Abstract
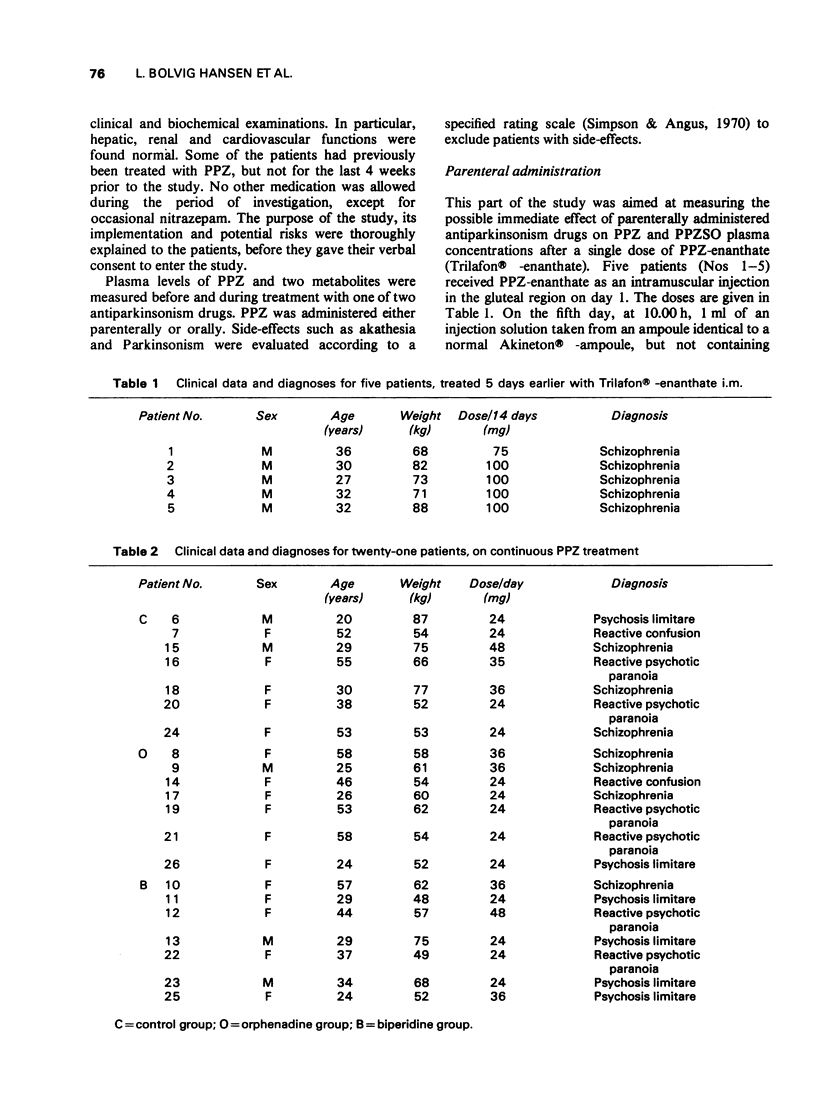
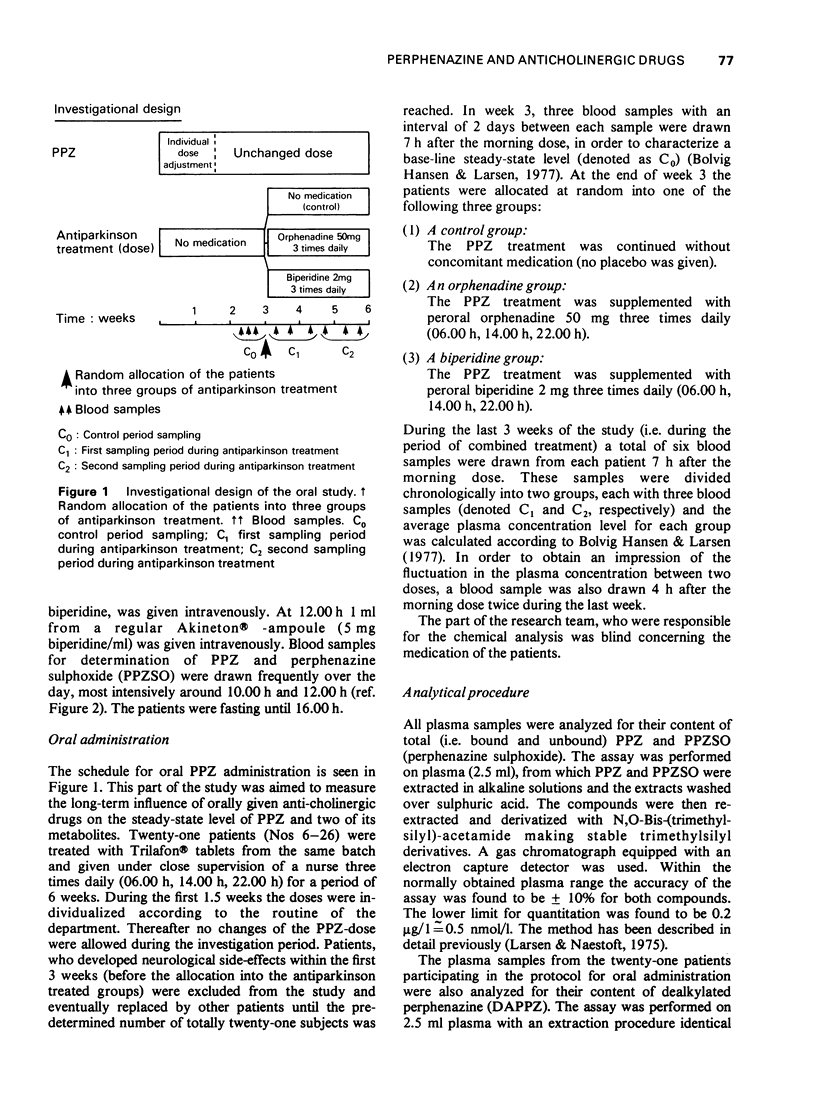
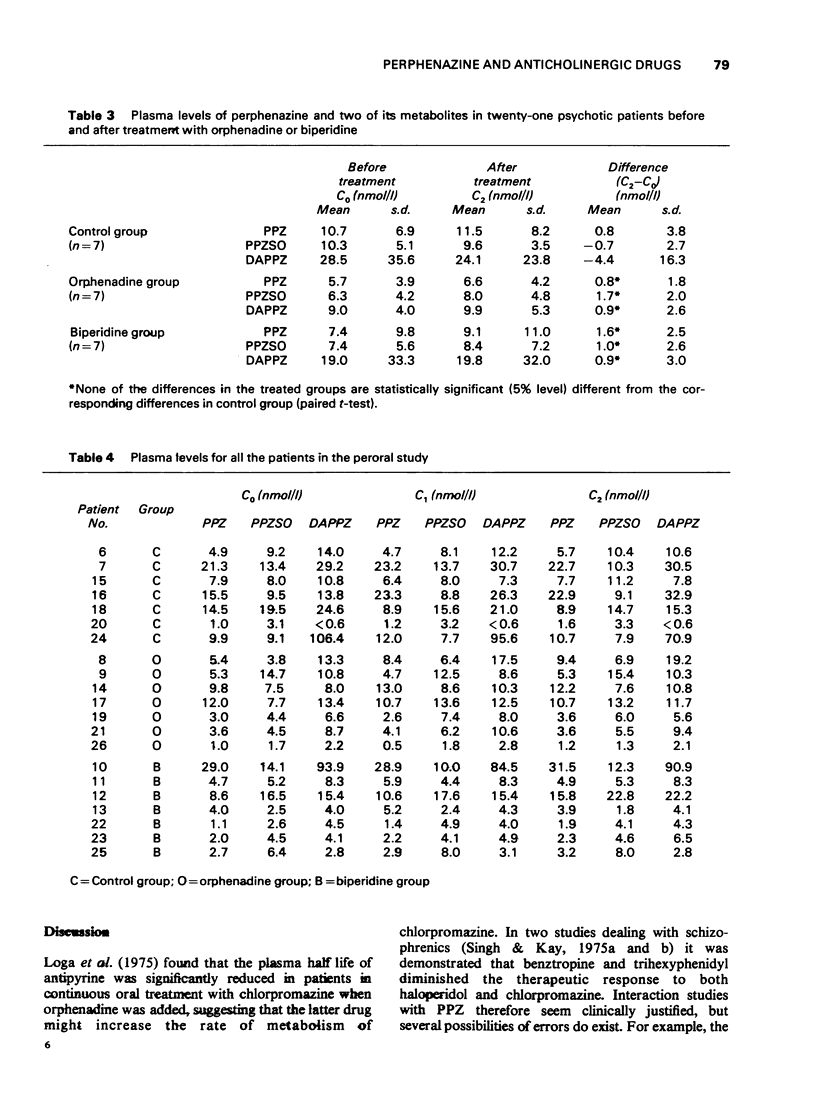
1. A gas chromatographic method was applied to study plasma levels of perphenazine (PPZ) and its major metabolites in man before and during simultaneous antiparkinson treatment. Twenty-six psychotic patients received various forms of PPZ administration as well as antiparkinson drugs. 2. Biperidine (5 mg) was administered intravenously to each of five patients, who 5 days earlier had had a single dose of PPZ-enanthate i.m. No significant alterations in plasma concentrations of PPZ were observed. 3. In fourteen patients receiving oral PPZ treatment the plasma levels of PPZ and its metabolites did not deviate significantly from controls after addition of biperidine or orphenadine given for 3 weeks in fixed oral doses. 4. The ratio between PPZ plasma concentration measured 4 and 7 h after the morning dose was not affected by concomitant antiparkinson therapy. 5. It is concluded that no clinically relevant pharmacokinetic interaction takes place between PPZ and two generally used antiparkinson drugs during steady-state conditions in psychotic patients.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Eggert Hansen C., Rosted Christensen T., Elley J., Bolvig Hansen L., Kragh-Sorensen P., Larsen N. E., Naestoft J., Hvidberg E. F. Clinical pharmacokinetic studies of perphenazine. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1976 Oct;3(5):915–923. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1976.tb00647.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen C. E., Larsen N. E. Perphenazine concentrations in human whole blood. A pilot study during anti-psychotic therapy using different administration forms. Psychopharmacologia. 1974 Jun 18;37(1):31–36. doi: 10.1007/BF00426680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen L. B., Larsen N. E. Plasma concentrations of perphenazine and its sulphoxide metabolite during continuous oral treatment. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1977 Jul 18;53(2):127–130. doi: 10.1007/BF00426481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen N. E., Naestoft J. Determination of perphenazine and its sulphoxide metabolite in human plasma after therapeutic doses by gas chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1975 Jun 18;109(2):259–264. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)91797-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loga S., Curry S., Lader M. Interactions of orphenadrine and phenobarbitone with chlorpromazine: plasma concentrations and effects in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1975 Jun;2(3):197–208. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1975.tb01576.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson G. M., Angus J. W. A rating scale for extrapyramidal side effects. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl. 1970;212:11–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1970.tb02066.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh M. M., Kay S. R. A comparative study of haloperidol and chlorpromazine in terms of clinical effects and therapeutic reversal with benztropine in schizophrenia. Theoretical implications for potency differences among neuroleptics. Psychopharmacologia. 1975 Aug 21;43(2):103–113. doi: 10.1007/BF00421012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh M. M., Kay S. R. A longitudinal therapeutic comparison between two prototypic neuroleptics (haloperidol and chlorpromazine) in matched groups of schizophrenics. Nontherapeutic interactions with trihexyphenidyl. Theoretical implications for potency differences. Psychopharmacologia. 1975 Aug 21;43(2):115–121. doi: 10.1007/BF00421013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


