Abstract
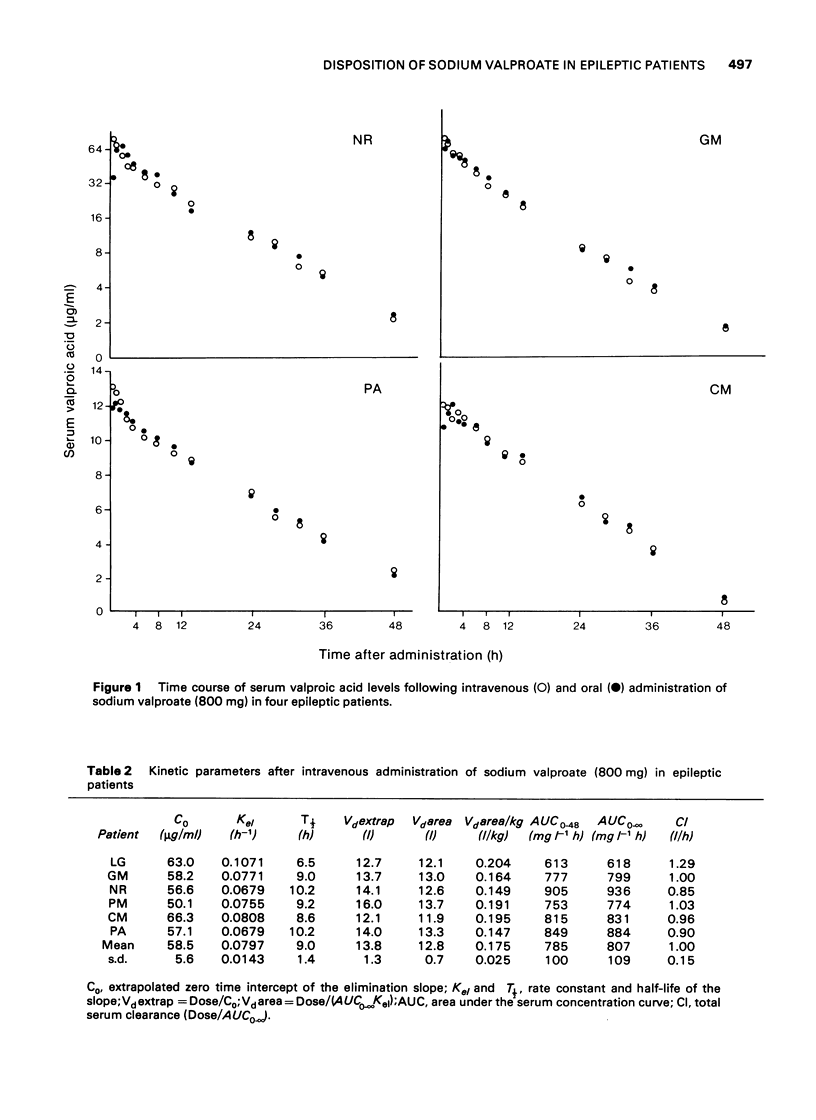
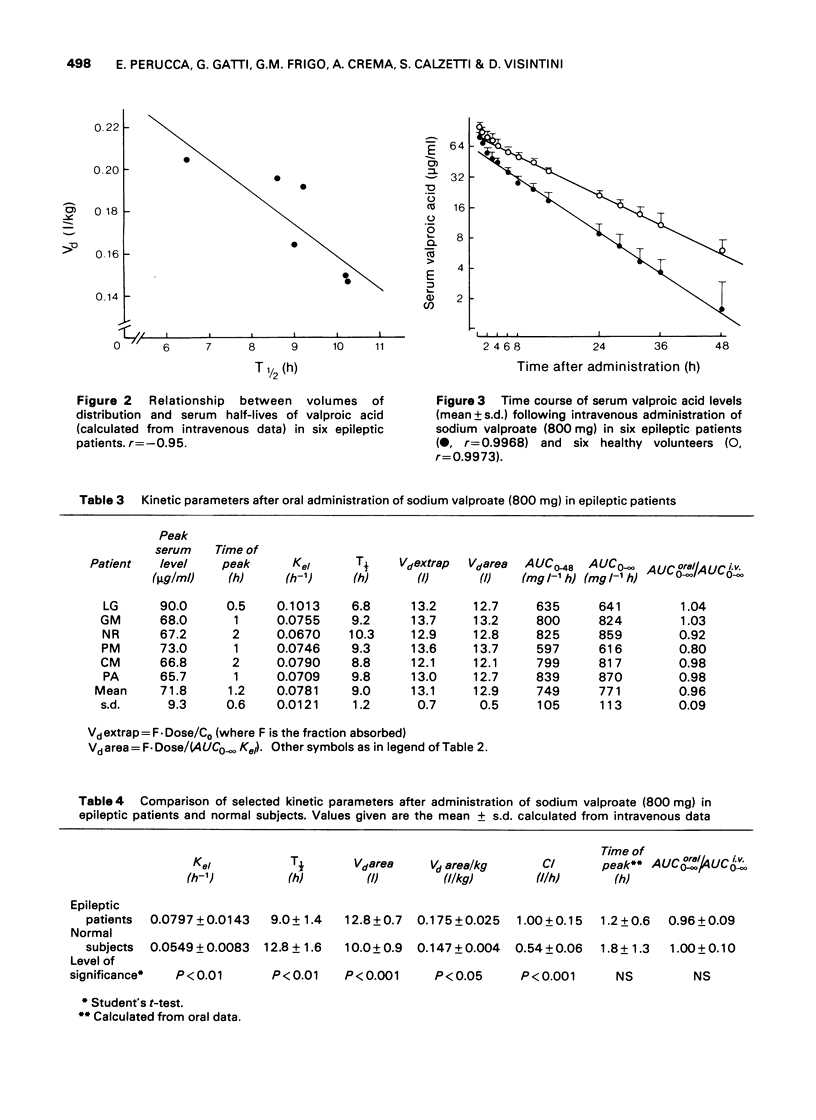
1 Serum levels of valproic acid have been determined at fixed intervals after the administration of single oral and intravenous doses (800 mg) to six epileptic patients receiving chronic treatment with other antiepileptic drugs. 2 Serum levels declined monoexponentially shortly after the intravenous administration. Biological half-lives averaged 9.0 +/- 1.4 h (s.d.). Volumes of distribution were 0.175 +/- 0.025 l/kg. There was a statistically significant negative correlation between volumes of distribution and serum half-lives (P less than 0.005). 3 After oral doses serum levels rose rapidly to peak values within 0.5--2 h. Biological availability was 96 +/- 9%. 4 Comparison with a previous study performed according to the same protocol in healthy volunteers showed significantly increased volumes of distribution and rates of elimination in the patients. Total serum clearance was 85% higher in the patients as compared to the healthy subjects (P less than 0.001). Possible explanations for these findings are discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hayes M. J., Langman M. J., Short A. H. Changes in drug metabolism with increasing age: 2. phenytoin clearance and protein binding. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1975 Feb;2(1):73–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1975.tb00475.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz U., Antonin K. H. Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of sodium valproate. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1977 Jun;21(6):736–743. doi: 10.1002/cpt1977216736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patsalos P. N., Lascelles P. T. Valproate may lower serum-phenytoin. Lancet. 1977 Jan 1;1(8001):50–51. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91693-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrier D., Gibaldi M. Clearance and biologic half-life as indices of intrinsic hepatic metabolism. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1974 Oct;191(1):17–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schobben F., van der Kleijn E., Gabreëls F. J. Pharmacokinetics of di-n-propylacetate in epileptic patients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1975 Feb 28;8(2):97–105. doi: 10.1007/BF00561557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- U-Schulz H., Toseland P. A. Determination of the anticonvulsant drug--dipropyl acetate (Epilim) in human plasma by gas chromatography. Ann Clin Biochem. 1977 Jul;14(4):240–242. doi: 10.1177/000456327701400164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson G. R., Shand D. G. Commentary: a physiological approach to hepatic drug clearance. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1975 Oct;18(4):377–390. doi: 10.1002/cpt1975184377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


