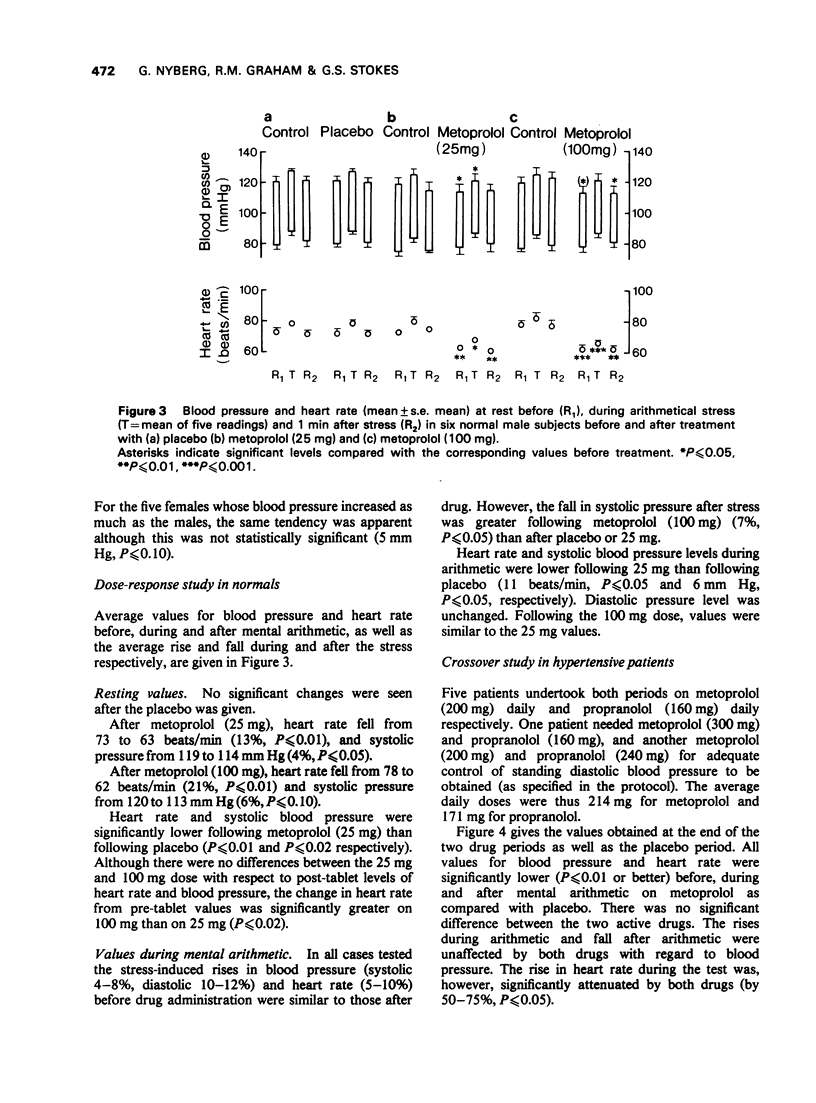
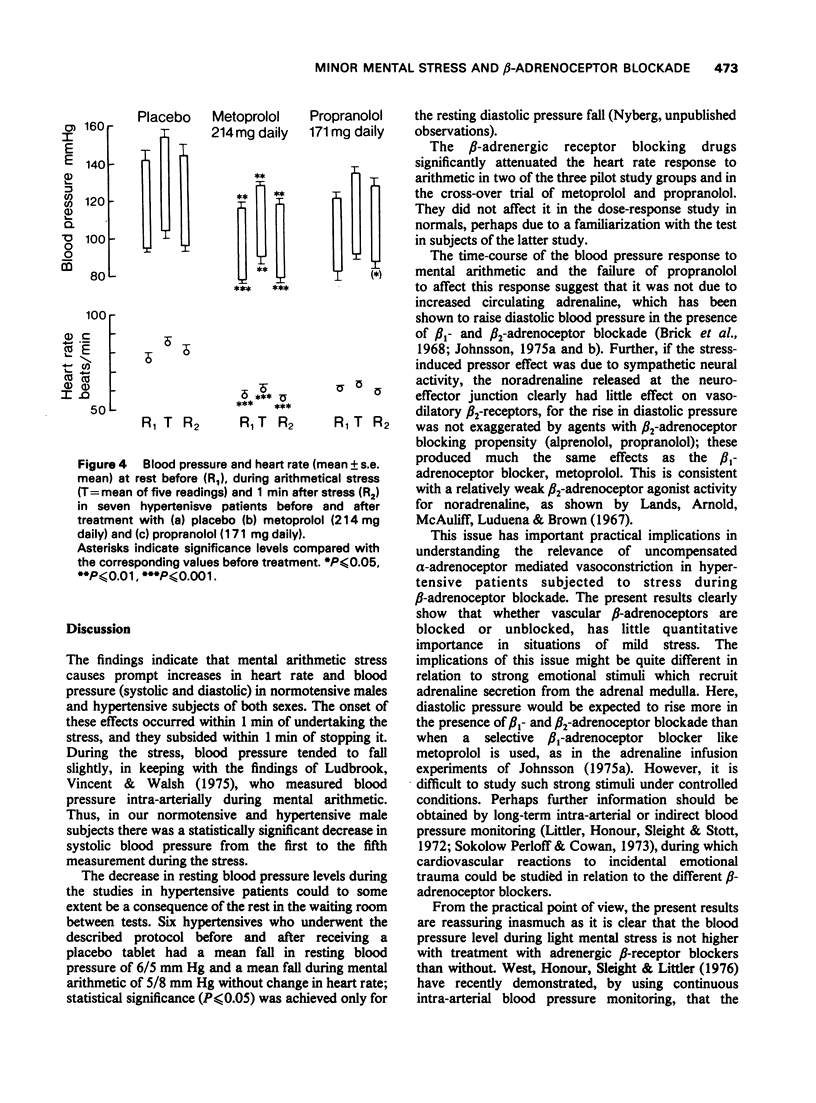
Abstract
1 The effects of a 5-min period of sustained mental arithmetic upon blood pressure and heart rate were determined in several groups of healthy subjects and hypertensive patients. 2 The arithmetic produced significant increases in heart rate and blood pressure (both systolic and diastolic) in both normotensive and hypertensive subjects. 3 The blood pressure changes were neither attenuated nor enhanced by the prior administration of basis. 4 In subjects habituated to the test the heart rate increase was unaffected by the drugs, but in those less familiar with the test it was usually attenuated. 5 Although the beta1-adrenoceptor selective blocker, metoprolol, caused decreases in baseline values for blood pressure and heart rate similar to those observed with the use of the two non-selective blockrs, it was shown in a double-blind crossover comparison with propranolol that the haemodynamic changes provoked by the mental arithmetic were not less in the presence of beta1-receptor blockade than when both beta1- and beta2-receptors were blocked. 6 These findings suggest that, during beta2-adrenoceptor blockade, the haemodynamic effects of minor mental stress are not exaggerated because of uncompensated alpha-receptor mediated vasoconstriction, such as occurs following adrenaline infusion.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROD J., FENCL V., HEJL Z., JIRKA J. Circulatory changes underlying blood pressure elevation during acute emotional stress (mental arithmetic) in normotensive and hypertensive subjects. Clin Sci. 1959 May;18:269–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brick I., Hutchison K. J., McDevitt D. G., Roddie I. C., Shanks R. G. Comparison of the effects of I.C.I. 50172 and propranolol on the cardiovascular responses to adrenaline, isoprenaline and exercise. Br J Pharmacol. 1968 Sep;34(1):127–140. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb07956.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnsson G. Influence of metoprolol and propranolol on hemodynamic effects induced by adrenaline and physical work. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1975;36(Suppl 5):59–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1975.tb03322.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lands A. M., Arnold A., McAuliff J. P., Luduena F. P., Brown T. G., Jr Differentiation of receptor systems activated by sympathomimetic amines. Nature. 1967 May 6;214(5088):597–598. doi: 10.1038/214597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littler W. A., Honour A. J., Sleight P., Stott F. D. Continuous recording of direct arterial pressure and electrocardiogram in unrestricted man. Br Med J. 1972 Jul 8;3(5818):76–78. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5818.76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludbrook J., Vincent A., Walsh J. A. Effects of mental arithmetic on arterial pressure and hand blood flow. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1975;Suppl 2:67–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestel P. J. Blood-pressure and catecholamine excretion after mental stress in labile hypertension. Lancet. 1969 Apr 5;1(7597):692–694. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)92645-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyberg G. Blood pressure and heart rate response to isometric exercise and mental arithmetic in normotensive and hypertensive subjects. Clin Sci Mol Med Suppl. 1976 Dec;3:681s–685s. doi: 10.1042/cs051681s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyberg G. Indirect blood pressure and heart rate measured quickly without observer bias using a semi-automatic machine (auto-manometer)--response to isometric exercise in normal healthy males and its modification by beta-adrenoceptor blockade. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1977 Jun;4(3):275–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1977.tb00712.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Rourke M. F. Pulsatile arterial haemodynamics in hypertension. Aust N Z J Med. 1976;6 Suppl 2:40–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1976.tb03322.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokolow M., Perloff D., Cowan R. The value of portably recorded blood pressures in the initiation of treatment of moderate hypertension. Clin Sci Mol Med Suppl. 1973 Aug;45 (Suppl 1):195s–1958. doi: 10.1042/cs045195s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West M. J., Honour A. J., Sleight P., Littler W. A. Blood pressure variability in patients on beta-blockers. Aust N Z J Med. 1976 Aug;6(3 Suppl):19–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1976.tb03329.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


