Abstract
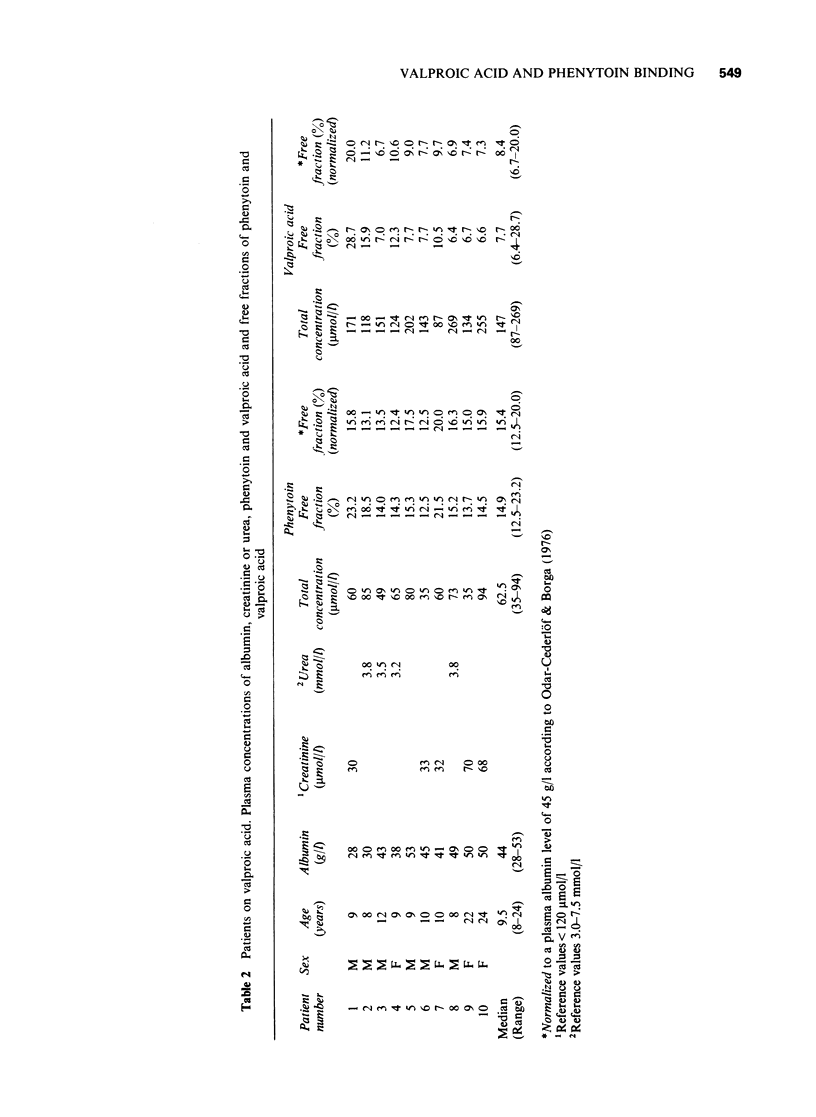
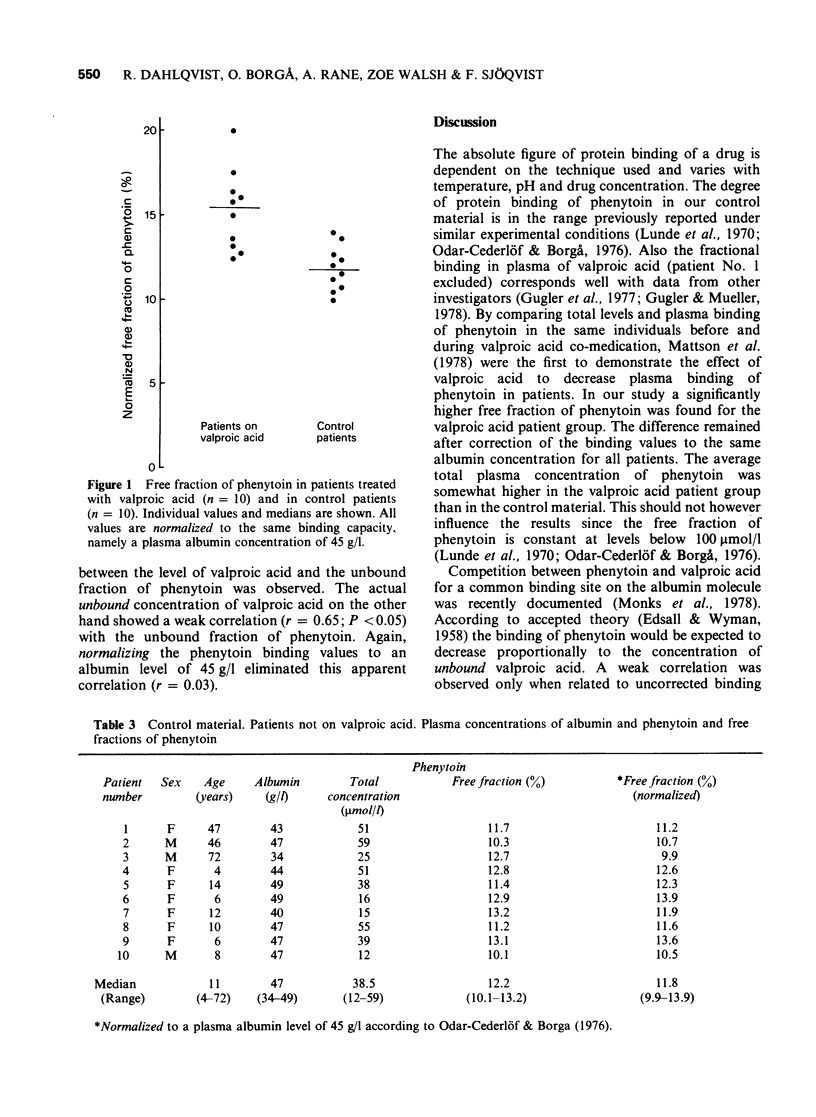
1 Plasma protein binding of phenytoin and of valproic acid were measured in ten epileptic patients on this drug combination. Ten other epileptics not on valproic acid served as controls. All patients had normal kidney function. 2 The measured free fraction of phenytoin among the patients on valproic acid ranged from 12.5 to 23.2% and after recalculation to a plasma albumin level of 45 g/l from 12.5 to 20.0 (median 15.4%). This differed significantly (P = 0.002, Mann- Whitney U-test) from the control patients where the normalized values ranged from 9.9 to 13.9% with a median value of 11.8%. 3 The measured free fractions of phenytoin and of valproic acid showed a significant correlation which, however, was due to the quantitative relation between the degree of binding of both these drugs and the concentration of plasma albumin. There was no discernable relation in this material between the free concentration of valproic acid and the free fraction of phenytoin. 4 It is concluded that patients on combined treatment with phenytoin and valproic acid have an unpredictably raised free fraction of phenytoin. This drug interaction therefore can complicate the important plasma level monitoring of phenytoin in epileptic patients unless the free concentration of this drug can be analysed or estimated.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. J., Luders H., Pippenger C. Sodium valproate in the treatment of intractable seizure disorders: a clinical and electroencephalographic study. Neurology. 1978 Feb;28(2):152–157. doi: 10.1212/wnl.28.2.152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardy A., Hari R., Lehtovaara R., Majuri H. Valproate may lower serum-phenytoin. Lancet. 1976 Dec 11;2(7998):1297–1298. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92053-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barth N., Alván G., Borgå O., Sjöqvist F. Two-fold interindividual variation in plasma protein binding of phenytoin in patients with epilepsy. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1976 Nov-Dec;1(6):444–452. doi: 10.2165/00003088-197601060-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eadie M. J. Plasma level monitoring of anticonvulsants. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1976;1(1):52–66. doi: 10.2165/00003088-197601010-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrnebo M., Agurell S., Jalling B., Boréus L. O. Age differences in drug binding by plasma proteins: studies on human foetuses, neonates and adults. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1971 Sep;3(4):189–193. doi: 10.1007/BF00565004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gugler R., Mueller G. Plasma protein binding of valproic acid in healthy subjects and in patients with renal disease. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1978 May;5(5):441–446. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1978.tb01652.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gugler R., Schell A., Eichelbaum M., Fröscher W., Schulz H. U. Disposition of valproic acid in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1977 Oct 14;12(2):125–132. doi: 10.1007/BF00645133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobs C., Bojasch M., Hanefeld F. New direct micro-method for determination of valproic acid in serum by gas chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1978 Nov 1;146(3):494–497. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)81210-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz U., Rapp T., Müller W. A. Disposition of valproic acid in patients with liver disease. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1978 Mar 17;13(1):55–60. doi: 10.1007/BF00606683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutt H., Penry J. K. Usefulness of blood levels of antiepileptic drugs. Arch Neurol. 1974 Nov;31(5):283–288. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1974.00490410031001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- L'Estrange Orme M., Borgå O., Cook C. E., Sjöqvist F. Measurement of diphenylhydantoin in 0.1-ml plasma samples: gas chromatography and radioimmunoassay compared. Clin Chem. 1976 Feb;22(2):246–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund L. Anticonvulsant effect of diphenylhydantoin relative to plasma levels. A prospective three-year study in ambulant patients with generalized epileptic seizures. Arch Neurol. 1974 Nov;31(5):289–294. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1974.00490410037002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunde P. K., Rane A., Yaffe S. J., Lund L., Sjöqvist F. Plasma protein binding of diphenylhydantoin in man. Interaction with other drugs and the effect of temperature and plasma dilution. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1970 Nov-Dec;11(6):846–855. doi: 10.1002/cpt1970116846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattson R. H., Cramer J. A., Williamson P. D., Novelly R. A. Valproic acid in epilepsy: clinical and pharmacological effects. Ann Neurol. 1978 Jan;3(1):20–25. doi: 10.1002/ana.410030105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monks A., Boobis S., Wadsworth J., Richens A. Plasma protein binding interaction between phenytoin and valproic acid in vitro. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1978 Dec;6(6):487–492. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1978.tb00871.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patsalos P. N., Lascelles P. T. Effect of sodium valproate on plasma protein binding of diphenylhydantoin. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1977 Jun;40(6):570–574. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.40.6.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schobben F., van der Kleijn E., Gabreëls F. J. Pharmacokinetics of di-n-propylacetate in epileptic patients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1975 Feb 28;8(2):97–105. doi: 10.1007/BF00561557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- U-Schulz H., Toseland P. A. Determination of the anticonvulsant drug--dipropyl acetate (Epilim) in human plasma by gas chromatography. Ann Clin Biochem. 1977 Jul;14(4):240–242. doi: 10.1177/000456327701400164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilder B. J., Willmore L. J., Bruni J., Villarreal H. J. Valproic acid: interaction with other anticonvulsant drugs. Neurology. 1978 Sep;28(9 Pt 1):892–896. doi: 10.1212/wnl.28.9.892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wulff K., Flachs H., Würtz-Jorgensen A., Gram L. Clinical pharmacological aspects of valproate sodium. Epilepsia. 1977 Jun;18(2):149–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1977.tb04463.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


